Trauma to the bones of the hand is one of the most common problems when visiting emergency rooms. This is due to the fact that the upper girdle of the limbs is mobile and is involved in most of the actions performed by a person. Displaced arm fractures are a more serious injury than simple ones. This is due to the formation of bone fragments, which, when displaced, damage soft tissues, muscles, nearby nerves and large vessels. The consequences become deeper and require long-term rehabilitation. Read more about displaced arm fractures (what they are, treatment tactics, emergency care for the victim and rehabilitation methods) further in this article.
A little about anatomy
The anatomical structure of the bony skeleton of the hand is varied. Therefore, the resulting injuries with a violation of its integrity can be of a different nature. It is necessary to have an understanding of the structure of the limb in order to understand the specifics of its fractures. The arms can move in different trajectories; they are very flexible and mobile due to the large number of articular connections between conventionally designated sections:
- Shoulder girdle. This section includes paired bones - the scapula and collarbone. They are a transitional place from the torso to the limbs. These are not all their functions. With their help, a person can make rotational movements in the shoulder joint and raise their arms in different projections.
- Shoulder. Includes the direct attachment of the humerus to the scapula by the acromion process (which is considered an integral part of the shoulder). As well as a large joint connecting the shoulder girdle and shoulder.
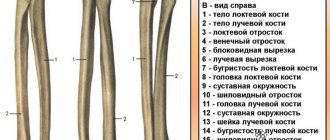
- Forearm. This section is represented by two main bones: the radius and the ulna. It also connects the elbow joint to the humerus. They are unpaired, but are next to each other. At the elbow joint, their epiphyses are connected to form a strong contact with the shoulder. They participate in the organization of rotational movements and help maintain the mobility and functionality of the arm as a whole.
- Brush. A complex and amazing education. Five fingers, each of which is formed by three phalanges. The connection between the hand and forearm is provided by many ligaments (radial collateral, pisiform-macula, semilunar, etc.). At the base of the hand lies a complex formation of eight bones, with the help of which rotation ability is maintained.
Interesting fact! Nature has protected such an important tool for humans as hands. She placed the muscle and tendon structures in a special protective “film” (fascia). With their help, the elements of the hand became more protected from mechanical influences.
Frequent fractures
The most common fractures occur in the radius, humerus, or femur.
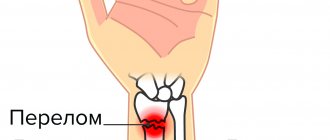
In fractures of the forearm, the radius bone is broken much more often than the ulna. The fracture is fixed with plaster. It is extremely important to follow all recommendations of a rehabilitation and treatment specialist, since if you are irresponsible, there is a chance that the hand will stop moving. Accelerated development of arthrosis is also possible.
A fracture of the humerus most often occurs due to a fall on an outstretched arm or a direct blow. The inability to raise the arm is added to the symptoms. During rehabilitation, the Codman exercise is prescribed as the most effective in developing the shoulder joint.
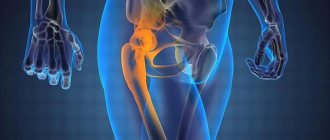
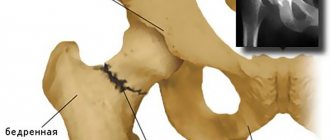
A femur fracture is considered one of the most complex and intractable fractures. The most common treatment for a hip fracture is surgery. Rehabilitation after treatment of debt, but with strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, the functionality of the hip joint will quickly be restored, and soon motor activity will be completely normalized.
Classification
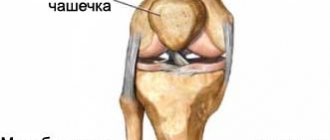
There are general principles for classifying all bone fractures. This includes open and closed. By the way, a displaced fracture of the arm is most often accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin. Therefore, open injuries are more typical for him. There are also intra-articular fractures. They are characterized by damage to the bone of the arm in the area of the articular capsule. The difficulty lies in the high probability of complications in the form of filling the joint cavity with blood. The consequences impair the functionality of the joints, which will further affect the function of the hand as a whole.
A narrow classification has emerged based on the external characteristics of the displaced fracture and the type and location of the injury. So this includes:
- Incomplete. It is characterized by a partial fracture of the bone with the formation of a fragment, while maintaining the integrity of a separate area.
- Wedge-shaped. It is characterized by the formation of a large bone fragment as a result of a double fracture of one bone.
- Multi-fragmentary. Complex, with multiple formation of fragments of different sizes. It is often a common characteristic of a wedge-shaped fracture.
- Torsion. Basis for classification based on the method of mechanical action. One piece of bone is held in place by one mechanical force, while the opposite piece is twisted and traumatized by another.
- Helical. Characterized by an oblique, twisting fracture line.
- Compression. Another type depending on the mechanical impact. Such arm fractures are formed from strong pressure exerted on the bone, under which it cannot maintain its integrity.
- Longitudinal. It runs along the axis of the bone and is characterized by elongation, but a simpler treatment regimen. Most often it is a closed fracture.
- Transverse. Runs perpendicular to the axis.
Interesting fact! The hand is an important verbal element. With the help of gestures, a person is able to verbalize his emotions, feelings and show intentions.
Rehabilitation
For a bilateral ankle fracture, the following rehabilitation measures are carried out:
- Massotherapy;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Gymnastics to provide a therapeutic effect;
- Application of an orthosis.
What are the tasks of the recovery period:
- Functionality should be restored in the ankle;
- Traumatic flat feet are prevented;
- Swelling of the limb is eliminated;
- Restoration of blood circulation;
- Prevention of foot and joint deformities;
- Preventing the formation of curvature;
- Prevention of the formation of heel spurs.
To reduce swelling in the ankle area with a double ankle fracture, the patient is prescribed warm baths in the morning and evening. The water temperature should be comfortable; you can add a herbal decoction with a calming effect or sea salt to it.
It is recommended to lie for about 15-20 minutes every day with your legs raised 120 degrees.
In addition to therapeutic massage, patients may be advised to independently stretch their lower leg and foot. When performing massage movements, you must be careful, start warming up from the foot and lower leg, gradually moving up to the knee joint.
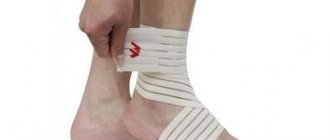
During the recovery period after a fracture, you should use an elastic bandage, wrapping it around the affected leg from the toes to the knee.
Diagnostics
When a patient with a suspected fracture comes to the doctor, he first performs a visual examination and palpates the damaged area. A fracture of the arm with displacement of fragments often manifests itself already at this stage of diagnosis, since fragments penetrate into the soft tissues and are palpated. Afterwards, radiography in different projections is required. This measure provides a complete understanding of the fracture pattern and allows us to develop a strategy for treatment and further rehabilitation. In addition to these measures, it is possible to use additional diagnostic tools:
- General tests. They allow you to assess the patient’s current condition and help make predictions for the process of bone fusion.
- Imaging methods - CT (computed tomography) or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Used when complications arise from other organ systems (nervous, circulatory, muscle groups, etc.)
- Puncture. Used to diagnose intra-articular fractures. Determines the presence of blood and the need to extract it and stop bleeding.
Possible complications after osteosynthesis of the middle third of the forearm.
Infection. There are certain risks of infectious complications with any surgical intervention, forearm osteosynthesis is no exception.
Damage to nerves and blood vessels. There is a small risk of damage to the nerves and blood vessels at the level of the forearm during surgery. If after surgery there is weakness and numbness in the hand area, or persistent limitation of movements appears, this is a reason to consult a doctor, since such neuropathy may not resolve without emergency intervention.
Synostosis. In some cases, after a fracture of both bones of the forearm, a bone bridge may arise between them, which will limit the rotational movements of the forearm.
Nonunion. The operation does not guarantee healing of the fracture. Sometimes the bone does not heal, and in such cases a repeat, more complex operation is required.
Smoking and drinking alcohol slow down the healing process and may lead to delayed fracture consolidation.
First aid
Correctly provided first aid will speed up the healing process and eliminate the risk of negative consequences. Following the algorithm in the correct sequence will help reduce the patient’s suffering. What is this algorithm:
- Anesthesia. Severe pain is the first symptom of an injury. To remove it, it is necessary to give the patient an anesthetic. This can be any painkiller that you have on hand. It is worth giving it according to the dosage, without exceeding it. It is better if it is possible to administer the drug intramuscularly. This will speed up the effect of the medicine.
- Immobilization. It is necessary to apply a splint from available materials or at least apply a fixing bandage. The simplest option is considered to be a scarf bandage, for which you only need fabric whose width corresponds to the length of the forearm. If the fracture is localized in the hand, then it is necessary to fix all its elements so that it is impossible to carry out any actions.
- Providing peace. After taking measures in case of a closed fracture, it is worth giving the victim a rest until the ambulance arrives.
- Disinfection. An open fracture must be disinfected. Iodine, brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine digluconate, and alcohol are suitable for this.
- Application of a tourniquet. If the bleeding is intense, then you need to apply a tourniquet 10-15 cm above the source of blood.
Important! When providing emergency care, do not try to dislodge fragments if they are palpable under the skin or visible in an open wound. This can cause damage to associated structures and cause additional consequences for the victim. It will be more difficult for doctors to correct the consequences and cure a broken arm.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment tactics are chosen and the expected time frame for bone fusion is put forward. It is fair to note that when treating displaced fractures, the surgical method is most often chosen so that bone restoration proceeds safely, without pathological processes.
Conservative
Includes wearing fixing items that provide limb immobilization. Such items include:
- Gypsum. The most famous and no less effective method among other options. It consists of applying bandages soaked in plaster to the damaged area to fix the hand. The wearing period of the cast is within 6 weeks.
- Orthosis. A modern fixation method that is individually selected for the patient. It is made of medical plastic and is used to treat hand fractures.
- Splint. For displaced fractures, it is used as a temporary option until it becomes possible to place a full-fledged fixator.
- Bandage. Used to treat the bones of the forearm and shoulder.
Fixation is not the last stage of conservative treatment. While wearing a cast or other brace, the patient is prescribed a healthy diet with a high content of foods rich in vitamin D, C and calcium. Vitamin D helps absorb calcium and strengthen bone tissue. Vitamin C is a participant in metabolic, energy and regenerative processes. Medicines are also used - anti-inflammatory, painkillers and chondoprotectors.
Operational
Osteosynthesis operations are performed for complex hand injuries. These include:
- Multiple formations of fragments.
- Fractures of several arm bones at once.
- Damage to muscles, blood vessels, nerves.
The operation involves combining the fragments and fixing them using plates, screws and knitting needles. So how long does it take for a fracture to heal? Complex, with displacement, it is restored after only six months of active treatment and rehabilitation. The degree of consolidation is monitored over time using x-rays. Once the bone has healed, a second operation is performed to remove the fixing instruments from the healed bone.
Useful tips
For at least six months after illness, you need to take care of yourself. Avoid sports that involve jerking. Do not run or jump, avoid sudden tension. When performing physical activity, you should consult your doctor.
For greater effect, the rehabilitation program must be combined with properly selected nutrition.
You should add more vitamins and calcium to your diet. If the amount of calcium you can get from food is not enough, your doctor will prescribe it in pills. To get vitamins in the right quantities, you should add more fruits to your diet.
If treatment is carried out at the wrong time or incorrectly, the fracture will most likely heal with serious complications. The success of treatment will largely depend on the experience of the doctors treating the patient. But the speed and quality of recovery after an ankle fracture largely depends on the diligence of the patient.
Source
Rehabilitation and how to develop a broken arm
The bone grows together within 1-1.5 months. The next 4.5 - 5 months are devoted to restoring the functions of the hand and strengthening the bones. Several methods are traditionally used for this:
- Exercise therapy (physical therapy)
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage.
- Proper nutrition, daily routine, etc.
Massage
Massage begins after the fixation is removed and after partial or complete healing of the wound. What are the goals of performing a massage:
- Prevention of atrophy. During a long stay in a state of immobilization, the strength of the arm muscles decreases. Massage helps restore muscle strength and gradually return to its original state before injury.
- Acceleration of blood circulation. Vibrations, claps, and pinches help increase blood flow in the area being massaged. Increased blood circulation helps accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues and reduces the time spent on recovery.
- Elimination of puffiness. Fluid that accumulates in soft tissues as a result of injury interferes with proper blood flow. Stroking and gentle vibrations help reduce excess fluid.
Example of massage technique:
- Stroke areas of the arm just above and just below the injury.
- After lightly patting, move in the direction from the shoulder to the hand.
- Then apply vibrations - these are low-amplitude movements towards the injury.
- The massage must be completed with stroking again.
Attention! All techniques, duration and intensity are determined by the attending physician. Self-indulgence in this matter can lead to irreversible consequences.
Physiotherapy methods
Such methods rely on the ability of bone tissue to be a dielectric and conduct electrical impulses. In addition, the effects of UHF therapy and magnetic therapy are used. Let's look at each of them in more detail:
- UHF. Allows you to reduce pain and remove excess fluid from the surrounding soft tissues.
- Magnetotherapy. Accelerates metabolic and regenerative processes and also fights pain.
- Electrophoresis. Performed with local anesthesia for patients with persistent pain. Helps start regeneration processes.
- Ultrasound. One of the few methods to improve the condition of joints after damage.
- Laser. Used to stimulate metabolic functions.
Exercise therapy classes
The right hand is the dominant one for most people, so restoring fine motor skills is extremely necessary for a full return to normal life. Exercises are used in writing, drawing and other operations with small objects that are made at multiple magnification. Gradually, as the functions of the right hand are restored, pens and pencils are reduced, and abilities are improved. If the left arm of a left-hander is broken, then similar exercises are performed with it.
What tasks does exercise therapy perform:
- Strengthening muscles. After prolonged immobilization, muscles lose their volume, endurance and strength. Exercise therapy exercises help you gradually return to your previous and even better state.
- Restoring motor function of the hand. Each exercise is based on performing actions that help develop joints, restore muscle response to brain signals, and improve motor functions.
- Acceleration of blood circulation. Any activity generates increased blood circulation, which in turn helps reduce rehabilitation time.
- Launching metabolism.
Indications for tibial osteosynthesis
Before the start of the surgical operation, before installing the reconstructive plate, the indications for its implementation are determined. The key indications are:
- obvious compartment syndrome, noticeable compression of muscles and skin as a result of damage;
- damage to nerve trunks or blood vessels;
- 2-3 degree open fracture;
- diagnosis of diaphyseal fracture in polytrauma;
- fracture instability, displacement of fragments;
- fracture instability with muscle or tendon damage;
- segmentation of the fracture;
- secondary displacement of the fracture after conservative treatment;
- varus deformity of the tibia more than 10 degrees;
- diagnosis of ipsilateral fracture in case of ligament damage
- fragmentation-rotation nature of a short oblique fracture with dorsal displacement of the sharp part of the bone.
There is also a list of indications for the use of percutaneous osteosynthesis. This method performs treatment using hardware structures. The decision on their use is made by the doctor after analyzing the nature of the injury and other factors. In case of an uncomplicated non-fragmentary fracture, a plaster cast can be applied (closed reduction), osteosynthesis with screws or submersion. For comminuted fractures, percutaneous fixation and appliances can be used.
The designs used in the treatment of tibia fractures are different:
- plates;
- rods;
- pins.
The choice of one or another metal fixator depends on the location of the fracture. In case of dermatitis or suppuration over the fracture, osteosynthesis is not performed.
Possible consequences
Unfortunately, bone fractures do not go away without leaving a trace. In some cases, the echoes of trauma bother a person throughout his life. For example, if fragments are improperly fixed, the bone grows together in an anatomically incorrect shape. Sometimes this is not noticeable externally, and sometimes external deformations occur in the form of pathological bends of the arm, shortening of the length of the limb, etc. In such cases, an osteotomy operation is indicated - the bone is broken and reassembled. Incorrect fusion is not the only possible consequence:
- False callus. This is a phenomenon when the bone does not fully regenerate and instead of bone tissue, a fibrous callus is formed. One of the symptoms of this complication is increased bone mobility where it should not be. It can only be treated surgically, also with a large number of consequences.
- Nerve conduction disorder. Nerve damage may be permanent. In this case, certain functions of the hand suffer, as the connection with the brain is lost. Or the sensitivity of certain areas of the skin is lost.
- Osteomyelitis. This is the name of the inflammatory process that affects bone tissue and bone marrow. With open displaced fractures, the risk of developing osteomyelitis is especially high due to the penetration of pathogenic flora into unprotected areas.
- Bleeding. Due to damage to soft tissues from fragments, injuries to large vessels (veins and arteries) are likely. Such bleeding leads to serious blood loss. This reduces the body's protective potential, increases the risk of infection and slows down regeneration processes. Therefore, in case of bleeding, it is so important to quickly stop it by applying a tourniquet and treating the open wound.
- Joint mobility disorders. In the case of intra-articular fractures, the joints suffer greatly. For their mobility, the release of a lubricating fluid is necessary. In case of injury, its synthesis decreases or stops. This consequence, if left unattended, can lead to disability.
Clinical picture
When a fracture occurs, the displaced bone damages the nerve endings, causing the person to experience severe pain. They become stronger when trying to move the injured limb and during palpation of the injury site. Pinched nerves can also cause decreased sensitivity or complete numbness in the fingers.
The displaced fragments rupture the blood vessels, which causes a hematoma. With an open type of fracture, a wound occurs, from which bone fragments may be visible, and external bleeding. If the blood flows in a small stream and has a dark color, then the vessel is damaged, but if the blood is bright, scarlet and gushes like a fountain, this indicates arterial bleeding and requires the immediate application of a tourniquet. A pulsating and rapidly growing subcutaneous hematoma also indicates damage to the artery.
Due to a violation of the outflow of lymph, swelling occurs at the site of injury. When displaced, the limb becomes deformed and may become longer. Pathological mobility occurs in the area of damage, that is, the hand moves in a place where there should not be movement. Upon palpation, the doctor hears crepitus - the sound of bone fragments rubbing against each other.