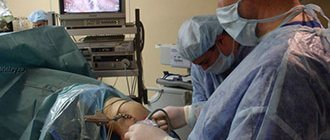
Total or partial rupture of the tendon of the long head of the biceps is not uncommon. This is a severe disorder that leads to limited movement of the upper limb. Only qualified treatment will allow you to regain full use of your arm in the future.
Some patients are inattentive to their health and do not rush to see a traumatologist. If the tendon is completely damaged, the function of the limb will not be fully restored if the disease is not treated, and pain will become a constant companion.
Our clinic has accumulated extensive clinical experience in treating such patients, which allows us to restore the function of the shoulder joint even in the most difficult cases.
Anatomy of the biceps brachii tendon
The biceps, or biceps muscle, is a flexor muscle. It consists of muscle fibers and tendon parts. When it contracts, the upper limb moves in the elbow joint.
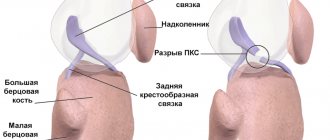
The long head of the biceps is attached to the tubercle of the scapula, and the short head is attached to its coracoid process. Both heads fuse to form a single tendon and attach to the tuberosity at the proximal end of the radius of the forearm. The biceps can not only bend the arm at the elbow joint, but also participate in rotational movements.
Fig. 1 a, b Structure of the shoulder joint (schematic representation)
The long head tendon of the biceps brachii runs through the shoulder joint and is longer than the short head tendon, so it is more susceptible to injury.
Causes and mechanism of rupture
A rupture of the distal biceps tendon is usually traumatic in nature. This injury occurs predominantly in men, as they are more likely to lift heavy objects and undergo intense physical activity.
In older people, a rupture of the head of the biceps tendon can occur for no apparent reason. This is due to age-related changes in the tendons and the consequences of microtraumas that have occurred throughout life. But the pathology often occurs in young, active men 35-40 years old. Predisposing factors are tendinitis resulting from constant microtrauma.
Professional sports and some activities that place constant stress on the biceps muscle over time make the anatomical structures vulnerable, and they rupture even with moderate force.
The injury usually occurs during sudden lifting of weight, as well as during sudden forced extension of the elbow joint. The tendon most often ruptures in the area of attachment to the scapula, the glenohumeral joint, or near the intertubercular groove.
Symptoms of a biceps tendon rupture
In clinical practice, complete ruptures of the biceps head are more common. In this case, the tendon is completely torn and separated from the bone, contracts and is pulled towards the elbow joint.
Upon examination, a pronounced tubercle is visualized on the inner surface of the lower third of the shoulder. Immediately after the injury, swelling occurs that quickly spreads throughout the shoulder.
Fig. 2 Appearance of the shoulder with a rupture of the long head of the biceps.
The rupture may be isolated or accompanied by damage to other structures, such as the rotator cuff. With concomitant disorders, the clinical picture is atypical.
At the time of injury, acute pain is felt, attempts to bend the elbow are painful or impossible. When a tendon is torn or injured in older people, the clinical picture is blurred. The pain syndrome is moderate, flexion strength is reduced.
To determine muscle tone on the injured side, you need to compare it with a healthy arm, since in some patients the tone may be initially reduced.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a rupture of the long head of the biceps is carried out in several stages. At the beginning, the doctor finds out the mechanism and circumstances of the injury, clarifies whether there were injuries before, whether the patient was involved in sports, whether his work involves constant physical activity.
After collecting anamnesis, the orthopedist-traumatologist proceeds to the examination. The doctor visually assesses the condition of the upper limb, determines whether there is a hematoma or tubercle in the distal part of the shoulder. An important factor is the presence, localization and persistence of pain. The volume of active and passive movements of the upper limb is also determined. If the case is serious and the gap is complete, active movements are limited.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the extent of damage, additional examination methods are used. Ultrasound is widely used; the method allows you to accurately determine complete ruptures. MRI is used to obtain more accurate information about the location of the injury, as well as to visualize small tears and intra-articular injuries.
Fig. 3 MRI picture of a tendon rupture of the long head of the biceps
Rupture of wrist ligaments
When a ligament ruptures, very severe pain is felt, sometimes even stronger than the pain caused by a bone fracture. A rupture of the ligaments of the wrist joint is characterized by symptoms depending on the depth and severity of the injury.
There are three classifications of degrees of wrist ligament damage: mild, moderate, severe.
Rupture of the wrist ligaments of the first, mild degree—tear of the ligament—occurs almost painlessly, but during flexion and extension movements of the hand, a feeling of pain appears. There is no tissue swelling.
Partial ligament rupture is typical for moderate wrist injury. The pain is felt clearly, movements are limited, there is swelling, swelling and hemorrhage.
If burning and sharp pain does not allow you to move your arm, and there is a large hematoma and swelling on the wrist, these are signs that characterize a severe degree of injury. The ligament has been torn.
Treatment
Treatment for a rupture of the head of the biceps can be conservative or surgical.
Tactics are determined depending on the degree of damage and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- middle and old age;
- contraindications to surgery;
- activities not related to the use of physical force;
- minor tendon damage.
After conservative therapy, the strength of supination is reduced by 20%, if the patient does not engage in activities associated with heavy load on the upper limbs, this factor does not affect the quality of life and allows one to fully take care of oneself.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated for young people, patients who play sports or do physical work. The operation completely restores range of motion and muscle strength. The most progressive treatment method for biceps tendon rupture is such a modern surgical treatment method as arthroscopy.
The technique is based on the use of an arthroscope, which is inserted through small punctures, allowing you to examine the area of damage in detail using optics, as well as carry out the necessary manipulations to restore the tendon.
The effectiveness of the procedure is high, and the recovery period is minimal. In some cases, a technique with traditional surgical access through an incision is also used.
Rice. 4 Schematic representation of tenodesis (fixation to the head of the humerus) of the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle with a screw (a) and an anchor fixation (b).
“I fell, I woke up...” What is a meniscus tear?
Deep squats, forced flexion and extension of the knee joint, running with a sharp turn and a host of other reasons can lead to damage to the knee joint.
We talked about such a serious injury as a meniscus tear with Ivan Viktorovich Kalashnikov, a traumatologist and orthopedist at the Expert Clinic Irkutsk.
— Ivan Viktorovich, what are menisci and where are they located?
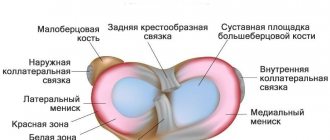
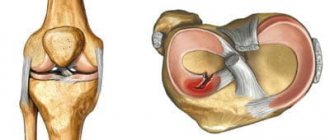
— Menisci are C-shaped (crescent-shaped) cartilaginous elements of the knee joint. There are two of them: external and internal. The menisci are, so to speak, a spacer between the femur and tibia.
— What role do the menisci play in the joint?
- They have a shock-absorbing and stabilizing role. The menisci complement the articular surfaces, increase the congruence of the joint (i.e., mutual correspondence of the articular surfaces), and soften sharp shocks.
Thanks to the menisci, the contact area of the articular surfaces increases, which contributes to a more even distribution of the load. This way the joint wears out less.
— Rupture of the meniscus of the knee joint - what does it mean?
- This is a violation of the integrity of the meniscal tissue. When a joint moves, the meniscus resists this movement. It stands still, and the articular part of the bone slides along it. The meniscus itself does not have nerve endings, but if the integrity of the meniscus is damaged during movement, the torn part is displaced, which leads to tension in the joint capsule at the site of attachment of the meniscus and causes pain.
— What could be the cause of the damage?
— The causes of a meniscus tear are most often unprepared forced actions: sharp flexion and extension, squats more than 90 degrees, running with a sharp turn, squatting, etc. If the muscle frame does not have time to prepare to stabilize the knee joint, then in addition to compression ), a sliding twisting movement also results in a displacement of the meniscal tissue. And here, of course, there is a gap. Injuries can also be caused by falls, blows to the knee, or degenerative disorders of the meniscal tissue.
— What are the symptoms of a meniscus tear?
— The main ones are pain and limitation of movements in the joint. Edema may appear and synovitis may develop. This is visible visually, and patients usually feel that fluid has accumulated in the joint.
— How to determine a torn meniscus of the knee joint?
— Methods for diagnosing meniscal tears, in addition to symptoms and anamnestic data, include X-ray, ultrasound, MSCT and MRI.
An X-ray examination does not show cartilage tissue, assessing only bones, but we carry it out in order to exclude pathology with similar manifestations. MSCT is also used when in doubt, when there is a suspicion of bone damage. Ultrasound diagnostics is used when more accurate methods are not available. It allows you to see not all structures.
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to visualize soft tissue components (ligaments, menisci, cartilage, etc.) in sufficient detail. What we subsequently see during operations almost completely coincides with the data obtained using MRI. The “gold standard” is radiography plus MRI. Such an examination is carried out only after examination by a doctor.
— What treatment methods are there for a meniscus tear?
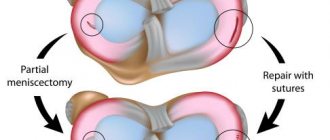
— Treatment methods, as in all medicine, are divided into two groups: conservative and surgical. The answer to the question of whether treatment is possible without surgery depends on the type of meniscus tear. If there is a restriction of movement in the joint due to a mechanical block, then manual reduction and elimination of this block are performed using special techniques. After this, the limb is immobilized (immobilized) in a straight position either with a plaster splint or a rigid splint (orthosis) for four weeks. This is possible only with certain types of rupture, which can heal themselves.
Knee arthroscopy
But more often than not, the meniscus does not heal on its own. And then surgical intervention is necessary, aimed either at restoring the meniscal tissue (meniscus suture) or at removing the torn part of the meniscus (in case of an unsutured rupture). Today, in this case, a high-tech minimally invasive method such as arthroscopy is used. A video camera is inserted through accesses in the form of punctures of approximately 5 mm, and the necessary instruments are inserted through another port, and the operation is performed. This significantly reduces postoperative recovery time.
— Is it possible to avoid damage to the meniscus? What preventive measures are there?
— We must try as much as possible to avoid twisting movements, deep squats under heavy load, sudden movements without preparation, as this is very dangerous for the meniscus. If we play sports, we must warm up well before training and start doing exercises after the warm-up.
The risk of getting a tear increases with excess weight, as the load on the menisci increases.
It is necessary to strengthen the muscle corset. If you do not touch upon force majeure circumstances, then with a stable knee joint, the menisci rarely suffer.
For reference:
Kalashnikov Ivan Viktorovich
In 2010 he graduated from the medical faculty of Irkutsk State Medical University
2010 – 2012 – residency in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics”
Currently, he is a traumatologist-orthopedist at the Expert Clinic, Irkutsk.
Receives at the address: Irkutsk, st. Kozhova, 9 A.
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment
After restoration of the anatomical integrity of the ligaments and tendons, the limb is immobilized for a period of 3-6 weeks. For quick recovery, physiotherapy and physical therapy are widely used, which is a set of exercises to improve muscle tone and increase range of motion in the joint.
Therapeutic massage is used to activate metabolic processes and improve muscle tone. Restoration of performance occurs within 6-10 weeks from the moment of injury.
Biceps brachii tendon rupture is a serious injury that can lead to dysfunction of the upper extremity if not treated properly.
If trouble occurs, seek medical help from an orthopedic traumatologist as soon as possible. High professionalism, individual approach, mastery of modern technologies, rich practical experience and good material resources allow the specialist to return patients to a full, active life.
Treatment of sprains and ligaments
For mild injuries, to restore the ligaments, it is enough to apply ice immediately after the injury, immobilize the joint and give the patient an anesthetic. The next day, you no longer need to apply ice; on the contrary, it is recommended to take a warm local bath and apply heparin ointment to the damaged joint. The ointment is gently rubbed into the skin 2-3 times a day. If after 2-3 days the pain persists and the swelling has not subsided, then you need to contact a surgeon to receive qualified help.
Treatment for ligament damage always depends on the severity of the injury. If there is a severe sprain, partial or complete tear of the ligament, resulting in severe swelling, the doctor may apply a plaster cast. If there is a large gap between the torn ends of the ligament and they do not touch each other, then the ligament will need to be surgically repaired. The operation will prevent the formation of a loose elongated ligament and chronic instability of the joint, as well as the development of degenerative arthritis.
To speed up the rehabilitation process, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic treatment, massage and therapeutic exercises. But restorative procedures are possible only after the acute stage of the disease is completed, that is, approximately 10-15 days after the injury.