Structure
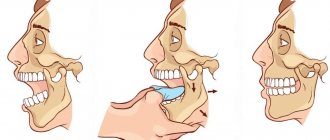
The formation of the mandibular region is the result of the evolution of the human body. In the process of development, the entire structure became mobile and autonomous, gaining the ability to move freely and perform the basic functions necessary for a person. The temporal joint is localized in the fossa, connecting to the bony part.
When a subluxation occurs, the head of the joint partially comes out of the fossa, succumbing to the influence of external factors. As a rule, this phenomenon becomes a consequence of a general weakening of the ligaments or disturbances in the articular cavity. If you have the proper skills and practical experience, you can restore the original position of the jaw yourself, but the systematic occurrence of such a problem is the basis for complex treatment.
Which doctor should I contact for help?
If characteristic signs of a dislocation appear, you should urgently see a specialist. As for which doctor treats such cases, it may be suggested to go straight to a dentist or a hospital emergency room. First, the joint needs to be realigned, and this can also be done by a traumatologist.
You should contact your dentist or emergency room right away
Further treatment may be carried out by an oral surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon. There is also an independent specialization - gnathologist. This area of dentistry studies the morphofunctional relationships of tissues and organs of the dental system.
Causes and classification
Displacement of the lower jaw is the result of the application of an external force that exceeds in intensity the force of natural fixation. For each person, such a threshold is individual - some patients may suffer from minor force, while others are able to endure strong mechanical impact without consequences.
The main factors determining the tightness of the fit are ligament tension and bone attraction. The weakening of these connections can provoke the occurrence of subluxation, both one-time and in a chronic form. The reasons that negatively affect the condition of the jaw region include:
- Advanced stages of rheumatism;
- Developing arthritis or osteomyelitis;
- The occurrence of cramps and muscle spasms;
- Consequences of encephalitis;
- Epileptic seizures.
They also note the existence of traumatic factors, the occurrence of which can cause subluxation:
- Mechanical injuries - impacts, collisions;
- Excessive opening of the mouth;
- Having bad habits;
- Congenital abnormalities that affect the formation of the articular fossa.
The classification used in dentistry differentiates pathology according to the following criteria:
- Based on the position of the articular head - anterior, posterior and lateral subluxation;
- According to the specificity of the displacement - one-sided and two-sided form;
- Depending on the severity - for simple and complex cases.
The choice of technique, as well as the timing of treatment, depend on the original source of the problem. It is easiest to cure the pathology in the early stages, so at the first symptoms of subluxation it is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
What happens if the problem is not treated - complications
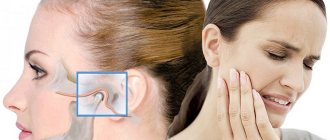
Even a slight crunch and moderate pain cannot be ignored. These are obvious symptoms, so you should not lead the situation to a complete restriction of joint mobility. If an inflammatory process occurs, it can quickly spread to the hearing organs and affect the trigeminal nerve. As a result, there is a risk of serious hearing problems and severe, excruciating pain.
It is worth noting that the pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia is so intense that it can even lead to mental disorders. Spasm of the masticatory muscles, which often occurs with joint dysfunction, can spread to the neck and back, causing spinal problems and severe pain in this area. Therefore, any problems with the functioning of the TMJ must be treated in a timely manner - then the therapy will be much easier and faster.
Symptoms and signs
For each form of subluxation, there are characteristic individual signs that indicate the presence of deviations. However, there are a number of universal symptoms observed in all types of pathology:
- The occurrence of pain of varying severity, aggravated when the patient attempts to move the lower jaw;
- Limited mobility of the temporomandibular joint, making it difficult to perform usual actions - eating or speaking;
- Active secretion of saliva associated with a swallowing problem.
In addition, with bilateral dislocations affecting the anterior zone, the following circumstances occur:
- Inability to close the jaws, forcing the patient to keep his mouth open;
- Pain in the skull and swelling of tissue in the ear area;
- Partial or complete dysfunction of the speech apparatus.
The unilateral form of subluxation has similar symptoms, but allows partial closure of the mouth, which significantly alleviates the patient’s problems. In turn, posterior bilateral subluxation is characterized by the opposite symptomatology - the inability to open the jaw, pressing of the lower part into the larynx area.
First aid and treatment
If a subluxation occurs, it is recommended to straighten the jaw using the infiltrative or guide method, after first calming the patient and giving him an anesthetic. The lack of such skills requires contacting a qualified orthodontist, who will not only restore the natural structure of the jaw apparatus, but also advise measures aimed at restoring and preventing recurrences. If the procedure aimed at realigning the joint is carried out in a timely manner, as well as medical recommendations are followed during the rehabilitation period, the prognosis for a complete cure is very favorable.
Treatment of dislocations of the lower jaw
If you or your loved ones have suffered a dislocation of the lower jaw, treatment should be provided to a specialist. Self-reduction of dislocations can result in serious consequences.
The first thing that needs to be done is to take the victim to a traumatology center, where a specialist will realign the displaced jaw. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. In dentistry, treatment of anterior displacement of the jaw is treated using the following methods: Hippocrates, Khodorovich, Blechman, Gershuni, Popescu (in cases where the dislocation occurred a very long time ago).
The first method is the most popular among specialists. The patient is seated on a low stand, with the back of the head firmly resting against a wall or other hard place. The position of the injured jaw should be at the same level as the elbows of the reducer, who is located opposite the patient. Next, wrapping your thumbs in several layers of soft cloth, he places them on the lateral front lower teeth; the remaining ones hold the outer side. Then, using a smooth but firm downward pressure, the jaw is moved to its anatomical location. During this manipulation, the dentist must remove his fingers from the teeth almost overnight so that the patient does not bite them. At the moment of reduction, a click and a strong clenching of the jaws will be heard.
If it is necessary to correct the posterior displacement of the jaw, then the reduction technique is identical, with the only difference being that the jaw is directed upward.
After displacement, it is necessary for the jaw to remain at rest for some time. To do this, wear a chin sling for one week or more if necessary. For posterior dislocation, immobilization is indicated for 3 months.
During the entire rehabilitation period, the patient must balance his diet and not eat solid foods. If it is impossible to correct the dislocation, surgical treatment of the pathology is performed. Dislocations that occurred a long time ago and have not been reduced are treated by resection of the joint heads, followed by mechanotherapy.
Patients are able to correct permanent dislocations on their own, but the technique does not exclude immobilization of the jaw; if necessary, prosthetics are performed.
Diagnostics
To determine the severity of the injury, the patient is sent for x-rays. It will help to identify the exact clinical picture of a certain type of dislocation (one or two-sided). The image will show how much displacement of the joint has occurred. This will help your orthopedic surgeon prescribe an initial course of treatment (for severe cases). X-rays can also help differentiate a subluxation from a jaw fracture. If the orthopedist still has doubts about the diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), axiography and arthroscopy of the joints are additionally prescribed.
In most cases, the subluxation is adjusted by the doctor manually, without applying significant physical force.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention is performed: the head of the joint is narrowed and fixed with staples. A timely visit to the clinic will help to avoid disturbances in chewing functions and prevent the recurrence of injuries.
Is it possible to solve the problem yourself - how to correct a dislocation at home
Many people are interested in the question of how to straighten the jaw themselves, without the help of specialists. Here you need to answer immediately and categorically - under no circumstances try to do this yourself, otherwise such an initiative could end very badly. The assistance of an experienced doctor is required, including a competent diagnosis and assessment of the degree of complexity of the injury, and in the future, strict adherence to the reduction technique. After providing first aid, the victim must be taken to a specialist.
How else are TMJ injuries treated?
After realignment of the joint, therapeutic treatment is required. Autogenic training demonstrates good effectiveness in this regard - it helps relieve tension and spasms of the masticatory muscles. In case of severe pain, local anesthesia is prescribed or the trigger zones are blocked. Physiotherapy methods are also often used and the wearing of individual joint splints is prescribed to stabilize the functioning of the TMJ.
Drug therapy is usually aimed at relieving inflammation and spasms, relaxing masticatory muscles and joints, and normalizing the patient’s emotional state. For this, he may be prescribed analgesics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants and nootropic drugs. Orthodontic correction may also be required to correct defects that lead to malfunction or impede the functioning of the TMJ - splints, mouthguards, bite blocks and other corrective devices.
The patient may be prescribed painkillers
In rare cases, the only option is surgery followed by long recovery. Prosthetics are used in situations where there is a chronic condition. That is, the injury was repeated so often that the joint literally became “loose.” In this case, it is also often prescribed to wear orthopedic removable and non-removable structures that protect the joint from excessive loads.