Back pain often occurs in a person due to the formation of incorrect posture while walking and sitting at a desk. But this is also one of the consequences of damage to the intervertebral discs, cartilage tissue and nerve fibers, resulting in the development of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
With lumbar osteochondrosis, degenerative changes occur in the lumbosacral spine. If the disease is not treated for a long time, the patient’s general well-being worsens: constant back pain, numbness of the limbs, spasms and cramps in the muscles, general weakness and loss of strength.
How does pathology develop?
During the development of the disease, degenerative-dystrophic and destructive disorders occur in the skeleton of the patient's spinal column. As a result, the anatomy and physiology of the articular elements of the spine changes. The human lumbar spine bears the main load in the form of the weight of the person’s upper body, loads during movement, training or performing any physical activity. As a result of all of the above, the following changes occur:
- the axis of the spinal column is distorted;
- posture changes;
- bones put pressure on internal organs. This leads to the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- coordination is impaired due to pinched nerve endings;
- the structure of the spinal column changes;
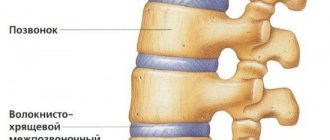
- cartilage tissue becomes thinner;
- the structure of the synovial fluid is filled with third-party components;
- the vertebrae are worn out, which reduces the distance between them;
- When the vertebrae touch, the nerves become pinched - this leads to acute pain.
At risk of developing lumbar osteochondrosis are athletes who lead an overly active lifestyle, people with a sedentary lifestyle (being in one unchanged state for a long time, they create an increased load on the spine), representatives of manual labor professions who work with heavy tools , elderly people, pregnant women, hyperactive children.
What can be seen on an MRI for osteochondrosis?
Thanks to MRI images, the doctor can clearly see pathologies in the intervertebral discs, articular cartilage, problems in connective tissues, pinched nerves, inflammation in the tissues of ligaments and muscles. Based on the results of tomography, neurologists can judge the location of the disease, the degree of osteochondrosis, the presence of a rupture of the nucleus pulposus and the appearance of hernial formations. Tomography data will allow you to diagnose:
- Displacement of intervertebral discs;
- Thinning of the intervertebral discs;
- Condensed formations;
- Salt deposits;
- Inflammation of soft tissues and muscles.
- The appearance of hernias and protrusions;
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes and displacements in the vertebrae;
- Ligament hypertrophy;
- Deformation of the facet joints.
| NORM | PROTRUSION | INTERVERTEBRAL HERNIA |
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
- acute pain in the lower back after a night's sleep;
- pain when turning the body sharply or lifting heavy things;
- the first signs of scoliosis appear;
- frequent urination;
- pain radiates to the legs, internal organs of the abdomen and pelvis;
- acute pain in the area of the kidneys and sacrum;
- difficulty moving, walking, bending and turning the body;
- rapid fatigue after minor exertion;
- numbness of the limbs;
- spasms and cramps in muscles;
- dizziness;
- decreased muscle tone and sensitivity.
Indications and contraindications for radiographs
Indications for conducting a study to identify osteochondrosis on x-ray are:
- pain in the lumbar region, back, cervical spine;
- limitation of mobility in various parts of the spinal column;
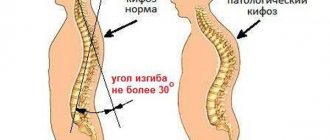
- poor posture: scoliosis, kyphosis, pathological lordosis;
- manifestations of radiculopathy (damage to the lumbosacral region), intercostal neuralgia (damage to the thoracic segment), plexopathy (damage to the cervical region);
- with cervical osteochondrosis, severe headaches, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, tinnitus;
- trophic disorders due to atrophy of the nerve roots (impaired skin sensitivity, the formation of muscle atrophies, the formation of skin ulcers).
Manifestations of osteochondrosis can already appear in adolescence. The peak incidence occurs in females aged 35-40, when degenerative changes are provoked by hormonal changes. With age, the development of pathology becomes more frequent due to a smaller supply of nutrients and calcium leaching. Regenerative mechanisms are depleted, disc destruction occurs faster.
Contraindications to radiography are common to all types of examination. The examination is strictly prohibited for pregnant women; research in children and lactating women is limited. This is due to the ionizing effect of X-rays.
Stages of development of lumbar osteochondrosis
Stage 1 – all degenerative disorders are just beginning to develop in the patient’s skeleton. But at the same time, the roots of the nerve endings are already affected. Blood flow worsens and the inflammatory process begins. It manifests itself as back pain after increased exertion, which often radiates to the legs.
Stage 2 – the fibrous ring in the spine is destroyed, the cartilage becomes thinner, and the distance between the vertebrae is reduced. The pain in the second stage is sharper and more acute.
Stage 3 – severe compression of muscle fibers and nerve endings occurs. There are burning pains and muscle spasms, as well as frequent numbness.
Stage 4 – the period of growth of neoplasms (osteophytes) in the bone structure. Arthrosis appears in the spine and joints. The back becomes inactive, and in the absence of correct treatment, completely immobile.
“Payback for upright walking”: causes of the disease
Osteochondrosis can develop for a number of reasons, ranging from a sedentary lifestyle to injuries and overload.
“There is an opinion that spinal osteochondrosis is a person’s retribution for walking upright,” notes neurosurgeon of the highest category at SM-Clinic, Ph.D. Sergey Alexandrovich Kuznetsov
. – Currently, the cause of osteochondrosis is considered to be a combination of factors affecting the spine during a person’s life. An additional risk of developing the disease comes from spinal injuries and poor posture. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of proper physical activity also play an important role. This leads to insufficient functioning of the natural muscle “corset” that holds the spine in an anatomically correct position. As a result of this, and also in the presence of excess body weight, the intervertebral discs are overloaded with the development of a degenerative process in them.”
As noted by the senior medical consultant of the Teledoctor24 service, Neya Georgieva
, to one degree or another, osteochondrosis develops in all people with age. “Roughly speaking, this is one of the processes of aging of the body,” she says. “However, injuries and overloads of the spine contribute to the earlier onset of this disease. The main point in the occurrence of osteochondrosis is the constant overload of the spinal motion segment: poor posture, individual sitting style (wrong posture), walking with an uneven spinal column cause additional stress on the discs, ligaments and muscles of the spine. The occurrence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is often associated with its overload when bending and lifting heavy objects.”
It is necessary to monitor your posture from early childhood. But, unfortunately, our lifestyle does little to contribute to this: first we slouch at our desks at school, then in an office chair - and so on until old age. Many of us no longer even remember what a straight back should look like.
“When sitting, the head, shoulders and pelvis should remain at the same level. The back must be kept straight even when walking, when additional dangers may await, for example, due to shoes with heels, since when wearing such shoes the center of gravity shifts. But that's not all. Shoes with flat soles also harm the health of the musculoskeletal system, because they lack shock absorption - the spine suffers from impacts on the surface during normal walking or running. Few people know, but the center of gravity can be shifted due to flat feet, because unnatural foot placement leads to a change in gait and a twisted body position,” says Sergei Aleksutov.
How is osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine diagnosed?
Diagnosis of pathology begins with consultation with a specialist. At the first manifestations of osteochondrosis, consult a rheumatologist, neurologist, surgeon or orthopedic traumatologist. If you find it difficult to choose a doctor, you should first consult with a therapist. Depending on the symptoms and suspected causes of the pathology, he will refer you to one of the highly specialized specialists.
- The doctor will examine your medical history and the frequency of their manifestations; you need to provide the specialist with a complete medical history and the results of earlier studies (if any). The specialist will conduct a visual inspection and palpation.
- During the examination, the doctor pays special attention to changes in posture, muscle tone, skin sensitivity and identifies the most painful areas. The purpose of the conversation is to find out the degree of development of the disease. If you have any questions, a specialist will advise you and conduct an examination.
- He will refer you for tests, because a complete diagnosis will allow you to make the correct diagnosis.
- Based on the results of the tests, the doctor will prescribe an individual treatment plan.
To identify the condition of muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, and detect inflammatory processes or tumors, an informative and safe diagnostic method is prescribed - MRI of the lumbar spine. During an MRI of osteochondrosis, the patient lies on a special sliding table with his back. Rollers are placed on the patient's head to relieve muscle tension, and the limbs are secured with belts. Any slight movement during the procedure can affect the quality of the result. Next, the table moves into the tomograph area. The procedure does not cause pain. The tomograph makes a lot of noise during scanning, so you can use headphones to avoid discomfort.
If MRI is contraindicated, there are other diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and radiography. X-ray is suitable only for primary diagnosis and does not provide a layer-by-layer image of the affected tissue. However, this study is the simplest and most economical, allowing you to examine the patient’s body in several projections. Due to the strong radiation exposure to the body, radiography cannot be performed frequently.
During a computed tomography scan, a scan is performed using one or more beams of ionizing rays. They pass through the human body and are recorded by detectors. The detectors move along the patient's body in opposite directions and record up to 6 million signals. The image displays tissues of different densities with precise definition of the boundaries of organs and the affected areas in the form of a section. The procedure allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image.
Signs of osteochondrosis on MRI images
An example of an MRI report describing the signs of osteochondrosis:
EXAMPLE OF MRI CONCLUSION - spine
MR signs of degenerative-dystrophic changes are revealed in the form of a decrease in the intensity of the MR signal from the intervertebral discs in the L1-S1 segments on T2-WI due to dehydration of the nucleus pulposus of the discs, with a decrease in height in the L4-S1 segments, small anterior and posterolateral marginal bones growths in segments L1-S1, with calcification of the anterior longitudinal ligament at the points of attachment to the vertebral bodies. In the intervertebral joints, degenerative changes are visualized in the form of compaction, unevenness of the articular surfaces, and hypertrophy of the yellow ligaments. In the adjacent sections of the vertebrae L4-L5, L5-S1, zones of heterogeneous increase in the MR signal on T1, T2-WI and hypointense on STIR-IP (due to fatty degeneration) are determined. Irregularities of adjacent endplates of the vertebral bodies Th12, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, S1 due to Schmorl’s cartilaginous nodes.
EXAMPLE OF MRI CONCLUSION - thoracic spine
On a series of MR images, weighted by T1 and T2 in three planes, degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs are determined, characterized by a decrease in the height and intensity of the MR signal from them on T2-weighted images. Kyphosis is preserved. At the level of the Th8-Th9 intervertebral disc, a left-sided paramedian dorsal hernia is determined, sagittal size up to 3 mm, compressing the anterior wall of the dural sac. The roots are intact. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 14 mm. There is a dorsal left-sided paramedian herniation of the intervertebral disc Th10-Th11, up to 3 mm in size, which compresses the anterior wall of the dural sac. The roots are intact. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 15 mm. A dorsal median herniation of the intervertebral disc Th11-Th12 is determined with a tendency of cranial migration up to 3 mm, up to 5 mm in size, which compresses the anterior wall of the dural sac. Convincing data on root compression have not been obtained. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 13 mm. At the level of the intervertebral disc Th12-L1, a median dorsal hernia is determined, sagittal size up to 5 mm, compressing the anterior wall of the dural sac. The roots are intact. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 16 mm.
Free diagnostic consultation
If in doubt, sign up for a free consultation. Or consult by phone
+7
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Depending on the stage of lumbosacral osteochondrosis, different treatment methods may be prescribed. One of these methods is physical therapy. It is carried out in a specially equipped room under the close supervision of a doctor. Classes are carried out when the patient does not experience pain. But if during physical education the patient begins to feel worse, the doctor adjusts or cancels the exercise altogether.
Another method of treating lumbar osteochondrosis is physiotherapy. It improves blood circulation and tissue nutrition, reduces inflammation and reduces pain. Physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- Electrophoresis – painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used, the procedure reduces the neurological manifestations of the disease.
- Magnetic therapy – an alternating magnetic field relieves inflammation.
- Ultrasound therapy – acts along the affected part of the spine.
- Diadynamic therapy - the effect on the affected areas occurs using currents of varying intensity.
- Hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches. Their effect improves microcirculation and metabolism of nutrients in the tissues of the back.
- Kinesio taping is a treatment using a cotton patch.
Drug treatment - prescribed in extreme cases using analgesics (have an analgesic or additional anti-inflammatory effect), antispasmodics (relieve muscle spasms), vasodilators (improve blood microcirculation).
What needs to be examined
To identify osteochondrosis, it is necessary to carry out X-ray diagnostics of the area where the damage is most likely localized. Osteochondrosis is shown by x-ray:
- cervical spine with functional tests;
- thoracic vertebrae;
- lumbar spine in functional tests.
X-rays of the sacrum are not performed, since there are no intervertebral discs anatomically in this section; the image is of little information for diagnosing degenerative pathology of intervertebral discs.
Where can I get examined and treated for lumbar osteochondrosis?
If you or your loved ones suffer from lumbar osteochondrosis, seek medical help. We treat osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine in Krasnoyarsk. Powerful equipment for CT, MRI and X-rays, experienced doctors who, if necessary, will conduct an initial examination at home, are waiting for you at Medunion.
At the Medunion medical clinic you can:
- get advice from an experienced specialist without queuing or waiting;
- undergo diagnostics using modern, international-class equipment;
- call a highly specialized specialist to your home if necessary;
- use the service of collecting biomaterials at home;
- undergo the entire examination in one place and without queues: with us you can get a doctor’s consultation, take tests, undergo any diagnostic tests, and more.
The cost of an initial consultation with a specialist in Krasnoyarsk starts from 1,200 rubles. For more information or to make an appointment, call 201-03-03.
Which is better - MRI, CT or X-ray for spinal osteochondrosis?
In addition to magnetic resonance imaging, osteochondrosis can also be diagnosed using a computed tomography scan of the spine or x-ray. All these types of studies will show whether a person has osteochondrosis. If you give preference to one of these forms of diagnosis, then, without a doubt, it will be an MRI of the spine. This scanning method, unlike radiation diagnostics, does not cause harmful radiation to humans. During the examination there is no x-ray radiation, no painful sensations. The diagnostic value of MRI images will also be higher than CT and X-ray tomograms. MRI for osteochondrosis will show not only the bone tissue of the vertebrae, but also connective tissue and articular cartilage.
Operating principle
An X-ray machine is a medical equipment that allows you to examine the internal structures of the human body. The principle of operation is quite simple - X-rays, passing through the body, create an image on a screen or photograph. Soft tissues that transmit X-rays well will appear black. And hard tissues that have a pronounced ability to absorb them will be light.
To make an accurate diagnosis, images are taken in two projections - this approach allows you to obtain the maximum amount of reliable information. The radiologist who interprets the obtained images compares the degree of staining of different structures and, based on this analysis, issues his conclusion.
Content:
- Operating principle
- What will an X-ray of the cervical vertebra show?
- Indications for use
- Preparing for X-rays
- Features of the procedure
- X-ray with samples
- Restrictions and contraindications
Today, two types of equipment are used to perform radiography procedures: digital and film. Digital cameras are modern, giving more accurate and detailed images. In addition, a digital image can be quickly sent for interpretation to specialists located in any corner of the world.
Preparing for X-rays
There is no need to pre-prepare the patient for the test procedure. It is enough to remove clothes from the upper part of the body and remove all metal elements: jewelry, cufflinks, fasteners, removable dentures. When undergoing routine radiography, the patient should be familiar with these requirements in advance so that he can choose clothes that are easily removed and leave all jewelry at home.
Why is it necessary to remove all metal objects? Metal is not capable of transmitting X-rays, so the results of the study may be unreliable.