Ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the spine and joints. The cause of ankylosing spondylitis is the aggressiveness of the immune system towards the tissue of one’s own joints and ligaments (inadequate immune response). The reason is a genetic predisposition in people who are carriers of a certain antigen (HLA-B 27); in this case, the immune system mistakenly perceives some tissues of the body as foreign, which is the cause of aggression.
- Ankylosing spondylitis. Why and how joints, ligaments and spine suffer.
- Symptoms, examination and diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
- How to relieve pain and maintain mobility of the spine and joints with ankylosing spondylitis
- Gymnastics for ankylosing spondylitis
- Diet for ankylosing spondylitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis and infections
- Ankylosing spondylitis and mental stress
- What is useful and what is harmful in ankylosing spondylitis
- Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis) at the Echinacea clinic
Ankylosing spondylitis. Why and how joints, ligaments and spine suffer
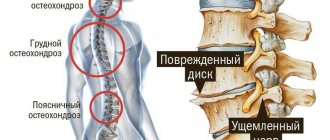
Favorite targets of ankylosing spondylitis are the joints and joints of the sacrum and spine, costovertebral joints. Inflammation of the joints of the extremities and peripheral enthesopathies (inflammation of the sites of attachment of tendons to the bone) are also often observed; less often – symptoms of damage to internal organs.
The basis of the disease is inflammation of the joints, tendons and ligaments. In addition, inflammatory changes occur in the synovial membrane of the joints and changes in bone tissue. Long-term uncontrolled inflammation of the articulations and joints of the spine leads to calcification and the development of ankylosis - immobility. Therefore, we strive to reduce the aggressiveness of the immune system and relieve inflammation as quickly as possible - this is the only way to maintain mobility and relieve pain in the back and joints.
Why do chondroprotectors really help?
Chondroprotectors
– drugs that contain
glucosamine
and/or
chondroitin
. These are natural substances in our body. With a decrease in their production, metabolic processes in the joints are disrupted, then degenerative changes occur in the cartilage tissue. The result is sore joints. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with chondroprotectors in the early stages will help slow down the degradation of joints, speed up the restoration of cartilage, and relieve pain.
Treatment with chondroprotectors can be effective in the early stages of Ankylosing spondylitis.
Symptoms, examination and diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
We often see patients with an “experience” of ankylosing spondylitis of 10 years or more, with an unknown diagnosis, and therefore who have not received the correct treatment. In the early stages, it is indeed difficult to recognize ankylosing spondylitis: early radiological signs are familiar only to specialists. In any case, if you have been experiencing morning pain and stiffness in the lower back and back for a long time, you should rule out ankylosing spondylitis. For early diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis, we perform x-rays in special projections and laboratory tests, including genetic ones.
Symptoms of spinal damage:
- An important early symptom is pain and stiffness in the lumbar spine; often occurring at night and worsening in the morning, it can last more than 2 hours after waking up and decreases after exercise and a hot shower. During the day, pain and stiffness in the spine with ankylosing spondylitis are observed at rest, in the morning and decrease with movement, sometimes disappearing in the afternoon. Spinal damage is a mandatory symptom.
- As the disease progresses, the inflammatory process with pain and stiffness spreads to the overlying parts of the spine.
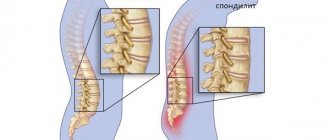
- The physiological curves of the spine are gradually smoothed out and pathological kyphosis (stooping) of the thoracic region is formed, so that in some cases the correct diagnosis can be made “at a distance”, based on the characteristic posture of the patient. The course of this form of the disease is usually slow, many years, with periods of exacerbations and improvements.
- As a reaction to the inflammatory process in the spine, painful tension in the back muscles occurs.
- In the later stages, in the absence of treatment, the limitation of mobility in the spine is aggravated due to fusion of the vertebral joints and ossification of the intervertebral discs, with the formation of intervertebral “bridges”, clearly visible on x-rays.
Symptoms of joint damage:
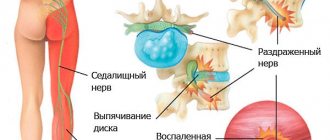
- An important manifestation of ankylosing spondylitis is inflammation of the joints of the sacrum - sacroiliitis. In this case, pain can be felt deep in the buttocks. Pain is often mistaken for a symptom of radiculitis or herniated disc, inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
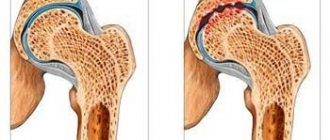
- More than half of patients with ankylosing spondylitis have damage to the joints of the extremities, most often the hip and shoulder. Pain and stiffness in the joints, as well as in the spine, are more intense in the first half of the day.
- Less common is inflammation and swelling of the small joints of the hands and feet. The period of inflammation of the joints of the extremities with Ankylosing spondylitis is most often short-lived (1 – 2 months), but sometimes it can drag on for a long time. Even in these cases, unlike rheumatoid arthritis, destruction and deformation of the joints does not occur (with the exception of the hip joints in advanced cases without adequate therapy).
Non-articular symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
About a third of cases of ankylosing spondylitis are accompanied by non-articular symptoms. With ankylosing spondylitis, inflammation of the eye tissue (uveitis, iridocyclitis), inflammation of the heart tissue (myocarditis, possible formation of valvular heart defects), aorta (aortitis), lungs, kidneys, and lower urinary tract occurs.
Ankylosing spondylitis usually begins at the end of the second, beginning of the third decade of life, but recently it has become increasingly common in adolescence.
In childhood or adolescence, the disease most often begins with damage to peripheral joints and is accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature.
Methods for diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis
Blood diagnostics during the activity of the inflammatory process can reveal an acceleration of ESR and an increase in the concentration of CRP, and in half of the cases of long-term illnesses it is possible to detect normochromic anemia. If an increase in creatinine is observed in the blood serum, then the presence of developing chronic renal failure is assumed. At the same time, it should be remembered that the presence of the HLA-B27 antigen is an indirect and nonspecific sign of ankylosing spondylitis. The presence of fibrin, sialic acids, protein fractions, seromucoid, etc. is also determined.- Examination of urine when nephropathy occurs helps to detect protein (proteinuria) and microhematuria - a small number of red blood cells as a manifestation of IgA nephropathy.
- Polypositional (in direct, lateral, oblique projections and with functional tests) radiography or computed tomography of the sacroiliac joints and overlying parts of the spine reveals limitation of mobility and specific radiographic changes (sacroiliitis, spondyloarthritis, sooner or later leading to the formation of ankylosis, deformation of the spinal column according to the “bamboo stick” type, as well as its kyphotic curvatures of varying degrees, up to the formation of a small hump.
- X-ray of peripheral joints allows us to see degenerative-dystrophic anomalies in them, which also lead to dysfunction, the development of osteoporosis, cystic restructuring, the formation of marginal osteophytes, etc.
- Ultrasound has a higher sensitivity in detecting enthesitis. Ultrasound of the hip joints - to detect inflammatory lesions and the presence of effusion.
- Osteoscintigraphy (scanning) – for diagnosing the skeletal system of the spine.
- ECG and EchoCG help determine signs of conduction disturbances, the formation of valvular insufficiency and other changes.
- Consultations with “narrow” specialists (cardiologist, ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon, rheumatologist, nephrologist) are carried out according to indications.
How to relieve pain and maintain mobility of the spine and joints with ankylosing spondylitis
How to relieve pain and maintain mobility with ankylosing spondylitis?
The treatment tactics are logical and quite feasible. The following is required:
- Reduce the aggressiveness of the immune system , and as soon as possible, because inflammation of the joints and ligaments leads to decreased mobility of the spine and joints (ankylosis);
- Control possible risks of exacerbation (infections, intoxications, and other factors that increase the aggressiveness of the immune system);
- Perform gymnastics to restore and maintain mobility;
- Avoid weight gain (overload your joints!); if necessary, we will help you lose weight.
Gymnastics for ankylosing spondylitis
Physical activity is the main condition for proper treatment, so we teach gymnastics to each of our patients . Exercises are selected individually, after assessing mobility impairments. We recommend performing the exercises daily, and if pain occurs, we adjust the gymnastics regimen.
Sometimes you have to develop mobility through the sensation of pain. With irregular exercises, when in the interval between training there is time for a change in the ligamentous apparatus with the formation of dense, sedentary areas in the ligaments and muscles. In these cases, massage helps well. Massage requires quite a long time and frequent courses, so we teach patients and their loved ones massage and self-massage techniques.
Objectives of exercise therapy for ankylosing spondylitis:
- Reducing the progression of ankylosis (if the patient is immobilized, ankylosis occurs quickly)
- Prevention of deformities
- Treatment of existing deformities
- Increasing muscle strength in weakened muscle groups
- Reducing muscle spasm and muscle pain
- Development of correct compensation, correct functional stereotype
- Increased respiratory capacity of the lungs.
Diet for ankylosing spondylitis
As with any chronic inflammatory disease, nutrition must be balanced and compensate for the body's costs. Nutrition should not lead to weight gain, which can increase the load on the spine and joints of the lower extremities. Sufficient consumption of protein foods is mandatory, with preference given to fish dishes and dairy products.
Since patients often have to be prescribed NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), which have undesirable effects on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, to relieve pain and inflammation, a more gentle diet should be followed.
Your doctor will recommend certain types and caloric intakes of food based on your age, gender, weight, and other important factors.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of the disease is pain in the joint apparatus. In the morning you feel stiffness and pain in the spine. Your health may improve with activity. Although the disease affects the spine, pain is possible throughout the entire back area. The reason for this is that the sensory roots of the spinal cord emerge from the spinal column. Because of this, the entire torso, upper and lower extremities are innervated. Therefore, pain can spread throughout the body.
Ankylosing spondylitis and infections
In the development of ankylosing spondylitis, the aggressiveness of the immune system against the tissue of one’s own joints and ligaments plays a role (a genetically predisposed perverted immune response to a certain microbial agent). The aggressiveness of the immune system can be maintained at a high level by various types of chronic infections , and this is a common cause of prolonged exacerbations and difficulties in treatment. Pathogenic microbes may not cause any symptoms, but their very presence in the body irritates the immune system.
In case of ankylosing spondylitis , we identify and treat chronic infections , which allows us to reduce the activity of the disease with minimal doses of medications.
Frequent cases of hidden infections:
- Chronic tonsillitis and pharyngitis (inflammation of the tonsils and pharyngeal mucosa);
- Chronic inflammation of the paranasal sinuses;
- Herpes (recurrent rashes on the lips and/or genitals);
- Intestinal dysbiosis and intestinal parasites;
- Infections of the genitourinary system (prostatitis, urethritis, cystitis, etc.);
- Inflammatory cysts in the area of tooth roots.
Seasonal viral infections can also cause arthritis to worsen.
Mechanism of disease development
Despite active study and collected statistics, the origin of the disease remains unclear. Most experts are inclined to the version of genetic predisposition: the presence of the HLA-B27 antigen in patients passes to first-degree relatives in 25-30%, and occurs within the family only in 7-8% of cases. In residents of the equatorial regions, the pathology is practically not diagnosed, and as we move towards the poles, its frequency increases to 30-40%.
Describing the causes of ankylosing spondylitis, experts talk about an inadequate immune response to the musculoskeletal system of the spinal column. Its tissues are perceived by the body as foreign, and the effect of their rejection occurs, characteristic of all autoimmune diseases. The subsequent inflammatory process is triggered by a cytokine substance consisting of TNF-α peptide signaling molecules called tumor necrosis factor alpha. Due to its active influence, the spine gradually becomes ossified and immobilized. Confirmation of the negative effect of the TNF-α molecule is the maximum concentration of the cytokine in the sacroiliac joint.
Concomitant pathologies or unfavorable external factors can accelerate the transition of ankylosing spondylitis to new stages. These usually include chronic infectious diseases, hypothermia, pelvic or spinal injuries, the consequences of which could not be completely eliminated. At risk are persons with hormonal disorders, infectious and allergic diseases, chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic and intestinal organs.
What is useful and what is harmful in ankylosing spondylitis
Useful for ankylosing spondylitis:
- Swimming (swimming – work of the spine and joints without gravitational load);
- Regular gymnastics, slow exercises - “toffees”;
- Massage (out of exacerbation);
- Dosed and systematic implementation of hardening procedures.
Harmful for ankylosing spondylitis:
- It is contraindicated to engage in traumatic sports; running, jumping, and sudden movements are not recommended;
- Hypothermia is contraindicated, so we recommend conducting rehabilitation exercises in comfortable conditions;
- Physiotherapy and massage are not recommended during an exacerbation; massage (not sports, but therapeutic) is prescribed when the inflammatory activity of the disease subsides; It is recommended to conduct courses at least 4 times a year;
- Treatment with immunostimulants (leads to exacerbation);
- Nervous and physical fatigue.