Therapeutic and health-improving swimming is a type of physical culture during which the human body is simultaneously exposed to water and dynamic movements.
In an aquatic environment, muscles work synchronously, receiving a measured load. Water procedures are considered an important component of the beneficial effect on the patient.
The wide prevalence of diseases of the nervous system of degenerative-dystrophic origin determines the need to use new methods of treatment. Swimming allows you to achieve regression of herniated intervertebral discs (IVD).
Clinical picture
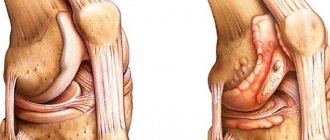
In many cases, lumbar pain is associated with the presence of a herniated disc. This pathology of the musculoskeletal system is caused by displacement of the nucleus pulposus of the IVD with rupture of the fibrous ring. Develops as a result of spinal osteochondrosis and trauma. Causes compression of nerve structures.
In contrast to the normal state of the spinal column, with lumbar hernias, a pattern of vertebral displacement is observed. The danger of spondylolisthesis is the development of chronic pain and weakness in the lower extremities.
The most striking manifestation of an intervertebral hernia is compression of the spinal root with the development of pain, sensory and motor disorders in the area of its innervation. Common placement is at the level of L4-L5 and L5-S1 IVD.
A hernia of the lumbar spine is characterized by:
- pain in the lumbar region, lasting several years;
- reduction in mobility in the motor segment;
- palpation determined tension of the paravertebral muscles;
- change in physiological curves (flattening of lumbar lordosis);
- disorders of the autonomic nervous system (hyperhidrosis, marbling of the skin);
- weakness, muscle hypotonia;
- decreased reflexes;
- disturbance of sensitivity (hypoesthesia, anesthesia, hyperesthesia).
In the initial stages of the disease, the only concern is periodic dull, pinching pain in the lumbar region. The severity of the pain syndrome increases gradually, later vertebral and radicular syndrome joins. Repeated exacerbations, increased pain when lifting weights or muscle tension are typical. As the disease progresses, pathological symptoms appear:
- Lasegue's symptom – pain in the lumbar region when lifting a straight leg in a supine position;
- a symptom of a cough impulse is a shooting pain or an increase in its intensity in the area of the affected nerve root when coughing or sneezing.
Without adequate treatment, loss of sensitivity of the genital organs and dysfunction of the pelvic organs such as urinary and stool incontinence occur.
How to swim after spinal surgery?
You should wait approximately 30 days after surgery for the scar to form and for any infection to not enter the bloodstream. Ideally, start 5-6 months after surgery, and consult a doctor before starting the course.
Those who are in remission should begin classes with caution. Increase the load gradually, coordinating new exercises with your trainer. Try not to make sudden movements or swim quickly: it is better to swim efficiently. Alternate between swims and relaxation, performing the “star” exercise on the surface of the water. Any pain in the spine is a signal to stop exercising.
The benefits and effects of water treatments
In case of lumbar hernia, recreational swimming occupies an important position among the means of correcting functional disorders of the spine. In combination with medical, biological, pharmacopsychological methods, it allows to achieve a positive result depending on the location of the hernial formation.
According to the mechanism of action and effectiveness for hernia of the lumbosacral spine, the optimal means of recreational swimming include:
- corrective exercises;
- isotonic exercises when swimming breaststroke, on the side;
- relaxation exercises (slow swimming with a board);
- stretching in water;
- breathing exercises near the edge of the pool in the water or while moving.
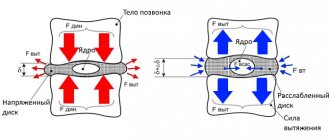
The effectiveness of classes depends on establishing a final diagnosis and a reasonable selection of swimming equipment. In water, the body finds itself in a state of weightlessness. All compressive loads on the IVD are completely removed.
The aquatic environment helps reduce muscle tone, tissue relaxation, and reduce the intensity of pain.
Swimming helps strengthen bone tissue and has a positive effect on joints. Mechanical traction of the spine occurs in water. This leads to decompression of nerve structures, improved blood circulation, reduced swelling, and elimination of subluxations of intervertebral joints.
The benefits of swimming for the musculoskeletal system
The spinal discs experience considerable stress every day due to the pressure of body weight. If you do not unload them, then over time the blood flow deteriorates, and with age the vertebrae also lose flexibility.
Water aerobics and swimming have a beneficial effect on the spine and other organs, namely:
- They relax, because in water the body loses weight, so there is no load on the spinal column, because of this the discs straighten.
- In the absence of compression, joints work effectively, restoring mobility and ease of movement. They practically take a break from constant, serious workload.
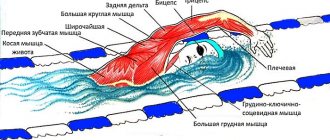
- Swimming is an excellent muscle workout; all muscle groups are involved in its various types. This is especially useful for the deep internal muscles that help support the vertebrae. Under normal conditions, they atrophy from inactivity.
Swimming is especially important for the back muscles
In addition to this, by increasing the volume of the lungs, breathing improves, and normalization of blood circulation during swimming leads to a better supply of oxygen to all tissues . The body is also hardened and immunity is increased. And the good mood that comes with swimming leads to improved sleep.
Interesting! During a 45-minute session in the pool, a person grows one and a half centimeters.
General recommendations
Swimming is an ideal sport for restoring spinal discs during treatment. There is no gravity in water, so movements become smooth, eliminating the risk of injury.
General rules for swimming with a lumbar hernia:
- before starting classes, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will select a set of exercises based on the general clinical picture;
- swimming is indicated only during the period of remission;
- It is necessary to warm up on land (breathing exercises, warming up the muscles);
- You should exercise 2-3 times a week in an indoor pool;
- loads must be strictly dosed and increased gradually;
- training time at the initial stage is no more than 30-40 minutes;
- water temperature for classes is from 25° to 28° C.
If you have an intervertebral hernia, you should absolutely not swim with your head raised.
Incorrect head position overloads the spine, neck and back muscles.
Water gymnastics: a set of exercises for intervertebral hernia
Water exercises or hydrokinesitherapy are carried out during the recovery period , during rehabilitation after surgery, but not earlier than a month and a half after it. In each case, an individual recovery complex is developed, which is carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
It is useful to do these exercises while wearing fins, masks with a breathing tube and other special devices. At the same time, you should not overcool or exercise after eating.
Complex for the cervical region
- Metronome. Turn your neck alternately left and right, holding each position for 10 seconds. When changing positions, keep your head straight, your back straight, and your hands on your knees.
- Spring. The exercise is similar to the previous one, but when turning, the head is tilted towards the shoulder.
- Frame. The head tilts either to the left or to the right shoulder, the opposite hand behind the head.
- Airplane. Hands horizontally, look forward. Then the left hand goes up and the right hand goes down. After this, the position of the hands changes. The back is always straight.
- Heron. Slowly bend your head back as far as possible with your back straight, then straighten it.
Do these exercises while sitting in shoulder-deep water with your back as straight as possible.
Complex for the thoracic region
Learn a set of exercises for each part of the spine in case of a hernia. Lie with your back on the rope between the paths of the pool, stretching your arms above your head, with your legs lying quietly. This is a good stretch for the sternum.- Holding one rope with your hands, lower your legs onto the other. This stretches the spine and treats deformities. You can also lie on your stomach with the mask on.
- The legs are on the side, and the pelvis touches it, the back lies on the water, the arms are spread to the sides. Lie relaxed with your eyes closed for ten minutes.
- Walk with long strides through water that reaches your chest, raising your legs high. Make movements with your hands as in a ski race. Repeat for 5 minutes, take a break and continue again.
For the lumbar region
- Move with a swimming board, using your legs smoothly, for 100 meters.
- Push off from the side with your feet and drift smoothly with your face down (wearing a mask). Legs and arms are parallel to the body. If you can’t swim on your own, then hold on to the swimming board.
- Stand up to the side and grab it with outstretched arms. With a straight back, work intensively with your legs.
- Lying on your back, spread your arms, take deep breaths, relax your body, breathe slowly.
- Standing waist-deep in water, bend left and right 6 times in each direction in turn.
- Holding the handrails in the water, squat on each leg 10 times, then the same amount on both legs.
- Holding the side, pull your legs to your waist 12 times.
Exercises 1-4 are also useful for the cervical and thoracic segments of the spine.
Which style to choose
In case of IVD hernias, you must carefully engage the body in movement in the water. During classes, complexes of general developmental exercises with fragments of sports swimming are used. Since swimming is necessary in order not to aggravate the condition, in case of a hernia of the lumbar spine using any style, the legs should work “from the hip.” This means that the entire leg is moving, and not from the knee down.
The swimming style is selected separately, taking into account motor capabilities. If you have a back problem, it is recommended to swim in the back crawl style. The head and body should be at the same level with the water. Due to the rowing movements of the upper limbs, rotational movements occur in the lumbar region in the anteroposterior direction, which increases the mobility of the spine.
Breaststroke unnecessarily strains the back muscles, so it is better not to use it in the initial stages. It is preferable to choose breaststroke with an elongated form of sliding, swimming on the back with breaststroke legs. Sudden movements and turns are excluded. It is recommended to use safety glasses and a snorkel.
How to swim correctly with a herniated vertebrae
The key to successful treatment of intervertebral hernia is the correct choice of swimming style.
The nature of the pathologies must be taken into account, namely:
- If the spine is compressed in the thoracic region, then swimming on the back is useful. This stimulates the development of physiological curves, and swimming on the stomach worsens the remission process.
- If your back is excessively arched back, you should not swim on it. Otherwise, the increasing load on the shoulder will provoke even greater curvature.
- Weak, elderly or untrained patients are not recommended crawl movements, which require more muscle tension.
Familiarize yourself with the complexes of therapeutic exercises for spinal hernia:
- To read about useful exercises for the lumbar region, go to page
- A set of isometric exercises for treating a neck hernia can be found at the link
- How and what exercises to perform for a herniated thoracic spine?
- Check out the exercises of rehabilitation gymnastics after surgery to remove a herniated disc by going here
What styles can you use?
Did you know that...
Next fact
For therapeutic swimming, the preferred styles are: backstroke, breaststroke, crawl and doggy style.
Learn more about each of them:
- When swimming on your back , it relaxes, the load on the cartilage and vertebrae is minimal, and all muscle groups (shoulder, back, hip, gluteal) work intensively. This type of water treatment is useful for any type of hernia; it relieves pain even with advanced processes. Only a sharp transition to a vertical position is harmful, fraught with displacement of the vertebrae. To avoid this, you must first roll over onto your stomach and then stand on the bottom of the pool.
- Breaststroke is not the most energetic type of swimming, but it strengthens the pectoral and back muscles well. It is used for lumbar and thoracic hernia. In case of cervical pathology, it is possible only in the initial stages of the disease with slight deformation of the discs. It is recommended to always keep your back straight while swimming, do not make sudden movements with your arms and legs, and do not develop high speed. It is best to relax and try to include all muscle groups in the process, getting only pleasure from it. It is also recommended to work with your legs, as in the crawl, because... Their vigorous movements create pressure on the vertebrae, which can worsen the condition.
- Swimming with crawl , a fast and energetic technique, is not recommended if you have breathing problems or weakly trained muscles. This style is suitable only for the initial stages of the disease in the cervical or thoracic regions.
- Anyone can swim “doggy style” in this style, the movements are slow, the muscles are not overloaded, and the spine is well relaxed.
All gymnastics exercises in water for hernias must be performed smoothly. In order for the treatment to bring maximum benefit, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Movements should be smooth and not fast.
- All muscle groups should be loaded evenly.
- Their loads should be alternated with relaxation.
- If pain occurs, you should immediately change your swimming style.
- After training in the pool, it is useful to put on a water aerobics belt and hang vertically in the water for a little while, relaxing.
Which styles are contraindicated?
Therapeutic swimming for vertebral hernia is limited in terms of style choice:
- Butterfly involves complex movements; for amateurs, this is fraught with microtrauma to the cartilage of the lower back and sacrum. This style can provoke a relapse of the disease.
- The crawl is not recommended for extensive hernia of the lumbar segment. It is dangerous due to asymmetrical twisting of the vertebrae, which increases pain and aggravates the course of the disease.
- Breaststroke is not advisable for protrusions of the cervicothoracic spine.
Cautions from experts:
- If there is pain and a crunch in the neck, you should not strain it, this will lead to increased spinal congestion, headaches and dizziness.
- If you have lower back pain, sudden movements are contraindicated when swimming “like a frog.” Rapid body turns increase compression syndrome.
- You need to enter and exit the pool only with support from the handrails.
- Jumping in the pool and from the side, twisting and fast movements are very dangerous.
Video: “The most effective methods of swimming for a herniated disc”
Contraindications
Swimming with degenerative diseases of the spine should be done with the permission of a doctor, under the supervision of an instructor. General contraindications to swimming for any hernia and lumbar hernia in particular are:
- period of exacerbation with severe pain;
- open wounds;
- skin rashes;
- intestinal disorders or infections;
- high body temperature;
- severe fatigue;
- recovery period after acute inflammatory processes.
Discomfort during exercise is a signal to stop. In a pool, if there are no contraindications, swimming with a hernia of the lumbar spine can be replaced with therapeutic exercises: in the pool and on land.
Swimming for cervical hernias
Not the most common hernia of the cervical spine, it greatly annoys the patient. In addition to pain and muscle spasms, a person has severe headaches, limited mobility, and in severe cases, circulatory disorders, manifested in the form of dizziness and fainting.
Swimming for a herniated cervical spine as an auxiliary method aims to strengthen this section and relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Before entering the pool, you should do a short gymnastic warm-up under the supervision of a doctor to improve blood flow to the muscles. After this, you need to carefully enter the water and wait time to adapt to the new environment and its temperature. Next, they begin to perform the exercises according to the program under the supervision of a doctor. Here are some of the main examples:
- The patient holds his breath, lies horizontally on his stomach in the water, and immerses his head under the water. He rests his feet on the side and stretches his arms forward. Press your legs together and stretch your entire body as much as possible, as if doing a morning stretch. After this, relax and return to an upright position. Do four to five repetitions.
- Holding the side with your hands, the patient needs to lie on his stomach, stretch out on straightened arms and swing his legs, performing the “scissors” exercise. In this case, while inhaling, you need to raise your head above the water and turn it in different directions, and while exhaling, lower it under the water.
- An exercise for trained patients with a developed muscular system - somersaults in water. You should perform somersaults both forward and backward, pinching your nose with your hand or a special clothespin.
Contraindications for this sport
Aqua aerobic training is developed by a coach or instructor, since victims of a herniated disc are strongly advised to avoid sudden movements and heavy loads that regular swimming may entail. Water gymnastics seems absolutely harmless, however, there are a number of contraindications for training. Contraindications include:
- acute stage of the disease;
- circulatory disorders;
- the presence of skin pathologies;
- heart failure.
Water aerobics will only be beneficial if you perform the exercises correctly and follow the instructor’s recommendations. You cannot swim if you are suffering from severe attacks of pain. It is also prohibited to swim if you have a cold, flu, or elevated body temperature. Patients who are prohibited from using swimming as a treatment for a hernia can replace it with hydromassage, Charcot's shower, or baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs.
Share this article:
Is it possible to do fitness with a cervical hernia?
The answer to the question of whether it is possible to engage in fitness with a cervical hernia will not be unambiguous. Some physical activity will even be beneficial. For example, to the question of whether it is possible to swim with a cervical hernia, any doctor will answer in the affirmative. Swimming in reasonable quantities helps relieve static muscle tension and improves blood supply to the collar area. This promotes faster recovery.
But the answer to the question of whether it is possible to do push-ups with a cervical hernia will be negative. This physical exercise puts excessive stress on the upper shoulder girdle and can provoke sequestration of the hernia. The question of whether it is possible to pull yourself up with a cervical hernia can be answered in a similar way - only after examining a doctor and eliminating the risk of intervertebral disc ruptures can you make the right decision about physical activity.