This material takes into account the results of clinical trials on the treatment of joints and spine, conducted in a number of large scientific and clinical centers of the Russian Federation and CIS countries: Research Institute of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Physiotherapy of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, RRC of Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Belarusian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, Chief Clinical military hospital of the Federal Border Service of the Russian Federation, Research Institute of Laser Medicine (Moscow), Main Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, Tver State Medical Academy, Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Republican Medical Center “Armenia” (Yerevan), etc.
OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic process that develops in the cartilage and bone tissue of the spine. This is the most common spinal disease, affecting more than 70% of the population. The resulting pain syndrome is explained by the fact that the intervertebral disc cannot withstand the load and its protrusion forms.
Nerve processes, blood vessels and the spinal cord are located around the intervertebral disc. A disc herniation, affecting any of the nerve processes, causes its inflammation, which leads to pain. The second cause of the pain symptom may be pinching of the spinal nerve at the site where its root exits the lumbar spine, and compression of the root can be caused by bone growths (reactive growth of marginal osteophytes).
Osteochondrosis most often affects older people, as well as overweight people. The disease is a serious medical and social problem, because has a chronic course and often leads to temporary or permanent disability.
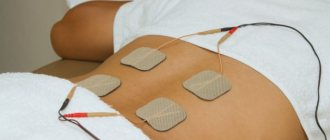
Clinical trials conducted in a number of clinics in Russia and the CIS countries have proven the high effectiveness of laser therapy for osteochondrosis.
Considering the fact that with this therapy, the paravertebral vessels running along the sides of the spine enter the treatment zone, i.e. Simultaneously with the local effect, the effect on the blood is also carried out; laser hemotherapy (LHT) is not carried out separately.
The concept of extrasystole
Extrasystole is an untimely contraction of any part of the heart, a subtype of arrhythmia. This violation does not pose a direct threat to life. Moreover, a mild degree of extrasystole is considered physiologically normal. An example of a healthy “failure” in the functioning of the heart muscle is the heart “fading” from happiness, “stopping” it from strong emotions, or a rhythm disturbance as a result of severe fatigue or lack of sleep.
There are 3 types of heart rhythm disturbances based on the frequency of extraordinary contractions:
- Rare – up to 100 per day;
- Medium frequency - extraordinary strikes number in the hundreds;
- Frequent – more than 700 per day.
Up to 70% of people experience symptoms of untimely contraction of the heart muscle. In most cases this is ventricular arrhythmia.
OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE CERVICAL SPINE
Cervical osteochondrosis, or osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, due to morphological and functional characteristics, is characterized by various clinical manifestations and, often, the diagnosis is difficult due to the many “masks”. Clinical manifestations are directly dependent on the location of the lesion. Radicular (radicular) syndromes in cervical osteochondrosis are a manifestation of combined damage to often several roots.
Damage to the nerve root can be of the type of irritation, compression or conduction disturbance. With irritation and compression, the main clinical sign is pain, and with a conduction interruption - radicular paralysis. The pain is accompanied by widespread irritation, which leads to poor circulation, swelling and fibrosis of the tissue around the root.
The figure below (Fig. 2) shows the zones of innervation by nerves emanating from the cervical spine. Knowing these zones, it is easy to imagine the clinical picture of damage to one or another nerve root of the cervical spine.
Fig.2
If the C3 root (3rd cervical vertebra) is affected, pain occurs in the left or right half of the neck, a change in taste in the mouth, a feeling of swelling of the tongue, and difficulty moving food with it.
Irritation of the C4 root causes pain in the clavicle, shoulder girdle, atrophy and decreased tone of the posterior neck muscles, leading to an increase in the supraclavicular air cushion, which is a characteristic symptom of irritation of the above root.
When the C5 root is compressed or irritated, pain appears in the shoulder girdle and along the outer surface of the shoulder, and hypotrophy of the deltoid muscle.
When the C6 root is irritated, pain occurs in the neck and scapula, radiating along the outer surface of the shoulder, forearm and thumb, and hypotrophy of the biceps muscle appears.
Traumatization of the C7 root leads to pain in the neck, scapula with irradiation along the outer surface of the shoulder, into the dorsum of the forearm and to the 2nd and 3rd fingers of the hand.
SYNDROMES CHARACTERISTIC FOR CERVICAL OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Vertebrobasilar syndrome is mainly a functional neurovascular disorder of the vertebral arteries in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Clinical signs of vertebrobasilar syndrome are expressed by headache in the occipital region or forehead, dizziness during a sharp turn of the head.
There are persistent blanching and sensory disturbances on the face that do not coincide with the zones of innervation of the branches of the trigeminal nerve. Pain or noise in the ears, vestibular disorders, decreased vision, changes in voice and taste sensations periodically occur. Often these signs are combined with pain in the arm or heart area.
Sympathalgic syndrome - characterized by neck-shoulder pain of a burning, squeezing nature, mainly at night. After leaving the arm at rest for a long time, various types of pain arise in it, which forces patients not only to wake up and change the position of the arm, but also to stand up in order to make swinging movements with the arm. Often the pain spreads to the back of the head and the glenohumeral-thoracic region.
The syndrome of glenohumeral periarthritis, which occurs with cervical osteochondrosis due to dystrophic and inflammatory changes in the joint capsule, is accompanied by intense pain in the shoulder joint. Abduction and rotation of the arm are sharply painful, which forces patients to spare the arm and keep it in a state of immobilization, which can lead to the formation of persistent adduction contracture or ankylosis of the shoulder joint, accompanied by atrophy of the muscles adjacent to the joint.
Shoulder-hand syndrome (Steinbrocker syndrome) is a symptom complex of reflex neurovascular autonomic dystrophy of the limb with cervical osteochondrosis and is manifested by pain in the joints and muscles of the affected arm, swelling, cyanosis of the hand, increased sensitivity and increased temperature of the skin of the hand. Limitation of hand function leads to flexion contractures and atrophy of muscles and skin. Later, diffuse osteoporosis of the arm bones may occur.
Anterior scalene syndrome is a reflex muscle contracture associated with cervical osteochondrosis. Spasm of the anterior scalene muscle leads to compression of the brachial plexus and subclavian artery. Clinic: pain in the neck with irradiation along the ulnar surface of the forearm and hand, pallor, coldness, paresthesia and sometimes swelling of the hand. The pain intensifies during a deep breath, when the shoulder is abducted and when the head is tilted to the healthy side. Sometimes there is swelling of the supraclavicular fossa. Later, hypotrophy and weakness of the hand muscles appear.
Cardiovascular syndrome occurs due to irritation of sympathetic formations in the pathology of the cervical discs of the fifth - seventh cervical vertebrae. Clinically, this is manifested by pain in the heart, chest, behind the sternum, and in the shoulder girdle of the left arm.
Pulmonary syndrome in osteochondrosis of the cervical and upper thoracic spine is characterized by congestive and inflammatory manifestations of the lungs, leading to oxygen starvation, which significantly worsens the general condition of the patient and aggravates the course of the underlying disease.
Vegetative-irritative syndrome. Pain syndrome that occurs with a combination of lesions of the gallbladder and the cervicothoracic spine, with cholecystitis and cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. This syndrome is manifested by a reflected impulse from the affected organ.
The pathological impulse arising from these two foci is directed along the phrenic nerve and sympathetic fibers to the cervical spinal cord and is summarized there according to the dominant type. Cholecystitis and osteochondrosis are in close pathological connection.
Treatment. The main directions of therapy for osteochondrosis are: impact on the affected spinal motion segments and extravertebral neurodystrophic foci; correction of psycho-emotional and autonomic dysfunction; relief of pain. For this, a wide range of therapeutic effects are used: medications, physiotherapeutic, manual and reflex.
Symptoms of the disease
Extrasystole in osteochondrosis suggests the presence of several symptomatic manifestations.
- A sick person feels something pushing in his chest. Sometimes there may be a feeling of freezing of the heart muscle.
- Patients are often diagnosed with fainting conditions.
- There is a strong tension in the interscapular region, after which a sharp impulse of the heart occurs, reminiscent of a revolution.
- Anxiety, a feeling that the air is about to run out.
- Regular hot flashes, feeling of weakness, discomfort and excessive sweating.
- When you try to feel the pulse, the effect of it dropping out or fading occurs, indicating a lack of filling of the heart ventricles.
- Reduced blood output, worsening blood circulation.
If these signs of the disease are detected, you should seek help and advice from a specialist.
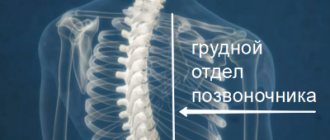
OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE THORACIC SPINE
It is characterized by a varied clinical picture, which is associated with the anatomical and physiological characteristics of this part of the spine. Despite the fact that the number of discs in the thoracic region is twice as large as in the cervical or lumbar region, clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are observed much less frequently.
This phenomenon can be explained by the lower mobility of the thoracic spine, the small size of the nucleus pulposus and the small thickness of the intervertebral disc, which less often leads to the formation of hernias, however, thoracic physiological kyphosis (bend) contributes to the formation of anterior and lateral osteophytes.
Osteophytes in the area of the spinal-costal and transverse-costal joints come into contact with the spinal nerves, causing intercostal neuralgia or leading to irritation of the sympathetic trunk and the occurrence of autonomic syndromes. The lower cervical and upper thoracic sympathetic nodes connect at the level of C7 - Th1 (Th1 - 1st thoracic vertebra), then the sympathetic branches extend to the heart, esophagus, bronchi, spine, carotid arteries and recurrent nerve.
From the sympathetic nodes Th5 - Th10, the abdominal nerve is formed, passing through the diaphragm and woven into the solar plexus. Clinical symptoms depend on the compression lesion of a particular nerve trunk.
Before using laser therapy for osteochondrosis, consult our specialists. They will tell you the most appropriate treatment option, the type of device and tell you about its use.
DYSTROPHIC CHANGES IN THE THORACIC SPINE
Apart from osteochondrosis, these are the most common lesions of the spine.
Clinic. Manifestations of the disease in the form of thoracalgia (chest pain) are associated with reflex syndromes and are often accompanied by cardiovisceral, hyperventilation and other syndromes. Clinically, this usually manifests itself as long-term non-healing gastric ulcers, erosive gastritis, cardialgia of unknown origin with ECG changes in the form of ischemia of various parts of the left ventricle, prolonged bronchitis, and disturbances in emotional stability.
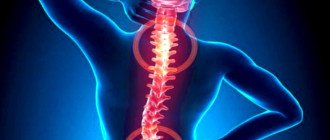
OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE LUMBAR-SACRAL SPINE
Damage to this part of the spine (Fig. 1) occurs most often, which is due to both the anatomical features of the structure of the spine and the characteristics of human life, because The lumbar region bears the greatest load. The most common pathologies found in this part of the spine are osteochondrosis and complicated forms of osteochondrosis, compression-radicular syndromes, and dysfunction of the nerve root in the form of neuropathies.
The most common syndromes of the lumbar spine are sciatica, lumbago, lumbar radiculitis (lumbar osteochondrosis) and intercostal neuralgia. Each of these syndromes consists not only of pain in the spine, but also secondary inflammatory changes in the muscles near the affected part of the spinal column, as well as symptoms of poor circulation and swelling of internal organs.
Clinic. Manifestations of the disease can be very diverse, depending on the stage of the process. Long-term pain syndrome, foot paresis (“slap foot”), compensatory scoliosis in the lumbar region, tension of the rectus muscles of the back, pain on superficial palpation, hyporeflexia of tendon reflexes, hypotonia of the lower leg muscles with impaired walking function, etc.
The results of clinical observations indicate a pronounced therapeutic effect of laser therapy in patients with osteochondrosis. After the first RT session, the absence of pain was observed in 60-65% of patients, improvement in motor activity was noted in 20-25%, and normalization of sleep in 50% of patients. After the first course of treatment, a positive effect was observed in almost 100% of patients with an early stage of the disease. When the process is started, it is achieved after 2-3 courses of treatment.
Proper nutrition
The diet of a patient with osteochondrosis and extrasystole should be enriched with foods rich in potassium and magnesium. It must contain:
- Berries (currants, raspberries, blackberries);
- Fruits (avocados, apples, grapefruits, apples, pears, plums, melons);
- Vegetables (potatoes, pumpkin, broccoli, tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers and others);
- Greenery;
- A variety of vegetable oils (not only sunflower and olive);
- Cereals and beans;
- Nuts and dried fruits;
- Milk;
- Honey;
- Plant-based natural drinks.
It is better to avoid fast food, fatty foods and large amounts of sugar altogether.
Compliance with the principles of proper nutrition preserves the health of the entire body, not only the musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems. In addition, a balanced diet helps to lose excess weight, which puts additional stress on the spine and aggravates osteochondrosis.
SPINAL HERNIA
Intervertebral hernia is one of the most complex diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The cause of the disease can be excessive stress on the spinal column, injuries, incorrect posture, and age-related changes. Under the influence of these factors, the membrane of the spinal disc is destroyed and its contents enter the spinal canal, compressing the spinal roots or the spinal cord itself. At an early stage of changes in the lumbosacral spine, they make themselves felt by aching pain in the lower back. If the disease is advanced, then the pain caused by the hernia depends on which roots it compresses, and clinically it can manifest itself as impaired movement in the legs, impaired urination and potency.
Treatment. Surgical intervention for this pathology gives quick results, but is fraught with postoperative complications and the development of diseases in other parts of the spine. It is indicated for only 10-12% of patients. The most effective method is a combination of laser and manual therapy. Laser therapy allows you to relieve swelling and inflammation in the hernia area, and manual therapy, which is carried out after a course of laser therapy, allows you to achieve stable and long-term remission, and live your life without surgery at all.
The disc is a completely avascular region, however, in its immediate vicinity the vascular network is quite wide. For example, many vessels are located in the vertebral body itself and along the periphery of the fibrous ring, which carry out exchange and nutrition of the disc. Actually, by improving this metabolism and tissue nutrition, the declared effectiveness of laser therapy is achieved. Blood circulation in the problem area improves, pain goes away, swelling and inflammation are relieved.
Before using laser therapy to treat joints and spine, consult our specialists.
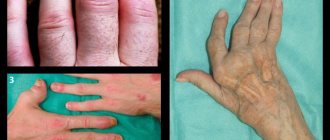
ARTHRITES AND ARTHROSIS
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joint. Arthritis can be either an independent disease or a manifestation of some other disease. One of the first clinical manifestations of arthritis is joint pain. It is most intense in the second half of the night and in the morning. Pain relief usually occurs after movement. With the development of the pathological process, changes occur in the soft tissues and capsular-articular apparatus, leading to deformation of the joints, disruption of their function, changes in temperature and color of the skin.
The disease can occur with damage to one joint (monoarthritis) or several (polyarthritis). The onset of the disease can be acute and accompanied by severe pain in the joint (acute arthritis) or develop gradually (chronic arthritis). The causes of arthritis are varied: infection, trauma, allergies, metabolic disorders, diseases of the nervous system, lack of vitamins.
Arthrosis is a group of diseases of a metabolic-dystrophic nature, which typically involve damage to all components of the joint. First of all, cartilage, as well as adjacent to the cartilage, bone, synovial membrane, ligaments, capsule, periarticular muscles. Characterized by pain felt deep in the joints, aggravated by physical activity and relieved by rest, morning stiffness, crunching in the joints, and limited movement in the joints.
The cause of arthrosis is a change in the biological properties of cartilage. These properties can change both under the influence of external and internal environmental factors (gene defects, excess body weight, estrogen deficiency in women, joint injuries, joint surgeries, etc.).
Treatment. Most often, arthritis and arthrosis occur as a result of diseases such as rheumatism, psoriasis, gout, as well as a number of other, most often autoimmune diseases. Laser therapy of joints, in this case, is carried out against the background of drug treatment of the underlying disease, which allows reducing the amount of medications consumed. Treatment involves eliminating the underlying cause of arthritis (arthrosis) and local changes.
If you have the listed diseases, you should not forget that laser treatment of joints should be combined with laser hemotherapy. It is indicated as a desensitizing, analgesic, immunostimulating and decongestant therapy. Treatment regimens for affected joints are given in specific techniques.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Belongs to the group of systemic autoimmune diseases. Its characteristic feature is the formation of autoantibodies to various types of collagen. One of the components in the mechanism of development of autoimmune diseases is inflammation. With the development of inflammation under the influence of infectious factors (streptococcus-A - in rheumatism, intestinal microbes - in reactive arthritis), its main signs are revealed in tissues and organs - pain, swelling, dysfunction. Impaired microcirculation is one of the early mechanisms of rheumatic inflammation. It is caused by an increase in the permeability of the capillary wall due to cross-hemocirculatory disorders, leading to the development of edema and hyperemia. The role of hypercoagulation factors especially increases (chronic DIC syndrome in chronic rheumatoid inflammation).
It is necessary to note the systemic, progressive, self-sustaining nature of chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Pathological metabolic disorders are diverse. Often, a complex metabolic disorder leads to inhibition of osteogenesis processes. Disruption of metabolic processes in articular cartilage leads to depletion of its main substance in proteoglycans, which causes the destruction of cartilage and the development of deforming osteoarthritis.
Arthrosis and metabolic arthropathy, as a rule, are generalized in relation to damage not only to many joints, but sometimes to internal organs. The central and peripheral nervous systems, especially the autonomic part, are involved in the pathogenesis of functional changes. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis experience symmetrical joint damage, muscle atrophy, osteoporosis, and various trophic disorders.
Treatment. It should be carried out taking into account all links of its pathogenesis. For this purpose, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and painkillers are used. Modern complex therapy also includes physical factors. The use of physical factors has the following goal: to reduce or eliminate pain, reduce signs of general and local inflammatory activity. Due to the effect on the neuroendocrine and vascular components of trophism, it normalizes metabolism in the affected tissues. Influence the violation of immunoregulatory processes. Considering the fact that laser therapy has all of the above properties, it must certainly be part of the complex treatment being carried out. RT is prescribed both as a local effect on the joints and as laser hemotherapy.
Diagnostic complex of measures
As the disease develops, osteochondrosis also manifests itself in extrasystole. For rare pathological processes, treatment is minimal; if the number of systoles per day is more than 700, a mandatory set of therapy is prescribed. When a patient approaches, the doctor’s duty is to listen to the heart, measure the pressure parameter, and assess the general condition of the fiber and skin. This is required to create a complete picture of the disease. In addition to the above list of activities, you need:
- Determine the type of pathology;
- study individual characteristics;
- find out the frequency of contractions;
- conduct instrumental and laboratory tests;
- do a long-term ECG study;
- take samples for arrhythmia;
- undergo MRI and ultrasound.
After determining the type and complexity of osteochondrosis and accompanying extrasystole, the treating specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment.
ARTHROPATHIC PSORIASIS
Arthropathic psoriasis. The most severe form and less manageable in terms of treatment in patients with psoriasis is arthropathic. According to established tradition, psoriasis still refers to skin diseases, although the systemic nature of this process and the ability of psoriasis to affect not only the skin, but also internal organs, the nervous system and joints have been established.
Psoriatic arthritis is characterized as a systemic process in which the most pronounced changes appear in the structure of connective tissue. Psoriatic arthropathy can occur benignly as monoarthritis or in the form of polyarthritis, and in some patients it takes on the character of severe destructive polyarthritis. Psoriatic arthritis often occurs in parallel with skin lesions or slightly later, and in some cases, articular syndrome may precede skin manifestations.
Joint involvement usually begins in the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands and feet. Gradually, medium and large joints are involved in the process, including the spine, with the development of ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis). Swelling, pain, and limited joint mobility are noted as a result of infiltration and compaction of the periarticular tissues. In the further course of the process, dislocations, subluxations, and ankylosis can form, leading to joint deformities, and the patient becomes completely disabled.
In addition, a progressive asthenic state sets in, up to cachexia, myalgia, atrophy of the muscles of the hands, forearms, and legs (12-15%). As with ordinary psoriasis, in patients with psoriatic arthropathy, insufficiency of liver and kidney function, immunodeficiency states, and cardiovascular pathology are determined.
Treatment. As with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment is comprehensive and is aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease, restoring metabolism in the articular cartilage and preserving the function of the affected joints. Drug therapy is aimed at achieving a desensitizing, detoxifying and anti-inflammatory effect.
We have already mentioned earlier that laser therapy has all these properties, and, in addition, it also has an immunocorrective effect - it must be included in the treatment process. Laser therapy is carried out both by affecting the blood (LHT) and locally on the area of the affected joints.
Treatment
PVCs are considered an indicator of the risk of sudden cardiac death. However, it is still unclear whether they actually play a causative role in the development of fatal ventricular arrhythmias. Cardiac arrhythmia research has clearly shown that even successful suppression of prognostically unfavorable PVCs does not protect against SCD. On the other hand, the apparently contradictory result of an early retrospective study is inconclusive.
Controlled studies show increased mortality among patients taking antiarrhythmic drugs. Flecainide was better tolerated in antiarrhythmic efficacy studies. However, the substance in particular has led to an increase in mortality. What properties of different antiarrhythmic drugs contributed to SCD are unclear.
Flecainide
Patients are not recommended to be prescribed medications for stress-related PVCs. Since a clear connection between mortality, morbidity and PVCs has not been established. Long-term use of drugs can only aggravate the course of arrhythmia and lead to fatal consequences.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/BdfNlet-AZU
GOUT
Gout. It is considered as a metabolic disease and is characterized by paroxysmal joint pain. Along with acute attacks of pain, gout is characterized by the deposition of salts (sodium urate) in the tissues, resulting in the formation of gouty nodules. In addition to uric acid, they contain a small amount of lime.
Favorite places for salt deposition are the auricles, cartilaginous covers of articular surfaces, especially the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, wrist, and knee joints. This does not exclude the possibility of salt deposits in other joints. In addition to cartilage, the process affects the synovial membrane, periosteum, and tendons.
The joints thus change noticeably. They become swollen, red and painful to the touch. With a long course of the disease, persistent changes in the joints may occur: the ligaments thicken, effusion appears in the joint, and it becomes painful. When moving, a slight crunching sound is heard. Gouty nodes can enlarge over time and change the shape of the joint. In addition to the joints, gout affects blood vessels, usually the vessels of the kidneys and heart; Sclerotic changes occur in the vessels.
Treatment. Patients with gout need dietary, medication and physiotherapeutic treatment. Laser therapy is performed both on the blood (in the absence of contraindications) and locally on the area of the affected joints.
SCHLATTER'S DISEASE
This disease refers to necrosis of the epiphysis of the head of the tibia in combination with destruction of the bone core, which is caused by local overloads, chronic injuries and local circulation disorders. Boys aged 10 to 15-18 years are most often affected. Schlatter's disease develops for no apparent reason, more often on one side, less often on both.
Sometimes a link can be made to re-injury or increased quadriceps function (eg, sports). Clinic. There is swelling and local pain in the lower part of the knee, which increases with pressure. Movements in the knee joint are painful, especially after physical activity. An extreme degree of flexion of the limb at the knee joint is possible, but sharply painful. The pain does not go away even at rest. The course of Schlatter's disease is long. The chances of recovery are quite high, since this disease is cured after the period of growth of the body is completed. But until complete recovery, it is necessary to avoid overloading the limbs.
Laser therapy. The impact of laser radiation on the pathological focus is carried out in the same way as with other pathologies of the knee joint.
ethnoscience
When treating extrasystole against the background of osteochondrosis, any self-medication is contraindicated. A doctor's help is needed here. But sometimes traditional medicine is also useful.
There are three groups of raw materials that are the basis for traditional medicines.
First group
Herbal preparations. Moreover, the vegetation can be of any kind, as long as it contains a lot of magnesium and potassium. The following plants are good to use:
It is useful to use essential oils: they heal the body.
There are also useful herbs.
Calendula is an excellent remedy for preventing arrhythmic attacks. Preparations based on it:
- normalizes the pulse;
- increase the secretion of bile;
- bring pressure back to life;
- restore the nervous system;
- improve blood flow through the coronary vessels.
The latter effect is extremely useful in preventing cardiac ischemia from developing or occurring.
Melissa effectively fights inflammation, pain, and infections. It is very rich in trace elements and ascorbic acid, and therefore is extremely useful for the treatment of extrasystole and osteochondrosis.
Horsetail infusions are good for the following:
- strengthening vascular walls;
- decrease in pressure;
- improving the removal of toxins.
Second group
Medicines based on animal raw materials. These are a variety of ointments. Very good for the treatment of advanced osteochondrosis in combination with mild extrasystole.
Third group
Medicines that are chemical products. This includes all analgesics, including ordinary analgin. Turpentine-based ointments, alcohol, tincture of iodine - these are the products that can be used to achieve the following effects:
- pain relief;
- warming;
- regeneration of bones and muscles.
At the same time, they do not have a side effect that disrupts the already disturbed heartbeat rhythm.
And there are also allergies to folk remedies, so caution is needed here. Before using them, you should make sure that there are no allergic reactions to the corresponding drugs
Before using products that contain any poisons, you should consult a doctor to obtain all the required information on such products. Consultation is most important before using medications containing snake venom.
HEEL SPUR"
It is a bone outgrowth at the site of tendon attachment, which is characterized by painful sensations in the area of the sole.
Clinic. At the beginning of the disease, pain occurs when walking. It is especially difficult to start walking when acute pain occurs during exercise. Then, during the day, the pain when walking subsides somewhat, and by the end of the day it intensifies again. Over time, the pain becomes persistent.
People with excess weight, diseases of the spine and large joints of the lower extremities, flat feet, as well as athletes with prolonged local overload in this area are predisposed to the development of heel spurs. Currently, the treatment of heel “spurs” consists of providing relief with the use of various types of insoles and heels, complex physiotherapeutic treatment, and if there is no effect, surgical treatment - surgical removal of the bone outgrowth and excision of the altered tissue.
Laser therapy. Highly effective for this pathology. As a rule, the full effect is achieved after 2-3 courses.
The high efficiency and safety of modern laser therapy allows the population to use it as a home doctor. The manual included with the device allows you to correctly carry out the appropriate treatment of various diseases of the joints and spine. A prerequisite for purchasing a device for treatment at home is to carefully study the attached manual.
Symptoms
A number of drugs effectively suppress PVCs. However, in some cases it is impossible to predict whether the extrasystole will disappear when taking a certain substance. This means that an effective antiarrhythmic drug must be determined empirically by trial and error.
It is not recommended to diagnose yourself based on subjective feelings. You need to consult a cardiologist.
Any antiarrhythmic drug can aggravate or even cause PVCs. This undesirable effect cannot be predicted individually. An increase in PVCs with antiarrhythmic drugs is common, affecting up to 28% of patients.
The view that such arrhythmogenic effects occur only at the beginning of treatment has recently been refuted. These side effects recur continuously throughout the 10-month long-term treatment. Unfortunately, patients with the highest risk of dangerous arrhythmia are those most likely to experience side effects from an arrhythmogenic drug.
A drug
Studies demonstrating antiarrhythmic efficacy of substances do not provide any information on the crucial question of the benefits of arrhythmia treatment. Antiarrhythmic therapy is not usually prescribed to patients with PVCs. Clinical studies that are limited to the question of the antiarrhythmic activity of various substances are useless in practice.
SPINAL HERNIA
Intervertebral hernia is one of the most complex diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The cause of the disease can be excessive stress on the spinal column, injuries, incorrect posture, and age-related changes. Under the influence of these factors, the membrane of the spinal disc is destroyed and its contents enter the spinal canal, compressing the spinal roots or the spinal cord itself.
At an early stage of changes in the lumbosacral spine, they make themselves felt by aching pain in the lower back. If the disease is advanced, then the pain caused by the hernia depends on which roots it compresses, and clinically it can manifest itself as impaired movement in the legs, impaired urination and potency.
Treatment. Surgical intervention for this pathology gives quick results, but is fraught with postoperative complications and the development of diseases in other parts of the spine. It is indicated in only 10-12% of patients. The most effective method is a combination of laser and manual therapy. Laser therapy allows you to relieve swelling and inflammation in the hernia area, and manual therapy, which is carried out after a course of laser therapy, allows you to painlessly correct the hernia. There have been cases where hernias disappeared only after several courses of laser therapy.
Diagnostics
- First of all, the patient undergoes an electrocardiogram and ultrasound examination.
- For a more detailed picture, Holter monitoring is prescribed. This is a continuous reading of the heart rhythm for two days, for which sensors are fixed on the patient’s body, and the patient himself keeps a diary in which he records his actions during changes in heart rhythm.
- The doctor may prescribe a bicycle ergometer test, that is, record an ECG against the background of physical activity.
- Cardiac MRI is also used to clarify the diagnosis.
- A general blood and urine test is performed.
When the diagnosis is made and the cause is osteochondrosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed, which depends on the type of extrasystoles.