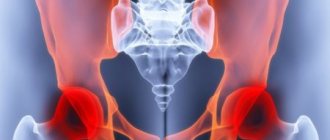
This pain is called lumboischialgia and occurs in many people over 30 years of age.
The reason is the modern lifestyle. During the day, we spend a long time in tension - sitting or standing. Some people after work continue to exercise themselves in the gym or in the pool, while others go home and continue to sit again, but this time watching TV. Our back does not receive complete relaxation during the day and responds with pain, which often radiates to the leg. To determine the causes of pain, the patient turns to specialists in various fields.
Center for Neurosurgery Dr. Baklanov A.N. deals with the diagnosis of the causes of various back pain and their successful treatment. We will answer all your questions by calling +7 (499) 746-99-50. You can also ask a question by filling out the request form below.
Main causes of back and leg pain
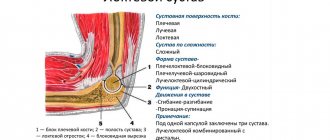
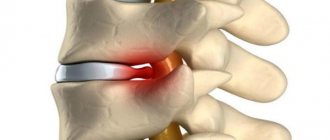
The spinal nerves form nerve trunks. The largest of them is the paired sciatic nerve, which leaves through the gluteal region into the lower extremities. With osteochondrosis, hernia or protrusion of the intervertebral disc, spondylosis and other diseases, the spinal cord roots that form the sciatic nerve may be pinched. The result is swelling, inflammation, poor circulation and lack of oxygen in the pinched spinal nerves, which causes sharp and severe pain in the back and legs
along the course of the sciatic nerve.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Radicular syndromes
The described phenomena in medicine are called radicular syndrome (radiculopathy) - this is a complex of neurological symptoms that occurs when the spinal nerves are pinched or irritated. Pain in the back and limbs
often occurs with intervertebral hernia, protrusions, and other diseases of the spine.
With radicular syndrome, pain is accompanied by various neurological symptoms. In addition to pain, sensitivity disorders are possible - patients complain of numbness, tingling, burning sensation on the skin. Reduced pain sensitivity. The skin is cold even on the hottest day. With advanced radicular syndrome, atrophy and weakness of the muscles of the lower extremities may be observed. But the most striking symptom remains pain along the nerves, the intensity of which varies from mild aching to unbearable.
Let us consider the variants of radicular syndromes and the causes of their occurrence separately.
Sciatica (sciatica)
Sciatica is called chronic pain in the lower extremities, most often arising from protrusion/hernia of the 5th lumbar/1-2 sacral vertebrae. The nature of pain in the acute period is described by patients as burning, shooting, boring, pulling. The pain spreads along the sciatic nerve, through the buttock, the outer surface of the thigh and lower leg, to the back of the foot. Increased pain is provoked by turning, bending the body, lifting weights, being forced to stand for a long time, and cold weather. With sciatica, there may be no pain in the spine itself.
The intensity of pain depends on the location of the intervertebral hernia, and to a lesser extent on its size. A characteristic sign is that pain occurs on one side, less often on both sides.
Shooting pain in the lower back (lumbago, lumbodynia)
Lumbago is an acute, sudden pain in the lower back. Most often, the cause of lumbodynia is osteochondrosis or protrusion/hernia of the intervertebral disc. Unlike sciatica, pain is localized at one point, in the projection of the affected segment of the spine. The provoking factor is lifting weights, physical activity, and a draft blowing through the lower back, especially after hard work.
A characteristic symptom is a forced position; attempts to straighten the lower back lead to increased pain. The reason is a sharp spasm of the back muscles that occurs in response to severe pain. The duration of an attack of pain with lumbodynia can vary from several minutes to days and even weeks. Rest and a firm bed may relieve pain in some patients.
Lumbalization and sacralization
Lumbarization and sacralization are anomalies in the development of vertebrae in the lumbosacral spine. During lumbarization, the first and/or second vertebra of the sacral spine in the process of development takes on the shape characteristic of the lumbar vertebrae, while maintaining mobility (normally, the vertebrae of the sacral spine completely fuse by the age of 18, forming the sacrum or sacrum). With sacralization, the 5th and/or 4th lumbar vertebrae in the process of development take on the characteristics of the vertebrae of the sacral spine and fuse with it into one whole.
Both anomalies lead to disruption of the biomechanics of the spine and improper distribution of loads. Often sacralization and lumbarization are accompanied by other anomalies (split vertebral arches, flattening of vertebral bodies). All this leads to the development of spinal osteochondrosis, provokes the formation of hernias and protrusions, which in turn cause lumbago and sciatica.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Pinched sciatic nerve (lumboischialgia)
Infringement of the spinal nerves forming the sciatic nerve, as mentioned above, is a consequence of osteochondrosis, hernias and protrusions of the intervertebral discs. And most often this condition is accompanied by both acute pain in the lower back (lumbago) and sharp, nagging pain along the sciatic nerve in the legs (sciatica). This condition is called lumboischialgia.
Stages of development of spinal degeneration
The patient may not notice most problems right away. This is due to the fact that in the early stages of the disease, all symptoms are practically invisible. Only sometimes a distant pain syndrome is felt, which is often perceived as fatigue. At rest, the unpleasant sensation disappears. With first-degree osteochondrosis, the patient may feel slight stiffness, a desire to stretch his back in the morning, and sometimes fatigue. Often these signs are not given importance, and the disease progresses further. But it is precisely at the beginning of its development, during diagnosis, that the simplest and most gentle treatment is prescribed.
The second degree is characterized by more pronounced symptoms:
1. The patient has back pain, radiating to the hip, knee, lower leg or foot.
2. Mobility decreases. Depending on the location of the deformity (cervical, thoracic or lumbar), it becomes difficult to turn or bend over, and any attempt to do so is accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
Advice. Any of the above factors is a reason to seek medical advice, and timely treatment will stop the course of osteochondrosis and prevent the formation of growths. Since the third stage is characterized by an intensification of all the above ailments, it is better to avoid it, because recovery will be very delayed.
Localization of pain in the back and legs
The localization of pain in the lower back and lower extremities depends on the location of the protrusion or herniation of the intervertebral disc. There are lateral, central (horizontal hernias) and internal (Schmorl's hernia) herniations of the intervertebral disc.
Pain radiates to right leg
Pain radiating to the right leg occurs with a lateral or horizontal herniation of the intervertebral disc that occurs on the right. In this case, the right spinal nerve is pinched, and the pain, accordingly, will radiate to the right leg.
Pain radiates to left leg
Pain radiating to the left leg occurs due to hernias/protrusions of the left half of the intervertebral disc.
Pain in the lower back and lower back
Isolated lower back pain of the lumbago type occurs with a central location of a hernia or protrusion, strictly at 12 o’clock. In this case, the hernial protrusion is directed into the spinal canal; there is no pinching of the spinal nerves in the intervertebral foramen, as occurs with lateral hernias. Because of this, there is no pain radiating to the legs. The source of pain is the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine stretched by a hernia.
What to do?
As with most other oncological pathologies, in this case surgery is indicated. The patient is additionally prescribed medications. It is possible to take medications to treat the underlying disease, and drug correction of concomitant disorders may be prescribed. Radiation is sometimes indicated. The most modern and effective method of surgery for spinal cancer is a gamma knife, that is, a narrow beam beam that destroys atypical cells without harming neighboring normal structures.
The best prognosis is for cases of early detection of the disease. True, a positive outcome is possible if the patient takes radical treatment. It is not possible to cure cancer without surgery. A conservative course is indicated to temporarily improve the patient’s standard of living. The drugs are used to relieve pain and reduce the risk of metastases.
Types of severe back pain that radiates to the legs
The nature of pain during hernias/protrusions of the lumbosacral region greatly depends on the location of the hernia, the individual characteristics of the patient (diameter of the intervertebral foramina, diameter of the spinal canal, age and severity of degenerative changes). The size of the hernia can also affect the severity of pain.
Drawing, burning, shooting pains in the back and legs are characteristic of the acute period of the disease, immediately after the onset of an attack of lumboischialgia. They are poorly relieved by analgesics, and may last 1-2 weeks before improvement.
Aching pain in the back and legs is often chronic and can last for years if the patient neglects a visit to a neurologist or treatment. Periodically, there may be periods of exacerbation associated with physical activity or heavy lifting.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Rules that facilitate treatment and speed up this process
To quickly achieve remission, you do not need to overload, exhaust yourself with workouts and diets, attend massages and similar events every day. It is enough to adhere to the correct daily routine, eat well and follow other instructions, including:
- Quit alcohol and smoking, which have a destructive effect on bones;
- Eat properly. It is better to divide the entire daily diet into 5-6 meals, instead of the usual 3, and eat in small portions. To get satiation, you need to chew each piece slowly, with pleasure, thereby stretching out the meal. Eliminate fried foods from your food - steam, boil, bake, stew, just don’t fry. The amount of salt and spices also needs to be reduced. Eat plenty of protein, fruits and vegetables, boiled meat (except pork), beans, drink fresh juices, compotes and jelly. Natural jellies with fruits have a beneficial effect on cartilage. For the first course, you can prepare vegetable soups, chicken broths and borscht without frying;
- After the meal, do light sports - not gymnastics, but, for example, simple race walking. This way you will get the blood pumping well and prevent the body from gaining excess weight, which is very important in such cases;
- If during gymnastics you feel unpleasant crunches or increased pain, stop exercising and consult a doctor.
- Watch your posture. Although it is sometimes difficult to keep your back straight, it is necessary to improve the situation. You need to maintain your posture even after recovery.
How is back and leg pain diagnosed?
The first stage of diagnosing the causes of back pain radiating to the legs is a consultation with an experienced neurologist. Radicular syndrome can be diagnosed during a routine neurological examination. A characteristic sign is the positive Lasègue symptom, which consists of increased pain in the leg when it is raised up while lying on the back. It is also called the spinal cord root tension symptom.
A neurological examination also reveals other disorders - decreased sensitivity of the skin to pain, absence or blurred reflexes, atrophic phenomena, weakness of the muscles of the lower extremities. To confirm the diagnosis, it is best to use magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbosacral spine.
The benefits of health resorts and swimming pools
Often during treatment and after its completion, in order to protect themselves from the disease becoming chronic, patients turn to special rehabilitation centers or sanatoriums. Here, experienced orthopedists and other doctors who have extensive experience in medicine will help restore or maintain the correct state of the skeleton. In addition, physiotherapy rooms with many types of exposure to natural factors on the diseased area and special exercise equipment for any department will contribute to recovery. Classes are prescribed and taught exclusively by doctors. Here you can follow proper nutrition and diet.
Swimming has a beneficial effect on the musculoskeletal system, relaxing it, but at the same time keeping it in good shape. The pool is an excellent alternative to therapeutic exercises, and a great way to restore mobility to joints.
How to relieve back and leg pain
A short course (2-3 days) of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, can be used to relieve back and leg pain. Drugs in this series have the ability to fight inflammation and can relieve pain of various origins. When the sciatic nerve is pinched, they have average effectiveness. It is strictly forbidden to take NSAIDs for more than 5 days due to the high risk of complications such as stomach ulcers and gastric bleeding. Rest and a firm bed may relieve pain in some patients. However, for others, these measures may lead to increased pain. You should try to find the optimal position in which the pain becomes less severe. Wearing an orthopedic corset can also be effective - it relieves pain by unloading the diseased spine, acting as a muscular frame.
Treatment
“You should not carry out any measures on your own to eliminate unpleasant signs - you must first consult with doctors.”
In books and on the Internet you can find many effective ways to reduce pain. Do not forget that the course of therapy is selected by a neurologist.
individually in each case. For example, if there is severe pain or inflammation, warming procedures, massage, or physiotherapy should not be used.
As a rule, doctors prescribe a set of measures for a specific patient, taking into account the stage and extent of the lesion, concomitant diseases, and the patient’s response to previous treatment.
Let's consider the option with osteochondrosis.
To return the spine to the required position and strengthen it, the following course is prescribed:
1. Medicines. The patient should take restorative medications and, if necessary, analgesics.
The “gold standard” of treatment is a combination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants.
2. Physiotherapy. It has a beneficial effect on growths, gradually eliminating excess tissue. The most commonly used are laser, shock wave and electrotherapy. The patient attends procedures 2-3 times a week for a month, then takes a break and returns to the treatments again.
3. Treatment with physical factors (laser, magnetic field, ultrasound, various waves, etc.) is used at all stages of the disease. First of all, procedures with an analgesic and relaxing effect are prescribed. When the pain syndrome subsides, those that stimulate the spinal cord and blood vessels in the affected area. Fibromodulating techniques help during the rehabilitation period.
4. Therapeutic gymnastics. Allows you to give the vertebrae the correct position, relax and strengthen the muscles of the body. location by physically influencing them. Exercises should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor, and the first time they are performed, they should be carried out under the supervision of doctors in order to be sure that they are performed correctly. There are several rules that allow you to achieve maximum productivity:
- Exercise smoothly, without sudden movements;
- Perform exercises before meals so that vitamins taken orally with food or with medications are better absorbed;
- Conduct training several times a day for high-quality results.
5. Massages.
Experienced massage therapists will help you relax your muscles and improve blood flow in the affected area to speed up your metabolism. This is very important at any stage of the disease. 6. Diet. Proper nutrition, intake of vitamins and useful elements, exclusion of fatty foods from the diet is the key to a healthy and strong skeleton.
If inflammation is detected (for example, with bursitis), some methods are contraindicated until the inflammation is eliminated. A person needs to take anti-inflammatory drugs, and at this time, in order not to aggravate the situation with the back, not to overload while at rest.
How to treat back pain that radiates to your legs
During the period of acute pain, it is recommended to rest, take painkillers, as well as drugs that eliminate spasms of the back muscles. After the acute pain subsides, physiotherapy, massage, and therapeutic exercises are prescribed, which are included in the rehabilitation program for all patients with diseases and injuries of the spine.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Why does it hurt?
Possible reasons:
- Lumbosacral radiculitis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteochondrosis
- Spinal injuries
- Changes in intervertebral discs
- Congenital spinal deformity
- Facet syndrome
- Neuropathies of various origins
- Inflammation and tumors
- Spinal circulatory disorders
Additional reasons:
- gynecological diseases
- oncology
- tuberculosis
- kidney and urinary tract diseases
- gastrointestinal diseases
- ectopic pregnancy
- post-injection complications