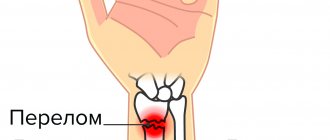
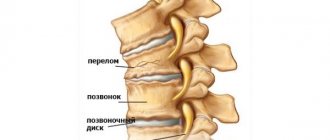
A radius fracture occurs when a person falls on an outstretched arm. Fractures differ in the direction and type of movement of damaged bone fragments and disruption of the integrity of the skin. Fractures of the radius can be displaced or non-displaced. At the Yusupov Hospital, rehabilitation specialists restore impaired function of the upper limb after a fracture of the radius using modern rehabilitation methods.
A senior instructor-methodologist of physical therapy exercises the development of the wrist joint using a set of gymnastic exercises. Patients restore muscle strength while working on mechanical and computerized simulators. Muscle massage relieves spasm and helps restore movement in the joint. Restoration of impaired limb function occurs faster after physiotherapeutic procedures.
Complications of a broken arm
Complications of radial bone fractures are divided into 2 large groups: immediate and long-term complications of injury. Immediate complications of injury develop due to the effect of damage resulting from a bone fracture on the normal functioning of the limb. Long-term consequences of injury are complications that arise as a result of inadequate treatment or disruption of normal healing after injury.
Immediate complications include:
- ruptures and injuries of the nerves that provide sensitivity or mobility of the limb;
- injuries to the finger flexor tendons;
- tight swelling of Turner's hand;
- damage to large vessels;
- complete or partial muscle rupture;
- separation of muscles from places of attachment to bone;
- acute infectious complications (with open fractures).
Long-term consequences of injury include:
- ischemic contracture - impaired mobility of the joints of the affected limb due to an incorrectly applied plaster cast, which compresses the soft tissues, disrupting the blood supply;
- long-term infectious complications;
- violations of the bone structure due to improper restoration of bone fragments, incorrectly applied plaster cast;
- long-term consequences of hemarthrosis.
Complications of a fracture of the radius aggravate the course of the pathological process, slow down the formation of callus and the restoration of function of the upper limb. From the first days after the reposition of bone fragments, rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital begin a complex of physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at preventing complications of a fracture of the radius.
Classification
Fractures can be classified according to the direction of the line, the presence of confusion, or depending on the location. Damage is identified:
- transverse;
- splintered.
In the scaphoid bone the fracture line passes:
- in the proximal part;
- in the middle part;
- in the distal part.
Treatment of fractured radius and joints
Adequate first aid for a fracture of the radius allows you to avoid complications of injury and speed up recovery after a displaced fracture of the radius. The goal of first aid is to reduce pain, ensure rest of the affected limb, and prevent damage to the soft tissues that surround the fracture site. In case of a closed fracture, the limb is fixed using a splint. If the fracture is open, stop the bleeding and apply an aseptic bandage to the wound, then immobilize. If the radius is fractured with displacement, there is no need to try to restore the normal position of the bone fragments at the scene of the incident, so as not to damage the surrounding tissues, vessels and nerves.
In the emergency room, patients with a fracture of the radius are provided with first aid. The traumatologist assesses the condition of the victim in order to determine the scope of further treatment and prevent the development of complications. After confirming the fact of a fracture, the anatomical and functional integrity of the injured limb is restored and the arm is immobilized to prevent displacement of fragments of the broken bone.
The traumatologist compares the bone fragments and fixes them with a plaster or polymer bandage. For some types of radial bone fractures, doctors perform closed or open reduction followed by fixation with knitting needles and apply an external fixation device. After treatment, patients need to restore impaired function of the upper limb.
Causes
This type of fracture most often occurs during a fall, when a person instinctively stretches his arms down, thus trying to land on them. This support does not support the weight of the person’s body, and injury occurs with or without displacement. And you can also injure your wrist when hit, if a person tries to push off from the object with which the collision occurs. A similar injury can occur in both an adult and a child.
A fracture of the wrist joint can occur as a result of the following reasons:
- Active sports.
- Diseases of the skeletal system. They significantly increase the risk of fracture not only of the wrist joint, but also of other joints.
- Falls. Most often, people fall on a slippery road in the winter, but similar situations can also happen indoors, for example, when going down a steep staircase.
- Road accidents. This is one of the most common causes of this type of fracture, especially among drivers.
- Disruption of the production process. The professional activities of some professions require strict adherence to job descriptions, which include the correct handling of instruments and apparatus. Incorrect position near the equipment - and a collision or pinching of the hand may occur, and along with it - a bruise, sprain or fracture of the wrist.
But there are also individual factors that provoke a possible violation of the integrity of the bone tissue in the radial joint. These include:
- Age-related changes. Most often they concern women, since only in them hormonal changes occur as quickly as possible - in 3–5 years. During this time, the synthesis of hormones decreases to a minimum, and with it the elasticity of various tissues, from mucous membranes to cartilage. The strength of bones is also determined by the ratio of hormones in the body.
- Accompanying illnesses. If they lead to disruption of the metabolic process, then they can also affect the structure of bone tissue.
Female gender, coupled with advanced age, increases the likelihood of a wrist fracture even with a minor blow or mild fall.
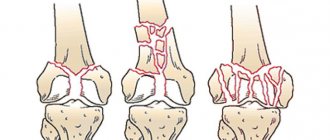
The most commonly damaged bone is the scaphoid. In this case, the injury may be:
- Splintered. In this case, the damage leads to fragmentation of the bone structure, resulting in the appearance of multiple small sharp fragments. In addition to the danger of injury itself, such fragments can damage soft tissue and nerve pathways around.
- Transverse. In this case, there is a violation of the integrity of the bone without displaced carpal bones.
Slightly less often, damage to the lunate bone occurs, and much less often to the wrist bone.
Rehabilitation and recovery
Complete recovery after a fracture of the radius consists of restoring bone structure and limb function (mobility and sensitivity). Even with absolutely adequate treatment, prolonged immobility in the joints and muscles of the upper limb leads to the fact that it is difficult for the patient to make movements in the joints that were previously accessible to him. The process of recovery from injury takes a long time and requires patience and desire from the patient to work.
Rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital begin to develop joints and muscles in case of a fracture of the radius as early as possible. The timing of the start of rehabilitation measures depends on the type of fracture and method of treatment. If the fracture is treated conservatively, then after 3-5 days, after the swelling subsides, they begin to work on the fingers.
First, passive movements are performed. Take the finger on the broken limb with your healthy hand and carefully begin to bend it in all joints. In this way, stretch all fingers except the thumb for 5-7 minutes 3 times a day. After a week of such training, they move on to active movements. The patient can begin to bend his fingers independently, without the help of a second hand. It is very important to distribute the load correctly. If pain or swelling appears again during the exercise, the exercise should be stopped.
Simultaneously with the beginning of passive movements in the fingers, active movements in the elbow and shoulder joints begin. The patient raises and lowers his arm, bends it at the elbow. Do these exercises for 3-5 minutes at least 2 times a day, gradually increasing the load. After 3-4 weeks, if active movements of the fingers do not cause pain, they begin to increase the load on these joints. You need to take a lump of plasticine and knead it in your fist. This exercise should be done as often as possible, throughout the week. After removing the cast, proceed to exercises with a wrist expander. You should exercise at least three times a day for 5-7 minutes.
A physical therapy instructor teaches a patient fine motor skills exercises. By the end of the fourth week, the patient may begin to draw or write with the affected hand. You can sort out rice or buckwheat grains one grain at a time. This will preserve not only the strength and mobility of the joints, but also the coordination of movements of the fingers. You can type texts on a computer keyboard as a coordination exercise. If the patient does exercises while he has a plaster splint installed, then after its removal, the rehabilitation period will be significantly reduced.
Exercises should involve all joints of the injured limb. It is important to regularly warm up your fingers. To relieve tension in the affected limb, some activities after removing the plaster cast should be done in water. The duration of the course of physical therapy is determined individually by rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital. The average duration of a course of therapeutic exercises is 1.5 months.
Rehabilitation therapists teach patients exercises that can be performed at home. Water gymnastics involves performing simple physical therapy exercises in water. Classes can be carried out in the bathroom. Cosmetic sea or table salt should be added to warm water. It will simplify the process of doing the exercises.
The complex consists of the following exercises:
- flexion and extension movements of the palms in the water;
- circular movements of the hand;
- rotations in the elbow joint;
- clenching and unclenching the palm into a fist.
The duration of the procedure is from 10 to 15 minutes. It is recommended to do 2-3 approaches daily.
Patients can also perform the exercise therapy complex recommended by the instructor at home. You should take the starting position “sitting at the table”. You need to place your elbows on the table, and place a thin, flat mat under your hands. The hands must be bent and unbent, and made rotational movements. Place your hands on the table edgewise, and then tilt your hand so that the little finger first touches the surface of the table, and then all fingers successively. Rest your elbows on the table, clasp your palms and tilt them alternately towards your left and right wrist.
First aid
First of all, it is necessary to achieve complete immobilization of the joint. You can make a simple splint from available materials, for example, a stick and a scarf. This design will limit the patient’s involuntary hand movements. Now you need to give the person analgesics. Despite the fact that at the very beginning the painful sensations may not be so strong, they will gradually increase.
In addition, many patients are in a state of shock, and taking sedative tablets also helps to correctly and adequately assess the situation. Finally, the patient must be taken to a medical facility (traumatology) or an ambulance team must be called.
Exercise therapy for quick recovery after injury
In the process of restoring the function of the upper limb after a fracture of the radius, thermal procedures play an important role. Physiotherapists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out warming in a variety of ways (paraffin or ozokerite applications). Massage is added to the complex of gymnastic exercises. The following procedures are used to treat a radius fracture:
- ultra-high frequency electromagnetic field (during the procedure, the tissues of the affected limb begin to heat up, the patient feels warmth, regeneration accelerates, pain weakens);
- low frequency electromagnetic field – reduces swelling, eases discomfort and pain;
- ultraviolet irradiation helps to increase the synthesis of vitamin D, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium from food in the digestive tract;
- Calcium electrophoresis on the area of injury helps accelerate the formation of callus and facilitates the restoration of damaged bone tissue.
You can undergo a recovery course after a fracture of the radius at an affordable price in a rehabilitation clinic. The contact center is open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Call the Yusupov Hospital and make an appointment.
Diagnostics
First of all, the doctor interviews the patient about how exactly the collision occurred. This will allow the doctor to more clearly understand which areas of the hand are damaged. Next, the specialist conducts a visual examination, palpation, and also tries to understand how severely the mobility of the wrist is impaired.
After this, the patient must undergo hardware examination. With this type of injury, it is enough to undergo an x-ray, and the patient needs to take two pictures, in two projections. In some medical institutions, the patient may be asked to undergo magnetic resonance imaging, but this is only necessary if there are multiple injuries to the wrist, with displacement of bones and bone fragments.
Dangerous consequences of wearing a plaster cast
What are the most dangerous side effects that await a patient when a limb is compressed with a plaster?
- Volkmann's contracture.
- Lack of sensitivity.
- Complete necrosis of a limb followed by amputation.
What other complications occur while wearing a cast, besides denting the limb:
- Bedsores. To avoid the appearance of bedsores, the doctor must extremely carefully and gently bandage the injured arm in a cast, especially for patients who are unconscious at the time of medical care. Ideally, the plaster cast should be uniform, without obvious lumpiness. The traumatologist needs to ensure that there are no cotton swabs or plaster crumbs left on the inside of the bandage - they can put a lot of pressure on the wrist.
Signs of bedsores are very characteristic:
- numbness in one area of the arm in a cast;
- the appearance of brown spots on the surface of the gypsum;
- feeling of tightness and constriction;
- putrid smell.
In this case, it is not enough to simply cut the plaster; it is necessary to carefully examine the limb and, if there are wounds, treat them with Levomekol and Vishnevsky ointments.
- Formation of abrasions and blisters on the skin. The plaster material must fit tightly to the hand; if this rule is not followed, bubbles will form inside. Inside they are filled with serous fluid, and it happens that a hemorrhagic admixture is formed. If it seems to you that there is a wet spot under the plaster, then we are talking about a bubble. The only way to get rid of it is by opening it. Soft bandages are applied to protect the wound from plaster.
- Allergy to gypsum material is very rare and manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- itchy skin;
- redness;
- dermatitis.
The way out of this situation is to treat your wrist with a knitted tubular bandage before applying a plaster cast.
Why does the radius bone in the wrist break?
To break your wrist, you need to fall on your outstretched arms or put your hand up and plop down on it with your whole body. A complicated fracture is characterized by displacement of part of the bone to the back of the hand, the fragments, in turn, move towards the palm.
If the fracture is not displaced, it is almost impossible to determine it by eye. Symptoms of a fracture do not appear as clearly as with displacement:
- the patient complains of aching or dull pain;
- the affected wrist swells;
- blueness of the skin appears.
You cannot touch your wrist; any touch causes severe pain. It is impossible to bend and straighten the joint - this also provokes pain. First of all, you need to observe whether your fingers move. If not, then the problem is much more serious than it seems at first glance; most likely, the integrity of the tendons is compromised. The presence of a fracture is determined by x-ray; if the doctor insists on a bruise, still ask to be sent for an x-ray to make sure there is 100% no serious injury.
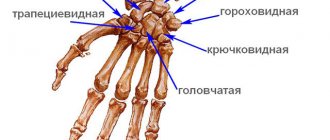
Anatomy
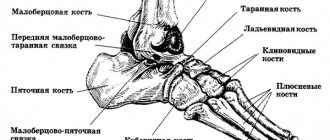
The wrist in the human body is located between the forearm and metacarpus and is an important functional part of the hand. The carpal bones are connected to the radius above, and also to the metacarpal bones below. There are a total of eight small carpal bones arranged in two rows. The distal row of bones relates to the metacarpus, the proximal row relates to the radius.
The three carpal bones, together with the radius, form the wrist joint. Injuries to the bones inside a joint are considered especially dangerous.
Product properties
Doctors and patients increasingly prefer plastic orthopedic structures, which is explained by the high efficiency of modern technologies. Such devices have unique properties, due to which they are widely used in sports medicine, pediatric orthopedics and other industries.
Thus, orthoses made of low-temperature plastic:
- create complete rest of the joint;
- distribute the load over the damaged area;
- help reduce pain;
- shorten the recovery period;
- have a “breathing” effect.
Orthopedic braces promote proper bone healing. The progress of treatment can be controlled - thermoplastic transmits x-rays. If necessary, the product can be corrected.