What are the most common elbow diseases?
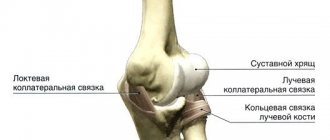
The elbow is a complex mechanism, which is represented by the connection of three bones (humerus, radius, ulna). Important blood vessels and nerve endings pass through it. Without realizing it, subjecting it to colossal stress in everyday life, people may increasingly encounter diseases of the elbow joint. Although the damage does not put the patient in mortal danger, it worsens the quality of life to a greater extent. Despite the periodic pain that bothers the elbow area, people attribute them to overwork, accidental bruises, the weather, and treat themselves by taking pills, applying compresses and using folk remedies. Unfortunately, in most cases, this leads to complications, loss of sensation and freedom of movement. Important! To determine the diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist.
Diseases of the elbow joints can be varied and the list of them is quite large:
- Various occupational injuries.
- Diseases caused by inflammation: tendonitis, epicondylitis, fasciitis, arthritis.
- Neurological diseases: nerve root lesions, carpal tunnel syndrome, neuritis, etc.
- Due to changes in tissues, both cartilage and bone: osteoarthritis, gout, chondrocalcinosis, osteochondrosis.
Main diseases of the elbow joint and their treatment
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the joint and involves a disruption of immune processes in the body.
Symptoms of the disease are: pain, malaise, swelling due to excess synovial fluid, increased temperature in the affected area, vomiting, muscle aches, etc. There are two forms of arthritis: acute and chronic. The presence of this diagnosis can be confirmed by an orthopedic doctor
after examination with palpation, and then referred for hardware examination - radiography, magnetic resonance, or computed tomography to determine the presence and localization of the inflammatory process.
“Ten percent of elbow pain is due to arthritis.”
Basically, the patient is prescribed conservative therapy, which consists of taking medications, physical therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Surgery is used in severe cases when the disease is already too advanced. Ulnar epicondylitis
Epicondylitis is a disease that is quite common in the musculoskeletal system.
It often occurs due to the patient’s professional activity associated with overload. This problem affects musicians, surgeons and massage therapists, athletes, builders, as well as those professions where the emphasis is on the hands. Damage to muscle tissue and ligaments is a characteristic of epicondylitis, the appearance of which is provoked by constant overload of the elbow, trauma and microtrauma, and impaired local circulation. Treatment consists of eliminating pain, restoring full movement, and preventing muscle atrophy. Physiotherapy is an integral part of recovery. Magnetic therapy, dynamotherapy, and infrared radiation are beneficial with conservative treatment along with medication. Therapeutic exercises are also indicated to improve blood circulation and metabolic processes, which contributes to better absorption of medications and vitamins taken. Exercises should be performed daily, increasing the duration of exercise and load according to the schedule prescribed by the doctor. If conservative methods do not help within 3 months, then surgical intervention will be required. Advice.
To prevent the appearance and further development of epicondylitis, you need to have the right approach to physical activity, follow the rules of doing exercises, warm up before activity, avoid monotonous movements that load the joint, and also take complex vitamins regularly. Tunnel syndrome
Another problem of the elbow joint, which manifests itself as a pinched nerve, is tunnel syndrome. Compression of the nerve occurs due to inflammation of the ligamentous apparatus, incorrect positioning of the hand during physical activity, when working at a personal computer, playing sports, etc. The main signs of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- numbness;
- tingling in fingers;
- shooting pain;
- muscle weakness and atrophy, cut.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can lead to loss of motor characteristics in the arm. Correct and timely consultation with a doctor is important here. The disease often requires surgical intervention, since conservative methods are possible only in the initial stages. During therapy, agents are used that increase blood circulation, reduce swelling and improve metabolic processes. An important part of non-surgical recovery is physical therapy aimed at strengthening muscles. Elbow arthrosis
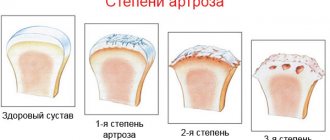
Arthrosis is a disease that occurs in people over 45 years of age. Tennis players, writers, violinists, pianists, drivers and women with hormonal changes are the main risk group. The causes of arthrosis are metabolic disorders, poor diet, chronic diseases (gastritis, tonsillitis, cholecystitis), inflammation due to infections entering the joint capsule, diseases of the endocrine system, etc.
Symptoms are divided into 4 groups: 1. pain when bending and straightening the arm; 2. crunching, which occurs as a result of bone friction; 3. restriction of movement in the joint; 4. modification of the shape of the elbow. To treat arthrosis, you must follow the following instructions:
- performing development exercises;
- refusal of loads on the sore arm;
- To reduce pain and inflammation, you need to take medications;
- in cases where the disease is advanced, surgery is required, but only in cases where conservative methods cannot help.
For arthrosis, it is advisable to adhere to a diet. It should be regular and varied.
The following should be removed from the patient’s diet:
- hot, spicy dishes;
- sparkling water, yeast dough, peas;
- rich broths;
- smoked fish and meat;
- strong teas and coffee.
Limit consumption:
- table salt (use sea salt);
- conservation;
- animal by-products (lungs, kidneys, tongue).
Be sure to include in your diet:
- jelly (no dyes);
- lean meats in gelatin, jellied fish;
- sufficient amount of water;
- vitamin and microelement complex;
- products containing calcium, phosphorus, manganese, magnesium, zinc, sulfur, vitamins B and C.
Causes of pain in the elbow joint
Traumatic injuries
The most common traumatic cause of pain is bruises.
They occur after a blow or fall on the elbow, manifest as moderate pain, which decreases over several days after the injury, and is accompanied by local swelling and some limitation of movements. With tears and ruptures of the ligaments, all symptoms are more pronounced, the pain syndrome intensifies when attempting passive movements in the direction opposite to the damaged ligament. With periarticular and intra-articular fractures of the lower end of the humerus, the upper part of the ulna, the neck and head of the radius, a sharp explosive pain occurs, which makes the eyes dark. Subsequently, the intensity of pain decreases, but the pain remains difficult to bear and intensifies with the slightest attempt to move the joint.
With fractures of the humeral condyles, fractures of the coronoid process, and Monteggia injuries, diffuse pain is felt deep in the joint. Fractures of the head and neck of the radius manifest as more localized pain in a specific area of the elbow. With olecranon fractures, pain is felt along the back of the elbow. Other symptoms of fractures are significant swelling, deformation, and severe pain with axial load.
Dislocations of the bones of the forearm are accompanied by unbearable pain, a clicking or crunching sound at the time of injury. Subsequently, the pain almost does not decrease until reduction. The joint is swollen, sharply deformed, active movements are impossible, and when passive movements are attempted, spring resistance is detected. In children under 5 years of age, after stretching or tugging on the arm, subluxation of the radial head sometimes occurs, which is manifested by moderate aching pain in the joint, which intensifies when trying to bend or palpate the ulnar fossa.
Inflammatory diseases of solid structures
Arthritis of the elbow joint is characterized by constant dull wave-like pain that intensifies in the early morning hours. The intensity of the pain varies from slight to very strong, depriving sleep and significantly limiting movement. The clinical picture is complemented by diffuse swelling, redness, local hyperthermia, stiffness, and dysfunction of the joint.
When infected, a severe variant of the disease develops - purulent arthritis, which is characterized by diffuse bursting, twitching or throbbing pain, combined with severe swelling, diffuse hyperemia, local hyperthermia, a significant increase in general body temperature, and symptoms of general intoxication.
Post-traumatic osteomyelitis of the periarticular ends of bones occurs after open injuries and operations on the joint, manifested by increasing sharp pain, rapid deterioration of the condition, general and local hyperthermia, and the appearance of purulent discharge from the wound. When transitioning to a chronic form, the pain becomes less intense, periodic, pulling or boring, and intensifies after exercise. A fistulous tract with purulent discharge is detected.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis affects the lower part of the humerus less often than the upper, and is detected in children. The pain quickly increases within 1-2 days, becomes tearing, throbbing, unbearable, intensifies even with minor attempts at movement, which makes patients “freeze” in bed. They are supplemented by general hyperthermia, chills, swelling, and redness of the joint.
Inflammatory pathologies of soft tissues
In acute aseptic bursitis, the pain is moderate, dull, bursting. Local edema, hyperthermia, and a fluctuating formation above the olecranon are observed. In the chronic form, the pain subsides, bothering mainly with pressure and physical activity. Swelling and redness disappear, the formation remains, the skin above it darkens. When infected, the pain syndrome increases sharply, the pain becomes tugging, bursting, and pulsating. The elbow turns red and swells. The temperature rises, symptoms of general intoxication appear.
Synovitis is not an independent pathology; it occurs with injuries and various diseases of the elbow joint. It manifests itself as a constant dull diffuse bursting pain, which intensifies as fluid accumulates. The joint increases in volume, its contours are smoothed. Upon palpation, fluctuation is determined.
Enthesopathies
A widespread cause of pain in the elbow joint is enthesopathies - inflammatory and degenerative lesions of the tendons at the point of their attachment to the bones. With lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow), dull, stabbing or aching pain is localized along the outer surface of the joint, radiating to the shoulder and forearm. They intensify with load, extension of the middle finger with resistance. Combined with increasing weakness of the hand.
Medial epicondylitis is provoked by repetitive hand movements and occurs in golfers, gymnasts, tennis players, seamstresses, and typists. The symptoms are the same as for lateral lesions, but differ in localization - pain is felt inside, not outside the elbow; upon palpation and flexion of the hand, pain appears above the internal epicondyle of the shoulder.
Degenerative diseases
Arthrosis of the elbow joint in the initial stages is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, slight pain at the beginning of movements and after heavy loads. As the pathology progresses, the initial pain becomes more pronounced and is combined with stiffness; after exercise, the pain persists longer at rest. Movements in the joint are accompanied by crunching sounds.
Later, pain appears even with little physical activity, bothers you at night, and becomes constant, aching, pulling, and boring. The joint aches due to the weather. Movements are limited, and the ability to self-care suffers. Deformations of varying severity are formed, contractures develop.
With chondromatosis, loose bodies form in the joint, which can become pinched and impede movement. This determines the characteristics of the pain syndrome. Along with dull, pulling or aching pain, intensifying after physical activity, piercing (shooting, explosive) pain periodically occurs, which is combined with joint blocking.
Osteochondritis dissecans most often occurs in children and young people and is manifested by pain that increases throughout the year. First, there is discomfort without clear localization. Then moderate dull pressing or aching pain appears, combined with a slight crunching and “jamming”, blocking of the joint. Subsequently, the pain intensifies and then weakens, blockades become more rare.
Autoimmune diseases
The elbow joint is often affected by rheumatoid arthritis. The characteristics of pain depend on the activity of the rheumatic process. With grade 1, pain in the joint is insignificant, usually aching, appearing in the morning and after exercise, combined with transient stiffness. For grade 2, diffuse deep nagging pain at rest and during movement is typical.
During movement, the pain intensifies, which leads to limited function of the joint. Prolonged stiffness, recurrent effusions, and local redness of the skin are observed. At level 3 of activity, the pain is intense, constant, and exhausting. They are combined with severe local hyperemia, constant stiffness, persistent synovitis, severe limitation of mobility, development of subluxations and contractures.
For rheumatism, multiple joint damage is typical. Pain quickly migrates from one joint to another. The pain is strong and varies significantly in nature (sharp, dull, burning, pulsating, pressing, pulling). They arise after an acute infection, persist for several days, after which they disappear or significantly weaken.
With systemic lupus erythematosus, pain in the elbow joints is usually symmetrical. Several joints (shoulder, elbow, knee, etc.) on one side of the body may be affected. In mild cases, the pain is insignificant, short-term, local, dull. For a severe course, long-term progressive nagging or bursting pain is typical, which intensifies and weakens in waves, combined with swelling and hyperemia. Severe restrictions on mobility are uncommon.
Neoplasms
Benign neoplasia of the articular ends of bones, cartilage and surrounding soft tissue structures is characterized by a long course. The pain is insignificant, short-term, dull, nagging, with a fairly clear localization. Symptoms may remain unchanged for a long time. The growth of the tumor provokes an increase in pain; in some cases, due to compression of the nerves, radiating pain occurs, a sensation of “electric shock” or a shooting along the forearm.
Malignant tumors manifest themselves as rapidly progressive pain. Initially, the patient complains of a dull pain of uncertain localization with a tendency to intensify at night. Then the pain spreads throughout the joint, acquires a jerking, burning, bursting or cutting character, restricts movements, and is combined with local swelling, increasing deformity, asthenia, low-grade fever, and loss of appetite. At the final stage, the pain becomes constant, painful, unbearable, and can only be eliminated with narcotic drugs.
Other reasons
Ulnar nerve neuropathy and cubital tunnel syndrome manifest as nagging pain in the form of a strip from the internal epicondyle of the shoulder to the hand. Painful sensations are combined with numbness of the 4th and 5th fingers, intensifying when the joint is flexed. When pressure is applied to the elbow, there is a stabbing pain or sensation of lumbago from the elbow to the little finger.
Sometimes pain in the elbow occurs due to diseases of the cervical spine. This type of pain is characterized by a shooting sensation, spreading along the limb - from the shoulder to the hand. Irradiation of pain to the left elbow joint is possible with ischemic heart disease and myocardial infarction. Pain syndrome in this localization can also develop with mental illness and depressive disorders, taking corticosteroids and anabolic steroids.
Injuries
Injuries are quite dangerous violations of the integrity of the elbow. They can be considered bruises, fractures and dislocations, and quite often they are accompanied by damage to blood vessels and nerves. After injury, before the regeneration period begins, the patient experiences severe pain, hematomas, ruptured tendons and deformities. As a result of the bruise, arthrosis or other problems may develop. The main injury to the elbow is a dislocation. It is necessarily accompanied by a bone fracture. A dislocation is accompanied by severe elbow pain, stiffness, and a person loses sensation in the wrist. Damage of this kind requires immediate consultation with a doctor and an x-ray of the elbow joint, which will show the extent of the damage, whether the muscles and nerve endings are affected. The doctor will restore the correct position by reduction, if possible, and apply a plaster splint. If the nerve has been damaged or the coronoid process is fractured, then treatment can only be surgical. Tissue bruising can occur due to a push, compression or blow to the elbow area. Symptoms of a bruise are pain when moving, bruises, increased skin temperature at the site of impact, and swelling. A bruise also requires consultation with a doctor.
How Covid-19 affects diseases of the spine and joints
Many doctors noticed that this year there was no usual seasonal decline in patients. On the contrary, during the pandemic, the number of patients complaining of joint pain has only increased.
Reasons for the increase in incidence
The main causes of outbreaks of musculoskeletal diseases include:
- Decreased physical activity. During quarantine, people did not play sports. The amount of physical activity has decreased to a minimum. Gyms were closed and walking was prohibited.
- Excess weight. Due to inactivity and boredom during quarantine, women stood more at the stove. As a rule, people began to eat more and gained extra pounds, which, in principle, negatively affects the spine.
- Lack of access to a doctor. People with existing diseases of the musculoskeletal system should be periodically observed by a doctor to prevent the onset of a critically dangerous stage of the disease.
- The effect of the virus on the body. Due to the fact that the body does not receive enough nutrients, there is a decrease in immunity, which provokes joint pain and inflammation. As a result, healthy cartilage becomes inflamed, and the entire musculoskeletal system suffers.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases. When a person with a chronic illness is infected with the virus, new symptoms appear that complicate treatment.
Joint pain is the most common complaint of patients
Every second patient consults a doctor with complaints of joint pain. Most often people talk about back and leg pain.
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system are common throughout the world. This is one of the most famous problems of an adult.
Such problems rarely lead to death, but have a profound impact on the body. A person’s performance decreases, the quality and life expectancy deteriorate, and chronic pain appears, which often makes itself felt.
According to the World Health Organization, the largest number of patients complain of back pain. Neck, joint, head and hip pain are also common problems. This was influenced by two factors. The first is that in the modern world, where everything is available online, people do not need to go anywhere. As a rule, physical activity decreases.
The second factor is an increase in life expectancy. Previously, people did not know what arthrosis, radiculitis and other joint pathologies were, because they simply did not live to old age.
What you need to know about treating joints for coronavirus
Doctors, one and all, warn their patients that during Covid-19 they should be extremely careful with medications. It is important to take into account not only the presence of chronic diseases, but also the state of the body’s immune system.
Therefore, medications that you have taken before for various joint pains should be taken only after consulting a doctor. The reason is that taking painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs at the same time as medications for Covid-19 can cause or develop side effects. Undoubtedly, this cannot but affect the general condition of the patient. The coronavirus will begin to worsen, new symptoms will appear, which can subsequently become serious complications.
For this reason, to relieve joint pain, many doctors prescribe devices for external use. Such drugs not only relieve pain, but also prevent the spread of inflammation in healthy bone tissue.
Preventive measures to help prevent complications from Covid-19
First of all, you need to remember that you need to closely monitor your health and pay great attention to the condition of the musculoskeletal system, especially if you have been diagnosed with coronavirus. If you notice any unusual symptoms, contact a specialist immediately. It is important to conduct a timely examination and prescribe appropriate treatment.
To prevent joint diseases it is recommended:
- monitor your weight. Obesity in general has a negative effect on a person’s condition, and it is generally dangerous for joints, as the load on the spine increases.
- eat a balanced diet. Try to eliminate fats and unhealthy carbohydrates, and give preference to plant-based foods. It's good for joints.
- monitor the water-salt balance and metabolic processes of the body. Don't drink too much liquid.
- do not abuse smoking and alcohol. Bad habits worsen the condition of bone tissue, and with coronavirus this is fraught with serious consequences for the entire body.
During coronavirus infection, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle. This is the only way to prevent exacerbation of joint diseases. Walk outdoors more often, not only in warm weather. A winter half-hour walk is a way not only to strengthen the body, but also to support the immune system.
Adequate healthy sleep is an important aspect. Therefore, stick to a daily routine so that you fall asleep at the same time and sleep at least eight hours a night. At least some physical activity is also important: running, swimming, dancing. All this is quite enough to prevent complications of existing diseases due to coronavirus.
When infected with coronavirus infection, about 5% of patients complain of pronounced pain and inflammation of certain joints.
Therefore, doctors advise seeking help in the early stages of disease manifestation. You shouldn’t start the disease and hope that everything will go away on its own. Also, do not self-medicate under any circumstances. You will not only aggravate existing problems, but also complicate the diagnostic process when you later consult a doctor. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Traditional methods of treating diseases of the elbow joint
We must not forget about the methods that our ancestors used to eliminate pain in bone joints. Attention! The use of these methods should be carried out as an aid to the main treatment, and not as a replacement for it. Let's look at the most effective treatment methods. 1. Rubbing the damaged area with tinctures of Kalanchoe and propolis; 2. Drink decoctions of chamomile, dandelion or St. John's wort; 3. Apply various compresses; blue clay is considered effective; 4. Baths with pine needles or sea salt; 5. Grind honey with apple cider vinegar. By following simple rules, eating right, without injuring or loading the limb, you can not only cure diseases that may appear in the elbow joint, but also completely prevent their reappearance.