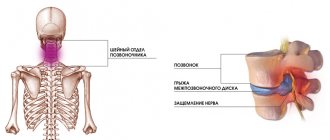
Paramedian disc herniation is a pathology in which part of the intervertebral discs is displaced into the spinal canal, which leads to compression of the spinal cord on one or both sides. The causes of the disease are injuries or chronic degenerative diseases of the spine:
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- dysplasia.
It is worth noting that this type of hernia is quite common and is considered the most dangerous for human health, as it can lead to disability.
Depending on the type of operation and category of complexity from 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
Included in the price:
surgery, anesthesia, dressings, medications, food and hospital stay, observation by a surgeon in the postoperative period.
40-60 minutes
(duration of operation)
2-3 days in hospital
Indications
- persistent and severe symptoms of compression of the spinal nerves by a herniated disc, not amenable to conservative therapy
- the patient's desire to get rid of pain
Contraindications
- chronic diseases in the stage of decompensation
- acute inflammatory processes in the body
Classification of paramedian hernias
Classification of paramedian hernias is carried out in accordance with their location.
Paramedian disc herniation L5-S1
Despite the fact that these vertebrae are the most powerful, they experience stress in all body positions. Paramedian disc herniations L5-S1 most often occur with complications, and when cauda equina syndrome occurs, they are an indication for urgent surgical intervention. Thus, treatment of medial-paramedian disc herniation L5-S1 in most cases is carried out surgically.
Paramedian disc herniation L4-L5
A hernia between the fourth and fifth vertebrae also occurs quite often. Typically, this occurs due to poor posture when sitting for long periods of time. In this position, the load on this area increases several times, which can cause this pathology.
Paramedian disc herniation C5-C6
Pathological changes in the cervical vertebrae are primarily due to their small size and less developed muscles compared to other parts of the spine. Paramedian hernia in this case can occur due to injuries and accidents.
Left and right paramedian hernia
Depending on which direction the nerves extend from the spinal cord, right or left, a right- and left-sided paramedian hernia is distinguished. Such pathologies are characterized by symptoms localized on one side:
- numbness;
- decreased muscle tone;
- pain;
- loss of sensitivity.
Microsurgical operations to remove herniated discs in all parts of the spine
The vast majority of the adult population periodically experiences pain in the spine. In severe forms of osteochondrosis, compression of one or more spinal nerve roots by a herniated disc develops. In this case, the patient develops pain in a “stripe” along the entire arm or leg, sensitivity is impaired, and strength in certain muscles may decrease. Initially, conservative treatment is carried out by a neurologist. If treatment is ineffective within 1-2 months, surgical treatment is indicated - removal of the disc herniation. It is urgently necessary to undergo surgery if severe weakness in the limbs and urination problems develop.
The following methods for removing disc herniations are used all over the world and in our clinic:
1. Microsurgical discectomy
2. Endoscopic discectomy
3. Removal of disc herniations from the ventral anterior-lateral approach, followed by fixation of the vertebrae with an implant.
Microsurgical discectomy - surgery is performed from the back through a small incision. Under an operating microscope, the disc herniation is removed and the compressed root is released. Then the wound is sutured.
Clinical example of an extraforaminal hernia at the L4-5 level on the right.
MRI - control after microsurgical discectomy - the hernia is removed, the roots are freed from compression.
Endoscopic discectomy (Easy Go technique) - the operation is also performed from the back. The skin incision is somewhat smaller; the muscles are not cut, but are pulled apart using special dilators. A special tube with an endoscope is installed and the disc herniation is removed. There are no fundamental differences in the removal of disc herniation between the microsurgical and endoscopic methods. Postoperative management is similar. But endoscopy is less traumatic for soft tissues and muscles, and allows a more complete examination of the area of the disc, root and dural sac (“look around the corner”).
After the operation, the patient is allowed to walk on the same or the next day, and a semi-rigid corset is used for about a month. Bend forward, straining, and heavy lifting are limited until one month from the day of surgery. Incapacity for work for non-physical workers is about a month, physical work is about 2 months.
Removal of disc herniations from the ventral anterior-lateral approach with subsequent fixation of the vertebrae with an implant - the operation is performed from the abdomen. After a 5–7 cm skin incision, retroperitoneal access to the vertebral bodies is performed. The entire disc and disc herniation are removed. The implant is installed and the wound is sutured. The patient is activated the next day, wearing a corset for about 2 months. The period of incapacity for work is from 3 to 6 months.
Foraminal disc herniation L5 – S1 before surgery.
MRI – control after removal of a disc herniation and spinal fusion with a porous titanium nickelide implant.
The advantage of these operations is that they are radical - the disc is completely removed, there are no relapses or instability, and there is less scarring and adhesions in the spinal canal.
When removing a cervical hernia, an incision is made along the front surface of the neck. The disc or disc herniation is removed, the roots and spinal cord are released from compression. The operation ends with the installation of the implant. After the operation, the patient is allowed to walk on the same or the next day, and a semi-rigid corset is used for about a month. The period of incapacity for work is about 2–3 months.
Clinical manifestations of paramedian hernias
The initial stages of the disease are characterized by mild symptoms, which are expressed in dull and aching pain due to fatigue. If you do not contact the multidisciplinary CELT clinic for treatment in time, intense pain syndrome may occur, which will be accompanied by:
- disruption of the functioning of internal organs;
- impaired motor function of the arms and legs.
When a C6-C7 disc herniation occurs, the following clinical manifestations are observed:
- pain in the place where the hernia developed;
- migraine-like headaches;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- numbness of fingers and hands
Types of foraminal hernia
Classification of this type of hernia is carried out according to several parameters:
- side of the nerve exit: left- and right-sided hernia;
- location in the spine: lumbar, cervical, thoracic hernia.
- direction: in the hole itself, at the exit/entrance to it, in the hole between the vertebrae (paramedian-foraminal disc herniation), inside the canal (dorsal).
Foraminal disc herniation L5-S1
Foraminal disc herniation L5-S1 is rightfully considered the most common. It is located in the lumbar region, which bears the entire load, which does not weaken even when the body is in a horizontal position. The maximum load on this area occurs during sports training, weight lifting and physical activity.
Foraminal disc herniation L4-L5
Foraminal disc herniation L4-L5 ranks second in prevalence. Its appearance and growth lead to severe pain, which may be accompanied by atrophy of the lower limb on the affected side.
Foraminal disc herniation C6-C7
Since foraminal disc herniation C6-C7 is located in the cervical spine, it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the neck and back of the arm;
- feeling of weakness when flexing/extending the wrist/shoulder;
- numbness in the middle and ring fingers;
- restriction of neck movements;
- weakening of the triceps muscle reflex.
Treatment of paramedian hernias
The success of conservative treatment of paramedian hernias directly depends on how competent the specialist is and on how responsible the patient is. If he fully complies with all the doctor’s instructions, the success of treatment can be predicted in most cases.
Conservative therapy is used if there are no indications for emergency surgery. It involves taking medications: analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, corticosteroids, drugs that have a positive effect on tissue nutrition. Injections can be performed directly into the location of the hernia, as well as massages, ultrasound therapy, therapeutic exercises, spinal traction, etc.
Surgical intervention at the CELT clinic is resorted to in the most extreme cases. The operation itself is performed by experienced specialists using modern equipment and drugs to minimize the possibility of complications and blood loss.
Diagnosis of foraminal hernia
If you suffer from severe pain that cannot be relieved with conventional painkillers, contact the CELT clinic. Our specialists will conduct diagnostic studies, determine the location of the hernia and its effect on surrounding tissues and, depending on the results obtained, prescribe treatment.
We have modern diagnostic equipment that allows us to conduct the following studies:
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography;
- radiography.
In addition, a doctor’s examination and medical history are taken.
Treatment of foraminal hernia
In most cases, our specialists begin treatment using conservative methods and only if there are undeniable indications, they offer their patients surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment is carried out in a complex and includes:
- taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and other drugs to reduce pain, eliminate inflammation, reduce swelling and improve blood and lymphatic supply to affected tissues;
- massage, physical therapy, manual therapy, which help strengthen the muscle corset and minimize traumatic factors;
- local injections, spinal traction, electrophoresis, which help to minimize hernia protrusion.
If the patient experiences severe pain that cannot be relieved, or paralysis of the limbs, our neurosurgeons perform an operation. We use the most modern treatment methods that have proven themselves!
Foraminal hernia
| Fig.1. Foraminal opening in the lumbar spine. Formed anteriorly by the lower edge of the vertebral body and disc, posteriorly by the facet joint, and superiorly and inferiorly by the roots of the arches. |
One of the forms of lumbar disc herniation is foraminal disc herniation. According to various authors, this type of hernia occurs in 4% to 10% of all hernias. Most often, this hernia occurs at the level of L4-L5, then at the level of L5-S1 and L3-L4. The peculiarity of this hernia is a pronounced pain syndrome, accompanied by a neurological disorder - loss of reflexes and/or weakness in the foot, as well as the difficulty of diagnosing it.
A foraminal disc herniation is a hernia located in the area of the foraminal opening (the place where the spinal root exits the spinal canal). The foramen is a canal about 1.5 cm long located between the roots of the arches of 2 adjacent vertebrae. (Fig.1)
In total, there are 4 types of foraminal hernias:
- Foraminal medial located at the entrance of the intervertebral foramen.
- Intraforaminal located in the intervertebral foramen
- Foraminal lateral located at the exit from the intervertebral foramen.
- Extraforaminal lateral located outside the intervertebral foramen, lateral to the roots of the vertebral arches.
Clinical manifestations of foraminal hernias have a number of features. Pain syndrome in patients with foraminal hernias usually has an acute onset and almost immediately becomes intense. Patients are in a forced pain position. These pains do not respond well to analgesic therapy and are sometimes relieved only by drugs. In addition, the pain syndrome is almost always accompanied by loss of tendon reflexes and/or weakness of the flexors or extensors of the foot (the patient cannot stand on his toes or heels).
The most informative diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine.
Conservative treatment of foraminal hernias of the spine rarely brings relief. After treatment fails for 2-3 weeks, patients usually seek surgical treatment. Foraminal medial hernias are removed using conventional interlaminar access. It is impossible to adequately remove lateral foraminal hernias from this approach; the facet joint must be removed. The operation takes longer and is often accompanied by large blood loss. After facet joint removal, lumbar scoliosis often develops with residual low back pain.
| Fig.2. Scheme of transforaminal endoscopic removal of a disc herniation |
I use a unique method of transforaminal endoscopic removal of foraminal disc herniations. The term transforaminal means that the m/n hernia is removed through the foraminal foramen - the place where the spinal root exits the spinal canal. (Fig.2)
| Fig.3. The operation is performed under the control of an image intensifier through a puncture without an incision. |
Transforaminal endoscopic removal of a disc herniation is performed without an incision through a puncture. First, under the control of an electron-optical converter (EOC), a needle is inserted into the disc outside the spinal canal and then a working tube with optics is inserted along the needle. This method removes a small part of the disc to reduce pressure in it and a sequester that compresses the spinal root. Those. the disc subsequently continues to perform its shock-absorbing function, and as a result of removal of the sequestration, the pain in the leg disappears. That. all manipulations are performed outside the spinal canal, avoiding scar changes in the canal and without incision with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues. (Fig.3)
To decide on the choice of treatment method, you must make an appointment with neurosurgeon Oleg Vladimirovich Durov by phone.