https://mz-clinic.ru/bolezni/spine/smeshchenie-pozvonkov.htmlWhen vertebral displacement occurs
The disease is caused by various pathologies:
- spinal injuries: dislocations, fractures;
- osteochondrosis;
- spine surgery;
- vertebral displacement in babies occurs due to a sudden backward movement of the head or birth trauma;
- congenital weakness of bone structures;
- age-related changes in intervertebral joints;
- spondylolysis is a vertebral defect that leads to a fracture of the vertebral pedicle;
- age-related changes in intervertebral joints;
- temperature changes;
- sharp contraction of the back muscles, stretching of the spine.
Vertebrae can become misaligned after a car accident, falling on your back, heavy physical labor, working in a fixed position, or lifting heavy objects. Weightlifters, gymnasts, rugby players, and relatives of people with spinal diseases are susceptible to spondylolisthesis.
What is vertebral displacement?
Displacement of the vertebrae cannot be called an independent full-fledged disease. On the one hand, this is always a consequence of injury, including congenital or other mechanical damage. On the other hand, displacement of the vertebrae itself is the cause of many diseases.
Displacement of the vertebrae is always an unpleasant, painful phenomenon; a person cannot walk or run normally, cramps occur, leg joints begin to ache, and pain appears in the knee and hip joint.
If this is a mild form, then these are headaches and muscle spasms and other unpleasant symptoms, when a person cannot even think that he has a displacement of the vertebrae.
In extreme forms, this leads to immobility and disability.
Treatment
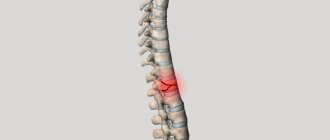
Treatment of compression fractures of the thoracic region is possible conservatively and surgically. Moreover, the choice of tactics depends not on the wishes of the patient, but on the degree of the fracture and the presence of neurological complications. In both cases, the doctors’ tasks are to eliminate pain, restore the anatomically correct position of the vertebra and accelerate regeneration processes.
Conservative treatment of thoracic spine fractures
Compression fractures of the thoracic spine of the 1st degree are successfully treated conservatively. In such situations, skeletal traction is usually initially prescribed. The goal of the procedure is to stretch the spine, allowing the vertebrae to return to their anatomically correct position.
After this, be sure to apply a plaster cast or put on a reclinator. This orthopedic device is a type of corset. It contains a hard platform designed to protect the injured area of the spine. Semi-rigid and at the same time elastic straps are attached to its corners, supporting the spine in the desired position and reducing the load on it.
Initially, all patients must adhere to strict bed rest. At the same time, they need a hard orthopedic mattress or shield. Also mandatory components of conservative treatment are:
- drug therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy.
Drug therapy
From the very first day of treatment, the patient is prescribed medications. The initial goal is effective pain relief. For this purpose, analgesics from various pharmacological groups, including narcotic ones, are prescribed. To quickly relieve pain, novocaine blockades are performed.
Also assigned:
- calcium and vitamin D preparations;
- chondroprotectors;
- corticosteroids;
- immunostimulants.
The length of time you take each drug varies from case to case. Some of them can be administered parenterally to accelerate the onset of the therapeutic effect and increase its severity with the same dose of the drug.
Exercise therapy
If the doctor has allowed the patient to stand up and walk, this should definitely be done, even if adopting a vertical body position causes discomfort. This is due to the fact that in a supine position, calcium is washed out of the body more actively, so walking contributes to a faster recovery after a fracture.
Massage
It is impossible to activate blood flow and maintain muscle tone during a forced sedentary lifestyle without a properly performed therapeutic massage. But it is important that the sessions are conducted by a qualified specialist, whose actions would not provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition and displacement of the injured vertebrae.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures potentiate other components of conservative treatment for compression fractures of the thoracic spine. Patients are prescribed courses of 10–12 procedures:
- UHF;
- reflexology;
- ultrasound therapy;
- Sollux;
- paraffin and ozokerite wraps.
Ultraviolet irradiation and electrophoresis with the introduction of calcium and phosphorus preparations are considered especially effective. The duration of each procedure is on average 10–15 minutes.
Surgical treatment of thoracic spine fractures
Today, neurosurgeons have many minimally invasive techniques in their arsenal for treating compression fractures. They make it possible to return a broken vertebra to its normal position without serious tissue injury and give it the necessary strength. All manipulations are carried out through a special thin needle or cannula, so after the operation there are no rough scars left, and recovery proceeds quickly. Such minimally invasive interventions used for fractures of the thoracic spine include vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.
But they can only be used for uncomplicated fractures. If there are signs of damage to nerve structures, spinal cord compression, or spinal instability, neurosurgeons resort to other surgical techniques. In such situations, open operations are indicated, during which the anatomy of the spine is restored with special plates, meshes and other fixing elements. Most often, transpedicular fixation is performed, the technique of which is now 100% proven.
In the most difficult cases, when the vertebra cannot be restored or seriously threatens the integrity of the spinal cord, it is partially or completely removed, i.e., a laminectomy is performed. If necessary, the removed vertebra is replaced with artificial implants or autografts.
Verterbroplasty
Vertebroplasty is a microsurgical operation during which a compression fracture of the spine is eliminated by injecting a special composition – bone cement – into the body of the injured vertebra. This substance is supplied to neurosurgery centers in the form of two components, which are mixed immediately before injection into the vertebra.
Vertebroplasty is highly effective and always leads to an improvement in the patient’s condition. Since the vertebrae are formed by porous spongy bone tissue, filling the natural pores with bone cement leads to a manifold increase in their strength. But since the procedure is not able to “straighten” a broken vertebra, they are performed only for those compression fractures that are accompanied by a decrease in the height of the vertebral body by less than 70%.
The essence of the operation is to insert a thin needle into the vertebral body under X-ray control (usually CT or image intensifier). Bone cement is then prepared. Initially it looks like a paste that easily fills all the natural voids of the bone, but within 8-10 minutes it hardens, turning the vertebra into a high-strength conglomerate and eliminating the risk of its fracture in the future. The needle is removed from the patient's body after the bone cement has hardened, and the remaining puncture is covered with a sterile dressing.
Since the bone cement contains an X-ray contrast agent, the neurosurgeon fully controls the process of filling the vertebra with it and avoids the composition leaking beyond its boundaries. The presence of an antibiotic in the composition eliminates the risk of developing an infectious and inflammatory process, therefore vertebroplasty is considered a safe and highly effective operation.
It takes about 40 minutes and is often performed under local anesthesia. But vertebroplasty cannot be performed if you are allergic to the components of bone cement and if you have malignant tumors or metastases in the spine.
Kyphoplasty
Kyphoplasty is a more advanced percutaneous surgery technique that does not have some of the disadvantages of vertebroplasty. The essence of both operations is similar, but with kyphoplasty, an empty balloon is initially inserted into the vertebral body, into which saline solution is injected.
This allows you to “straighten” the vertebra and completely restore its natural size and position. X-ray contrast barium sulfate is dissolved in advance in the injected solution, so the neurosurgeon can accurately see its position and the degree of restoration of the parameters of the vertebral body on the X-ray machine monitor. As soon as it is possible to achieve its normal size, the fluid and balloon are removed, and bone cement is injected into the vertebral body, as with vertebroplasty.
An additional advantage of kyphoplasty is the ability to eliminate kyphotic deformity of the spine, often observed with compression fractures of the thoracic spine. With it, the risks of bone cement getting outside the vertebra are sharply reduced, and the achieved result allows you to avoid not only repeated fractures, but also restore normal posture, and also avoid limitation of mobility.
Unlike vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty can be performed even with compression fractures accompanied by a decrease in vertebral height by more than 70%. But it is performed under general anesthesia, so it requires more serious preparation.
Transpedicular fixation
This type of surgery involves fixing damaged vertebrae with special titanium screws and rods. They are produced in different types and sizes, which allows you to select the optimal type of screws for each patient with vertebral fractures at any level.
Transpedicular fixation is performed for unstable fractures. During the operation, an incision is made over the injured vertebra. The neurosurgeon then separates the spinous processes and vertebral arches. Direct fixation of the vertebra occurs by screwing screws into the intersection points of the transverse and articular processes.
Once all the titanium screws are installed, rods are passed through the holes in them, designed to evenly distribute the load on the entire system. Ultimately, the created structure reliably holds the vertebra in a given position and is not subject to distortion. The postoperative wound is sutured in layers and covered with a sterile bandage.
When performed correctly, transpedicular fixation does not lead to the development of undesirable consequences and complications. But it cannot be performed for certain diseases, including bleeding disorders, decompressed diabetes mellitus, pregnancy and others.
Laminectomy
In some cases, it is necessary to perform one of the most traumatic operations on the spine - laminectomy. It involves making a large incision in the projection of the damaged vertebra and carefully separating the soft tissues from the elements of the spine.
During a laminectomy, the surgeon can remove the spinous processes, vertebral arches, sharp fragments, and the vertebral body. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire spinal motion segment, which is subsequently replaced with an artificial implant or graft.
Laminectomy is used for compression and fragmentation fractures complicated by damage to the spinal cord and nerve fibers. But it requires long and complex rehabilitation.
Symptoms of vertebral displacement
Displacement of the vertebrae occurs in the cervical spine, as well as in the thoracic and lumbar spine. The consequences of this disease can be:
- headaches, migraines, runny nose, insomnia, amnesia, chronic fatigue - with cervical spondylolithesis;
- peptic ulcer, gastritis, pancreatitis - with thoracic spondylolithesis;
- lameness, weakness and pain in the legs, inability to move normally - with lumbar spondylolithesis.
If the disease is neglected, it leads to poor posture and its accompanying diseases (scoliosis, kyphosis, etc.). All this is accompanied by severe pain.
If left untreated for a long time, vertebral displacement can lead to disability.
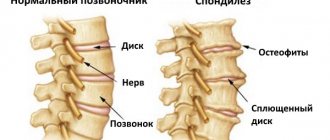
General characteristics of the disease
The disease is a displacement of one vertebra relative to the underlying one. In this case, it can move:
- to the right or left side - in this case, the diagnosis will indicate “laterolisthesis”;
- forward – anterolisthesis;
- back – retrolisthesis.
In addition, it is important to understand that pathology does not appear immediately, but develops over time. The more attentive you are to your health, the earlier the disease can be detected. If a neurologist
determines that the vertebra has shifted by 25%, then you have the first degree of spondylolisthesis, 50% - the second, 75% - the third, from 75% to 100% - the fourth. The fifth occurs when the vertebra completely “leaves” from its place, a phenomenon called “spondyloptosis”.
Diagnosis of vertebral displacement
In order to correctly diagnose vertebral displacement, you need the help of a neurologist.
At the initial appointment, the neurologist conducts:
- conversation with the patient (to identify painful areas and determine the nature of pain);
- taking anamnesis;
- reflex diagnostics;
- comprehensive examination to determine:
- muscle conditions (hypertonicity, hypotonicity);
- presence/absence of sensory impairment.
- presence/absence of decreased mobility of the spine and joints
In addition, the doctor may prescribe additional examination methods, such as:
- MRI
- Ultrasound
- X-ray
- Lab tests
DIAGNOSIS OF SPONDYLOLISTHESIS
Examination for spondylolisthesis is performed using technical visualization tools, since it is impossible to determine the displacement, as they say, “by eye.” A mandatory method is radiography of the spine in frontal and lateral projection. Computed tomography visualizes the area of vertebral displacement and their structure more informatively.
IT IS USED TO DISTRIBUTE DEGREES OF LYSTHESIS DEPENDING ON THE SEVERITY OF VERTEBRAL SLIPPING:
Grade 1 is limited to 25% displacement.
2nd degree – up to 50%.
Grade 3 – up to 75% (risk of surgery).
4th degree – 100% displacement.
How to treat vertebral misalignment
Methods for treating vertebral displacement are similar to methods for treating instability of the spinal system. The Alan Clinic Center for Neurology and Orthopedics in Kazan offers its patients comprehensive treatment for spinal displacement WITHOUT SURGERY! Having a modern treatment room on its territory, specializing primarily in drug-free treatment methods, minimizes the risk that the body will not accept the treatment, and there will be no side effects in the form of a reaction in the gastrointestinal tract.
The treatment package is selected individually for each patient, based on many factors (severity, age, presence/absence of concomitant diseases and contraindications). The entire treatment process is carried out under the constant supervision of the attending physician, who carefully studies the body’s sensitivity characteristics and, if necessary, quickly adjusts the treatment strategy.
Our methods of non-surgical treatment of disc herniation include:
- Various types of reflexology - influencing active points of the body in various ways (helps relieve pain and muscle spasms):
- Acupuncture - exposure to biologically active points with microneedles.
- Pharmacopuncture is the introduction of medicinal drugs of natural origin to the source of the problem.
- Tsubotherapy is a gentle effect on the reflex points of the body using metal balls.
In addition, each patient is assigned a mandatory active recovery program (this includes special exercises for the spine to be performed at home), and personal recommendations on nutrition and movement are drawn up.
All these and some other procedures are designed to relieve the patient of pain, restore activity and freedom of movement.
Therapy and prevention
In case of a spinal fracture, it is important to provide first aid correctly and quickly. It is not recommended to touch or move the victim until doctors arrive. Before transportation, a person is placed on a flat and hard surface, and the position of the body is fixed with special belts. Severe spinal injuries are treated in a hospital setting.
Orthopedic traumatologists deal with various spinal injuries. Treatment of a fracture, as well as displacement, consists of a set of measures:
- conservative therapy;
- taking medications;
- gymnastics and massage;
- wearing a support bandage or collar for the neck area.
At first, you need to stay in bed. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and painkillers. When choosing a medicine, take into account the nature of the damage and the presence of chronic diseases.
In some cases, surgery is performed (if the brain is damaged). Physiotherapy is actively used: UHF, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser and ultraviolet treatment. Professional massage and exercise therapy, breathing exercises are also prescribed.
To prevent displacement and fractures of the vertebrae, it is necessary to lead an active but adequate lifestyle in terms of physical activity. It is useful to engage in light sports or recreational exercises, but limit heavy lifting and avoid intense exercise. If a person has concomitant diseases (for example, osteochondrosis or metabolic disorders) that cause spinal pathologies, it is necessary to compensate for them with timely treatment.
Causes of vertebral displacement
- At a young age, displacement of the vertebrae is often due to congenital weakness of their structures. It is usually observed in the lumbar spine and is accompanied by a distortion of the pelvic bones. This leads to curvature of the spine and pain, the inability to walk, run, sit and stand; leads to cramps, pain in the knee and hip joints, pain in the foot and toes.
- In old age, vertebral displacement often occurs due to age-related changes in the intervertebral joints. Usually it leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal, which is accompanied by pinched nerves and the development of paralysis.
- Also, displacement of the vertebrae can be caused by sudden movement or heavy load.
Causes and symptoms of thoracic spondylosis
Causes of spondylosis of the thoracic spine
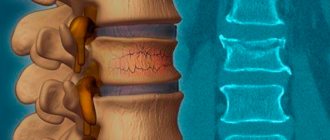
Age is the main cause of thoracic spondylosis. Most cases of spondylosis of the thoracic spine develop in people over 45 years of age. Due to the natural involutional process of aging, the discs in the spine begin to wear out and lose their strength and function. This can lead to rupture of the annulus fibrosus and the formation of disc herniations or protrusions. These degrading discs do not perform their shock-absorbing functions, which leads to excessive stress on joints, muscles, ligaments and back pain.
Types of vertebral displacement
- Displacement of the cervical vertebrae is more common, since the discs in this part of the spine are more mobile. The consequences of a displaced cervical vertebra are headaches, migraines, runny nose, insomnia, amnesia, and chronic fatigue.
- Displacement of the thoracic vertebrae is much less common. However, it is associated with the risk of developing peptic ulcers, gastritis, and pancreatitis.
- Displacement of the lumbar vertebrae is usually accompanied by a fracture of the articular process, and only after this does displacement of the vertebral disc occur. It can lead to lameness, weakness and pain in the legs, and the inability to move normally.
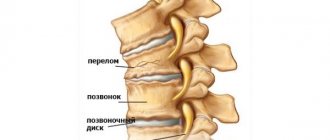
What is a thoracic spine fracture
Violation of the integrity of the vertebral structure can occur as a result of pathology, impact, or fall. Damage sometimes occurs as a result of a pinpoint blow of great force, a sharp and excessive extension or flexion of the spine. One or more vertebrae may be deformed.
Injuries to this section are equally common among women and men. Older people are prone to fractures due to osteoporosis. A feature of damage to the spinal column is the risk of complications, mainly when damage to muscle tissue, ligaments and cartilage is observed.