Good afternoon, my dears! Today we will touch on such a pressing problem today as training for scoliosis . Is it possible to go to the gym with scoliosis , and what are the specifics of training for a person who has such a problem? During my work as both an instructor of group programs and an online trainer, I periodically encounter the fact that a fairly large percentage of people have back problems, in particular scoliosis or osteochondrosis. Therefore, when creating individual training programs, I often have to work with such clients. I’ll say right away that training for scoliosis is not contraindicated, but you need to organize the training correctly so as not to harm your health in any way, since we come to the gym not only for a beautiful, toned body, but also for our health.
Let's first define what scoliosis is?
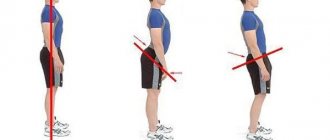
Scoliosis is a deviation of the spine from its vertical line, in simple words, curvature. A person with scoliosis has a curved spinal column, unlike a healthy person without scoliosis.
There are several types of scoliosis depending on where the curvature is located:
- lumbar and cervical lordosis;
- thoracic and sacrococcygeal kyphosis;
- flat back.
Healthy spine
Scoliosis
Now let's move on to the practical side of the issue and find out whether training is contraindicated for scoliosis, or is it still not worth writing yourself off so early?!
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a congenital or acquired curvature of the spine as a result of deviation of the vertebrae to the right or left relative to their axis. The disease often develops in children aged 6-15 years, and occurs as a result of improper posture. Despite this trend, the number of adults suffering from scoliosis today is predominant.
It is impossible to cure scoliosis without the direct participation of the person himself, since the disease does not respond to any medications or physiotherapeutic procedures. The only way out is to completely change your lifestyle, following the rules of healthy eating and physical activity. Leading orthopedists strongly recommend exercise therapy for scoliosis, including therapeutic massage, reflexology, yoga, physiotherapy and wearing special orthopedic corsets.
Restrictions on sports activities
For scoliosis, exercises are divided into three groups: necessary, limited and contraindicated. There is no clear answer to the question of whether it is possible to play sports with scoliosis. In each case of scoliosis, there are absolutely contraindicated exercises (for example, rhythmic gymnastics, boxing and other sports) and exercises that will not harm even if there is a 2nd degree curvature.
All exercises for a patient suffering from scoliosis are divided into 3 groups:
- exercises that should not be done with scoliosis;
- exercises that have limited contraindications (they can be performed, but only in certain quantities);
- exercises that are necessary for scoliosis (they help prevent further curvature of the spine, and sometimes completely get rid of scoliosis).
Thus, scoliotic postural disorders and sports are completely compatible concepts. The main thing is to consult a doctor to make a correct diagnosis, choose a course of treatment and receive recommendations regarding restrictions and contraindications.
Find out more about treating scoliosis with physical activity:
- The importance of preventing scoliosis in children at an early age
- Find out how to cure scoliosis in a child using therapeutic exercises on the page
- You can read about the causes of dysplastic scoliosis here
What exercises are contraindicated for scoliosis?
Did you know that...
Next fact
Drug treatment can affect pathological processes, but to a small extent. That is why the emphasis is on therapeutic exercises . Exercises contribute to, if not complete, then at least partial restoration of the normal configuration of the spinal column. In addition, they help strengthen the muscle corset, normalize the functioning of internal organs, and improve blood circulation.
Exercises for the treatment of scoliosis should be chosen by a doctor. There are exercises that can aggravate the curvature, so they are contraindicated :
- Run . Considered a relative contraindication. With rapidly progressing scoliosis and grade 3-4 scoliosis, running is prohibited, but with moderate and minor curvature of the spine, it is possible, but only with the permission of the doctor.
- Power training . Any exercises with a barbell and dumbbells increase the load on the spine several times. Particularly dangerous are exercises that are performed on one leg (standing, lunges to the side and forward with and without dumbbells). Such exercises negatively affect the configuration of an already curved pelvis, so they are prohibited.
- Somersaults . In terms of injury, they are too dangerous, even for a healthy spine. Performing somersaults with scoliosis increases the likelihood of injury several times.
- Jumping . Movements of this kind affect the intervertebral discs and vertebrae, increasing the load on them.
- Team sports (basketball, rugby, football, hockey). These sports are associated with uneven load on the spine, a high risk of injury and sudden movements. For the same reason, it is not recommended to snowboard and ice skate, play badminton and tennis.
- Acrobatics, gymnastics, any exercises for spine flexibility . Such exercises involve performing sudden and asymmetrical movements, which is strictly contraindicated for scoliosis.
- Exercises involving circular movements with turns and vertical axial load on the spinal column.
- Yoga . It is a relative contraindication, because Some poses do not have the best effect on the condition of the spine. One such pose is the lotus pose, in which the legs are turned out at the knee joints.
Video: “Harm from incorrect activities from scoliosis”
The effectiveness of exercise therapy
The success of treatment through exercise therapy depends solely on the stage of scoliosis. As practice shows, stages 1 and 2 are best treated, while to improve the condition of a patient with scoliosis at stages 3 and 4, you will have to resort to surgical treatment. The first case is characterized by complete recovery after just six months of regular and persistent physical therapy exercises.
Such therapeutic physical training will be effective only in the first 2 stages, while curvature of the spine is best treated before the age of 25. It is during this period that the most active development of tissues of the musculoskeletal system occurs. Of course, treatment also helps at an older age, but it may take much longer.
Additional prevention methods
What, in addition to an exercise program in the gym for scoliosis, can cure your back? For severe stages of scoliosis (fourth and fifth), surgical treatment is usually prescribed. In milder cases, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, and manual therapy can be effective. A neurologist can also prescribe you medications to improve local blood circulation and replenish essential vitamins. The fastest effect is observed if the problem is approached comprehensively.
Rules for conducting exercise therapy for scoliosis
Ideally, the first classes should be carried out under the supervision of an orthopedic specialist, which will allow you to develop the correct execution of each scoliosis exercise at home, which will be repeated daily for a certain time. When performing gymnastics on your own, it is important to follow the following rules:
- Before each lesson, a general warm-up is carried out to warm up all muscle groups;
- all exercises for curvature of the spine are performed at a calm pace, without jerky movements and jumps;
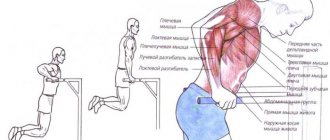
- Strength training with lifting dumbbells or barbells is contraindicated;
- It is prohibited to perform exercises using hanging on the crossbar, while stretching the spine is best done in a lying position;
- It is important to alternate exercises for different parts of the body, starting with training the legs and ending with the load on the shoulder girdle.
Before starting exercise therapy, you should definitely consult with a doctor who, based on a comprehensive examination, will be able to create an individual set of exercises for scoliosis to perform at home. In the event of a general deterioration in the patient’s well-being, physical therapy should be discontinued.
Exercises with dumbbells
People often wonder whether it is possible to do exercises with a barbell or dumbbells for scoliosis. After all, most basic workouts aimed at strengthening the muscles of the buttocks and legs contain similar exercises. The answer from experts is clear: exercises with dumbbells for scoliosis should absolutely not be done in the gym. This puts axial stress on the spine, worsening existing problems. What should those who want to pump up a beautiful and harmonious body do? You can always find an alternative in the gym. For example, instead of squats, you can use a crossover to move your leg back. And instead of lunges, do leg curls in the simulator.
Types of exercises
Regular exercises for scoliosis significantly speed up the recovery process, and at the same time prevent the progression of the disease. An important condition is a responsible attitude towards exercise therapy for the treatment of scoliosis on the part of the patient himself. All exercises for spinal scoliosis are divided into two groups.
- Symmetrical. The principle of performing such gymnastic exercises is to maintain a straight spine. With scoliosis, tension in the back muscles occurs with varying intensity, which is why maintaining the middle position of the vertebrae will help not only eliminate the curvature, but also strengthen the lagging muscles.
- Asymmetrical. In this case, the load moves to a separate area of the spine, which reduces deformation in the lateral plane. This set of exercises is compiled on an individual basis, so performing asymmetrical exercises without consulting a doctor is strictly contraindicated.
Since symmetrical loads are the simplest and safest, we will consider exercises for spinal scoliosis at home while keeping your back straight.
Types of necessary loads embodied in exercise therapy
Curvature of the spine, which is a pathology, leads to a redistribution of loads on the ligaments not in favor of the latter. In addition, the muscles that grow on our body in pairs receive completely different tension loads.
The side that is convex constantly suffers from muscle tone. The inability to relax for muscle tissue means only one thing - a gradual loss of tissue contractility.
The other side is constantly in a relaxed state, which in turn causes the development of atrophic processes, that is, the loss of the muscles’ ability to perform their functions.
Therefore, it is very important that all exercises aimed at combating scoliosis, carried out at home, fall into the following several categories.
Category 1. Asymmetrical exercises
These exercises allow you to train muscle tissue on only one side of the body. The opposite one remains unused.
Category 2. Symmetrical
These exercises help the muscles support the spine, since the load aimed at their development is distributed evenly, helping to equalize the tone on both sides.
Category 3. Detorsion
These exercises help reduce the load on constantly toned muscles, while simultaneously challenging the relaxed part of the body.
Category 4. General strengthening
This type of exercise is responsible for stimulating the immune system, helping the entire body strengthen and become stronger.
A set of exercise therapy exercises for scoliosis
Even with a slight curvature of the spine, it is recommended to consult a doctor regarding exercise therapy at home. At stages 1 and 2, physical therapy will help restore normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system, and thereby cure scoliosis. In later stages, such exercises for scoliosis can even harm the already curved spine.
On the stomach
After preparing the place for practice, we lie down on our stomach, stretch our arms in front of us, and at the same time bring our legs together. As you inhale, stretch your palms forward and move your feet back. Gently stretch the spine for 5 seconds, then slowly relax and repeat the exercise again.
Lying in the same position, bend your arms in front of you and lower your forehead onto your forearms. We take a deep breath, and, bending our knees, try to touch our heels to our buttocks. As we exhale, we gently move our legs toward the floor, but do not lower them completely.
After completing the previous exercise, we remain lying down with our head on our forearms. We bend our knees at a right angle, and alternately, while inhaling, raise our legs up. To avoid injury, we try to maintain the angle in the knee joints.
On the back
We lie down on a flat surface and bring our legs together, placing both hands at our sides. We take a deep breath and tighten the knee so that a right angle is formed between the thigh and the body. As you exhale, lower the limb and repeat the exercise with the other leg.
Lying on your back, we spread our arms to the sides, taking the “cross” position. As you inhale, slowly raise your arms above your chest and touch your palms to each other. We exhale smoothly and lower our limbs to the floor, after which we repeat the exercise several more times.
Without changing the position, we move the straight arm behind the head, while the second limb should be held next to the body. While inhaling deeply, we simultaneously change the position of our hands. Between movements we exhale briefly, after which we repeat the exercise while inhaling.
On knees
Get on all fours with your shoulders over your wrists and your hips perpendicular to your knees. We arch our back in the thoracic region and fix the position for a few seconds. After this, we bend in the opposite direction, using the lower back, and in the same way hold for a short time in this position. We perform deflections as smoothly as possible so as not to damage the joints.
Remaining in the same position, we take a few steps forward with our hands, after which we lower our stomach, pulling ourselves towards our hips and straightening our arms. We touch our forehead to the floor and try to relax our neck as much as possible. For maximum stretching, we forcefully pull our arms forward along the floor, and move our hips back, while keeping our back straight.
How to train clients with spinal hernias and excess weight?
We are being asked this question more and more often. It appears that the "first generation" of fitness enthusiasts have reached the age when degenerative changes in the spine begin to appear, and a legion of younger office workers are experiencing back problems with increasing frequency and at a younger age.
This topic is especially close to me, because... I work a lot personally with clients who have serious problems with the musculoskeletal system: restoration of motor skills after complex operations, advanced cases of scoliosis and osteochondrosis.
It is, of course, worth working with such clients. They need it even more than others. But the difficulty is that you won’t be able to work with them according to a template like with ordinary people. Here you need a 100% individual approach: exquisite work on the selection of exercises - all in order not to cause harm. And most often you work with them not within a specific type (strength, aerobics, Pilates, functional training, exercise equipment, etc.), but give exercises from literally any type, selecting what a given person needs at a particular moment depending on his condition, possibilities and limitations.
When planning to work with such clients, you should first find out the maximum information about the hernia: between which vertebrae, size, pain symptoms, how long ago it appeared, as a result, what was done to get out of the pain crisis, etc. This will allow us to formulate a general concept of the problem. Very often, back problems are attributed to an intervertebral hernia, and the cause of pain may be a reflex spasm of the deep back muscles (rotator muscles, multifidus muscles, etc.). Thus, the multifidus muscles surrounding the intervertebral joints are capable of “stopping” the spinal joints in a very unfavorable position, which will cause pain with subsequent inflammation of the joint itself, if the optimal range of motion is violated.
Excessive tension (contraction) of the intertransverse and interspinous muscles of the spine compresses the intervertebral disc, which causes severe pain and ultimately leads to the formation of a hernia. Moreover, muscles can be in a state of reflex spasm for a very long time - years and even decades.
It is assumed that the pathological process primarily occurs in the deep muscles of the back; it consists in excessive tension of these muscles, exceeding their working tension, which leads to a long-term reflex spasm of these muscles. A muscular blockade of the intervertebral disc develops, involving the spinal nerves and accompanying vessels in the pathological process. Compression of the spinal nerves leads to loss of sensitivity of organs and tissues, compression of blood vessels leads to swelling and pain.
Any hernia or protrusion of a disc (no rupture of the fibrous ring) is a destruction of the disc. If you remove the compression of the disc created by spasming muscles (this is done by chiropractors) in the presence of a hernia, then the disc will still not return to its original (healthy) state. Just like it is impossible to return toothpaste that has already been squeezed out into the tube.
If there is damage to the stabilizing ability of the disc and surrounding connective tissues - ligaments, capsules of intervertebral joints, damage to the fibrous ring, then sooner or later problems with the spine will arise.
Considering the problem with the presence of a hernia (and this is the main problem), when planning you should choose (especially at the beginning) the most gentle loads. This can be done by stretching, Pilates, and strength training in gentle positions.
The second problem is excess weight. It will greatly influence the spine when choosing body positions to perform exercises in training. Of course, you need to lose weight. It turns out to be a vicious circle: to lose weight, you need to move, and moving is extremely difficult due to the presence of a hernia. What to do? Pay attention to your diet - reducing the total number of calories. At the same time, you need to start training!
ON THE BACKGROUND OF SCOLIOSIS AND OSTEOCHONDROSIS IT IS NECESSARY:
- choose safe (for the back) starting positions in which it is possible to perform exercises (reducing gravitational loads when performing the exercise);
- take into account such characteristics of the exercise as purposefulness, amplitude, intensity, power, duration, mode;
- analyze the adequacy of the load to the client’s capabilities;
- Constantly monitor the client’s reaction to physical activity.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR EXERCISES:
- eliminate jerking movements;
- do not use hangs to stretch the lumbar spine;
- At the initial stage of training, use cardio exercises on an exercise bike with a semi-recumbent starting position of the body;
- perform exercises with dumbbells in a lying position (on your back, stomach - to eliminate vertical loads on the spine);
- perform exercises at a slow pace with a small amplitude.
In order to intelligently build a training process based on the client’s initial data, all of the above is not enough. It is necessary to find out the purpose of our training activities: to pump up and lose weight of the client, relieve pain and improve physical qualities, teach the “correct” to move without pain, etc. Any of these goals is good enough and will be a priority at different stages. So at the first stage it is important to implement the following tasks:
- restore control of muscle contraction;
- restore movement patterns;
- teach the neutral position of the spine;
- teach the spinal stabilization system.
Completing these tasks can take a very long time, but without solving them, all further training activities will be useless.
We have several seminars where you can learn how to work with such clients. There is a seminar called Fitness for Scoliosis and Osteochondrosis. Of course, the Pilates course. Additionally, it is very useful to use MFR - Myofascial Release. You can learn a lot about restoring functionality in the Functional Training course.
When training is useless
A coach cannot take on the role of a doctor. We are not omnipotent, and we should not think that by “pumping up” the back muscles, strengthening the abdominal muscles, osteopathy and massage, we can solve any problem with the spine. After a certain stage of degenerative changes in the spine, only surgery can help. We are very afraid of it, and, alas, this fear is often justified, since the probability of a successful outcome is too small. Fortunately, there are options. Unfortunately, they are very expensive. But if funds allow, we recommend considering this option - it can give you several decades of life with a high level of quality and normal motor activity. Here's a clear example of how this works.
Lumbar spine after reconstruction - 1
Lumbar spine after reconstruction – 2
The photographs show the lumbar region of one of our friends after surgery in Israel. The white elements are the titanium structure that now supports the reassembled back. The white stripes are artificial intervertebral discs that replaced dead ones. This is the back of an athlete who trained to the last “no matter what” until critical problems occurred. This is a very common case: a former athlete (34 years old at the time of surgery) playing a very tough contact sport (handball). For the last 15 years, problems with the lower back have been regular. And 3-5 years before the operation there is a classic vicious circle: attacks every 3-4 months, most often after competitive games. Usual Russian classical treatment: all types of pain relief, blockades, bed rest, “therapeutic massage”, etc. Between attacks there is constant severe pain in the back and leg down to the very bottom, lameness in one leg, numbness of the limb. But, as often happens with athletes, ignoring all this, continuing games, during which the symptoms cease to be noticed on adrenaline; Well, the “rest” regime for a few days after. But the next attack simply did not end: after actual immobilization for several days and in the absence of positive dynamics, a decision was made on surgical intervention. The lumbar region was “reassembled” again. As it turned out, 2 intervertebral discs were not just herniated, but were torn into several parts (this was not visible on numerous MRIs; or we are not able to decipher this). They were completely replaced with artificial ones; and a segment of 3 vertebrae was fastened with a titanium structure. According to the surgeons, all this was still supported by well-developed muscles, but at any moment it could end in disastrous paralysis if adequate measures were not taken. Well, if not, then the quality of life would become worse and worse. Now, 5 years after the operation, this man has fully recovered, and has long since returned to big-time sports - he plays for the national handball veterans team at the world level. After the operation, we trained this man in a recovery mode for several months before he returned to game training.
The conclusion from this story on our topic: the reserves and strength of the human body are enormous. A person can withstand extremely heavy physical activity even against the background of very serious problems with the musculoskeletal system. However, the instructor here must understand the medical fundamentals and be in touch with the doctor in order to be able not only to select an adequate load, but also to determine in time where training will no longer help (or even harm), and when it is necessary to engage in serious treatment.
PS: if anyone needs direct contacts of doctors and clinics, write to us directly using the feedback form.
Creation date: April 19, 2015
Exercises in the gym for scoliosis
One of the main reasons for the formation of lateral scoliosis is uneven development of the spinal muscles. That is why in the practice of treating spinal curvature, gymnastics for scoliosis is combined with symmetrical strength exercises. To strengthen your back muscles, the following training plan is recommended:
- warm-up in the form of moderate walking on an elliptical trainer;
- pull-ups in the gravitron;
- Bent-over rows with a rubber expander;
- crossover pullover with straight neck;
- forearm plank.
It is better to select the number of repetitions based on your own feelings, so that you do not feel failure during the last repetitions. In this case, the purpose of the scoliosis exercise is not to pump up the muscles, but to strengthen the muscles to support the spine.
Features of the disease and statistics
Disorders in the structure of the spine are diagnosed in approximately 30% of the population. In the early stages, especially in children under 15 years of age, scoliosis can be successfully corrected with the help of exercise therapy.
The following signs indicate a possible curvature of the spine:
- pain when taking a deep or sharp breath;
- frequent dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- digestive problems;
- diseases of internal organs;
- frequent nausea;
- decreased activity, weakness.
In children, the disease may be accompanied by nervousness, absent-mindedness, loss of appetite, lethargy and forgetfulness, and problems with school performance.
Pathology can be caused by:
- congenital and genetic abnormalities;
- injuries;
- previous illnesses accompanied by prolonged bed rest;
- deformities of the lower extremities;
- osteochondrosis (including in children);
- rickets;
- poor posture when sitting or walking;
- physical inactivity.
In the younger generation, curvature of the spine usually occurs due to bad habits: incorrect sitting posture, carrying luggage on one shoulder.
Victory over scoliosis is quite possible, especially if the disease is diagnosed at the beginning of its development. However, for this you need to fully comply with all medical prescriptions: devote the required amount of time to exercise therapy, not refuse physiotherapeutic procedures, and take prescribed medications.
Exercises to prevent scoliosis
Scoliotic disease often manifests itself in adolescent children, since it is at this time that the most active formation of the spine occurs. To prevent scoliosis, orthopedists recommend performing the following exercises at home:
- Squats. Holding the bar with both hands, the child needs to place his feet at shoulder distance, then, keeping his back straight, lower himself into a deep squat and return to the starting position without delay.
- Lying leg raises. Positioned not far from the wall bars, the child lies on his back and grasps the lower bar with outstretched arms. As you exhale, he raises his legs so that his toes can touch the middle crossbar, and with an inhalation he returns to the starting position.
Such exercises will help to form a strong muscular frame for the child, and thereby prevent the development of scoliosis.
Scoliosis – a disease of the 21st century
According to official medical statistics, there are about 50 million people worldwide who suffer from scoliosis. Every sixth person on the planet has a deviation of the spinal column from the vertical axis. Scoliosis is not a fatal disease, but it can bring a lot of trouble to the patient. What does spinal curvature lead to?
- neurological disorders;
- digestive tract disorders;
- paralysis;
- loss of sensation in the body;
- pain in the back and head;
- muscle spasm.
Scoliosis is acquired only in childhood. A sedentary lifestyle, studying at school and an incorrect position at a desk lead to curvature of bone structures. The diagnosis of “first degree scoliosis” is made if the deviation from the vertical is 5 - 7 degrees. This is considered normal and cannot be treated. But if the deviation reaches 14 degrees or higher, then the patient should consult a doctor to prescribe treatment. As preventive measures, the patient is recommended massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as strengthening the muscle corset.
The effectiveness of exercises for the treatment of scoliosis
Only a doctor should determine what types of exercises a patient needs. Before this, a complete diagnosis is necessary, and not just a visual inspection. Due to incorrectly prescribed gymnastics, the child’s condition can only worsen.
Correctly selected back exercises for scoliosis almost immediately reduce headaches, nausea and weakness, and reduce fatigue. This is facilitated by normalizing blood flow and saturating the brain with oxygen. The most effective are regular exercises of sufficient duration.
Corrective exercises help correct pathological curvature of the spine. Symmetrical exercises help strengthen weakened muscles and at the same time reduce the tone of overly tense muscles. Asymmetrical exercises reduce the curvature of the spinal column, returning it to its normal position. Detorsion exercises help align the position of the vertebrae, stretch and relax overly compressed muscles, and strengthen overstretched, weakened muscles.
By performing therapeutic exercises, the muscle corset is gradually strengthened and the shape of the spine is normalized, which allows you to correct your posture. The functioning of the ligamentous apparatus improves, mobility and endurance increase, and freedom of movement returns to the child.