Surgery to remove a spinal hernia is associated with many risks, so it is prescribed only as a last resort, when drug treatment has proven ineffective, and the hernia affects nearby tissues, which leads to the development of serious complications.
Indications for surgical intervention are the following situations:
- strangulated hernia;
- acute inflammation of the hernial sac or surrounding tissues, regardless of the cause;
- severe compression of the spinal cord herniation, which threatens the patient with partial or even complete paralysis.
Preparation for surgery to remove a spinal hernia, accordingly, first of all includes the diagnosis of these conditions, which are an indication for surgical intervention.
CLINIC EXPERTS
- Konovalov Nikolay
Make an appointment
Konovalov Nikolay Leading spinal neurosurgeon, spinal surgery, combined treatment of tumors of the spine and spinal cord
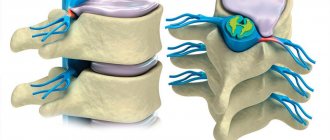
Intervertebral disc herniation is one of the most common pathologies of the spine, leading to rupture of the fibrous ring due to displacement of the nucleus pulposus. According to statistics, every hundredth person on our planet suffers from this disease. People in the age group 25-50 years old who have sedentary work or regular heavy physical activity are at risk. If not treated in a timely manner, intervertebral hernias quite often become the cause of a certain degree of disability in the musculoskeletal system, up to the complete impossibility of independent movement. Therefore, early diagnosis and the correct therapeutic course determine the effectiveness of medical care. The quality of treatment is also influenced by the qualifications of the surgeon, since spinal surgeries are considered one of the most difficult, and without them, the patient’s full recovery (especially in the later stages of the pathological process) is almost impossible.
Depending on the location on the spine, hernias are distinguished:
- The lumbosacral region is the most common;
- Cervical spine - much less common;
- The thoracic region is the rarest type.
To treat spinal hernia, the clinic uses various invasive and non-invasive techniques, applied in accordance with international protocols. To select a specific method, it is necessary to conduct a full examination of the patient followed by a risk assessment in each case.
Microsurgical hernia removal: how is this spinal surgery performed?
Microsurgical removal of a spinal hernia (microdisectomy) is performed under general anesthesia. After X-ray marking, which allows you to most accurately determine the area of localization of the hernia, the neurosurgeon makes an incision of up to 3 cm in the skin and, also under X-ray navigation, installs a special gentle retractor in the projection of the location of the intervertebral hernia or stenosis.
Surgery is performed using magnifying optics and micro-instruments, which allows you to carefully bypass muscles, ligaments and spinal nerves without damaging them. The hernia is removed with micronippers, and after the intervention the wound is sutured. The duration of the operation is 30–90 minutes.
Indications for surgery
Choosing a treatment strategy for a herniated disc is the most important and most difficult issue for the attending physician. To date, the list of indications for surgery has not been fully formed, so each patient with a suspected hernia requires an individual approach.
The medical community has established three conditions in which it is necessary to perform surgery to remove a herniated disc:
- presence of cauda equina syndrome;
- paralysis and paresis of the limbs or other neurological diseases in the stage of rapid progression;
- the presence of ischialgic syndrome that is not amenable to drug treatment for more than 3 months.
The second no less important and very difficult issue for spinal hernias is the determination of contraindications to surgical treatment. So, at the moment, surgery is not recommended for:
- the patient has ischialgic syndrome along with severe, ongoing back pain (in this case, surgical intervention is highly likely to have no positive effect);
- conservative treatment was not carried out or was not completed;
- the surgeon who will perform the operation does not have complete diagnostic information on the patient and his problem.
Surgical removal of a herniated disc is a complex invasive procedure, the cost of which depends on the stage of the disease, the extent of the intervention and the type of operation chosen according to the indications. On average, the price of a minimally invasive operation to remove a herniated disc is in the range of 150,000-200,000 rubles.
Spinal hernia. Types of surgical treatment of hernias
A spinal or intervertebral disc herniation is a rupture of the fibrous ring of the disc and protrusion of the gelatinous substance. The intervertebral disc is a layer of cartilage that connects the vertebrae and ensures their mobility. It consists of a dense membrane (fibrous ring) filled with a whitish-transparent gelatinous mass. And it is the rupture or weakening of the walls of the membrane and the spread of its contents beyond the ring that is a hernia of the spine, the treatment of which is a rather lengthy process and not always pleasant, but if all the doctor’s instructions are carefully followed, it is quite possible.
As practice has shown, most often intervertebral hernias occur in the lumbosacral segment of the spine; somewhat less frequently, this disease affects the cervical part of the back, and even less often the thoracic part. Typically, the majority of patients successfully get rid of a spinal hernia with conservative treatment after completing a course of non-surgical procedures and taking medications.
And only if gentle treatment turns out to be ineffective or leads to a deterioration of the patient’s condition, a decision is made on surgical intervention. In any case, surgery is considered a last resort and in domestic practice is used in no more than 10% of cases of disease. While abroad (America, Germany) more frequent removal of intervertebral hernia is practiced and the cost of the operation is quite affordable for a wide range of the population.
Main manifestations of vertebral hernias
The main manifestation of a spinal hernia is pain. It also includes other symptoms, which mainly depend on the location of the disease. For example, the formation of a hernia in the lumbar and sacral region will be characterized by lumbodynia (pain in the lower back), radiating to the gluteal muscle and the back of the thigh (ischalgia). Treatment of lumbodynia is necessary to eliminate the feeling of weakness and sensory disturbances in the lower extremities (numbness, tingling), difficulties in the functioning of the internal organs of the pelvis (genitourinary system, intestines, rectum).
The formation of hernias in the thoracic part of the back is accompanied by pain in the sternum, which intensifies with prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position and the development of spinal diseases such as scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis.
Clinical symptoms of cervical intervertebral disc degeneration are characterized by pain at the site of localization, radiating to the shoulder and arms, numbness, tingling and a feeling of coldness in the phalanges of the fingers. There are also frequent surges in blood pressure, accompanied by headaches, dizziness and poor health.
Diagnosis and treatment
A spinal hernia can be determined using X-rays, and magnetic resonance imaging can diagnose it more accurately. If necessary, the patient may be prescribed other non-invasive studies (MR or CT myelography).
Typically, pain and other manifestations of the disease subside after 3-4 months, after which a period of chronic disease begins (remission) and surgical intervention is not required.
Non-surgical treatment of intervertebral hernia consists of prescribing painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. The use of so-called spinal blockades (injection of analgesic substances directly into the site of pain) has shown excellent results. In parallel with drug treatment, courses of physical therapy, massage, swimming and manual therapy sessions are prescribed. Of great importance in treatment are the internal strengths of the patient’s body, his perseverance, mood and desire to recover.
Surgical intervention for spinal hernia
As mentioned above, in the treatment of this disease, surgery is prescribed only in extreme cases. For example, when neurological disorders rapidly develop or the pain syndrome is not relieved by medications.
Surgical intervention is also necessary when the so-called “cauda equina” (a bundle of spinal nerve roots passing through the lumbar, sacral and coccygeal spine) is pinched. As a result of this compression, severe pain spreads throughout the lower back and buttocks, moves to the lower abdomen, intensifies even with minor reflex movements (coughing, sneezing), urinary and fecal continence is impaired, and potency deteriorates.
Of course, the operation gives a quick effect and relief from annoying symptoms, but it is always associated with a certain risk: to gain access to a certain segment of the spine, you have to make a fairly large burr hole, cut the muscles and ligaments that support the spine, and all these actions are complicated by the possibility of damage to the spinal column. brain, adjacent nerve endings and blood vessels.
Types of surgical treatment for spinal hernia
Until recently, surgery for herniated intervertebral discs was performed using the classical method of laminectomy. But this technique had serious drawbacks - quite large damage to the skin and muscle tissue, a long period of recovery of the body and some likelihood of developing other spinal diseases (scoliosis, kyphosis, osteochondrosis, etc.).
The first breakthrough in spine surgery was the invention of a special microscope, which made it possible to carry out intralaminar microsurgical access to the pathological area and reduce trauma during surgery. To date, this method of intervention is considered the most optimal.
Further development of medical technologies and optics, reduction in the size of surgical instruments made it possible to use microsurgical and endoscopic methods of intervention more widely, and thereby make the operation even safer. The latest techniques suggest removing and treating vertebral hernias using a laser. The cost of such procedures is quite high, but the results are not always impressive. This is due to the difficulties of controlling the beam generated by the laser and the likelihood of damage to other internal organs.
Microsurgery. Removal of herniated intervertebral discs using the microsurgical method (microdiscectomy) is recognized today as the most gentle. This neurosurgical intervention is performed under high magnification of the same microscope or operating loupe, which allows the surgeon to more accurately perform manipulations in the spinal canal and minimize the likelihood of traumatic damage to nerve clusters.
Microsurgical hernia removal allows you to operate and remove protrusions of any location and varying degrees of density. The procedure itself is performed under general anesthesia and usually the trepanation incision is only 3-5 cm. After a day, the patient is activated (allowed to stand up and move independently), and after a week is discharged from the hospital. After about two weeks, a person who has undergone spinal surgery will be able to begin simple, non-physical work. After about a month, you can move on to physical activity, but in a gentle manner.
After leaving the hospital, doctors strongly recommend limiting the time spent in a sedentary state for a certain period. And if necessary, they may prescribe wearing a special rigid or semi-rigid orthopedic corset for 1.5-2 months to maintain posture. Of course, after such measures, the muscular belt of the back will noticeably weaken, and it will need to be restored through exercise therapy, massages and other physiotherapeutic measures prescribed by the doctor.
Endoscopy. This is one of the newest and most promising techniques for operating on a spinal hernia, but like everything new, it is invariably subject to criticism and testing. The main advantage of the endoscopic method of surgery is the minimal entrance hole (from 1 cm to 2.5 cm), but there are some restrictions on the location of hernial protrusions. After such an intervention, the patient becomes active on the same day as the operation, is discharged from the hospital within 3-4 days, and within a week can begin to work and recovers quite quickly.
If you are worried about chronic pain in the back, in the occipital part of the head, sudden jumps in blood pressure have become more frequent, or you have noticed a gradual limitation in the motor ability of the spine - do not suffer and do not self-medicate, consult a specialist.
The spine treatment center in Moscow or Dr. Bobyr's clinic in Zelenograd will provide you with a full range of diagnostic procedures, consultation with highly qualified doctors, proper non-surgical and surgical treatment, as well as a full range of restorative physiotherapy procedures.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Types of operations to remove intervertebral hernia
If it is necessary to remove a spinal hernia, 2 main types of operations can be performed - radical surgical and minimally invasive laser. The choice of a specific procedure depends on diagnostic data, individual patient preferences, risk assessment and the planned positive effect.
Thus, the first group includes such radical operations as discectomy and laminectomy. The peculiarity of these methods of surgical intervention is that they are used for complicated hernia, when the pathological process affects the intervertebral disc itself. In this case, both the hernia itself and the affected disc must be removed, in place of which an implant is subsequently installed.
Methods from the second group belong to minimally invasive treatment methods, and their action is based on the use of laser technology. Such operations are used and give a positive effect only in case of a true hernia, when the pathological process has not yet affected the core of the intervertebral disc. The essence of the method is quite simple: using a laser, through a small puncture, the intervertebral disc is irradiated in order to dehydrate it. The so-called “draining” of the disc is necessary to reduce its size and, as a result, relieve pressure on the nerve roots, which leads to relief from pain. Laser treatment is a minimally invasive procedure, has no negative consequences and is completely safe for the patient.
Treatment methods for spinal hernia are quite varied. Each of them has its own pros, cons and indications for use. But whatever type of operation is chosen, the final result largely depends on the competence and professionalism of the operating surgeon. Our clinic offers its patients to choose a surgeon from leading specialists in Israel and Europe who have extensive international experience in the treatment and removal of intervertebral disc herniations of various locations.
The rehabilitation time after hernia removal is individual, depending on the neurological deficit. In the postoperative period, therapeutic work is also carried out aimed at preventing adhesions, which reduces the likelihood of relapse.
Laser irradiation
A modern technique that involves the use of laser exposure. This is the latest approach to repairing a hernia, which is carried out in three stages:
- Introduction of a light guide into the spine.
- Heating tissues that have been bulged.
- Evaporation of liquid, which triggers the spine’s own regeneration processes.
This effect helps eliminate the problem without harming the intervertebral disc. Recovery is quite long, pain can be felt for months after surgery, decreasing gradually. For rehabilitation, it is very important to perform physical therapy exercises.
Recovery after surgery
After removal of the herniated disc, the patient will need some time to return to his normal life.
This may take from 6 to 12 months, provided that the person operated on adheres to all recommendations and regularly visits the doctor for examinations. During the recovery period it is recommended:
- do not take a bath until the stitches are removed and the wound is completely healed after hernia surgery;
- use a waterproof patch during other water procedures;
- choose smooth and careful movements;
- give preference to poses and positions that do not load the back or carry minimal load;
- do not lift things weighing more than 5 kilograms in the first 2 months after surgery;
- start driving for short trips no earlier than 2 weeks after surgery, for long distances - after 2 months.
To speed up the recovery process and maintain muscle tone, it is also recommended to engage in physical activities such as:
- cycling on roads without bumps and potholes;
- swimming;
- fitness without sudden bends and turns;
- race walking.
It is better to start practicing more labor-intensive sports (alpine skiing, hockey, football, tennis and others) no earlier than 1 year after surgery to remove a spinal hernia, and only after consultation with your doctor.
The Medis Clinic offers its clients treatment for herniated discs at reasonable prices and at any stage of the pathological process. We cooperate with the best doctors from Israel and Europe and work using modern world methods. You can calculate the cost of all procedures necessary for treatment even without visiting our clinic. To do this, you need to send all available diagnostic reports and medical records to our email address, and we will be able to create an individual treatment plan based on your preferences and budget.
Endoscopic removal
This technique uses fiber optic equipment, which allows the surgeon to perform movements with maximum precision and control of the technique with high-resolution images. The tissues are minimally injured, due to which the pathology is eliminated effectively, and the recovery process is not complicated by a full-scale intervention.
To provide access, a small incision is made in the back area. The patient can walk normally within a day after the intervention, the risk of complications is minimal.
Special preparation
Any activities at the stage of preparing a patient for surgery are divided into mandatory (uniform for each operation) and special , which are performed exclusively in preparation for certain operations. Interventions to correct scoliosis, for example, include:
- X-ray examination of the thoracolumbar spine in direct and lateral projections;
- MRI or CT scan of the thoracic, lumbar and cervical spine;
- X-ray of the thoracolumbar spine in a direct projection, tilted to the right and left sides
Height and weight measurements are required!
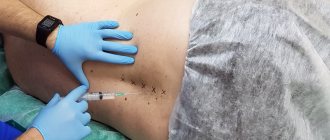
Percutaneous operations (by puncturing the skin) – “outpatient” neurosurgery
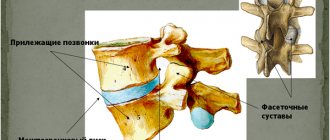
1. Radiofrequency denervation of the facet joints. It is used for facet syndrome (when the source of pain is altered intervertebral joints), special needles under image intensifier control (mobile X-ray unit) are installed in the area of the joints, through which radiofrequency effects are applied to the nerves of the affected joints. This eliminates pain.
2. Percutaneous puncture removal of disc herniation. The intervertebral disc is punctured with a special needle under image intensifier control, then its central part (nucleus pulposus) is removed using the following techniques:
- Percutaneous cold plasma nucleoplasty - evaporation under the influence of cold plasma.
- Hydrodisectomy – crushing and removal, high-speed fluid flow (900 km/h).
- Spiral nucleotomy is the introduction of a thin needle spiral, which makes rotational movements to remove part of the nucleus pulposus.
- Laser vaporization - removal occurs by exposure to a laser.
- Chemonnucleolysis - a special substance is introduced, leading to liquefaction of the nucleus pulposus and a decrease in its volume.
3. Vertebroplasty. Hemangioma, pathological fractures of the vertebral bodies impair the strength and stability of the spine, the geometry of the vertebra is disrupted, which can lead to damage to the spinal cord. The technique of execution is under image intensifier control, a thin tube with a guide, the vertebral body is punctured and filled with special cement.
3. Kyphoplasty. This is a similar procedure, but it allows not only to restore the strength of the vertebra, but also to compensate for its deformation, leading to a curvature of the spine that requires correction. Technique: under image intensifier control, special chambers are inserted into the body of the damaged vertebra through 2 hollow needles, which are then inflated. The pressure in the chambers is strictly controlled so that as a result the vertebra takes the required height without distortions (this is why two inflatable chambers are used). After the required position is restored, the chambers are removed and to fix the vertebra, the cavities in which the chambers were located are filled with cement.
4. Regeneration of intervertebral disc tissue. After removing the nucleus pulposus, part of the material is sent to a special laboratory, where normal cartilage cells are isolated and cultured (reproduction). Subsequently, the grown tissue is implanted into the intervertebral disc of interest using the percutaneous puncture method.
Advantages and disadvantages of the endoscopic method
Taking into account the correct selection of patients for this operation, in skillful hands the intervention is almost completely devoid of disadvantages compared to traditional microsurgical methods.
- Endoscopically, there is no destruction of the facet joint;
- The muscles are not crossed or destroyed, the wound channel is tiny, which does not cause local postoperative pain and, accordingly, does not require the prescription of narcotic analgesics;
- Given the minimal trauma, the risk of wound infectious complications is significantly reduced and long-term use of antibiotics is not required;
- Allows you to rise to your feet on the day of surgery;
- Early discharge from hospital, quick return to work.
Increasing the patient's body resistance
Timely care for strengthening the patient’s immunity contributes to better wound healing and rapid recovery of the body. Approximately a few weeks before the planned surgical intervention, the patient needs to start taking a vitamin complex, while giving up alcoholic beverages. Seriously ill patients may be prescribed anabolic hormones, plasma, blood or albumin transfusions.