Author, editor and medical expert – Yulia Yuryevna Muraeva.
Number of views: 48 531
Last updated date: 08/26/2021
Average reading time: 9 minutes
The number of surgical interventions is growing1, and surgical techniques and pain management techniques are being improved. However, postoperative pain remains an expected phenomenon and still requires the attention of doctors. Intense pain syndrome, which is observed in at least 40% of patients1, aggravates the recovery period, contributes to the development of complications2, increases recovery time, and can become a chronic process3.
The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) adopted a declaration in 2010 that recognized adequate pain treatment as a fundamental human right3.
According to large studies4, high intensity of postoperative pain is noted by patients after obstetric, gynecological, orthopedic and abdominal (on the abdominal organs) surgical interventions, which are associated with postoperative pain in the abdomen, chest, and joints. The characteristics of pain on the first day are very important; it determines how the pain syndrome will develop in the future and whether it will become chronic4.
Up to contents
Causes of pain in the shoulder joints
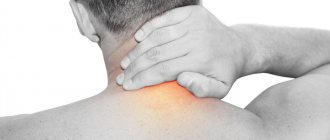
There are many reasons for the appearance of painful sensations. Pain in one or both shoulders can be a consequence of inflammation of the tendons, microtrauma of the articular cartilage, inflammatory-degenerative pathologies of the joints and cervicothoracic spine. The discomfort can be either minor or so intense that you cannot move your arm.
Among the causes that cause sharp or aching pain in the shoulder are:
- one-sided intense load for a long time;
- scoliosis, lordosis and other deviations in the normal position of the spine;
- physical inactivity.
In addition, pain can occur due to infections, inflammatory processes, hereditary predisposition, diseases of internal organs, and tumors.
In cases where the right shoulder hurts, the following pathologies may be present:
- Tendonitis is inflammation of tendons and soft tissues due to significant physical activity.
- Myositis - when the muscles of the shoulder joint are involved in the inflammatory process.
- Arthrosis is the destruction of articular cartilage.
- Arthritis is an inflammatory process in a joint due to infection, allergic reaction or autoimmune diseases.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Bursitis is an inflammation of the joint capsule.
- Capsulitis is a pathological change affecting the joint capsule and synovium.
- Brachial nerve neuritis.
- Tuberculous lesion of the joint on the right.
- Humeroscapular periarthritis.
- Metastasis from a nearby tumor.
- Chondrosarcoma.
- Right-sided pneumonia.
Pain in the left shoulder joint is much less common, especially if the person is right-handed. Still, the load on the left hand is significantly less compared to the right. When your left shoulder hurts, the reasons may be the following:
- sprain;
- biceps tendinitis;
- intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine;
- calcification in the tendon;
- angina pectoris or myocardial infarction.
There are cases when the shoulder hurts when raising your arm. Here we can talk about pathologies such as:
- joint injuries;
- rheumatic lesion;
- rotator cuff tendinitis;
- tenosynovitis;
- tendobursitis and bursitis;
- myositis;
- hernia of the cervical spine.
The appearance of pain in the shoulder when trying to move the arm back indicates the presence of bursitis, radiculitis, tendinitis, spinal overload, arthrosis-arthritic joint damage, myocardial infarction.
Shoulder joint diseases
Although shoulder pain is not uncommon, most patients do not immediately receive proper and effective treatment. In most cases, this is due to diagnostic difficulties. There are quite a few causes of pain, and it is usually not possible to make a correct diagnosis right away.
We list all the main reasons in descending order of their likelihood.
Humeroscapular periarthritis
Almost half of patients with pain in the shoulder joint are diagnosed with glenohumeral periarthritis (or adhesive capsulitis).
If you develop adhesive capsulitis, it becomes difficult to perform everyday activities, such as reaching behind your back, reaching into a sleeve, or combing your hair, due to limited movement and pain.
The essence of the disease is damage to the tissues around the shoulder joint; the joint itself is usually not affected. This disease develops after unprepared movement, often after sleeping in an uncomfortable position, and is manifested by limited movement in the shoulder joint. Symptoms usually appear gradually, usually after sleep or some time after a minor injury.
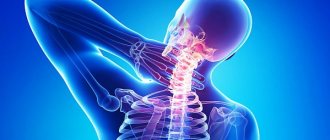
Diseases of the cervical spine
In second place we have intervertebral hernias and osteophytes (bone growths) that compress the nerve roots.
Read also: Protrusion and hernia of the spine. What it is?
In such cases, not only the shoulder joint area hurts, but the entire arm. The pain is usually described as a “lumbago”. Tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand may occur.
Symptoms usually appear suddenly. In this case, although movements bring pain, the patient is practically not limited in the shoulder joint. Most often, this is the cause of joint pain in those who work in a forced position (for example, hairdressers, dentists).
Arthrosis
The next most common cause of joint pain is arthrosis. In fact, it is not the shoulder joint that suffers most often, but the acromiocleidoid joint. However, pain may still be felt in the shoulder joint area. Arthrosis develops gradually over several months and even years.
The pain usually occurs with movement and intensifies in the morning. Sometimes when moving you can hear a crunching sound in the joint.
Arthrosis usually occurs in those who have been loading the shoulder joint for many years: athletes, builders.
Arthritis and other diseases
More rare causes of pain include arthritis - inflammatory lesions of the joints.
In these cases, the body temperature usually rises, and the joints may become swollen and red. Almost always, not only the shoulder joints are affected, but also other joints.
Such joint changes occur in rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and infectious diseases.
Don't forget about other causes of pain. For example, pain from internal organs can radiate to the shoulder joint area - with inflammation of the gallbladder, some gynecological diseases (adnexitis).
Survey
As you can see, there are quite a few reasons for pain in the joint area, and you should not delay visiting a doctor. Often, to establish a diagnosis, you not only have to visit several different specialists (for example, a traumatologist, neurologist, rheumatologist, surgeon), but also undergo a fairly thorough examination. Blood tests, x-rays, and magnetic resonance imaging of the joint and cervical spine may be needed.
Symptoms of the disease
Shoulder pain manifests itself in different ways depending on the cause. Acute is typical in case of injury. When a bruise, dislocation or sprain occurs, the patient experiences discomfort that increases when moving the upper limb. When a fracture occurs, it becomes impossible to move the arm.
Unbearable pain radiating to the neck and upper back is observed with capsulitis. In addition to pain, there is an inability to move the arm back or raise it. Severe pain also occurs with brachial neuritis and arthritis. The first is characterized by the absence of signs of inflammation in the joint; in the second case, swelling of the soft tissues and limited range of motion are noticeable.
Aching pain in the shoulder may be a sign of osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine. Often the symptom is accompanied by numbness of the hand, burning and tingling sensation in the fingers. Aching pain is also observed with deforming arthrosis, but in this case, along with discomfort, a person notes stiffness of movement and swelling in the shoulder joint in the morning, crunching and clicking when bending/extending the arm. With the gradual destruction of cartilage, lifting heavy objects or active movement provokes increased pain.
Constant pain for several weeks is characteristic of bursitis, when the inflammatory process develops in the periarticular bursa. The disease is accompanied by the formation of a compaction, upon pressing on which a fluid transfusion is felt.
Ointments and osteochondrosis, what to choose?
How does the ointment work?
We cannot always use the usual medications to cope with the symptoms of osteochondrosis, then ointments come to the rescue. Being used externally and having a fairly soft structure, they work only on the upper layers of the skin, covering the sore spot with the thinnest layer. Despite the tight fit, the mentioned compositions cannot be absorbed by the skin. Some ointments can penetrate into the deepest layers through the sebaceous glands and sweat ducts - their action is penetrating, because they carry the substance throughout the body.
How to classify ointments?
The effects of each ointment are different, as is the active ingredient. You can try to classify them:
- Preventing inflammatory processes. Non-steroidal ointments are based on suppressing the production of histamine, which is a catalyst for inflammation;
- Absorbing action. Used for bruises and bruises;
- Decongestants. Improves kidney function, due to which the body speeds up the process of cleansing itself;
- Warming effect. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a very painful disease, and the substances included in the composition will improve blood circulation and the regenerative properties of the body;
Such products often contain active ingredients (Finalgom, Voltaren, Chondroxide).
Very often, doctors prescribe these ointments, because they are a universal remedy for pain that is caused not only by osteochondrosis of the neck, but also by diseases associated with the musculoskeletal system. The actions of ointments are different:
- They can be antispasmodics;
- Relieve pain,
- Have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- Promote regeneration and relieve swelling.
What kind of medicines are there?
In the treatment of osteochondrosis, painkillers with a warming effect are often used, which improves blood flow in the area of the disease - the “non-steroidal” group.
Let's look at existing ointments to understand which one is right for you:
- An ointment containing nimesulide. This substance is the main active agent here, helping not only to relieve pain, but also to remove swelling in any part of the spine. Nise and Nimesil have a similar effect.
- Adding declofenac will also reduce the pain effect, but will cope with it an order of magnitude faster. Compositions based on declofenac sodium are a simple and quick remedy for suppressing pain in the cervical spine due to this pathology.
- The family of ointments that include ibuprofen comes to the fore due to an additional property. In addition to pain relief, they are able to almost completely remove possible atrophic consequences in the area of the disease.
But, if the main cause that worries you is not pain, but inflammation, then the substances should remove it and reduce the body’s reaction - severe complications that can follow osteochondrosis. Such as rheumatism or neuralgia. Artrosan and Voltaren will have a similar effect.
The group of warming ointments that help improve blood circulation includes Menovazin and Capsicam. Care should be taken when using these products - apply only to the required area, as there is a possibility of developing hyperemia.
Anti-inflammatory compounds
These include:
- Having “indomethacin”;
- With "ortofen".
The effect of indomethacin on the body regarding inflammatory processes is much higher than other ointments. It quite strongly resembles an antihistamine substance, so that the action is corresponding - when applied to the skin, it reduces inflammation.
Indomethacin is capable of producing anesthesia of the area to which it was applied. It is very similar in action to ibuprofen, also making it possible to recover or prevent the development of atrophic processes.
Ortofen belongs to the group of “non-steroidal” origin and can also help with edema in getting rid of inflammatory processes.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Diagnosis of pathology
Naturally, when there is discomfort, the question inevitably arises: what to do if your shoulder hurts? Don't wait for the symptoms to go away on their own. It is imperative to consult a doctor, whose specialization will depend on the cause of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
If the pain appears after a fall or bruise, then contact a traumatologist. Osteochondrosis and neuritis are treated by a neurologist, a surgeon and a rheumatologist eliminate the consequences of arthrosis, arthritis and tendonitis.
When painful sensations are accompanied by a general deterioration in well-being, it is recommended to consult a therapist, oncologist, cardiologist or gastroenterologist. Indeed, sometimes pain is reflected when there is a discrepancy between the localization of discomfort and the location of damaged organs or tissues. It is very important to diagnose in time, because shoulder pain can appear due to myocardial infarction, pneumonia, pleurisy, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and neoplasms in the chest.
For diagnostic purposes, the doctor may prescribe the following types of examinations:
- X-ray of the shoulder or entire upper limb;
- Ultrasound of the shoulder joint;
- MRI of the joint and/or spine;
- ECG.
In addition, you may need to take a general blood test, as well as biochemistry and sexually transmitted infections. The patient is also prescribed fluorography and fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Types of pain
Shoulders most often begin to hurt due to overload. By strenuously playing sports and lifting weights, we provoke the appearance of pain. It can be a symptom of various diseases. Let's look at what diseases cause what type of shoulder pain.
Acute
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine . The pain radiates to the arm and intensifies when turning the head. They get worse at night and become unbearable. In advanced cases, a person does not raise his hand.
Arthritis is inflammation of a joint. With arthritis, the right or left shoulder hurts a lot.
Arthrosis is a common cause of acute pain in the shoulder joint. More common in older people. It is painful for a person to raise his arm and perform another movement. Arthrosis can be caused by bruises, dislocations, fractures, and sprains.
Brachial nerve neuritis . It is caused by inflammatory processes, tumors, and injuries. A person suddenly feels a sharp pain in the shoulder joint.
Tendobursitis is inflammation of the joint capsule. It is caused by deposits of calcium salts. Tenobursitis is characterized by acute pain throughout the entire arm from the neck to the fingertips. It is difficult for the patient to move his arm.
Damage to the rotator cuff . The disease is caused by non-standard hand movements - for example, painting the ceiling. The day after painting work, a person may feel a sharp pain in the shoulder.
Capsulitis of the shoulder joint . The disease causes stiffness in the muscles of the shoulder girdle. A person has severe pain in his right or left shoulder, he cannot freely raise his arm up, move it to the side or put it behind his back.
Shoulder injuries - fractures, sprains, dislocations. Injuries must be treated, otherwise they will lead to permanent impairment of shoulder function and become chronic.
Chronic
Tendinitis . This is an inflammation of the tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. Tendonitis is usually caused by overuse. During heavy physical work, the tendons rub against the surface of the joint. This causes chronic aching pain.
Biceps tendinitis . This is an inflammation of the tendon of the muscle on the inside of the shoulder. A person constantly has shoulder pain. The pain intensifies when moving the arm and palpating the muscle. When the biceps tendon ruptures, a balloon-shaped swelling appears.
Bursitis . Occurs when there is excessive load on the joint, after injuries to the periarticular bursa or tendons. The person experiences sharp pain, accompanied by swelling. It is impossible to sleep on the affected shoulder.
Pain when moving
Collision syndrome . The disease causes the deposition of calcium salts. The pain occurs suddenly when raising the arm, it is intense and constant. The syndrome most often affects people aged 30-50 years.
Overextension of shoulder ligaments . This problem is familiar to bodybuilders. Sprains are caused by strenuous exercise. The pain intensifies when moving or palpating the muscle, and bruising appears.
Aching
Intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine . Causes intermittent aching pain in the shoulder joint and neck. It is accompanied by headaches and dizziness. As the disease progresses, the situation worsens. The pain becomes constant and unbearable.
Humeroscapular periarthritis . The pain can be burning, aching and shooting. It begins gradually, without obvious reasons. Often “wakes me up” at night, and my hands get cold. Movement causes pain in the joints. In advanced cases, the functions of the hand are impaired and the hands become numb.
Myalgia . The disease is caused by physical overload, hypothermia, and viral infections. A person feels aching, sometimes sharp pain in the muscles, and cannot move his arms at full strength.
Treatment for pain in the shoulder joint
When complaining of pain in the shoulder, the specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment. Therapy includes:
- Local and general anesthesia. Can be achieved using medications or physiotherapeutic methods, acupuncture, etc.
- Eliminating the root cause of pain. Manual therapy, osteopathy, PRP therapy and Kinesitherapy help with this.
- Symptomatic therapy. They use products to relieve swelling of soft tissues, hyperemia of the skin, and reduce temperature.
- Rehabilitation treatment. This includes kinesitherapy.
During the rehabilitation period, physical therapy and physiotherapeutic treatment are widely used to restore joint mobility. In advanced cases and in the absence of effect from conservative therapy, surgical treatment is possible.
The article was reviewed by traumatologist-orthopedist V.Yu. Bogdanov.
How to reduce post-operative pain
Experts include the following tasks for postoperative pain management:
- quality recovery period,
- acceleration of rehabilitation and discharge from hospital,
- reduction in the number of complications, including the development of chronic postoperative pain.
The most effective is the so-called multimodal scheme4 of postoperative pain relief, the concept of which involves the use of an optimal combination of drugs from different groups in minimal doses4.
Groups of drugs that are used as painkillers after surgery:
- Opioid analgesics. Traditionally, they were considered the basis for surgical anesthesia, but their isolated use gives the expected result in only 25-30% of cases4, and the introduction of the maximum effective dose is associated with a high risk of side effects4, including respiratory depression. Also, after their withdrawal, even greater pain sensitivity often occurs.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The formation of postoperative pain syndrome is directly related to tissue injury and inflammation. Therefore, the prescription of NSAIDs, as drugs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, is indicated from the first minutes after surgery, and sometimes during surgery.
They act directly on the cause of the development of hypersensitivity, namely the production of prostaglandins and other biologically active substances involved in the inflammatory process. There are methods that suggest using NSAIDs 20-30 minutes before the incision, which can reduce the intensity of pain in the area of postoperative sutures.4
When prescribed with drugs from the previous group, NSAIDs make it possible to reduce the dose and enhance the effect of opioids and prevent their side effects4.
- Non-opioid centrally acting painkillers. They do not affect the mechanisms of inflammation, but are able to suppress secondary increased pain sensitivity at the level of transmission of nerve impulses. Their use half an hour before the end of the operation ensures a calm and painless awakening after anesthesia4. They have proven themselves well in complex pain relief.
- Drugs that affect the perception of pain. Introduced to prevent hypersensitivity and the development of chronic pain syndrome4.
- Regional anesthesia (analgesia). The application of the method is based on interrupting the flow of pain impulses from the damaged area to the spinal cord and brain4.
For each patient, a comprehensive pain relief regimen is selected individually. Factors such as age, gender, extent of surgical intervention, concomitant pathology, mental characteristics, sensitivity to pain and its presence before surgery are taken into account.
Up to contents
Cost of treating shoulder pain in our Center
| Services list | Price |
| Initial consultation with a kinesiotherapist | 1600 |
| Interim consultation with a kinesiotherapist | for free |
| Session with a kinesiotherapist (1 patient) | 3900 |
| Individual lessons with a personal trainer | 2700 |
| Subscription for 1 month of training in the gym on simulators | 10 000 |
| Subscription for 6 months of gym training | 45 000 |
| Physiotherapist consultations | 1600 |
| Physiotherapist consultations during the cycle | for free |
| UVT 1 procedure | 2000 |
| HIVAMAT up to 15 min./1 body unit | 2200 |
| HIVAMAT up to 15 min./2 body units | 3200 |
| Appointment with an orthopedist-traumatologist | 1600 |
| Intra-Articular PRP Injection | 6500 |
| Massage of one upper limb (15 min.) | 2200 |
| Massage of two upper limbs (30 min.) | 3000 |
| Kinesio taping | 1100 |
| Complex taping (joints) 1 zone | 1600 |
| Complex taping (joints) 2 zones | 2200 |
Contact us
Call now
8 (495) 803-27-45
Make an appointment through our service
Make an appointment
Treatment process at the Innovation Center
Our Innovative Clinic has created excellent conditions for the diagnosis and treatment of pain in the shoulder joints of various types and origins. After finding out the causes of the pathology, the doctor will select tactics and methods of treatment. We practice using the following techniques:
- Acupuncture.
- Manual therapy.
- Kinesitherapy.
- Osteopathy.
- Massotherapy.
- Physiotherapy.
We achieve excellent results using shock wave therapy and Hiwamat therapy. The course of treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, whose efforts are aimed not only at relieving unpleasant symptoms, but also at eliminating the cause of discomfort. The professionalism of our specialists and an individual approach will help you completely get rid of the problem, and if this is not possible, then avoid complications and achieve stable remission. This is confirmed by a large number of reviews about the work of our center and doctors both on our website in the Reviews section and on other sites on the Internet.