Clubfoot in children (congenital equinovarus deformation of the feet) is one of the most common congenital skeletal deformities affecting the feet. Occurs with a frequency of 1:250-1:1000 depending on the population. More common among boys. 1/2 cases with bilateral lesions. Genetic predisposition is determined, so if one of the children had congenital clubfoot, the chance that another child will be born with the same disease is 2.5-6.5%. Congenital clubfoot may be accompanied by other congenital defects: hand anomalies, arthrogryposis, hemimelia, myelodysplasia and many others.
The pathogenetic mechanism of clubfoot is a difference in the tone of several muscle groups, which leads to muscle contracture on the one hand and their hyperextension and weakness on the other.
1) Cavus deformity of the midfoot (due to contracture of the intrinsic muscles of the foot, flexor hallucis longus and flexor toes longus)
2) Adductor deformity of the forefoot (contracture of the tibialis posterior muscle).
3) Varus deformity of the hindfoot (contracture of the gastrocnemius muscle, tibialis posterior muscle, tibialis anterior muscle)
4) Equinus deformity of the hindfoot (contracture of the gastrocnemius muscle)
Symptoms of clubfoot.
-The small size of the foot and lower leg is determined.
-Shortening of the tibia.
-A skin fold is determined along the posteromedial surface of the foot.
-Equino-cavo-varus-adduction deformity of the foot.
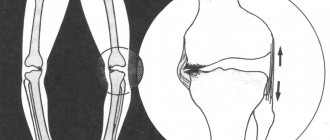
Clubfoot clinical diagnosis. When performing radiographs, a reduced (less than 35°) talocalcaneal angle is determined in the lateral projection in the dorsiflexion position. In the anteroposterior projection, the talocalcaneal angle is also reduced (less than 20°).
About the disease
The medical name is equinovarus deformity.
The frequency is about 3 cases per 1000 newborns. The bilateral variant is more common, and among boys the incidence is 2 times higher. The disease can be combined with other developmental anomalies - torticollis, congenital hip dislocation, scoliosis. Unilateral clubfoot makes one leg shorter than the other. The following degrees of severity are distinguished:
- easy – movements in the ankle joint are possible in full;
- medium – movements in the joint are somewhat limited; when trying to straighten the position, an obstacle and springiness are felt;
- severe - the bones and ankle joint are deformed, it is impossible to return the foot to its place using manual correction methods.
A severe degree is accompanied by dysfunction of the muscles and nerves of the leg; there may be other developmental anomalies.
Up to 4 months, some clubfoot is considered normal. The baby is just learning to walk, and the body gains greater stability when the toes are turned inward. This makes it more comfortable for the knee and hip joints. As the child grows, this clubfoot goes away. However, in all doubtful cases, it is better to consult a pediatric orthopedist-traumatologist.
Who should I contact if I have a clubfoot?
An orthopedic doctor can diagnose and treat any pathology of the feet in children and adults. To fully examine your child, as well as make a correct diagnosis and begin timely treatment, make an appointment with a doctor at a specialized orthopedic clinic.
Now you know how to eliminate clubfoot. If you strictly follow all the stages of plastering using the Ponseti method, you can correct foot pathology in a short period of time. To prevent the recurrence of the pathology, it is recommended to wear braces after achieving a positive result and strictly follow all the advice of the orthopedic doctor.
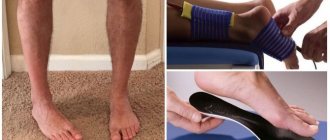
Symptoms of congenital clubfoot
Clubfoot is visible even at birth: the bent foot is turned with the sole inward and upward, movements in the ankle joint are limited.
If the child is already walking, he rests only on the outer edge of the foot. The baby steps over the leg on which he leans. The gait is swaying and uneven. Without treatment, bone deformation worsens, and subluxations occur in the small joints of the foot. The outer edge of the skin of the foot becomes rough. The lower leg muscles that are not involved in the walking process gradually weaken and atrophy. As a result, the function of the knee joints and pelvic joints is impaired. The later treatment is started, the more severe the disorders and the harder they are to correct. General features are the same for all degrees:
- plantar flexion is visible in the ankle joint;
- the sole is turned inward, the outer edge hangs;
- the forefoot is adducted inward;
- the lower leg muscles are poorly developed and atrophied in older children;
- a waddling gait is noted;
- with a unilateral lesion, one leg is several centimeters shorter than the other.
When walking or standing, children quickly get tired, rub their skin, and complain of nagging pain in their legs.
How to suspect that a child has club feet
- The deformation is noticeable to the naked eye.
- Changed gait.
- The muscle tone of the lower leg is weakened.
- The child's footprints are not even and do not run parallel to each other.
- Toes point inward when walking.
- The leg bones are twisted (optional).
- The sole on the inner edge is tilted upward.
- The plantar margin is strongly curved inward.
- The fingers are curved inwards.
There is a nuance! Up to 4 months, the last three points are not a pathology - this is the age norm.
Causes of congenital clubfoot
It is not always possible to establish the exact cause in each specific case. The most common are the following:
- the impact of adverse factors on the mother’s body in the first trimester, when the formation of the lower extremities occurs;
- maternal addictions - smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- pressure (mechanical) of the umbilical cord or fetal sac on the foot;
- a small amount of amniotic fluid, in which the uterus presses on the legs of the fetus;
- congenital pathology of the spinal cord or peripheral nerves;
- uncontrolled use of medications in high doses;
- some infections;
- uterine tumors.
The fetus is most vulnerable in the first trimester. Damage suffered during this period is extremely difficult to repair later. A particularly difficult situation is created if genetic problems are combined with external aggressor factors.
Read also
Polyneuropathy
Diabetic polyneuropathy is a pressing problem for patients with diabetes.
Diabetic polyneuropathy is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus. The incidence of polyneuropathy is 26-50%... Read more
Myasthenia gravis
MYASTHENIAS – a disease associated with a disruption of the immune system, as a result of which antibodies are produced against the body’s own tissues involved in the transmission of nerve impulses, which...
More details
Ankylosing spondylitis/ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the spine and joints, accompanied by progressive pain, stiffness and limited movement at the beginning...
More details
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
– “One of the most terrible human diseases... 3 letters...” – “Cancer” – “Not suitable...” Yes, dear ones, there is something worse than cancer. And this disease is called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or...
More details
Rehabilitation
Restoration of the body after diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, operations on the brain and spinal cord, conditions after removal of the mammary gland due to a tumor, consequences...
More details
Diagnosis of congenital clubfoot
The task of diagnosis is to distinguish true clubfoot from positional clubfoot, when all bones are developed normally, but the joints are in a state of subluxation.
During the examination, the doctor tries to return the feet to the correct position with his hands. This is only possible with the postural (positional) option. In this case, transverse folds are determined on the back of the foot, and the mobility of the ankle is high. Children under 3 months of age undergo an ultrasound of the lower extremities, since the bones are not yet visible on an x-ray. With sonography (ultrasound), you can see only one projection.
From 3 months, x-rays are taken in two projections, in which the foot is placed in the position of maximum extension - plantar and dorsal. Comparison of images gives a complete clinical picture.
Diagnostics includes assessment of four parameters:
- how far the heel is turned inward (varus);
- how much the heel is shifted upward, the arch is increased, how much the foot is curved towards the sole (equinus);
- how the inner edge is turned upward (supination);
- how much the forefoot is brought to the conditional midline of the body (adduction).
Based on the relationship between these components, a diagnosis is made. In particularly difficult cases, an MRI is performed, but the information content of this study is not much higher than routine radiography.
Stages of the plastering procedure
Therapy for clubbed feet, according to the Ponseti method, includes three stages that are aimed at eliminating the pathology.
First stage
At the first stage, you need to correct the curvature of the foot using plaster splints. The plaster boot is placed up to the groin area, with the knees bent. The course of therapy consists of six changes of plaster casts. If the doctor increases the number of dressings, then this will no longer be considered treatment according to the Ponseti method.
The plastering procedure is carried out by a doctor and an assistant. The doctor fixes the foot in the desired position, and the assistant applies a plaster cast.
Second phase
Since the Achilles tendon is always shortened in pathology, in many cases it needs to be lengthened. Once the tendon has been cut, a cast is applied for three or four weeks. During this period, it will grow together to the desired adjusted length. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
Third stage
At the last stage it is important to consolidate the result. Braces are used for this. The boots are connected to each other using a sliding bar. They fix the feet in the required position, so that the deformity cannot return.
During the first three months after the end of plaster casting, it is recommended to wear the braces 23 hours a day. They are removed only to change clothes or bathe the child.
After three months, the braces must be worn during daytime and nighttime sleep. In this mode, orthopedic devices are worn until the child is two to four years old. If this recommendation is not followed, recurrent clubfoot may occur. For walks and indoor games for your baby, buy regular shoes.
Further treatment is carried out based on the results obtained according to the age of the child.
Treatment of congenital clubfoot
The treatment method is chosen by a pediatric orthopedic traumatologist, focusing on the severity of the disease and the general clinical situation.
In the vast majority of cases, persistent conservative treatment is sufficient to correct the situation. The most active treatment is carried out from the first days of life, while ossification is incomplete and it is possible to bring the foot to the physiologically correct position without much difficulty. A combination consisting of the following methods is prescribed:
- therapeutic exercises to maximize ankle mobility and prevent muscle atrophy;
- foot massage;
- soft fixation in physiological position with flannel bandages;
- after being brought into the correct position - splint, cut or stage-by-stage plaster immobilization;
- after plastering - wearing special anti-varus high orthopedic shoes (braces);
- physiotherapy – pine baths, paraffin.
Correctly selected conservative treatment allows you to cope with the disease in the first year of life.
If conservative methods fail to get rid of clubfoot, surgery is performed, but not earlier than 1 year.
The surgical plan is developed individually, the position of the bones and joints is changed, and the ligamentous apparatus is adjusted. The scope of intervention is determined by individual data. After surgery, plaster immobilization is required for up to 6 months.
Principles of the method
The Ponseti method of plastering has the following principles:
- One procedure should abduct the foot no more than 15 degrees.
- The first casting leads to the restoration of the adduction angle of the foot and cavus.
- To correct varus deformity of the foot, as well as eliminate plantar flexion, 2–4 castings are used.
- After this, abduction of the heel over the area of the talus is corrected using a fixed bandage. Thanks to the splint, all components of a healthy foot are fixed in the desired position.
- It is important to remove the equinus and perform an achillotomy.
- To consolidate the results obtained, the doctor prescribes wearing special braces - boots that are fastened together with a strap.
It is recommended to change plaster boots every seven days. Each stage of the method corrects a certain type of deformation.
Prevention of congenital clubfoot
There is no specific prevention. It is important for a pregnant woman to avoid exposure to adverse factors, lead a healthy lifestyle, and follow the gynecologist’s prescriptions. After the birth of the baby, you must strictly follow the recommendations of the orthopedist. The team of experienced specialists at the SM-Doctor clinic will help your child get rid of clubfoot. Our orthopedic traumatologists will conduct a comprehensive examination and draw up a program for improving the health of the musculoskeletal system. Sign up for a consultation at convenient office hours!
Re-development of clubfoot
Clubfoot occurs again during the period when braces are used. Relapses occur due to the fact that parents do not follow the recommendations regarding the use of braces. To fix the problem, you will need to repeat one of the steps above. Sometimes a child needs surgery.
But in order to prevent recurrence of foot pathology, it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and instructions, since the child’s health is only in the hands of his parents.