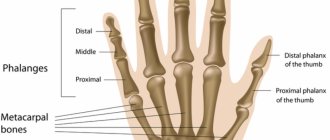
Today, the concept of bone cancer is a collective one, since bone cancer pathology is quite rare - only in 1 percent of all tumor cases.
Most cancers that arise in other organs and systems metastasize to the bones as the disease progresses. In such cases, we should talk about secondary damage to bone tissue.
Children and adolescents are at risk; cases of detection of such pathology (primary bone damage) in elderly people are rare.
Primary bone tumors include:
- Multiple myeloma (40% of all bone cancers; formed from bone marrow cells);
- Osteogenic sarcoma (33% of cases; affects knees and arms);
- Ewing's sarcoma (tumor of the hips and pelvic bones);
- Chondrosarcoma (a cartilage tumor that mainly affects the upper legs and arms);
- Malignant fibrous histiocytoma (a rare tumor that affects the arms and legs; quite rare).
In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish between benign and malignant bone cancer. Benign bone tumors are characterized by slow growth and are surrounded by normal bone tissue, while malignant tumors are characterized by ragged edges and rapid growth, leading to pathological fractures.
Description and danger of pathology
Men are more often affected by the disease due to rapid growth and formation of bone tissue. Bone cancer is divided into several types. They are determined depending on the results of laboratory and instrumental examinations prescribed by the oncologist. The following types of pathology are distinguished.
| Type of bone cancer | Description |
| Osteogenic sarcoma | It develops primarily in bone tissue, quickly spreads to neighboring formations, and gives metastases. The upper extremities are most often affected by the disease. The primary formation of osteoporosis is the leaching of minerals from the bones with the formation of pores. Then needle-like growths form, turning into a tumor |
| Chondrosarcoma | The disease primarily develops in cartilage. More often it forms in older men in the shoulder girdle, ribs, and proximal parts of the lower extremities. On x-ray, areas of destruction and destruction of the cortical layer are formed |
| Ewing's sarcoma | It is less common than other types of cancer. Often affects tubular bones. Adolescents, especially boys, suffer from this pathology. This is an aggressive tumor that forms metastases in a short time |
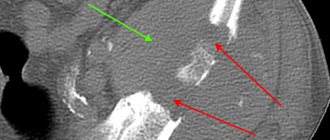
To identify pathology and classify it, diagnostics are required. Instrumental examination includes radiography, CT, MRI, PET, ultrasound, angiography. Be sure to take a biopsy of the tumor, as it can be benign or malignant. The seized material is examined under a microscope.
In the development of any cancer, it is customary to distinguish 4 stages. Each of them has a specific clinical picture depending on the location of the tumor. Read more in the article: “the last days of a cancer patient: stage 4 symptoms.”
Causes of the disease
What is the cause of the appearance and development of bone cancer? So far, medicine is unable to answer. The percentage of people diagnosed with malignant bone tumors does not change from year to year. The greatest risk of getting hand bone cancer is in children and adolescents. Among the adult population, this form of cancer is less common.
It is worth noting! Bone cancer is more common in smokers.
There are only factors that suggest the development of oncology of this organ:
- frequent injuries;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic inflammatory processes of bones and skin.
Read here: Lung cancer
In adults and elderly people, as a rule, metastases—cancer cells from other organs—lead to the appearance and development of arm bone cancer. Such tumors are called metastatic or secondary.
There are three main types of cancer that metastasize to the bones of the arms - lung, prostate, and breast cancer. Tumors that arise directly on the bones are called primary. In a sense, hand bone cancer is an indicator of cancer in another organ, which is much more dangerous. But, in turn, bone cancer, in addition to bone destruction, can metastasize to other organs.
The oldest rule of medicine is well known: the earlier a disease can be diagnosed, the greater the chances of curing it. For oncological diseases, this truth is three times relevant!
Symptoms of different types of cancer
Advertising:
Typically, cancer symptoms are nonspecific. Each symptom can be observed in different pathologies. But if they are detected, the doctor may suspect a malignant process and order an examination.
- Osteogenic sarcoma
. Dull pain for no apparent reason, localized in the affected area. The ends of the bones thicken, and voids are located in their thickness. A venous network is formed on the skin. The pain intensifies and becomes unbearable. - Chondrosarcoma
. The pain immediately becomes acute. It makes movement difficult. Soft tissues are swollen. If the lumbosacral region is affected by pathology, signs of radiculitis occur. The course is slow, metastases do not form for a long time. Therefore, the patient has a chance to detect the disease in the early stages. - Ewing's sarcoma
. The pain intensifies at night, dulls with prolonged rest. When the pain becomes more intense, sleep is disturbed. There is a severe limitation in the mobility of the musculoskeletal system, which is why the patient confuses the disease with arthritis. Appetite is disrupted, the body is exhausted, and body temperature rises. Due to anemia, the patient becomes pale and lethargic. The saphenous veins dilate, so the affected area manifests itself as hyperthermia.
It is impossible to determine a diagnosis based on symptoms alone. Therefore, they turn to an orthopedist. Thanks to instrumental examinations, he identifies the cause, sending the patient to an oncologist.
Neurobics is a set of exercises that trigger the work of both hemispheres of the brain, synchronizing them. Thanks to regular exercises such as gymnastics, learning ability increases, memory improves and brain activity is activated. Read more in the article: “how to restore brain neurons.”
General clinical symptoms
When a tumor forms, the primary symptoms begin. It is important for the patient to identify them in the first stages in order to consult a doctor in a timely manner. The following signs are distinguished:
Advertising:
- puffiness, swelling of soft tissues localized in the area of the affected bone;
- pain when pressing, which is dull at first, then becomes sharp and sharp;
- increased pain at night;
- if the pathology develops in the upper extremities, it becomes difficult for a person to carry things, write, or draw;
- with diseases of the lower extremities - lameness, pain in the feet;
- if the lesion is in the spine, the back hurts, signs of radiculitis appear;
- painkillers relieve discomfort over time or have no effect on the person at all;
- nausea, dizziness, headaches;
- frequent bone fractures due to osteoporosis;
- weight loss, exhaustion, fever.
Often, an increase in body temperature does not occur systemically, but in the affected area. The skin in this area is thin, pale, veins are visible. The patient constantly experiences malaise, weakness, and fatigue. The sensations intensify with increased load on the musculoskeletal system and frequent movements.
The earlier treatment is started, the lower the risk of cancer metastases and relapses.
Treatment depends on the extent of the pathological process. In mild cases, surgery is performed. If the risk of metastases is high, chemotherapy is prescribed.
Laboratory diagnostics
Advertising:
Using instrumental examination, the presence of a tumor is determined. But the cells in it can be normal or atypical. To identify the structure, laboratory tests are carried out.
- General blood analysis
. Non-specific test. It can suggest a disease. This is evidenced by an increase in leukocytes and ESR. - Blood test tumor markers
. In malignant bone tumors, the concentration of tumor marker TRACP5b increases. - Biopsy, histology
. First, a piece of bone tissue that is susceptible to tumor formation is removed from the patient. The resulting material is transferred to the cytology laboratory. Smears are made and atypical cells are identified under a microscope. A biopsy can be performed not only for bones, but also for lymph nodes. This helps to identify the spread of metastases during the development of a malignant process.
After determining the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. During its implementation, laboratory and instrumental analyzes are repeated. Monitor trends in the development of the disease.
Laboratory tests are carried out in the oncology department; if they are not available, you can contact private laboratories.
Gradually, the patient enters remission, that is, a period of recovery. But it is recommended to undergo analysis for tumor markers and other tests every 6 months. This eliminates the risk of sudden relapse, which the patient may not notice.
Exercise for Strong Bones
Exercise can help keep bones strong and can also reduce the risk of falls and fractures.
Consult your healthcare professional before starting any exercise program.
High-impact and weight-bearing exercise helps strengthen bones and keep them in shape. Examples of high impact and weight bearing exercises:
- fast dancing;
- high impact aerobics;
- hiking;
- running, including jogging;
- jumping rope;
- climbing stairs;
- tennis.
Low-impact and weight-bearing exercise can also help keep bones strong. They may also be safer for people who are unable to perform high-impact exercises. Examples of low impact and weight bearing exercises:
- exercises on elliptical trainers;
- walking;
- stair training such as the StairMaster®;
- a ride on the bicycle;
- rowing;
- tai chi;
- yoga;
- Pilates;
- swimming;
- water aerobics;
- golf;
- cross-country skiing;
- ballroom dancing.
to come back to the beginning
Blood test results for cancer
Advertising:
When examining blood, a general analysis and other tests are determined. Comprehensive diagnostics are required to make a diagnosis and monitor the disease. Laboratory test results are presented in the table.
| Laboratory blood test | Delivery conditions | Indicators for bone cancer |
| General analysis | Last meal 8 hours before the test. The test is taken from 8:00 to 10:00 on an empty stomach. | Increased level of leukocytes and ESR, decrease of red blood cells |
| Total alkaline phosphatase (ALP) | Delivery only in the morning on an empty stomach. Do not eat fatty foods for several days before the test. | Increased levels in bone cancer. Significant increase in metastases to the lungs and liver. Control over the treatment of pathology |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) | Giving on an empty stomach in the morning | The test is non-specific, but enzyme levels increase in bone cancer |
| Tumor markers | The test can be taken at any time; in case of cancer, the level is always elevated | The amount of tumor marker TRACP only type 5b increases. Level 5a remains normal |
During treatment, the OAC is repeated, ALP and tumor markers are determined. If therapy is completed, all tests are not required. But tumor markers are examined every 6 months. A study such as a general blood test is not very informative. An increase in white blood cells and ESR may indicate the development of other diseases. Therefore, after the end of the illness it is not prescribed.
Evaluation of analysis for tumor markers
Advertising:
Tumor markers are specific enzymes that are constantly present in a person’s blood, but their concentration increases during the period of illness. Therefore, it is recommended that testing be performed only on patients who are likely to develop a malignant process. No preliminary preparation is required, since food intake and time of day do not affect the analysis result. In bone cancer, the level of the TRACP type 5b enzyme is increased. For women and men, its indicators are different. The following normal values are distinguished:
- women before menopause - 1.03-4.15;
- women after menopause - 1.49-4.89;
- men at any age - 1.5-4.7.
The difference for women is determined by the fact that in the postmenopausal period the ratio of enzymes changes, so not only bone cancer, but also osteoporosis can form. If the increased value allows the doctor to suspect bone pathology. But it doesn't have to be cancer. Therefore, additional radiography, biopsy, and cytological examination are performed.
Calcium-rich foods
| Product | Serving Size | Calcium per serving (milligrams) | Calories per serving |
| Dairy | |||
| Yogurt without additives, low fat | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 265 | 150 |
| Cheddar cheese | 1½ oz (45 g) | 307 | 171 |
| Gruyère cheese | 1½ oz (45 g) | 430 | 176 |
| Parmesan cheese | 1½ oz (45 g) | 503 | 167 |
| Low fat milk | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 305 | 102 |
| Milk, whole | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 276 | 149 |
| Dairy-free products (as an alternative) | |||
| Soy milk without additives, fortified with calcium | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 301 | 80 |
| Plain rice milk fortified with calcium | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 283 | 113 |
| Almond milk, vanilla, fortified with calcium | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 451 | 91 |
| Seafood | |||
| Sardines, canned in oil, with bones, without liquid | 2 pcs. | 92 | 50 |
| Salmon and sockeye salmon, canned, without liquid | 4 oz (115 g) | 263 | 189 |
| Sea bass, Atlantic, cooked | 4 oz (115 g) | 39 | 109 |
| Steamed mussels | 4 oz (115 g) | 37 | 195 |
| Fruits and vegetables | |||
| Collards, cooked | ½ cup | 134 | 31 |
| Turnip leaves, cooked | ½ cup | 104 | 29 |
| Kale, cooked | ½ cup | 47 | 18 |
| Bok choy (Chinese cabbage), fresh | 1 cup | 74 | 9 |
| Brussels sprouts | ½ cup | 28 | 28 |
| Figs, fresh | 2 pcs. (average) | 35 | 74 |
| Nuts, beans, beans and soybeans | |||
| Almond | 1/4 cup | 96 | 207 |
| White beans, canned | ½ cup | 96 | 150 |
| Edamame (soybeans), cooked | ½ cup | 49 | 95 |
| Tofu, firm, prepared with calcium sulfate* | ½ cup | 253 | 88 |
| Other food and drinks | |||
| Fortified, ready-to-eat cereal flakes (various)** | ¾ to 1 cup | 250–1000 | 100–210 |
| Orange juice fortified with calcium** | 1 cup | 500 | 117 |
| Oatmeal porridge without additives, instant, enriched** | 1 packet after cooking | 98 | 101 |
| Mineral water (e.g. San Pellegrino®, Perrier®) | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 33 | 0 |
| Basil, dried | 1 teaspoon | 31 | 3 |
*Calcium content is based on tofu prepared with calcium salt. Tofu prepared with other salts does not contain significant amounts of calcium.
**Check product labels as calcium levels may vary.
Source: USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference
Can be found at https://ndb.nal.usda.gov
to come back to the beginning
The importance of timely diagnosis
Advertising:
The sooner a person suspects problems that have arisen in the body, the higher the chance of a timely diagnosis. Cancer is dangerous because it can lead to metastases in other organs. If a malignant process additionally develops in the liver, lungs, or brain, it is almost impossible to save the patient.
A favorable outcome occurs in the first 2 stages; at stage 3, only a portion of patients survive.
Therefore, it is recommended to listen to the state of your body. If the patient feels discomfort in the spine, upper and lower extremities, pain when pressing, causeless lameness, it is better to consult an orthopedist.
Thanks to x-rays, ultrasound, and biopsy, it is possible to promptly predict the presence of a tumor in the body. But to determine whether it is malignant or benign, laboratory tests of the blood or the tumor itself are required. The sooner the patient is diagnosed, the easier treatment will be for him. In the early stages, only surgery may be required. If chemotherapy is prescribed when there is a risk of metastases, the treatment is much more difficult. Due to this therapy, the patient becomes exhausted and experiences constant nausea and vomiting.
Foods containing vitamin D
| Product | Serving Size | Vitamin D per serving (IU) | Calories per serving |
| Cod liver oil | 1 tablespoon | 1360 | 123 |
| Salmon and sockeye salmon, canned, without liquid | 4 oz (115 g) | 953 | 189 |
| Sea bass, Atlantic, cooked | 4 oz (115 g) | 66 | 109 |
| Tuna, light, canned in water, drained | 4 oz (115 g) | 53 | 97 |
| Sardines, canned in oil, without liquid | 2 pcs. | 46 | 50 |
| Orange juice fortified with vitamin D* | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 100 | 117 |
| Low-fat milk fortified with vitamin D | 1 cup (8 oz (240 ml)) | 117 | 102 |
| Egg including yolk | 1 PC. (large) | 44 | 78 |
| Shiitake mushrooms, dried | 4 things. | 23 | 44 |
| Chanterelle mushrooms, fresh | ½ cup | 114 | 21 |
*Check product labels as calcium levels may vary.
Source: USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference
Can be found at https://ndb.nal.usda.gov
to come back to the beginning