Compared to other degenerative diseases, arthrosis of the elbow is diagnosed quite rarely, since this joint is almost not subjected to increased stress. But when the first symptoms of pathology appear (pain, swelling, stiffness of movement), you need to consult a doctor. Arthrosis of the elbow joints of grade 1 and 2 responds well to conservative treatment.
Description of arthrosis of the elbow joint
The disease occurs against the background of deterioration of blood circulation and disorder of cartilage trophism. They become less strong and elastic, which inevitably leads to their damage when the bone surfaces are displaced. Arthrosis of the elbow joint in elderly patients develops slowly - over several years. But in young people the disease progresses quite quickly:
- the synovial membrane thickens, villi form on its surface;
- To stabilize the elbow joint, bone growths are formed - osteophytes;
- The size of the capsule increases, and areas of coarse fibrous tissue, devoid of any functional activity, are formed in it.
More than 80% of arthrosis of the elbow joint is diagnosed in elderly patients. The main reason for the development of the disease is the natural aging of the body and the slowdown of recovery processes. Degenerative-dystrophic pathology is detected in young patients, mainly leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Video on the topic
Disappointing data from numerous studies indicate that arthrosis has become the most common ailment of the musculoskeletal system.
City bustle, a sedentary lifestyle, and injuries of various types accompany this disease, and without proper diagnosis and treatment it leads to disability and loss of ability to work.
Most often, arthrosis affects the elbow joint, as the most important vital function of the hands.
Degrees of pathology
The classification of elbow arthrosis is based on clinical manifestations characteristic of a particular radiological stage. There is a relationship between the resulting destructive changes in cartilage, bones, ligamentous-tendon apparatus and the intensity of symptoms. It is the severity of the disease that determines the tactics of its treatment.
1st degree
At the initial stage of development, there are no pronounced symptoms, so patients rarely seek medical help. Mild discomfort occurs only after physical activity. Upon examination, slight muscle weakness is revealed, and some tension is noted when trying to raise the arm.
No pronounced morphological changes are observed on radiological images. But the composition of the synovial fluid has already been changed, which becomes the cause of nutrient deficiency.
2nd degree
With grade 2 arthrosis, pain appears not only when flexing and extending the elbow joint, but also at rest. This is predisposed by the growth of the edges of the bone plates, the destruction of hyaline cartilage, and inflammation that occurs and then subsides.
The functional activity of the muscles located near the elbow joint is noticeably reduced. The patient experiences difficulty lifting weights and performing previously habitual movements. Thinning and thickening of the cartilage layer is indicated by a specific sound when bending or straightening the elbow.
3rd degree
Arthrosis of high severity is characterized by thinning of the cartilage and the formation of extensive foci of destruction. The articular platform is deformed, which leads to a change in the axis of the arm. The normal relationship between the anatomical structures is disrupted, the ligaments are shortened, the gap is completely or partially fused, and the natural range of movements is significantly limited.
Causes of the disease
Many external and internal factors predispose to the development of arthrosis of the elbow joint. But sometimes doctors are unable to determine the causes of the disease, so it is called idiopathic, or primary. Secondary arthrosis always occurs against the background of some pathological condition:
- previous injuries - fractures, dislocations, severe bruises, damage to the meniscus, ligaments, tendons;
- congenital dysplastic developmental disorders of the elbow joint;
- metabolic disorders;
- autoimmune pathologies - ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- specific and nonspecific inflammation accompanying purulent arthritis, tuberculosis, brucellosis, syphilis;
- endocrine diseases, for example, diabetes, hypothyroidism;
- hemarthrosis occurring after injury or relapse of hemophilia, scurvy, hemorrhagic diathesis;
- Peters disease, osteochondritis dissecans, occurring with gradual destruction of hyaline cartilage;
- joint hypermobility.
Excess body weight, excessive physical activity, surgical interventions, hereditary predisposition, hypothermia, and lack of foods high in microelements and vitamins in the diet also act as provoking factors.
How Noltrex intra-articular injections work
Noltrex is an artificial endoprosthesis that can replace the missing synovial fluid in the elbow and any other joint. Once inside the joint space, the drug evenly covers the surfaces, creates a shock-absorbing effect and gradually restores the desired viscosity of the joint fluid. Therefore, cartilage and bones stop rubbing against each other, the joint space widens, and the pain goes away.
Unlike injections based on hyaluronic acid, Noltrex:
- It is biocompatible with body tissues, therefore does not cause rejection or allergic reactions;
- does not contain components of animal origin, therefore it is eliminated from the body much longer;
- has a minimum of contraindications, including only inflammation of the joint and in some cases diabetes.
The molecules of the polymer drug "Noltrex" are practically invisible to the body's immune cells, so the drug remains in the joint for a long time and has a prolonged effect. It is necessary to take a repeated course in the treatment of arthrosis of the elbow joint every 9-24 months, depending on the degree of the disease. During this period, the mobility of your elbow is completely restored, the pain goes away - you can enjoy life again!
Symptoms of pathology
The leading symptom of arthrosis of the elbow joint is pain. It is weakly expressed in pathology of the 1st degree of severity, so it is often mistaken for muscle fatigue at the end of the working day. As arthrosis progresses, the intensity of the pain syndrome increases many times. To minimize the likelihood of its occurrence, a person tries not to use the injured hand again. He often assumes a forced body position, which suggests the development of arthrosis at the first examination by a doctor. Constant pain is accompanied by other specific symptoms:
- morning stiffness;
- swelling of the elbow, increased pain when pressing on the swelling;
- crunching, clicking when raising the arm, bending and (or) straightening the joint;
- increase in local body temperature, redness of the skin with the development of inflammation due to injury to soft tissue by osteophytes.
Sometimes, upon palpation, round, dense nodules localized around the elbow are determined under the skin.
In the acute and subacute periods, arthrosis manifests itself with intense symptoms. During remission, mild pain occurs when the weather changes, after physical activity or hypothermia. But these factors can also provoke a relapse of the pathology.
When to see a doctor
The elbow of the right hand hurts (it can be treated without going to the doctor) - with a slight bruise, it is enough to immobilize the hand and apply a cooling compress to the site of injury so that the condition will soon return to normal.
But in some cases, consultation with a specialist is necessary:
- if the pain does not subside despite immobilization and compress;
- if swelling and redness appear on the elbow with any movement;
- if pain in the elbow is accompanied by an increase in general body temperature;
- if the shape of the joint has changed, the bone protrudes;
- if your arm hurts and it is impossible to bend or straighten it.
Diagnosis of the disease
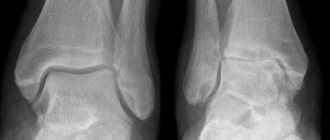
The basis for making a diagnosis is a combination of radiological signs and characteristic symptoms of osteoarthritis of the elbow joint. A number of functional tests are also carried out, the results of which help to assess muscle strength and preserved range of motion. X-ray of the elbow, performed in two projections, is the most informative in the diagnosis of arthrosis of any location. The following signs indicate the emerging pathology:
- formed osteophytes;
- uneven outlines of the joint space, its narrowing, complete or partial fusion;
- subchondral osteosclerosis;
- deformation and flattening of the bone platform;
- cyst-like formations.
X-rays do not always allow an accurate assessment of the condition of the joint. Therefore, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the elbow is performed. Using CT, it is possible to identify the features of bone tissue destruction. And MRI is used to detect pathological changes in connective tissue structures - ligaments, muscles, tendons, blood vessels, nerves.
Methods for treating arthrosis
With arthrosis, destructive and degenerative changes occur that are irreversible. Therefore, treatment of the disease is aimed at achieving stable remission. During this period, the patient’s well-being improves significantly, and arthrosis ceases to affect healthy articular and periarticular structures.
In case of exacerbation of pathology, a gentle regimen is indicated. Patients are prohibited from putting any strain on the injured arm, including lifting heavy objects. To stabilize joint structures and alleviate symptoms, patients are recommended to wear orthopedic devices. Their degree of fixation depends on the severity of arthrosis. At the initial stage of its development, elastic bandages are used to slightly limit movement. Patients with grade 3 pathology are advised to wear semi-rigid or rigid orthoses.
Drug therapy
With some exceptions, the drugs used in the treatment of arthrosis of the elbow joint are intended only to eliminate symptoms. In the acute and subacute period, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to reduce the severity of pain:
- solutions for intramuscular administration Xefocam, Movalis, Ketorolac, Diclofenac;
- tablets Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Ketoprofen, Nimesulide, Ketorol, Celecoxib.
During the period of remission, NSAIDs in such dosage forms are undesirable due to their pronounced side effects - ulceration of the gastric mucosa. If the need for them still arises, then they should be combined with proton pump inhibitors, for example, Omeprazole.
| Clinical and pharmacological group of drugs for the treatment of elbow arthrosis | Names of medicines | Therapeutic effect |
| Muscle relaxants | Sirdalud, Tizanidine, Baklosan, Mydocalm | Elimination of muscle spasms by relaxing skeletal muscles |
| Systemic chondroprotectors | Artra, Teraflex, Alflutop, Structum | Partial restoration of cartilage tissue, reduction in pain severity |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Kenalog, Dexamethasone, Diprospan, Prednisolone | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antiexudative, immunosuppressive |
| Products with B vitamins | Milgamma, Combilipen, Neuromultivit, Neurobion | Improving innervation, restoring optimal tissue trophism |
Physiotherapy
In the treatment of elbow arthrosis of any severity, galvanic currents, ultraviolet irradiation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, and shock wave therapy are used. Patients are prescribed up to 10 sessions of physiotherapy to improve blood circulation, speed up metabolism and restore damaged joint structures. When muscle weakness is detected, electrical stimulation is performed - a therapeutic effect on the muscles and sensitive nerve endings with pulsed electrical currents.
In the subacute period, ultraphonophoresis or electrophoresis with dimexide, glucocorticosteroids, B vitamins, and trimecaine is used. At the stage of remission, when carrying out these measures, chondroprotectors, anesthetics, and solutions of calcium salts are used.
Patients are recommended acupuncture, hirudotherapy (treatment with medicinal leeches), applications with ozokerite or paraffin, and balneotherapy.
Ointments
In the treatment of elbow arthrosis at the remission stage, ointments and gels with NSAIDs are used - Voltaren, Fastum, Artrosilene. Their active ingredients penetrate the bloodstream in small quantities, so they rarely provoke systemic adverse reactions. External medications help quickly get rid of mild pain. They are also prescribed in the subacute period to reduce the pharmacological load on the body by reducing the doses of systemic drugs.
If arthrosis is not complicated by inflammation of the soft tissues, then treatment regimens include ointments with a warming, locally irritating, analgesic effect:
- Finalgon;
- Nayatoks;
- Ethkamon;
- Viprosal;
- Capsicam.
Chondroprotectors for local application (Chondroxid, Chondroitin-Acos, Teraflex cream) are used quite rarely. Experienced orthopedists do not prescribe them to patients due to clinically unproven therapeutic effectiveness.
Surgery
In case of severe deformation of bone structures, ineffectiveness of conservative treatment for several months, or rapid progression of the disease, operations are performed. Arthroplasty is performed to restore the functional activity of the elbow. This is a minimally invasive surgical technique, which is characterized by low trauma to healthy tissue.
An arthroscope is inserted through punctures into the cavity of the elbow joint for a detailed examination of its internal structures. Then, using arthroscopic instruments, free intra-articular bodies are removed from the joint. Osteophytes are resected with a bur followed by mobilization of the synovial bursa.
But more often, patients are offered a more effective way to restore the mobility of a damaged arm - endoprosthetics, or replacing the elbow joint with an implant.
Physiotherapy
Daily exercise therapy is the most effective method of eliminating painful symptoms and preventing the spread of the destructive-degenerative process. Only when performing exercises does blood circulation accelerate, the reserves of nutrients and oxygen in hyaline cartilage, bones, and connective tissue structures are replenished. Even in the postoperative period, immediately after restoration of the integrity of the soft tissues, a course of mechanotherapy is carried out. Using a special computerized apparatus, flexion and extension of the elbow joint are performed.
A set of exercises is compiled by a physical therapy doctor. When choosing them, the doctor takes into account the severity of the disease and the severity of symptoms.
Folk remedies
Remedies made according to traditional medicine recipes are ineffective in the treatment of elbow arthrosis, and can sometimes cause harm. Therefore, the advisability of their use should be discussed with your doctor. Official medicine specialists recommend to patients only teas based on St. John's wort, valerian, and motherwort to improve their psycho-emotional state. To prepare a soothing infusion, pour a teaspoon of dry plant material into a glass of boiling water, filter after an hour and drink 100 ml before bed.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of deforming arthrosis of the elbow joint at home is carried out over a long period of time and under the supervision of a specialist. As a rule, complex therapy is used with an individual approach to each patient. The main goal of treatment is to relieve pain and restore joint tissue as much as possible. Today, medication is used to treat elbow arthrosis, supplemented by physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises. Folk remedies also remain relevant.
Medication method
While there are no symptoms, a person usually does not take medications, as he is unaware of the developing pathology. When a diagnosis of grade 2 osteoarthritis of the elbow joint is made, treatment should begin immediately. The doctor prescribes medications from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are available in the form of tablets, ointments, and injections. Most often these are Diclofenac and Ibuprofen.
- Bruise of the elbow joint - symptoms, causes, treatment and consequences
In case of severe pain, a joint blockade with novocaine can be performed. In later stages of the disease, when the cartilage is significantly destroyed, injections of hyaluronic acid are used, which replaces the natural lubrication and softens the cartilage. After relieving inflammation and relieving pain, chondoprotectors are prescribed to restore the structure of cartilage tissue. The drugs are considered effective, but their disadvantages include high cost and the need for long-term use.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
For elbow arthrosis, treatment is often carried out using paraffin therapy. During the procedure, soft tissues are deeply warmed up, and blood circulation is activated in the problem area. Such patients are also prescribed electrophoresis - drugs are administered locally, which improves their penetration and effect.
In the presence of osteophytes, laser therapy helps well. The laser destroys calcium compounds and the growths disintegrate - this returns mobility to the joint. A popular method of physiotherapy for arthrosis is mud applications, which prevent degeneration of cartilage and muscle tissue. Acupuncture has a good effect. Impact on reflex points restores muscle tone.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine has long and successfully treated joint diseases. Her methods can also help with elbow arthrosis. The advantages of this treatment are its availability, harmlessness and effectiveness. It is important to follow the following recipes exactly:
- Pour several buttercup plants into 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes and use for a bath, diluting with hot water to the required level. The remaining infusion should be heated in the evening and used as a compress on the sore elbow, leaving it overnight.
- Regular compresses with cabbage juice will relieve the aching pain. A piece of film is placed over the cloth soaked in the juice and then a warm scarf is wrapped around the elbow.
- Lotions made from chalk and kefir relieve swelling and improve blood circulation. They are also done before bed to keep the hand warm.
- A rubbing mixture of honey, glycerin and alcohol with the addition of iodine is effective for arthrosis. You should not expect results right away; they will appear after some time.
- If you have pain, you can rub your elbow joint with black radish juice. The course of procedures is 20 days.
- It is recommended to take a decoction of equal parts of nettle leaves, elderberry flowers, parsley root and willow bark internally. Grind the ingredients and brew 1 tbsp. l. mixture with a glass of boiling water. Then the composition is kept on low heat for 5 minutes, left until cool and filtered. You need to drink 1 glass of the decoction in the morning and evening, before meals.
- Pour several buttercup plants into 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes and use for a bath, diluting with hot water to the required level. The remaining infusion should be heated in the evening and used as a compress on the sore elbow, leaving it overnight.
- Regular compresses with cabbage juice will relieve the aching pain. A piece of film is placed over the cloth soaked in the juice and then a warm scarf is wrapped around the elbow.
- Lotions made from chalk and kefir relieve swelling and improve blood circulation. They are also done before bed to keep the hand warm.
- A rubbing mixture of honey, glycerin and alcohol with the addition of iodine is effective for arthrosis. You should not expect results right away; they will appear after some time.
- If you have pain, you can rub your elbow joint with black radish juice. The course of procedures is 20 days.
- It is recommended to take a decoction of equal parts of nettle leaves, elderberry flowers, parsley root and willow bark internally. Grind the ingredients and brew 1 tbsp. l. mixture with a glass of boiling water. Then the composition is kept on low heat for 5 minutes, left until cool and filtered. You need to drink 1 glass of the decoction in the morning and evening, before meals.
The main condition for using folk remedies is regularity. The cycle of procedures usually lasts at least 3 weeks.
Set of exercises
It is important to know that exercises for the elbow joint with arthrosis are contraindicated during exacerbations. Physical activity becomes possible no earlier than 5-6 days after the acute period. The purpose of the classes is to improve lymph flow and blood circulation, as well as relieve muscle spasm. It’s good when physical therapy is combined with swimming.
Dr. Bubnovsky’s exercise technique has gained particular popularity for elbow arthrosis. The complex is designed to relieve pain and restore motor function of the joint. At the same time, muscle tone will improve. Exercise therapy according to Bubnovsky is based on strength exercises. They need to be performed at a slow pace, smoothly, gradually increasing the load.
Breathing is controlled in rhythm with the movements. The following sequence of exercises is recommended:
- You need to clench your fists tightly, followed by bending and straightening your fingers.
- With a healthy hand, the patient grasps the sore limb and turns it smoothly in different directions.
- Place the affected hand on the table surface and cover it with the other hand. Then the lower hand needs to be lifted, overcoming the resistance.
- The elbows are placed on the table with the hands together. Then they are moved apart and moved again.
- Place your hands on the table, then alternately raise and lower your fingers.
- Clasp your fingers and then forcefully spread them apart. Repeat 5-7 times.
- Press the thumb of one hand onto all the fingers of the other one at a time. Change hands.
- Press the top of the small ball with your palm using springy movements.
- The final exercise is performed with dumbbells. Your arms should be raised and then spread to the sides. Don't forget about correct exhalation.
According to the author of the technique, the effect will occur after a month of regular exercise. You need to start exercising as early as possible so as not to trigger the disease. Such gymnastics can be performed not only as a treatment, but also as a preventive measure for arthritis and arthrosis of the elbow.
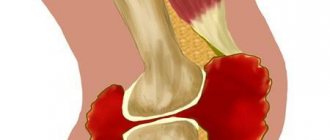
Even the slightest movement becomes one of the causes of pain in the patient’s hand
- Symptoms and treatment of arthrosis of the elbow joint with drugs and folk remedies
In the first stages, deforming osteoarthritis of the elbow joint has frequent exacerbations, which alternate with remission, which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis during the initial examination and collection of the patient’s medical history. Treatment methods for grade 2 arthrosis of the elbow joint are selected taking into account the stage of development of the degenerative process, the patient’s age and his individual characteristics. The result depends on correctly selected therapy, which can be adjusted during the treatment process.
The disease has 3 stages of development, each with its own symptoms and treatment methods:
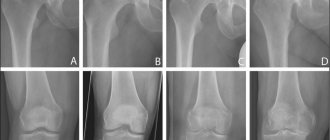
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint of 1st degree is characterized by a slight narrowing of the joint space. During this period, the patient notes some muscle stiffness and pain, which is often perceived as post-traumatic. Diagnosis of arthrosis of the elbow joint of the 1st degree of the disease is performed using computed tomography, which can detect the onset of the degenerative process.
Thus, stage 1 of the disease is effectively treated with the help of therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy, which is why it is important to identify arthrosis as early as possible.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the elbow joint occurs with severe atrophy of muscle tissue in the area of the elbow joint. A computed tomogram clearly shows deformation and destruction of the cartilage and changes in the contours of the bone. The joint space narrows even more, and osteophytes are formed - pathological growths on bone tissue.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint grade 2 is characterized by severe pain during and after exercise. In especially severe cases, the patient becomes disabled. Therapy for this stage of the disease includes physiotherapy, massage and medications.
Osteoarthritis of the elbow is accompanied by severe, ongoing pain even in the absence of load. Images of the elbow show multiple osteophytes and deformity. At this stage, only conservative treatment is used. Attempts to solve the problem surgically bring temporary relief.
When an elbow injury occurs, tissue rupture occurs, resulting in inflammatory processes. The causes of post-traumatic arthrosis of the elbow joints are dislocations, sprains, and fractures. Any minor damage can trigger a degenerative process in the joint. Other factors predisposing to the development of arthrosis include:
- Improper metabolism, in which there is a deficiency of elements that are necessary for the proper functioning of body systems.
- Arthritis of the rheumatoid type, which, as the disease progresses, affects all joints.
- Inflammatory processes resulting from infection in the joint capsule.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- Heredity.
- Chronic pathologies.
- Respiratory diseases.
Self-medication for arthrosis is unacceptable. Without proper diagnosis, the patient may develop a disease and see a doctor late. Such delays can lead to loss of productivity and a significant reduction in a person's quality of life.
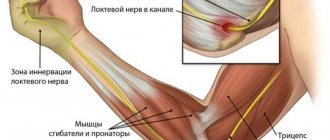
- Pinched nerve in the elbow joint - symptoms and treatment of the disease
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease, physicochemical research methods are used, which also make it possible to establish the characteristics of the course of the disease and conduct a differentiated diagnosis of the pathology:
- A laboratory blood test makes it possible to determine the presence of rheumatoid factor and rule out arthritis.
- Using radiography, the stage of the disease is determined.
- An ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine the thickness of the cartilage.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and CT provide more accurate diagnostic indicators.
A preliminary diagnosis of arthrosis of the elbow joint is established when the patient is examined by a doctor. To diagnose osteoporosis, densitometry is used.
The main factor in getting rid of arthrosis is timely and correct treatment. Modern treatment methods effectively cope with the disease in the early stages, at the first signs of the disease. The following methods are used in anti-arthrosis therapy: therapeutic exercises, physiotherapeutic procedures, immobilization of the elbow joint, treatment with drugs, surgical methods, traditional methods.
At each stage of development of DOA, different pharmaceuticals are used:
- Stage 1. For grade 1 arthrosis of the elbow joint, chondoprotective drugs, vitamin complexes and vasodilators are prescribed to improve blood flow. For significant pain caused by an acute inflammatory process, painkillers are prescribed.
- Stage 2. During the 2nd stage of arthrosis of the elbow joint, the patient experiences severe pain. To relieve pain when the joint is deformed, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs of varying degrees of effect are prescribed. If taking the drugs does not produce results, the patient is prescribed a course of blockade. Hyaluronic acid is becoming increasingly widespread in the treatment of joint diseases; when introduced into the joint cavity, it replaces joint fluid and facilitates the process of flexion and extension of the elbow. Thanks to this substance, the process of deformation by abrasion of bone tissue slows down during the movement of the patient's hands.
- Stage 3. Medicines at stage 3 of arthrosis do not bring significant relief to the patient. Their action is aimed at slowing down the degeneration of cartilage tissue. If the disease is accompanied by an acute inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes NSAIDs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Massage is one of the therapy methods used in combination with medication
If the mobility of the elbow joint is almost completely lost, the recovery process should not be rushed. To regain lost flexibility, you must strictly follow your doctor's instructions for quite a long time.
For post-traumatic arthrosis of the elbow joint, treatment with special ointments is used. Depending on the type of active substance, such ointments are divided into the following groups:
- NSAID ointments are used during the acute stages of the disease, their action is aimed at relieving pain: Ketonal, Nise, Finalgel.
- Capsacin is an ointment based on red pepper that has a warming effect and eliminates pain in the joint.
- Salicylates are anti-inflammatory ointments that work effectively for injuries and bruises of joints.
With the help of ointments, it is possible to achieve relaxation of joint tissues. Ointments are prescribed primarily for the symptomatic treatment of arthrosis. In the treatment of arthrosis of the 1st degree, ointments based on bee and snake venom show positive results: Viprosal, Nyatoks, Virapin, Apizatron, Sophia cream. Such ointments warm up the treated areas well, speeding up metabolism and increasing blood circulation in the area of the affected joint.
Among the various folk methods for treating post-traumatic arthrosis of the elbow joint at home, you should choose those that will not cause harm. These are mainly lotions and compresses based on herbs and other beneficial substances. When choosing components, you must ensure that there are no allergic reactions. Treatment of arthrosis of the elbow joint with folk remedies should be agreed with the attending physician, since some medicinal herbs neutralize the effect of pharmaceutical drugs.
The following available measures can be used as methods that the patient can effectively apply at home:
- Compresses from tinctures.
- Rubbing.
A honey compress gives good results, especially after bath procedures. Honey must be diluted with alcohol. One part of alcohol is mixed with two parts of honey, and the resulting substance is applied to the elbow joint. The elbow should be wrapped in warm cloth and plastic wrap. The compress should be kept on the joint for about 30 minutes. There are a number of traditional ways to treat arthrosis of the elbow joints, but you should not limit yourself to them.
Traditional methods can be considered as auxiliary, and their use must be agreed with the attending physician.
Certain stages of the disease significantly reduce the patient’s ability to work and make it impossible to find employment in certain types of work. The patient may also experience difficulties in everyday life and other areas of life. In such cases, a special commission decides to register disability and assign an appropriate pension.
When the elbow joint is injured, tissue rupture occurs, resulting in inflammatory processes. The causes of post-traumatic arthrosis of the elbow joint are dislocations, sprains, and fractures. Any minor damage can trigger a degenerative process.
Endoprosthetics is recognized as the most optimal treatment method for post-traumatic arthrosis of the elbow joint.
Surgery for arthrosis is used in exceptional cases: severe physical pain that cannot be controlled by NSAIDs, long-term unsuccessful therapy, significant destruction of cartilage. During the operation, the patient is fitted with a prosthesis. This method of treatment is a temporary measure; after 15–20 years, the patient will be scheduled for a second operation.
To avoid being forced to undergo surgery, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible and strictly follow the recommendations received. If the course of arthrosis is favorable and medical prescriptions are followed, recovery occurs within six months from the start of treatment. Lack of proper treatment inevitably leads to patient disability.
You can also read: Treatment of stage 1 osteoarthritis
Complications
As arthrosis progresses, ligaments, muscles, and tendons are involved in the destructive-degenerative process. They weaken and lose the ability to hold the elbow joint in its anatomical position, so painful subluxations are often observed. A characteristic sign of progressive arthrosis is contracture. This is the name for a condition in which the arm cannot be fully bent or straightened at the elbow joint. Muscles shorten or stretch, and their fibers cannot fully contract.
With complete fusion of the joint space, ankylosis occurs - immobilization of the elbow joint. It can only be eliminated with the help of endoprosthetics.
Preventing Elbow Pain
You can prevent elbow pain by avoiding muscle strain. To do this, it is worth taking breaks from time to time in work where the elbow joint is constantly involved. It is better to choose the right position and use convenient equipment.
- Services and prices
When moving your arms monotonously, it is useful to periodically bend and unbend them, as well as do self-massage. When reading books or talking on the phone, you should not constantly lean on your elbows.