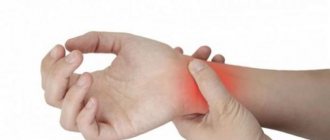
Causes of wrist pain
The wrist joint is often susceptible to damage, since it bears the maximum load. Diseases that cause joint pain include:
- Injuries: sprains, bruises, fractures and dislocations. Appear as a result of a blow or fall with emphasis on the wrist joint.
- Arthrosis. It mainly develops in old age, but post-traumatic arthrosis is also common.
- Arthritis is inflammation of the joint capsule and articular surfaces.
- Tenosynovitis or de Quervain's disease. More often it occurs with constant stress on the hands and hormonal changes in the body.
- Tunnel syndrome. The cause is compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
Video showing normal carpal bone anatomy
The carpal joint is an elliptical joint formed by the radius and articular disc proximally and the proximal row of carpal bones distally. The carpal bones on the ulnar side are only intermittently in contact with the proximal side - the triquetrum is in contact only when the ulna is retracted. The sac is loose and unbranched, thin dorsally and may contain synovial folds. The capsule continues into the metacarpophalangeal joint and is strengthened by numerous ligaments, including the palmar and wrist ligaments, the elbow ligaments, and the radial collateral ligaments. Other triggers include bone spurs, reactive arthritis, and gout. Tendinitis is often caused by prolonged physical activity, sprains and sprains.
Symptoms and Treatments for Wrist Pain
The clinical picture depends on the disease that causes pain in the wrist joint. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment with the help of additional research.
Injuries
Injuries to the wrist joint include: bruises, sprains, dislocations and fractures.
Injuries occur when a joint is impacted by a heavy, hard object due to a blow or fall. Their symptoms are similar:
- with a strong blow, a sharp pain in the wrist may appear, radiating to the fingers;
- swelling;
- moderate or complete restriction of movement in the joint;
- hematoma or hemarthrosis may appear;
- pain on palpation;
- joint deformation.
If an injury occurs, immediately provide first aid and consult a doctor.
First aid:
- Immobilization of the hand with bandages or improvised means.
- If the wound is open, stop the bleeding.
- Apply cold to the damaged area (every half hour for 10 minutes to prevent hypothermia) to relieve pain and relieve swelling.
- Deliver the patient to a medical facility.
After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment for the wrist. For dislocations and fractures, a plaster cast is applied and medications are prescribed. The recovery period is accompanied by physiotherapy and exercise therapy.
Arthrosis
Arthrosis often occurs in older people due to degeneration of cartilage tissue. It can also be a consequence of injury. Symptoms of arthrosis:
- wrist pain when flexing and extending the hand with a characteristic crunch (then occurs at rest);
- pain on palpation.
In the treatment of arthrosis, drugs are prescribed - chondroprotectors, which help slow down the processes of degeneration of cartilage tissue. Kinesiotherapy, physiotherapy and massage have a positive effect on recovery.
Arthritis
Inflammation of the joint capsule can be caused by various factors: infectious, metabolic, autoimmune. Arthritis causes severe pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joint.
Treatment of the disease depends on the cause. After diagnosis, additional studies and tests, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment measures.
De Quervain's disease (tenosynovitis)
De Quervain's tenosynovitis is an inflammation of the tendon sheath of the 1st osteofibrous extensor canal. Develops with frequent similar movements of the hand (for example, in loaders, skiers, pianists). Characteristic symptoms of tenosynovitis:
- pain occurs when moving the hand and thumb, sometimes radiating to the elbow;
- pain on palpation in the area of the styloid process.
For tendovaginitis, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. They are used both internally and locally. Physiotherapeutic procedures are also recommended. In case of chronic disease, surgery is prescribed.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome appears due to compression of the nerve during the same type of work (for example, in people who work at a computer or as machinists), due to hormonal disorders. Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- pain spreading along the palmar surface of the hand and wrist;
- tingling and numbness;
- Sometimes my fingers hurt.
In case of tunnel syndrome, it is recommended to consult a neurologist or orthopedic traumatologist. Treatment is carried out using anti-inflammatory drugs (orally and locally), B vitamins and nicotinic acid (injections). In severe cases, surgical intervention is indicated in which the carpal ligament, which compresses the nerve, is dissected.
The structure of the human hand
The human hand has a very complex and very non-trivial structure.
It consists of the following parts:
- Skeleton of the hand , which gives strength to the limb.
- Muscles with bones connecting tendons . They make the brush flexible and quite elastic.
- Tissues of the human hand , nourished with the help of the vessels located in them.
- Nerves that are responsible for the reflex response to the action of the environment. They increase sensitivity and contract the hand muscles.
- The skin has the property of protection, but it also draws boundaries between the human body and the external environment and maintains the temperature in the body.
Skeleton of the hand
The human hand includes 27 small bones .
Sections of the hand:
- Fingers . The hand includes 4 fingers, which consist of 3 phalanges, and there is also a thumb, consisting of two phalanges.
- Pastern . This is the part of the hand that is located between the fingers and the wrist. It consists of five small bones, oblong in shape.
- Wrist . This is a system that consists of 8 bones connected by ligaments.
Carpal bones:
- Trapezoid.
- Scaphoid.
- Hook-shaped.
- Lunar.
- Trapezoidal.
- Capitate.
- Pisiform.
- Triangular.
The bones that make up the hand section are quite small, but this feature allows the hand to maintain its flexible and stable properties.
Muscular apparatus
Muscles are the main factor that helps move human bones. If we talk about those that are in the hand, they are located on both sides through layers. This is necessary for flexion and extension of the palm. With the help of tendons, muscles are attached to the bone apparatus. Ligaments or tendons attach to the base of the bone. Only the palm consists of muscles.
Subdivisions of the muscles of the palmar part:
- Average.
- Thumb muscle.
- Small finger muscle.
Short muscles result in clear and precise movements of the arm, but at the same time greatly complicate its structure.
Leather
The skin here is very heterogeneous. In some places it covers the skeleton with a more delicate layer, and in others with a rougher one. The palm contains thickened skin, but the back side is thinner. All this is due to the fact that the palm itself more often endures various frictions and contacts with the outside world, therefore a thicker version of the skin helps protect muscle tissue.
As for the back part, it contains many sweat and sebaceous glands. Collagen and elastin help give the skin elasticity and firmness. But these proteins tend to be destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Signs such as dry skin of the hands, wrinkling, the appearance of small cracks, all this indicates a decrease in collagen and elastin in the skin of the hands.
Diagnosis of wrist pain
To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Sometimes one diagnostic method is enough, and in some cases it is necessary to use a complex of studies. Diagnostic methods:
- blood analysis;
- radiography;
- joint puncture;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- CT.
If you experience pain of any kind in your wrist, the first thing you should do is consult a doctor. The main principle of treatment is to eliminate the cause of pain. You cannot treat yourself, as you can make a mistake in the diagnosis and aggravate the course of the disease.
| Hand surgeon | To the list of articles | History of carpal tunnel syndrome |
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
A doctor should be contacted immediately if a person experiences symptoms such as:
- Loss of sensation in fingers.
- Painful sensations persist for several days.
- After putting pressure on the arm, the pain becomes stronger.
- The wrist is deformed.
- Swelling or thickening forms in the affected area.
- The person cannot move the limb.
- The pain gets worse when you move your arm.
- When you try to move the brush, you hear a crunching and squeaking sound.
Video of normal hand bone anatomy
The English word “wrist” is etymologically derived from the Old High German word wristiz, from which modern German rist (“instep”, “wrist”) and modern Swedish wrist (“lift”, “knuckle”) are derived. The stem writh- and its variants are related to the Old English words “wreath,” “wrest,” and “squirm.” The sound of this base apparently originally symbolized the action of twisting. During the evolution of man, in connection with his professional activities, the bones of the wrist moved forward in their development. Thus, in Neanderthals the length of the cephalic bone was 20-25 mm, and in modern humans it increased to 28 mm. There is also a strengthening of the wrist region, which is relatively weak in apes and Neanderthals.
Hand bones
At first there is slight discomfort in the wrist, then sharp pain in the tendons. Symptoms appear mainly during active movements; they decrease during rest. The skin on the affected area is swollen, red, and warmer to the touch than the rest of the epithelium. A crunching sound is heard when bending the wrist. Carpus, a set of small bones in the five-fingered forelimb (q.v.) of vertebrates, adjacent to the forearm on one side and the metacarpal bone on the other. Z. in its most complete form consists of two rows of bones. The first row contains the radius, ulna, intermediate and two (rarely three) medial bones, and the second row contains five bones called carpals. In human anatomy, radiale = scaphoideum; ulnare = triquetrum; intermedium + centrale 2 = lunatum; centrale 7 = centrale; carpale 7 = trapezium s. multangulum majus; carpale 2 = trapezoides s. multangulum minus; carpale 3 = capitatum; carpale but 4 + 5 = hamatum.
…. watch
Structure of a human hand
Point 8 usually affects the digestive system and is useful for problems with indigestion, bloating, and constipation. The dot in the center of the palm, next to the number eight, is a general indicator of health. With stronger pressure, a distinct sensation of pain occurs - a sign of internal disease. Perhaps we are dealing with some kind of hidden inflammatory process or metabolic disorder. Note: the nerve endings on the fingers are so sensitive that if you cut the surface layer of the skin with a piece of paper, the receptors react violently to the air, and the person feels pain stronger than when cut with a knife.
Possible diseases and pathologies
The ulnar and radial arteries pass from the forearm to the hand, then descend through the wrist joint to the palm and dorsum of the hand, forming deep and superficial arches. At the dorsum, the vein divides into four metacarpal arteries, and then each divides into two more digital arteries, which pass through the fingers to the nails. A network of small capillaries supplies blood to the fingers. The abundance of branched blood vessels protects the fingers from severe blood loss when the hand is injured. Thus, the thumb is responsible for the lungs, bronchi, liver and heart, the index finger is for all digestive organs, the middle finger is for the circulatory system, the ring finger is for the nervous system, and the index finger is for the kidneys and small intestine. These areas can be used to stimulate certain processes using massage, pressure or acupuncture. In humans, the wrist consists of two rows of small bones (4 in each). Increases hand mobility... Watch The wrist is covered with thin skin. Each bone is covered with protective tissue. In the central part of the joint there is a large cartilage. It is necessary for shock absorption and arm rotation. It softens the blow and protects the bones from wear. Additional cartilage provides maximum articulation of the wrist elements. In its depths, protected by soft tissues, there are nerve fibers.
Ligaments and joints
For problems with the digestive tract, liver and pancreas, prepare a decoction. To do this, take 50 g of crushed cinquefoil roots. Pour 250 ml of boiling water and keep in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then leave for 2 hours, strain and take 50 g daily in several doses. The product should be drunk fresh daily. The wrist has a complex structure. The palm of the hand resembles a boat, concave inward. The back side is slightly convex and articulated. The wrist consists of eight small, irregularly shaped bones arranged in two rows. Compared to other structures of the wrist, there is no radial structure.
Characteristics
Creative, highly sensitive, emotional and hypersensitive. Lives by feelings and intuition. Can do light physical work, but does not tolerate heavy work. They cannot stand stressful situations, haste, or competition. They feel comfortable in a safe environment. It is important to learn to control emotions and avoid apathy and depression. Cultivate self-confidence and willpower. Loses and gains weight easily, metabolism is quite fast. They may suffer from endocrine disorders, as well as mental illness and sleep disorders. Health in general depends on the emotional background; during times of stress, the immune system is seriously affected. They are susceptible to viral infections. It is worth spending more time in nature, running, swimming, cycling, dancing, doing yoga and all other aerobic activities.