Good afternoon, dear readers. In anatomy classes at medical universities, the structure of the hand is sometimes missed (or just lightly mentioned). Also, in some departments there are no high-quality specimens of the human hand at all.
Of course, this state of affairs cannot please me - as you know, I am a big fan of fundamental medicine. That is why I decided to analyze the structure of the bones of the hand clearly and in detail, so that no one would have any confusion in this difficult topic.
By the way, the hand is the most mobile part of the human body. The development and complication of the anatomy of the hand played an important role in the formation of homo sapiens as the most developed species of living beings on the planet. People have access to the most complex surgical procedures, virtuoso playing of musical instruments and the creation of real masterpieces of fine art.
Let's find out what this amazing tool - the human hand - consists of and look at the structure of the bones of the hand.
Wrist coordinates
Simply put, the wrist is a set of bones that are located in the crook of the arm between the hand and forearm. This is a joint, not very large in size, surrounded by many tissues, tendons and ligaments.
More precisely, it is located between the radius and ulna bones and the metacarpal bones, as shown in the photo.
Pastern:
The wrist has eight bones in total. This:
- Hook-shaped.
- Capitate.
- Trapezoidal.
- Trapezoid.
- Pisiform.
- Triangular.
- Lunar.
- Scaphoid.
Ligaments of the palms are attached to all bones except the pisiform. A bit boring. In general, the function of the wrist is to ensure mobility of the hand in a certain plane.
Lexical minimum
As always, I'm posting a list of all the Latin terms I used in this article. This is for those readers who continue to learn Latin after the basic set of words from my first three lessons (first, second, third).
- Manus;
- Сarpi;
- Metacarpi;
- Ossa digitorum;
- Os scaphoideum;
- Os lunatum;
- Os triquertum;
- Os pisiforme;
- Os trapezium;
- Os trapezoideum;
- Os capitatum;
- Os hamarum;
- Ossa metacarpi;
- Ossa digitorum.
Wrist injuries
Typically, the wrist is injured when a person falls onto a straight arm. This somersault threatens to fracture the ulna and the end of the radius.
Due to the fact that the wrist performs an important daily mission, serious medical intervention is necessary.
Quite a lot of fractures are accompanied by dislocation of several fragments, which is a direct indication for surgical intervention.
When falling, the scaphoid bone is most often affected. Long-term treatment is required for complete recovery. In addition, this fracture is quite difficult to diagnose at the initial stage. Also, all this is fraught with sprained ligaments, which is also not a problem due to their extremely complex structure.
The meaning and functions of the hand bones
The bones of the hands perform key functions in the human body.
The main ones are:
- container function;
- protective;
- supporting;
- motor;
- anti-gravity;
- mineral metabolism function;
- hematopoietic;
- immune.
It has been known since school that the human species evolved from primates. Indeed, human bodies anatomically have much in common with their less developed ancestors. Including the structure of the hands.
It is no secret that during the course of evolution the human hand has changed due to labor activity. The structure of the human hand is fundamentally different from the structure of the hands of primates and other animals.
Bone marrow
As a result, it acquired the following features:
- The tendons of the hand, as well as nerve fibers and blood vessels, are located in a certain groove.
- The bones that form the thumb are wider than the bones of other fingers. This can be seen in the figure below.
- The length of the phalanges from the index finger to the little finger is shorter than in primates.
- The bones in the hand, located in the palm area and articulated with the thumb, have shifted towards the palm.
Comparison of the human and primate hand
Preventing Wrist Injuries
Warm up and warm up the wrist:
- Massage the base of the palm.
- A simple pull-up on a horizontal bar with any grip greatly strengthens your wrists, along with general physical training.
Any physical work with your hands: chopping wood, digging potatoes, hand washing have a general strengthening effect.
- In a sitting position (preferably), take dumbbells and place them on your knees, palms up, so that you can make flexion movements with your hand.
- A good old rubber expander (donut). Start with a soft one, gradually moving to a harder one.
- Push-ups. Preferably with fists. Better with bouncing.
- Get on the floor in doggy style. Palm rest. Start swinging in different directions without lifting your palms from the floor. Amplitude to the maximum of your capabilities.
- Yoga, Pilates.
Physical exercise is important in itself, because other muscles and tendons will be included in the training complex. Now you know where the wrist is. Take care of yourself, be healthy!
Anatomy of the human hand muscles and ligaments. Knowledge is the root of success
Knowledge of human anatomy will certainly help an athlete consciously achieve planned results. And work specifically on muscle configuration. Here we must remember that body architecture should be studied in a complex manner, evenly paying attention to all muscles. Then you will achieve a harmonious texture.
Therefore, bodybuilders have not only the goal of their work in the gym, but also a consistent pattern of exercises, which muscles and how to pump them up, and with what tools. Muscle complexes for individual training are outlined by training days, since we all differ in our constitution.
If we look at the muscles of the right and left arms, so to speak, in cross-section, we will see bundle-shaped fibers that are divided into:
- anterior, superficial, and
- rear, deep.
Flexor and extensor muscles of the shoulder and forearm. Each has its own names. Those responsible for flexion movements are called:
- shoulder;
- two-headed;
- coracobrachial.
And the second row of responsibility is for the extensor muscles -
- ulna;
- triceps.
Most of all we talk about biceps, triceps, deltoids. These are the superficial muscles of the human arm.
The biceps is a biceps muscle, one head is long and the other is short. Thanks to it, the upper part of the arm bends, the palm and shoulder rotate.
The three-headed muscle, called the triceps, starts from the back, or rather from the shoulder blade, and extends to the elbow. With the help of this muscle, the arm bends and extends at the elbow joint and shoulder.
The forearm is represented by the following muscles:
- brachialis;
- coracoid;
- flexor carpi radialis;
- brachyradialis.
They also relate to the elbow, forearm rotation, finger extension, and drawing the arms toward the chest. By imagining how these muscles work, you understand more clearly what equipment and exercises you should choose to strengthen your arms.
What structures can become inflamed in the wrist?
The wrist has a complex structure, so the process of inflammation can begin in any area. Moreover, some diseases will subsequently become local, while others will spread to the surrounding tissues.
Inflammation of structures in the wrist
- The bones of the wrist tend to change pathologically, which occurs when their structure is damaged, namely, with dislocations, sprains and fractures. Next, osteoporosis develops, in which the quality of bone tissue decreases.
- The wrist joint becomes inflamed due to various types of injuries, which cause dislocation of the joint itself and damage to its structure. Very often the disease osteoarthritis develops here.
- The synovium of the wrist joint usually becomes inflamed with synovitis or arthritis, which occurs with fractures and injuries to the wrist.
- The ligaments of the wrist joint are a very common case in which they are damaged. All this occurs under large, excessive loads.
- The vessels and nerves of the wrist become inflamed, undergoing pathological changes, during prolonged work with an uncomfortable hand position, as well as with heavy loads. Very often, in this case, carpal tunnel syndrome develops.
Diseases
Throughout his life, a person experiences enormous stress on his hands . All its main departments are connected here. Pain in the areas of the hand or wrist may indicate diseases of the articular system or diseases of the internal organs of a person. Such symptoms often occur when this part of the arm is injured. If a person has damaged the wrist, he will immediately feel a sharp pain, which will subside over time, but the movements of the hand will be limited. All this is accompanied by painful sensations.
The result of dislocation of the phalanx of the finger is swelling, bone deformation, sometimes pronounced, as well as decreased functionality of the finger. If a fracture of the hand occurs, then large swelling occurs, the crunching of fragments is heard, which causes pathological mobility and limited movement.
Injuries are treated with a variety of methods. This can be a conservative treatment, which consists of restoring the functionality of the damaged part, but with the help of an orthosis or plaster, massage, and physical procedures. Sometimes surgery is required. It is prescribed for serious fractures. There are other hand diseases:
- Tendinitis.
- Osteoarthritis of the hand joints.
- Tunnel syndrome.
- Aseptic necrosis.
Tendinitis
This disease manifests itself as a result of the same type of movements, which can constantly appear in a person’s hobby or even in his occupation. The pain is initially not expressed, but then acute pain appears. Experts recommend eliminating stress on the arm and keeping it at rest until the pain goes away. Next, you should take warm baths and perform special gymnastics.
Osteoarthritis of the hand joints
This disease has many causes. It can also occur with poor nutrition, when metabolism is disrupted, and with various types of fractures, especially when bones do not heal properly.
All this is accompanied by pain in the hand area. They occur when a given part of the body is stressed, or when the disease steadily progresses, pain is experienced even in a state of inactivity. With this disease, fine motor skills of the hands deteriorate significantly. Arthrosis is treated with complex therapy, which is carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
This disease occurs when the median nerve is pinched. This occurs when playing musical instruments for a long time, as well as when working at the computer.
The signs are:
- Periodic numbness of the hand.
- Painful sensations.
- Limited finger mobility.
With this disease, a person must change his occupation, as well as undergo therapy that is aimed against inflammation. In rare cases, surgical intervention is also required.
Aseptic necrosis
The causes of this disease are frequent fractures of the arm or inflammation. The disease is serious, which gradually affects the muscles and bones of the wrist. This area of the body has poor blood supply, so the tissue may die over time. Inflammation occurs here, this place is accompanied by pronounced pain and swelling. Very often it is necessary to correct the problem through surgery.
Anatomical parts of the hand
The entire hand as a whole includes the following sections.
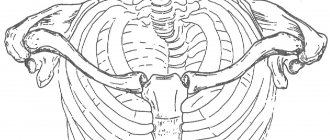
Shoulder girdle, consisting of parts:
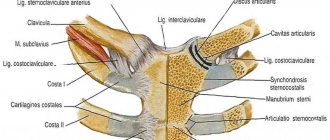
- The scapula is a predominantly flat, triangular-shaped bone that provides articulation between the collarbone and shoulder.
- The clavicle is a “tube” shaped bone, made in an S-shape, connecting the sternum and scapula.
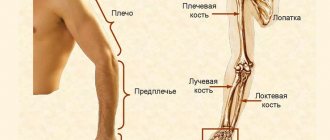
The shoulder itself, which contains the humerus - a long tubular bone that serves as the bony base of the shoulder.
Forearm, including bones:
- The radius is a paired bone of a part such as the forearm, resembling a trihedron.
- The ulna is a paired bone located on the inside of the forearm.
The hand contains bones:
- Wrist.
- Metacarpus.
Structure of the hand
Shoulder structure
The main movements of the arms are performed by the shoulder joint.
It contains two main bones:
- The humerus, a long tubular bone, serves as the basis for the entire human shoulder.
- The scapula bone provides the connection between the clavicle and the shoulder, while it is connected to the shoulder by the glenoid cavity. It is quite easy to detect under the skin.
Bones of the shoulder girdle
From the back of the scapula you can see the spine, which divides the bone in half. The so-called infraspinatus and supraspinatus muscle clusters are located on it. Also on the scapula you can find the coracoid process . With its help, various ligaments and muscles are attached.
The next arm bone to the scapula is a tubular, curved bone called the clavicle. Flexion and extension of the arm, as well as other movements, are performed by a muscle called the rotator cuff.