The back is often susceptible to various injuries, especially the lumbar region. After all, the lower back bears most of the load. Despite the fact that the vertebrae in this section are thicker and the muscles are stronger and stronger, sprains and bruises often occur, which lead to temporary loss of mobility and pain. In any case, even the slightest bruise of the lumbar spine can cause inconvenience, so you need to know how to correctly classify a bruise and how to treat it.
Where is the sacrum located?
Many people cannot pinpoint where the 4th spine is located. Most people confuse pain in the sacrum with discomfort in the lower back and tailbone.
The sacrum is located just below the lumbar region. Visually you can see a characteristic bend bending inward. Upon palpation, it is easy to identify the protrusions on both sides of the spine - these are the so-called “wings” of the pelvic bones.
On women, they look like attractive dimples on the cheeks. The 4th section of the spine begins in this area and ends at the junction of the buttocks.
General information
By bruise of the lower back we mean a closed form of injury in which there are no open wounds or ruptures of muscle, ligamentous, and tendon structures.
Experts divide the disease according to the complexity of its course:
- Mild form – soft tissue damage and hematoma formation are observed. There are no neurological disorders, no problems with the movement of the lower extremities, sensitivity is preserved.
- Medium form – the sensitivity of certain areas in the lower back decreases. The peculiarity is associated with the conductivity of the spinal cord - sections are affected, the innervation of which depends on the bruised part.
- Severe form - there is an absolute lack of sensitivity below the injured area of the spinal column. In some cases, neurological pathologies cannot be treated.
Sacral contusion: causes of injury
Injury from a fall on the sacrum can occur at any age. Such injuries occur even in children, but at this age the injury is not considered particularly dangerous. But when an adult loses consciousness, the consequences can be very serious.
The main cause of a bruise is a person falling or a strong blow to the sacral region. In practice, more of this pathology is observed in:
- athletes; parkourists;
- service technicians and construction workers;
- disabled people walking on crutches;
- overweight people;
In particular, no one is immune from bruises. Injuries can occur as a result of an accident, accident, or other unforeseen situations.
Sacral contusion: symptoms
After an injury, pain occurs not only in the sacrum, but pain spreads to the legs and lower back. When examining the patient, the following symptoms are revealed:
- Hyperemia of the skin in the sacral area;
- presence of hematoma;
- throbbing sensation of pain when pressing on the lower spine;
- the appearance of swelling at the site of the injury;
- painful sensation when walking;
Symptoms of a sacral injury appear almost immediately. If you do not see a doctor in time, this condition can lead to serious troubles.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures directly depend on the complexity of the disease.
In mild forms, treatment takes place on an outpatient basis, using certain medications:
- NSAIDs - drugs against inflammation and pain are prescribed in the form of local medications: Diclofenac, Ketorol, Naise;
- Analgesics - used to reduce pain: Analgin, Tempalgin, Baralgin.
Patients are advised to reduce physical activity to reduce the load on the muscle tissue of the lumbar spinal column. Restrictions apply to walking, bending, carrying heavy objects, and sudden body movements.
In severe forms, the patient is sent to the hospital. Glucocorticoid drugs are added to painkillers to reduce swelling and inflammatory reactions: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone. After completing the main course of drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed: magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, laser therapy.
In the absence of obvious contraindications, massage and physical therapy sessions are prescribed.
Emergency measures
If a back injury occurs and it is impossible to visit a medical facility, you must follow the primary care algorithm:
- Immediately after the injury, a heating pad with ice or a bag of frozen food pre-wrapped in cotton cloth is applied to the problem area. The duration of each procedure does not exceed 20 minutes - to avoid frostbite. Manipulations are carried out within the first 72 hours.
- Maintaining bed rest - it is better to spend several days in bed, avoiding sudden attempts to change body position or bend over. All movements must be made at a slow pace.
- A hard surface is the preferred resting place after a lower back injury. To reduce pressure, you should place a small soft cushion, about 5 cm in volume, under the damaged area. The device will help you relax your back and avoid additional muscle strain.
- After three days, the cooling procedures end, the sore spot is warmed up with an electric or water heating pad. Anti-inflammatory ointments are applied to it: Finalgon, Fastum-gel, Biofreeze.
If there is no positive dynamics within three to five days, a consultation with a traumatologist is necessary.
Possible consequences
Complications arise in the absence of professional help or ignoring prescribed therapy. The main consequences include:
- absolute or partial paralysis of the lower limbs;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs;
- problems with normal bladder emptying;
- decreased libido - in both sexes;
- paresthesia in certain anatomical areas.
If there are severe problems with the spinal column, the victim’s gait may change; he begins to move with a transfer of body weight from one leg to the other. The movement resembles the movements of a duck.
Bruised sacrum: first aid
In the first minutes, it is important to provide first aid to a person who has sustained an injury to the sacral spine. With the right approach, you can reduce the risk of any complications.
The victim should apply a cold compress to the injury site.
The steps are as follows:
- The patient should be in a horizontal position on his side or stomach. The position will be chosen depending on how comfortable the patient feels.
- Apply a cold object to the bruise.
- Try to keep all traffic out of the affected area.
This action can free the sacrum and, in the event of a fracture, prevent displacement of the fragment. Cold effectively slows down tissue reactions, relieves pain and relieves swelling.
Sacral contusion: diagnosis
In order to detect a sacral injury, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination. During the examination, the doctor determines the consequences of the injury and looks for the best solution to the problem.
Visual inspection and palpation of the sacrum and adjacent areas of the body can exclude the presence of a fracture and other types of injuries. To make an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray of the lumbosacral region is taken in two projections.
If after the x-ray there is still a suspicion of a fracture, the doctor will refer the patient for a CT scan.
Medicines:
- Ointments and gels for external use with a warming or cooling effect.
- NSAIDs can be prescribed in the form of tablets for oral administration, rectal suppositories, and creams for external use.
During pregnancy, treatment of injuries to the sacral spine becomes extremely problematic. This is due to the fact that many drugs are prohibited for use. There is a possible risk of harm to the unborn child.
It is important to know that a hematoma formed in the area of a bruise cannot be opened at home; an abscess may form in the wound due to infection. Swelling at the injury site usually goes away on its own within 24 hours. If the hematoma does not disappear, it is opened only in a hospital setting.
Additional treatment methods include:
- Physiotherapy. During their use, the regeneration of the healing process is accelerated, preventing the risk of pathological growths.
- Therapeutic gymnastics restores the mobility of the limbs and strengthens the muscles.
Physiological procedures for bruised sacrum accelerate healing and restore mobility
Follow all your doctor's directions. Increased load during rehabilitation is very undesirable. Just sleep and lie on your stomach. Sit on an orthopedic pillow.
When complex pathologies are identified during diagnosis, surgical treatment is performed. In most cases, surgery involves either releasing the pinched nerve or opening the hematoma.
Difference from fracture
A lumbar bruise can easily be confused with a fracture, although both types have certain differences in symptoms. When the integrity of bone tissue is damaged, the following is observed:
- non-standard mobility of joints in the problem area;
- inability to bend or turn the lower back;
- the pain syndrome intensifies not only with movements, but also increases over time - when muscles contract, bone fragments are affected and displaced;
- hematomas and swelling increase gradually, over the course of one day.
Serious fractures of the spine provoke a complete loss of sensitivity of the body located below the line of trauma.
With a bruise in the lower back, all of the above symptoms are less severe, starting from the third day, swelling and bruising disappear on their own, and motor activity is restored.
Complications
A bruise to the sacrum can cause certain complications, which may manifest as:
- fracture of the sacrum or adjacent bones;
- spine fracture;
- dislocation of adjacent vertebrae;
- rectal bleeding;
- urinary incontinence;
- damage to genital and internal organs;
- pinched nerve roots.
- spinal cord injuries;
- leg paralysis;
It is important to consult a doctor in time and exclude all possible complications. Even if the patient does not experience obvious symptoms after the fall. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment that will prevent the development of further consequences.
Necessary examinations
The surgeon or traumatologist carries out a number of diagnostic measures.
- Survey. The patient's complaints and the circumstances of the injury are clarified. The general clinical history is studied.
- Clinical examination. The presence of hematomas and edema is detected. In some cases, it is necessary to consult a neurologist who will evaluate the reflexes of the lower extremities, tactile and temperature sensitivity of the damaged area.
- X-ray. The diagnostic procedure allows you to assess the condition of the spine, identify its deformation, exclude or confirm the presence of fractures or cracks of the vertebral bodies.
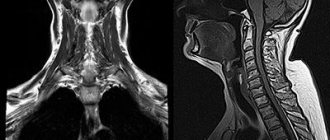
- MRI, CT. Allows you to examine in detail the intervertebral discs, nerve roots, assess the level of soft tissue damage and the degree of injury.
Based on the results of the examination, the tactics of further therapy are determined.
MRI of the lumbar region
Prevention
There are many ways to protect yourself from injury.
- If a person has fallen more than once, he should learn to do it correctly. If you fall, you should squat, pressing your arms to your body and pressing your palms to your stomach. If you feel like you're falling on your back, try turning around and falling on your side.
- It is not recommended to wear high-heeled winter boots. When buying shoes, pay attention to the sole of the shoe so that it does not slip and the heel is stable.
- You should play sports and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Eat healthy.
- Always try to strengthen your immune system.
When walking you need to be careful and look at your feet. Only caution and vigilance can prevent a fall.