Each of us has suffered from headaches in one way or another. Headaches have different localization and intensity, are accompanied by other symptoms, and have an acute and chronic course. As a rule, such pain is not a primary disease, but develops against the background of other pathologies of various etiologies.
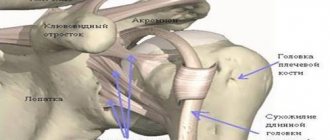
One of the etiological causes of headaches is cervicocranial syndrome or cervicocranialgia. This pathology is classified as a neurological symptom, which is expressed in the presence of chronic recurrent pain in the patient in the occipital region and neck area. Often occurs in people over 60 years of age. It can be a consequence of head and neck injuries, including traumatic brain injury, as well as the result of a number of diseases of the spinal column.
| Avenue G Flickr |
Among the etiological causes of the development of cervicocranial syndrome, it is customary to distinguish the following:
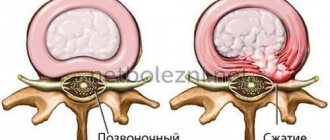
- protrusion or hernia of the spinal column;
- osteochondrosis;
- arthritis of various origins (rheumatoid, psoriatic, reactive);
- benign or malignant neoplasms;
- history of meningitis and/or brain abscess;
- hypertension;
- hemodynamically significant narrowing of the carotid arteries and branches;
- muscular dystrophy;
- various pathologies of skeletal bones, etc.
All pain in cervicocranial syndrome is caused by impaired cerebral circulation, which occurs for various reasons. Thus, it can be argued that this disease is not a primary, but a secondary pathology that accompanies various changes in the patient’s body. The nature of pain directly depends on the underlying disease and can be variable in nature, frequency and intensity.
Symptoms
As a result of spasm of the vertebral arteries passing in the transverse processes of the vertebrae at the cervical level, dizziness may occur. Headaches in the occipital region and neck pain appear gradually over several years. The pain is provoked by sudden turns of the head and prolonged uncomfortable position. Symptoms may worsen over time and become permanent. Patients may also be bothered by noise or ringing in the ears and/or head, dizziness, numbness of the skin of the face and neck.
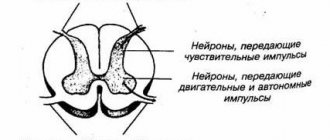
An objective examination of the patient reveals a general cerebral syndrome (80%), pain on palpation of paravertebral points and spinous processes in the cervical spine, pain and tension in the cervical-occipital muscles (70%), limited range of motion in the cervical spine (70%). In 50% of cases, trigger points are identified in the neck muscles.
Causes of the disease
Even an adult cannot withstand the stress that a newborn experiences. Due to the softness and flexibility of the bone structures, displaced vertebrae gradually return to place, reducing the risk of developing birth trauma. However, during the birth of the baby, there is a danger of damage to the vertebral arteries. This occurs when the baby's shoulders and head emerge. At the same time, the obstetrician-gynecologist tries to protect the perineum of the woman in labor.
Turning the head can cause displacement of the vertebrae along with the arteries. This is the cause of serious consequences. This pathology is provoked by squeezing the baby due to muscle tension of the mother.
We advise you to study – Pilonidal hernia
Breech presentation of the baby creates additional difficulties when removing the head from the birth canal. There is a risk of fetus getting stuck, which will lead to displacement of the vertebrae.
Diagnosis of cervicocranial syndrome
- Dopplerography of neck vessels.
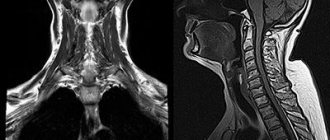
- X-ray of the cervical spine (degenerative-dystrophic changes).
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine (manifestations of osteochondrosis).
Differential diagnosis:
- Cervicocranialgia caused by herniated intervertebral discs.
- Cervical migraine.
- Vertebral artery syndrome.
- Neuralgia of the occipital nerve.
- Craniovertebral anomalies.
| Trigger points in the neck muscles |
Most common problem
Cervical radicular syndrome is the most common
The most common is, of course, cervical radicular syndrome, the symptoms of which are quite unique. Naturally, the main manifestation is pain, which most often appears in the neck area. But pinching of a nerve root in this area can affect itself in a rather unexpected way; pain can appear quite far from the lesion.
So, pain may appear in the lower back and limbs. But the most unpleasant thing is that this pain syndrome can quite successfully imitate the pain that is characteristic of diseases of some internal organs.
So, sometimes there is quite severe pain in the heart area, which is characteristic of angina pectoris. But at the same time, drugs for the corresponding disease help little, or turn out to be completely ineffective.
However, an experienced specialist will always understand the situation, since the pain has a slightly different nature. So, with angina pectoris, the pain is usually paroxysmal, and it does not last long, only a few minutes. But with radicular syndrome, the pain lasts for hours, or even days on end.
Also, with such a problem, you can encounter pain in the stomach, which quite accurately imitates a peptic ulcer, and in this case the imitation is much more “reliable”. The only difference is that the pain does not subside after the use of anti-spasm drugs, which are supposed to reduce the pain of a peptic ulcer.
Treatment of cervicocranial syndrome
Treatment: analgesics, physical therapy, exercise therapy, drug blockades, wearing a Shants collar. Prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
| 1 | Diclofenac sodium (Voltaren, Diclofenac, Diclonate P) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with an analgesic effect. |
1. Enteric-coated tablets
Start of reception
It is recommended to take the drug immediately after the first symptoms of the disease. The duration of treatment depends on the overall clinical picture and the dynamics of symptoms (usually the course of treatment is several days). In the absence of severe pain (in mild cases of the disease), you should start with a dosage of 75-100 mg per day. In more complex cases, a dose of 100-150 mg per day is recommended.
How to use
The drug must be taken in several doses (each time before meals). Swallow the tablets whole with liquid. For severe night pain or morning stiffness, supplement treatment with diclofenac in the form of a suppository (take before bed).
Dosage (amount of drug per day)
| maximum | 150 mg |
| initial | from 50 to 100 mg |
| for rheumatoid arthritis | increase by 3 mg per kilogram of body weight |
| during the menstrual cycle | increase to 150 mg |
| with primary dysmenorrhea | determined individually (usually about 50-150 mg) |
For children
For children weighing ≥ 25 kg, give the drug in two or three doses, depending on the severity of the disease, at a rate of 0.5 to 2 mg per 1 kilogram of body weight (per day).
2. Extended-release film-coated tablets
Dosage
An initial dose of 100 mg (or one extended-release tablet) per day is optimal for initiation, as well as for the treatment of relatively mild cases of disease or long-term therapy.
How to use
Take the medicine with food, swallowing the tablets whole. If pain is severe in the morning or evening, it is recommended to take pills at night.
For children
Extended-release tablets should not be prescribed to children.
4. Rectal suppositories
Start of reception
You should start with a dose of 100-150 mg per day. The drug should be taken immediately after the symptoms of the disease appear. For the treatment of relatively mild cases of disease or for long-term therapy, the optimal dose is 75-100 mg per day. The amount of the drug taken per day should be divided into two or three parts and taken, respectively, in two or three doses.
With severe pain syndrome
Additionally, take diclofenac in suppositories. Drink at night before bed. The total daily dose is no more than 150 mg.
Dosage (amount of drug per day)
| maximum | 150 mg |
| initial | from 50 to 100 mg |
| initial for migraine | 100 mg |
| during the menstrual cycle | increase to 150 mg |
| with primary dysmenorrhea | determined individually (usually about 50-150 mg) |
| for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis | increase to 3 mg per kilogram of body weight |
A course of treatment
Individual (several days). The duration of treatment depends on the overall clinical picture and the dynamics of symptoms.
For children
Take two to three times a day depending on the severity of the disease. Dose calculation: 0.5 to 2 mg per 1 kg of body weight for children weighing ≥ 25 kg.
Attention! Children should not be prescribed 50 and 100 mg suppositories.
5. Solution for intramuscular administration
How to enter
Deep injection into the buttock. Inject the drug carefully so as not to get into the nerve or other tissues. The optimal point for administering the drug is the upper square of the buttock.
Dosage
| for migraine | take immediately after the onset of an attack; administer intramuscularly; dosage - 75 mg |
| maximum starting dose | 175 mg |
| daily dose | 75 mg (or one ampoule) |
Treatment of severe cases
Increase the dose to 2 injections per day of 75 mg at intervals of several hours. In this case, the second injection is carried out in the opposite gluteal muscle. You can combine the first injection with disclofenac in other forms (rectal suppositories or tablets). The total dosage of medications is no more than 150 mg.
A course of treatment
No more than two days in a row*.
* You can continue treatment with the same drug in a different form (diclofenac tablets or rectal suppository).
| 2 | Tizanidine (Tizanidin-Teva, Tizalud, Sirdalud) is a centrally acting muscle relaxant. |
| How to use | How much to take | |
| with muscle spasm | inside | 2-4 mg three times a day, for severe pain - an additional 2-4 mg at night |
| with spasticity of skeletal muscles | take three times a day, increase the dosage gradually by 2-4 mg every 3-7 days, it is possible to obtain a good therapeutic effect when taking the drug in a daily dose of 12-24 mg in three or four doses after an equal amount of time | initial recommended dose: no more than 6 mg, maximum dose per day: 36 mg |
| for renal failure | increase the dosage gradually, based on the clinical picture, tolerability of the drug and the effectiveness of its use | initial recommended dose: 2 mg once daily |
How to treat
The approach to the treatment of back diseases, especially those with developed complications, should be comprehensive.
It is important not only to get rid of symptoms, you need to stop degenerative processes and remove their effect on the body. For cervicocranialgia due to osteochondrosis, treatment at home is acceptable.
Typically, when treating osteochondrosis, a number of medications are taken to help relieve pain, as well as manual and physiotherapeutic procedures.
It is also often extremely important to change lifestyle; often the development and course of osteochondrosis depends on a person’s mobility and physical activity. Typically, the treatment of this back disease requires the following remedies and procedures:
Anti-inflammatory and painkillers
They help relieve pain, but do not fight the causes of the disease. Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac and their analogues are usually used. Stronger drugs are prescribed as a last resort; it is possible to use an anesthetic blockade, usually based on Novocaine.
Gymnastics
Treatment of osteochondrosis requires an appropriate level of physical activity; therapeutic exercises should not be neglected. Exercises are usually selected by a specialist; they help strengthen the skeleton, muscles, improve blood circulation and relieve tension. All exercises should be performed without excessive tension; sharp, severe pain should not occur during exercise.
Physiotherapy
Before starting it, consultation with a specialist is required, since it is not allowed in all cases of osteochondrosis. Electrotherapy, laser therapy, shock wave technique and others are usually used. The procedures must be carried out by a trained specialist.
Massage
Physiotherapeutic procedures in the development of cervicocranialgia syndrome may be contraindicated, but massage is permitted. In combination with therapeutic exercises, it helps improve blood flow and prevents the formation of lactic acid accumulation in the muscles. Let's say self-massage at home; acupressure is considered the most complex and effective technique; it can only be performed by a specialist in this field.
Reflexology
This word combines several different techniques, the essence of which is to influence certain points, leading to relief and reduction of pain. Reflexology can only be performed by a well-trained doctor or specialist in the field. The most common methods of reflexology include magnetic therapy, acupressure, electropuncture and others.
Treatment with folk remedies
Of the folk methods, the most effective is warming massage with honey. The cervical area is smeared with honey, then the massage begins. All movements should be smooth, rubbing, and under no circumstances should you put pressure on the spinal column. After the massage, you need to put cling film directly on top of the honey, wrap yourself in a woolen scarf or blanket, after a few hours, remove the compress and rinse off the honey.
For compresses and after massages, it is recommended to use sheep wool. It is believed that its warming effect is most useful for osteochondrosis and will help you recover faster.
It is also important to normalize your sleep and rest patterns, and you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle. You should sleep at least eight hours a day, you need to spend enough time in the fresh air, and it is advisable to eat right. At the discretion of the doctor, additional procedures and medications may be prescribed.
At the discretion of the doctor, additional procedures and medications may be prescribed.
If you follow all the rules for treating cervical osteochondrosis, pain, headaches, and complications of the disease will go away. It is worth considering that this disease usually requires long-term therapy, sometimes it takes quite a long time before the result of treatment becomes noticeable.
Almost every person experiences headaches, but episodic and short-term pain is one thing, and their constant nature is another. In the first case, the treatment is simple - taking a painkiller tablet, and in the other - a mandatory appointment with a doctor, a thorough examination and appropriate effective treatment. One of the most common diseases associated with headaches is cervicocranialgia against the background of cervical osteochondrosis, the treatment of which is prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
We advise you to study - Spinal stenosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Recommendations
A consultation with a neurologist and x-ray of the cervical spine with functional tests are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Possible consequences
With age, cervical insufficiency syndrome in a child begins to progress due to impaired blood supply to the brain. This condition will be expressed in unpleasant symptoms, including:
- rapid fatigue (mental and physical);
- poor performance at school;
- sudden mood swings;
- poor memory;
- sleep disturbance;
- problems with posture;
- enuresis;
- osteochondrosis;
- myopia.
In an infant, injuries to the cervical spine have little effect on motor function, but after a few years neurological problems will become obvious. The consequences of SPCI depend on the location and severity of the injury. Under the influence of provoking factors, there is a risk of developing concomitant neurological diseases.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 18 | 18 | 30 | 36 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 18 | 18 | 30 | 36 |
Main reasons
All reasons that can cause a decrease in the lumen of the artery can be divided into those that are associated with the spine (vertebrogenic) and those that are not associated with the spine (non-vertebrogenic).
The main causes of the syndrome should be indicated:
Weakening and gradual destruction of the vertebral discs in the neck. It can develop as a result of injury or for other reasons.
For example, people who lead a sedentary lifestyle and pay little or no attention to sports and moderate physical activity are more likely to develop “instability” of the vertebrae and, accordingly, cervical syndrome. As a congenital cause, one can name asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries. In the case of such an anomaly, the arteries develop unevenly.
It is not possible to cure it, however, you can live with it all your life and not experience any discomfort. But sometimes it can provoke the syndrome. Birth trauma is another reason for the development of pathology. For example, it may be caused by the fact that the fetus was pulled out of the birth canal with forceps. In some cases, cervical osteochondrosis can also become a provoking factor for the appearance of the syndrome. Tortuosity of the vertebral arteries is one of the reasons. This pathology is dangerous. Because of it, not only the syndrome can develop, but also a stroke. People with such an anomaly are automatically at risk, so they need to carefully monitor their health and lifestyle.
The syndrome on the left side develops much more often than on the right side. This is explained by the fact that this vessel arises directly from the aorta and is more often affected by atherosclerosis.
Features of the pathology
Cervical syndrome at its core is a pinched artery, which leads to disruption of blood flow in it. It is characterized by the following features:
As a result of infringement, which can occur for various reasons, the brain experiences a lack of oxygen and substances necessary for its full functioning. The lesion can affect either one or two arteries at the same time.
As a result of partially blocked blood flow, symptoms begin to appear, which at first make it very difficult to recognize the problem being sought.
If the syndrome is not treated, an ischemic attack and even an ischemic stroke may develop. Other diseases may also occur, since the brain is responsible for the functioning of all organ systems.