Publication date: July 24, 2020
The causes of numbness in the right hand vary. Often this pathology is caused by pathology of the spine, blood vessels, and nerves. The appearance of such a symptom is not always associated with danger to the body. Short-term numbness, especially at night, is often associated with an uncomfortable position at night, during sleep, or with clothes that are too tight. If your hand goes numb often, for no apparent reason, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination to find out the cause of the pathology and eliminate it with the help of a specialist.
- Causes
- When should you see a doctor?
- Prevention
- Expert advice
What to do if your right hand goes numb
Eliminate the temporary cause. With repeated episodes, look for a chronic disease that gives this symptom. Most often it is associated with the musculoskeletal system. It could be:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- scoliosis;
- spondylosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- cervical migraine;
- vertebral displacement;
- other.
Often, people whose work involves computers or playing musical instruments develop carpal tunnel syndrome (compression of a nerve under the influence of monotonous movements).
Vascular disorders
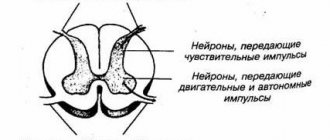
One of the complications of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy, damage to sensory, motor and autonomic nerves as a result of impaired blood flow in small vessels. One possible symptom is numbness in the limbs.
There is a large group of diseases - vasculitis. Autoimmune inflammation develops in the vessel wall, it thickens, becomes weakened, and scarring occurs. In the lumen of the vessel, areas of narrowing appear in which blood flow is disrupted. Various organs, including nerves, can suffer from this.
With one of the systemic connective tissue diseases - Raynaud's disease - a spasm of the small vessels that supply blood to the fingers and toes occurs. In response to cooling or stress, a feeling of coldness and numbness occurs in the fingers.
The right hand is going numb: treatment begins with a neurologist
It is necessary to establish a diagnosis in order to correctly understand what to do. If the right hand goes numb, the doctor, based on the indications, selects a diagnostic method: radiography, MRI, CT, electroencephalogram. The first doctor a patient with these symptoms turns to is a neurologist. Then he may recommend contacting a doctor of another profile (cardiologist, endocrinologist, orthopedist, surgeon) or request their consultation in case of a mixed nature of the disease.
The strategy and tactics of drug correction are aimed at eliminating chronic pathology.
Everyday reasons
Numbness of the right hand very often occurs due to impaired blood flow or pinched nerve. In these cases, as a rule, the symptom appears at night. It can be provoked by an uncomfortable body position, which causes stagnation of blood and lymph in the limbs. To remove discomfort, just change your position and stretch your hand. During sleep, a limb may become numb due to the habit of placing your hand under your head. In this case, you need to change the pillow and try to get rid of the habit.
Other reasons:
- Uncomfortable posture while working.
- Carrying uncomfortable bags or suitcases;
- Occupational activity that requires holding the arms in an upright position.
- Hypothermia
- Physical stress for a long time.
Right arm goes numb: treatment with physiotherapeutic methods
Positive dynamics are achieved by combining physiotherapy with medications. The impact occurs using gentle but effective methods, without side effects (subject to proper prescription).
Center for Progressive Medicine "Doctor Pozvonkov" offers:
- relieving compression load using underwater and dry traction of the spine;
- underwater shower, mud and heat therapy;
- massage;
- administration of medications to biologically active points (pharmacopuncture);
- interstitial electrical stimulation;
- electro- and phonophoresis;
- other.
Physiotherapy can eliminate the causes of numbness or achieve stable remission. They are carried out in a course of 10-15 procedures and provide a cumulative effect.
Diseases of the brain and spinal cord
One of the most common causes of numbness in different parts of the body associated with brain damage is a stroke, as well as a transient ischemic attack, which is popularly called a “mini-stroke”. Severe injuries to the brain and spinal cord can lead to sensory impairment.
Less common are such lesions of the central nervous system as an aneurysm (a pathologically enlarged, weakened area) of a cerebral vessel, arteriovenous malformation (incorrect communication between an artery and a vein, when blood is discharged directly, bypassing the network of capillaries), tumors of the brain and spinal cord, paraneoplastic syndrome ( damage to the nervous system caused by a tumor that is located outside the brain).
The article lists only the main common causes of numbness in the arms and legs. There are others. In order to get an accurate diagnosis and begin proper effective treatment, you need to visit a doctor.
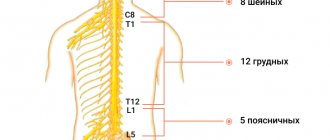
Osteochondrosis or hernia of the cervical spine
Osteochondrosis, disc protrusion, intervertebral hernia, cervical spondylosis (in old age) can cause severe numbness of the hands at night.
Advertising:
These diseases are characterized by degenerative changes in the bone and cartilage tissue of the spine, which lead to compression of the nerve roots.
Nicotinic acid is often included in complex therapy for various diseases. Injections of this drug are prescribed for severe pathologies and are highly effective in maintaining the functioning of the body. Read more in the article: “What is nicotinic acid prescribed for?”
If the cause of the condition is in the spine, numbness is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Crunching and feeling of stiffness in the neck
. This happens when you turn your neck or bend over. - Weakness of hands and arms
. It may be impossible to hold objects in your hands, it is difficult to manipulate small objects - a pen, a needle. - Pain in the neck
, forearm, under the shoulder blade. The nature of the pain is different - pulling, shooting. - Dizziness
. More pronounced with a sharp turn of the head. - Tinnitus
, congestion, hearing loss. - Visual impairment
- “midges” in front of the eyes, blurry pictures.
A neurologist will prescribe an examination to establish a diagnosis: x-ray, computed tomography or MRI of the cervical spine.
Spinal diseases require long-term and complex treatment; in its absence, the development of the disease can lead to disability.
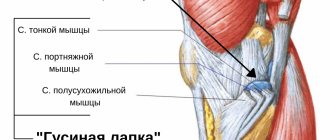
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal or tunnel syndrome is an occupational disease of those specialists who constantly make the same monotonous movements with their fingers or hands for many years:
Advertising:
- pianists;
- typists on keyboards and typewriters;
- cashiers;
- drivers; builders;
- athletes.
The first symptom of the disease is transient short-term numbness of the fingers, tingling or burning. The progressive disease is manifested by aches and pains in the hands and fingers.
The pain may spread to the elbow joints. At night these pains make it difficult to fall asleep. Relief comes from rubbing and rotating the hands. The cause of this pain is pinching or compression of the nerve in the median canal of the wrist. Destruction of the canal itself from mechanical stress, trauma, failure of metabolic and hormonal processes in the body (diabetes mellitus, arthritis, pregnancy) leads to damage to the median nerve.
Prevention of the disease (comfortable workplace, hand exercises during work) will help avoid its development.
The neurologist, after conducting an examination (Tinel and Phalen tests, ultrasound or MRI), will choose the most appropriate treatment: a conservative method or surgical intervention. Sometimes, with such a disease, a person is forced to change his profession and occupation.
Examination for numbness of extremities
- Depending on the suspected cause of numbness in the limbs, the doctor may prescribe different types of diagnostics. X-rays help diagnose diseases associated with disorders of the skull and spine, such as intervertebral hernia. If there is a suspicion of vascular pathology, angiography is performed - an X-ray examination with the introduction of a contrast solution into the vessels.
- If necessary, you may be prescribed other imaging methods: ultrasound, CT, MRI.
- In order to check in which nerves the conduction of impulses is impaired, electroneuromyography is used - a study using special electrodes.
- Sometimes they resort to the method of evoked potentials. Special sensors are placed on the patient's head to record brain activity. The affected nerve is stimulated through the skin using electrical impulses and the brain is observed to respond to the stimulation.
Since dozens of different reasons can lead to numbness in the arms and legs, the diagnostic program must be individual for each patient. In some pathologies, if left untreated for a long time, even more serious, irreversible neurological disorders may occur. Visit a neurologist, make an appointment by phone: +7 (495) 120-08-07
Treatment
For each patient, treatment is developed individually based on diagnostic results and detected diseases. In most cases, they begin by prescribing conservative therapy appropriate to the situation. It may include medication, physical therapy and exercise therapy.
Drug treatment may include drugs from different groups. They are selected based on the causes of numbness in the fingers, but they must take into account concomitant diseases, age and other characteristics of the patient. Typically used:
- NSAIDs - prescribed during an exacerbation of neuropathy to reduce the intensity of pain and eliminate swelling of soft tissues;
- corticosteroids - indicated for severe inflammatory processes, as well as complex neuropathy;
- B vitamins - used to improve the transmission of bioelectric impulses along nerve trunks;
- antiplatelet agents - prescribed to reduce blood viscosity and improve blood circulation;
- calcium antagonists - used to increase the lumen of blood vessels, which is indicated for Raynaud's syndrome;
To increase the effectiveness of drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are often used. The most effective for neurological disorders are:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- UHF;
- electromyostimulation;
- applications with paraffin;
- ozocrete treatment;
- mud therapy.
To eliminate numbness, an individually developed complex of exercise therapy must be prescribed. It helps to develop the joints of the hands, activate blood circulation and relieve muscle tension. As a result, tissue trophism and innervation of the fingers improves. But exercise therapy should be done systematically, devoting the proper amount of time to gymnastics every day.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
Numbness as a symptom cannot be ignored. Sometimes it becomes the first sign of the development of a serious disease. Numbness often accompanies a stroke. Therefore, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist. If numbness occurs frequently, you should contact a neurologist.
When to visit a doctor:
- There is no way to explain why the numbness occurs.
- Painful sensations appear in the forearm, fingers, and neck.
- The urge to urinate becomes more frequent.
- A rash appears on the body or limb.
- Numbness is accompanied by dizziness, muscle dysfunction and other symptoms.
- Large areas of the body are involved in the pathological process.
- Numbness is bilateral.
Which doctor treats hand numbness?
If numbness occurs, you should contact a neurologist. The doctor will examine the patient, clarify his complaints, and evaluate the presence of other neurological signs.
If the doctor deems it necessary, he will refer the patient to other specialized specialists:
- Patients with vasculitis and Raynaud's disease are referred to a rheumatologist.
- People with suspected cardiovascular disease are referred to a cardiologist.
- Patients with diabetes are referred to an endocrinologist.
- Patients with injuries and tumors are referred to a neurosurgeon.
- Patients with infectious diseases are referred to an infectious disease specialist.
- Patients who have been exposed to harmful substances in the workplace are referred to an occupational pathologist.