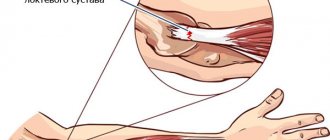
Surely, each of us at least once in our lives has encountered “strange” pain in the forearms after long and monotonous work with our hands in the country or at home, or after carrying a heavy schoolbag on one hand every day to school and back. Moreover, these painful sensations were often combined with another nuisance - an incomprehensible weakness in the hand, which sometimes made it impossible to even bring a cup of coffee or tea to the mouth. If all this is familiar to you, most likely you are faced with the manifestation of epicondylitis. Which means – you have serious prerequisites for visiting a doctor, which should not be postponed!
Properties of NSAIDs for joint pathologies
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory therapy is used not only to relieve the clinical symptoms of ulnar epicondylitis, but also to influence the source of inflammation.
Drugs from this group are characterized by a multifaceted effect - they relieve pain, inflammation and swelling of the joints, activate blood circulation and improve tissue trophism.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a fairly large number of contraindications for use and side effects. The dosage form in the form of an ointment is characterized by greater safety than tablets or injection solutions. This is due to the fact that the drug has an exclusively local effect, penetrating into the systemic circulation in limited quantities.
A doctor should select an ointment for the treatment of epicondylitis, since each drug has disadvantages. The specialist will definitely take into account the presence of contraindications for use in order to prevent the development of complications and adverse reactions.
NSAIDs in any dosage form are strictly prohibited for use by people with cytopenia, severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys in the stage of decompensation, gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer. The period of pregnancy and breastfeeding is prohibited.
Like any drug, anti-inflammatory ointment can lead to an allergic reaction. This is possible if a person has hypersensitivity to the main active ingredient or auxiliary components. The main manifestations are skin rash, itching and swelling at the site of application of the gel. Sometimes severe dryness of the epidermis occurs, which appears immediately after applying the drug.
General treatment tactics
Treatment of epicondylitis is selected individually, depending on the general condition of the patient, professional activity, and the nature of the pain syndrome.
The main objectives of traditional therapy are:
- pain relief;
- restoration of joint movement;
- normalization of blood circulation and metabolic processes;
- prevention of secondary damage in the joint area.
It is of great importance to ensure functional rest of the affected limb with the help of devices such as a tight elastic bandage, an orthosis for the elbow joint and a special bandage. To enhance effectiveness, immobilization should be maintained for 10 days, after which a gradual transition to dosed physical activity and a complex of exercise therapy is recommended.
Literature sources
- Arshin V.V. Orthopedic diseases of the hands from functional overstrain: abstract. dis. Dr. med. Sciences / Arshin V.V. -Samara, 1996.-39 p.
- Builova T.V. Rehabilitation for epicondylitis of the shoulder. Clinical recommendations / T.V. Builova, M.B. Tsykunov // Bulletin of Restorative Medicine / - 2021. - No. 1 (71). - With. 80-84
- Bukup, K. Clinical study of bones, joints and muscles / K. Bukup. - M., Medical literature, 2008. - 320 p.
- Vorotnikov, A.A. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of tendopathies of the upper and lower extremities in patients with aggravated somatic status / A.A. Vorotnikov, A.N. Cymbal.
- Zulkarneev, R.R. Shock wave therapy for injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system / 6. R.R. Zulkarneev, K.E. Valeev, Yu. R. Stepanov // Kazan Medical Journal/ - 2009. - No. 5 (90). — P.753-754. 6. Karateev, Yu.A. Ermakova // Modern rheumatology. - 2015.-No. 3(9). — P. 33-42.
Signs and symptoms
Doctors identify characteristic signs that make it easier for a doctor to distinguish epicondylitis from various types of arthritis:
- painful sensations occur during flexion-extension movements;
- the severity of the pain is not related to the load: even a small amplitude of movement of the upper limb provokes discomfort;
- negative sensations were noted when trying to turn the sore arm inward. It is noteworthy that the help of a healthy limb during movement eliminates pain in the problem joint;
- muscle tone decreases, the patient easily lets go of even light objects, such as a cup or scissors;
- when shaking hands, pain in the elbow joint also occurs;
- the appearance of the problem area does not change, there is no swelling or redness;
- with the development of the external type of pathology, there is no discomfort during extension, pain appears only during flexion of the elbow;
- At night the affected elbow does not bother me. The exception is rest after carrying heavy objects during the day; discomfort may also appear during sleep.
The early stage of the pathological process is characterized by severe discomfort, gradually negative sensations persist for a longer period.
Origin history and description
The concept of “tennis elbow,” which is common in Western countries, is associated with the main cause of epicondylitis - chronic overload of the entire forearm. Frequent cyclical repetitions of the same movements negatively affect the condition of the rubbing tendons, bones and periosteum. As the disease develops, degeneration of individual sections of the radius bone occurs. This threatens the occurrence of styloiditis and chronic pain when moving the joints.
The general course and development of the disease are mild. The disease is directly related to the degree of wear and tear on the forearms and develops between the ages of 40 and 60. First, epicondylitis forms on the dominant hand; if a person works with both hands equally, it may develop on both hands.
Diagnosis of epicondylitis
If symptoms similar to those of epicondylitis appear, you should consult a traumatologist or orthopedist.
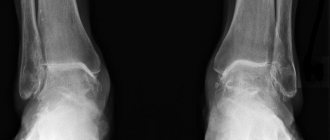
To establish a diagnosis, a questioning and examination of the patient by a doctor is crucial, since no abnormalities are observed in blood tests, and there are no changes in radiographs of the elbow joint. Sometimes x-rays reveal signs of calcium salt deposition in the tendon area, but, as a rule, in the advanced stage of epicondylitis, and only in 10% of cases.
The survey clarifies the nature of the complaints, issues related to profession and sports, as well as how long ago the symptoms appeared and their connection with the load on the limb.
During the examination, the following functional tests are carried out:
- Welt test. To carry it out, you need to stretch your arms forward in front of you and turn the open palms of both hands up and down at the same time. On the affected side there is a lag behind the healthy limb when performing movements.—Mobility test. The doctor fixes the patient's elbow, turning the hand to the side. Next, he invites the patient to turn the hand in the opposite direction, overcoming the resistance of the doctor’s hand. With epicondylitis, intense pain occurs.
If epicondylitis is suspected, diseases such as osteoarthritis and arthritis of the elbow joint, fractures of the bones of the forearm and epicondyles of the shoulder should be excluded. They are characterized by symptoms that are not observed with epicondylitis, for example:
- passive movements in the joint with arthrosis and arthritis are sharply painful, - swelling and redness of the skin in the joint area are observed, - inflammatory elements are determined in blood tests, increased C reactive protein, positive rheumatological tests for rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, etc. - with ultrasound of the joints effusion in the articular cavity is determined, that is, inflammatory fluid - when radiography of the joint, arthrosis is manifested by a narrowing of the interarticular space and changes in the articular surfaces of the bones, and in the event of a fracture - a violation of the integrity of the bone and possible displacement of fragments.
If the doctor prescribed additional examination methods, and they did not reveal such signs, then most likely the patient has epicondylitis. But in most cases, the patient does not need such an examination to make a diagnosis.
How to treat?
Orthopedic doctor, candidate of medical sciences Litvinenko Andrey Sergeevich:
The treatment program for epicondylitis is drawn up depending on the form, stage, and the presence of concomitant pathologies. The set of measures includes: protective regime, drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, blockades, and the use of special fixatives. An integrated approach allows you to restore joint function, avoid surgery and return to a full life.
Which doctor should I contact?
- Epicondylitis is treated and diagnosed by:
- An orthopedic traumatologist is the main specialist: makes a diagnosis, prescribes an examination, gives recommendations, performs injections and surgical operations.
- A sports medicine doctor will help you choose the right training regimen and give advice on the nature of permissible loads.
- Physiotherapist - helps select and conducts the necessary physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Specialist in physical therapy - necessary during the recovery period to strengthen muscles and develop movements in the joint.
At first glance, the clinical picture of epicondylitis seems harmless, since it does not cause excruciating pain or clear signs of inflammation. As the disease progresses, it becomes chronic, and it becomes difficult for the patient to lift and hold even light objects in his hands. Over time, atrophy of the forearm muscles and limited mobility in the elbow joint develop.
First aid
Epicondylitis is characterized by a gradual development of symptoms, however, if severe pain appears after exercise or injury to the elbow, a number of measures should be taken:
- If pain occurs, it is recommended to stop the load and create rest for the elbow and shoulder joints, immobilize the arm; for this purpose, you can use, for example, a scarf bandage.
- In the first 24 hours, apply cold for 15-20 minutes every hour to reduce swelling and pain.
- If the pain is unbearable, you can take a painkiller or use topical ointments.
- If symptoms persist, you should consult a doctor.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy is effective in 80-90% of cases, and if all doctor’s recommendations are followed, it usually gives good results, aimed at eliminating pain, restoring blood circulation in tissues, movements and muscle strength. In case of epicondylitis, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the provoking factors, rebuild the training regimen, eliminate physical activity, and change the work and rest schedule.
Video description text
Drug therapy
Includes drugs that are used in the form of ointments and gels, compresses, tablets and injections:
- Anti-inflammatory ointments - they relieve local inflammation well, relieve symptoms, help relieve muscle tension after exercise, are effective at the initial stage, use: Voltaren-gel, Diclak, Fastum-gel, Traumeel, for a course of up to 2 weeks.
- Compresses with dimexide are used to reduce inflammation, pain, and tissue swelling. The compress is applied for 1-1.5 hours, novocaine and voltaren-emulgel are added along with dimexide.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - have an analgesic effect, reduce inflammation, tissue swelling, and act on the symptoms of the disease. NSAIDs are considered the first step in the treatment of epicondylitis; movalis, nimesil, nise, arcoxia are prescribed. The course of admission is from 7 to 14 days.
- Chondroprotectors and collagen-containing preparations strengthen tendons and muscles, help restore articular cartilage, and increase tissue elasticity.
- Vitamin complexes - contain the necessary macro- and microelements, improve metabolism, speed up the healing process.
Injection techniques
- Corticosteroids, hormonal drugs (diprospan, kenalog, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, betamethasone) have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and analgesic effect, providing a “tip of a needle” effect. They are used in a solution with novocaine or lidocaine (the composition of the blockades can be single- or multi-component). They require use strictly according to the instructions and prescription of a doctor, as they have side effects and a number of contraindications, they are used in the form of medicinal blockades, the injection is made directly into the area of the inflamed epicondyle and tendon. Prescribed for severe pain and ineffectiveness of other methods, treatment is symptomatic.
- A number of authors recommend adding a lidase solution to the classic blockade to soften scar tissue. Others additionally add homeopathic preparations Traumeel-S, goal-T, it is believed that this reduces the severity of the side effects of hormones.
- Injections of hyaluronic acid, according to some authors, improve tendon gliding and tissue swelling. However, they have not been used in widespread practice due to low efficiency, questionable results and the high cost of the drugs.
Drug blockade for inflamed epicondyle
Orthobiology methods
- Injections of the patient’s own blood plasma (PRP therapy) are widely used in the treatment of epicondylitis, the effect is based on the introduction of autoplasma enriched with platelets with a high content of biologically active substances (cell growth factors) into the inflammatory focus, which creates a powerful anti-inflammatory effect in tissues, stimulates regeneration and blood supply, angiogenesis (sprouting of new microcapillaries).
- Plasmolifting is a domestic method of using platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which is not inferior in effectiveness to PRP therapy. It should be noted that after plasma injections, the pain may intensify somewhat, this is a normal reaction and goes away after 3-5 days. During this period, cold is applied to the injection site and stress is eliminated.
- SVF+PRP therapy is a technology of using stromal fraction cells obtained from one’s own adipose tissue and plasma, used when conservative methods are ineffective, with the aim of regenerating damaged tendons and stopping the inflammatory process. A number of authors consider the method as a last resort before surgical treatment.
Traditional methods of treating epicondylitis
They have an auxiliary value in therapy and should be used by the patient only after agreement with the attending physician. The following methods of traditional medicine have proven themselves well:
— Ointment made from comfrey herb, honey and vegetable oil in proportions of one to one. Oil can be replaced with lard or beeswax. Currently, such an ointment can be purchased at a pharmacy. Use at night for seven days or more.
— Warming clay compress. Mix 200 grams of cosmetic clay purchased at a pharmacy with hot water, apply to the elbow, wrap in several layers of gauze and woolen cloth. The compress has an effect similar to the effects of physiotherapy. Cannot be used in the acute stage. Apply three times a day, each time the compress should be kept on the hand for at least an hour, replacing it with a new portion of the mixture as it cools.
— A compress made from an alcoholic tincture of horse sorrel, the disadvantage of which is long-term infusion (at least 10 days). It is prepared by mixing crushed leaves, ethyl alcohol and water.
— Frequently rubbing the joint area with nettle leaves, which must first be doused with boiling water.
Review of some tools
There are a huge number of ointments for the treatment of epicondylitis of the elbow joint. The doctor will select the appropriate drug for the patient, taking into account contraindications to the use of a particular drug.
The rating of the best ointments from the NSAID group is headed by the following drugs:
- Ibuprofen. It is highly secure. Effectively relieves pain and swelling, reduces the severity of the inflammatory process. The product should be applied to the skin 3-4 times a day. The ointment should be rubbed in carefully so as not to accidentally further damage the joint. The minimum interval between treatments should be 4-5 hours, otherwise the risk of an allergic reaction increases.
- Indomethacin. A highly effective ointment, the positive result after application of which is noticeable very quickly. It relieves swelling well, thereby increasing mobility in the affected joint and resuming normal range of motion. Eliminates morning stiffness. The maximum daily dose of Indomethacin should not exceed 15 cm of the drug.
- Diclofenac. The therapeutic effect of the ointment is due to the inhibition of the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the inflammatory process in the human body. Relieves pain and inflammation, removes redness and swelling. Diclofenac is able to accumulate in tissues, so the effect persists even after the end of treatment. The ointment should be applied to sore joints 3-4 times a day for 1-2 weeks. It is undesirable to exceed the recommended dosage, since the medicine has accumulative properties, as a result of which it can provoke adverse reactions.
- Piroxicam. Has anti-inflammatory and anti-edema effects. Restores joint mobility and relieves pain. The duration of treatment with the drug should not exceed 2 weeks. The product must be rubbed into the skin in the joint area 3-4 times a day. Piroxicam can provoke the development of complications in the form of redness, itching, peeling and photosensitivity of the skin. Discontinuation of the drug is indicated only if systemic reactions develop in the form of urticaria, Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock, which happens extremely rarely.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/kOXwz2NesL4
Under no circumstances should you try to solve the problem yourself. Only a doctor is able to adequately assess the presence or absence of positive dynamics from the therapy and promptly adjust the prescriptions.
Using a compress with beeswax
To treat external epicondylitis of the elbow joint with folk remedies, you should use an oil compress of beeswax and comfrey along with medicinal decoctions. The leaves of the crop and roots are added to hot olive oil, everything is thoroughly mixed. Afterwards, the product is removed from the heat and left to infuse in a warm place. The beeswax is ground in a blender and transferred to the same pan. The resulting mass is placed in the refrigerator for one day. After a certain time, the composition should be applied to the diseased area, securing with a bandage.
Causes of epicondylitis of the elbow joint
The following factors can trigger the development of epicondylitis:
1. Sports activities. Frequent loads, long-term training, monotonous movements invariably lead to the formation of cracks in the tendons and epicondyles of the shoulder, causing degenerative changes in the tendon. The elbow joint is most often affected during professional activities in the following sports: - tennis - characterized by external epicondylitis, called "tennis elbow", - golf - characterized by internal epicondylitis, called "golfer's elbow", - kettlebell lifting, weightlifting, training with a barbell.
2. Injuries. In approximately 25% of all cases, significant injuries to the elbow area lead to the development of epicondylitis.
3. Constant overstrain of the shoulder and forearm muscles in patients with certain professions. For example, pianists, drivers, machinists, milkmaids, painters, plasterers, carpenters, massage therapists, loaders and seamstresses often suffer from epicondylitis.
4. Constantly carrying heavy bags, doing household chores such as sawing firewood, painting surfaces, etc. can contribute to the onset of the disease. The presence of congenital connective tissue dysplasia in a patient can also contribute to the occurrence of degenerative changes in the tendons of the elbow joint due to a predisposition to an initial change in the structure of connective tissue fibers .
Diagnosis
First, the doctor will find out detailed details of your medical history. You will answer questions about the nature of the pain, possible injuries to the elbow area in the past, as well as professional and sports activities. Physical examination is a very important step in the diagnosis of epicondylitis. Special diagnostic tests may be performed by your doctor to diagnose this condition.
You may be ordered to have an x-ray of your elbow joint. This will rule out other diseases that manifest as pain in the elbow.
The symptoms of lateral epicondylitis are very similar to those of another condition called radial tunnel syndrome. This disease is caused by compression of the radial nerve in the elbow area. If pain does not improve with conservative treatment of epicondylitis, your doctor may order diagnostic tests to rule out tunnel neuropathy.
If the diagnosis is unclear, special research methods are prescribed. Magnetic resonance imaging is a method of examining bones and soft tissue using magnetic waves. Ultrasound examination is based on the difference in the reflection of tissues with different densities and structures of ultrasonic signals generated by a special sensor. These research methods are highly informative, completely safe and painless.
Disease prevention
To prevent the onset of symptoms and treat epindocolitis of the elbow joint, it is necessary to lead a correct lifestyle. If a change in activity leading to illness is impossible, then you need to follow a set of simple rules so that the illness does not return again.
For example, if the main activity is related to sports, then training must be carried out in special devices - orthoses. Before starting classes, you need to warm up your muscles and warm up.
You need to protect the limb from injury, eat right, including healthy minerals and vitamins in your food, follow a regimen, and undergo regular examinations with a doctor.
If you are at risk and perform work that provokes the development of epicondylitis of the joint, then it’s time to worry about preventive measures. By following the following recommendations from doctors, the course of the disease can be stopped or its occurrence can be completely prevented:
- When playing sports, always follow the correct technique and strictly adhere to the trainer’s recommendations.
- Try to avoid the same type of repetitive movements at work, take breaks.
- Before any physical activity, be sure to warm up the ligaments and get a massage.
Drug treatment for epicondylitis of the elbow joint
- Diclofenac;
- Ibuklak;
- Ibuprofen.
Medicines are used in different forms - ointments, tablets, injections. The determining role in choosing the form of the drug is played by the physiological characteristics of the patient, the location of inflammation, the degree of damage, and a number of other factors. The treatment program is compiled individually.
Typically, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a good effect, relieving pain and stopping the inflammatory process. But if epicondylitis has been ignored for a long time, if the pain is unbearable, there is only one way out - joint blockade. What it is?
First, the doctor accurately determines the location of the inflammation. Then a strong, fast-acting anesthetic and at the same time corticosteroids are injected directly into this area to relieve inflammation. The procedure has a number of contraindications, so it is performed only in extreme cases.
Compresses with vinegar
You can eliminate epicondylitis with folk remedies quite quickly if you use a vinegar-based compress. To prepare, take 1 tablespoon of acid and mix with ½ glass of water. Soak a bandage in the solution and apply it to the painful area of the body, putting a bandage on top. This application helps to quickly eliminate pain and restore diseased tissue.
A common and effective compress is a product based on laundry soap and onions. This remedy helps get rid of the chronic form of the disease. To prepare the product, grate 1 onion and ¼ bar of soap. The resulting slurry is placed in a steam bath. Next, the finished product is applied to the sore elbow joint. It is important to secure the composition on top with a bandage. You need to continue holding the compress for 1-2 hours.
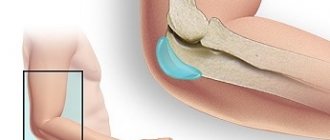
What is epicondylitis
Epicondylitis is inflammation of the elbow joint. It usually appears at the junction of muscle and bone. There are two types of this disease: both occur due to inflammation of the muscles, but either inflammation is diagnosed on the inside of the elbow joint or on the outer area.
What is epicondylitis?
This disease is most often characteristic of adults who engage in heavy physical labor or have great physical exertion: for example, agricultural workers, construction workers, weightlifters and other athletes who do exercises specifically for strength. Epicondylitis can also occur in older people.
Pathogenesis
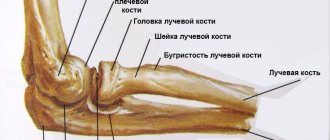
The part of the humerus that participates in the formation of the elbow joint contains small tubercles called the outer (lateral) and inner (medial) epicondyles. The tendons of the forearm muscles are attached to them. With a significant increase in the functional load on the hand flexor muscles, which are attached to the medial epicondyle, microdamage to the fibers of their tendons, as well as the bone base of the attachment area, is formed with the development of an inflammatory reaction.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Provocation of the disease is possible due to the following conditions:
- Sport. Sports loads, long workouts, and monotonous movements inevitably lead to the formation of cracks in the tendons and supracondylar part of the shoulder. Such damage leads to degeneration. Quite frequent changes and lesions in the elbow joints are found in athletes who engage in the following sports:
- tennis – external epicondylitis occurs. The disease even has a special term - “tennis elbow”;
- playing golf – the internal form of the disease develops, and there is also the term “golfer’s elbow”;
- weightlifting, kettlebell lifting, barbell exercises.
- Damage and injuries to the elbow. They contribute to the occurrence of the disease in 25% of traumatic cases.
- Occupational diseases. Due to permanent tension in the forearm and shoulder muscles, inflammation of the elbow joint develops in musicians, drivers, machinists, painters, massage therapists, workers, tailors, milkmaids, and builders.
- The disease can also arise from everyday household stress, if you carry heavy objects (bags), glue wallpaper on the ceiling, saw trees, paint, and so on. If a patient has a congenital disease, for example dysplasia, then it becomes the source of irreversible lesions in the connective tissues in the elbow. This is the result of a congenital pathology, due to the fact that the tendons and connective tissue already have a predisposition to degenerative changes.
At present, the exact causes of epicondylitis of the elbow joint have not been identified.
It is known that people suffer from this disease due to numerous movements of a monotonous nature (flexion and extension of the elbow joint).
The causes of epicondylitis of the elbow joint can be:
- characteristics of professional activity (athletes, construction and agricultural workers are more often susceptible to the disease);
- lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- great physical activity;
- performing heavy construction (repair) work.
It is important to know!
- When performing monotonous movements, microcracks can form in the muscles of the forearm in the area of the humerus. Because of this, an inflammatory process of an aseptic nature appears in adjacent skin areas.
- More often, the disease affects the lateral epicondyle in the area of the humerus, resulting in the development of external epicondylitis.
- Internal epicondylitis occurs due to destruction of the muscle tendons of the flexor hand.
- These two forms of epicondylitis do not occur at the same time.
The inflammatory process develops under the influence of the following factors:
- high load on the elbow, often short-term (sudden lifting of weight, jerking with the hand, injury);
- monotonous movements in the elbow joint for a long time;
- physical overexertion (more often in athletes).
Categories of people experiencing high load on the joint in the elbow area:
- wrestlers, weightlifters, boxers;
- masons, painters;
- seamstresses, designers;
- milkmaids, tractor drivers;
- fans of homemade preparations.
The greatest likelihood of epicondylitis develops after 40 years of age due to the weakness of the ligamentous apparatus at this age.
Surgical treatment treatment of epicondylitis
Surgical treatment is used quite rarely, in cases of advanced epicondylitis, when conservative complex therapy does not help the patient get rid of excruciating pain in the arm for six months or more. Then the following operation is performed - a small incision is made on the back surface of the forearm and the doctor cuts the tendon, after which the skin over the wound is sutured.
Restoration of limb function can begin one to two weeks after surgery. A similar operation can be performed using a puncture instead of an incision - an arthroscopic technique under the control of special devices, arthroscopes.
Possible complications
The main complication is bursitis. Inflammation in the joint capsule is often accompanied by the release of pus, the elbow swells, and the tissues are painful and hot. If the case is severe, it is sometimes necessary to remove part of the bursa.
OP When calcium metabolism is disturbed, calcifications accumulate in the tendon area due to epicondylitis. The problem area becomes inactive, and it is difficult for the patient to perform certain types of work.
Preventive recommendations
It is difficult to completely rule out problems in the elbow joint, especially for those at risk. Take care of the joint, avoid unnecessary stress.
How to proceed:
take breaks from work and, if possible, change the type of activity throughout the day; Do not ignore elbow pain that occurs over several days. Some patients turn to a rheumatologist and arthrologist after discomfort that has been annoying for several weeks
During this time, the disease has entered a chronic stage, treatment is delayed, and the prognosis is less favorable; If possible, avoid high loads, do not lift too heavy loads; If you need to carry a heavy object, never pull the handle, do not jerk, act carefully. Epicondylitis often occurs precisely after unsuccessful weight lifting; massage your elbows and other parts of your upper limbs at home; A bath with herbal infusions will help relax muscles and ligaments
Green tea lotions and Troxevasin pharmaceutical gel are effective; limit the amount of salt in your diet; do gymnastics, remember the exercises for the shoulder girdle and arms; Be regularly examined by an arthrologist or rheumatologist; if you experience discomfort in your elbows, seek medical help.
After identifying epicondylitis in the elbow joint, do not despair; begin treatment immediately. The more accurately you follow your doctor’s recommendations, the sooner the problem will disappear. Combine ointments, tablets, folk remedies, and after relieving the inflammatory process, undergo a course of physical therapy. With an integrated approach to therapy, the disease has a favorable prognosis.
Attention! Only today!
Therapeutic exercises for epicondylitis
Used to restore the function of tendons and muscles. Prescribed by a physical therapy doctor in the absence of pain in the elbow area as the acute stage of the process subsides. The following exercises can be performed for two to three minutes each twice a day:
- the patient alternately squeezes and unclenches his hands, keeping his forearms bent at chest level, - flexes and extends the forearms of both hands separately, - alternately rotates the forearms in different directions, - the patient locks his hands together and flexes and extends the forearms of both hands together, - the patient clasps the hand with his healthy hand and begins to slowly bend it at the wrist joint, holding it in the position of maximum flexion for several seconds; - scissor exercises - horizontal swings of the arms extended forward, alternating the right over the left and vice versa.
Any exercises should be used only as prescribed by the doctor conducting the treatment, since starting exercises prematurely can harm the tendons that have not yet recovered, leading to even greater overstretching.