A person does almost everything with his hands, i.e. the main physical activity falls on them. But it often happens that a person does not seriously injure his arm, but at the same time the mobility in it is significantly reduced. This suggests that he suffered a fracture of the olecranon. We will talk further about what kind of injury this is, why it is so terrible and how to get rid of it.
General information
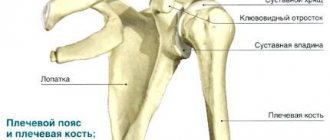
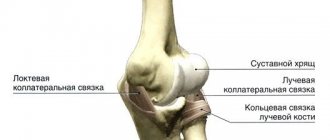
The olecranon process is a protrusion located on the back of the elbow. With its help, a person performs extension movements and moves his arms.
If this area is damaged, the patient:
- feels severe pain throughout his entire arm. Moreover, when palpating the front surface of the arm, the pain only intensifies;
- sees a hematoma, swelling at the site of injury. And if a person has seriously injured his hand, then he sees a violation of the shape of the hand, protruding fragments. They act in case of an open type injury;
- cannot move his arm normally at the elbow. When trying to move a hand, a person feels severe pain and feels a springy sensation. Sometimes the patient cannot even move his arm without assistance;
- feels excessive, unnatural mobility in the hand. When the olecranon is fractured, the elbow makes movements that it should not normally make;
- feels a sharp decrease in sensitivity in the injured limb. It becomes numb, and the patient is unable to move his fingers normally.
Symptoms of an olecranon fracture
When examining the patient, the following signs are revealed:
- The damaged joint is deformed and there is swelling.
- Movement in this place is limited (extension does not occur completely).
- There is bleeding visible under the skin in the joint.
- When palpating the appendix, the injured person feels pain.
- With a displaced fracture, the protruding part becomes sunken.
The pain syndrome forces the patient to keep his arm in a hanging position.
Causes
A person receives such an injury for various reasons.
It is caused by:
- falling on an elbow;
- a direct blow to the elbow with a heavy object. For example, such injuries occur when a person is hit with a baseball bat or gets into an accident;
- falling onto a straight arm. In this case, the triceps brachii muscle, which is attached to the process, becomes very tense, even torn off along with a fragment of the bone, and the person’s articular ligaments are damaged.
Clinical case of triceps brachii avulsion.
A 46-year-old patient, a professional athlete, came to the clinic with complaints of weakness in extension of the left elbow joint compared to the opposite limb. From the anamnesis it is known that he was injured two weeks before contacting a traumatologist. Mechanism of injury: direct blow to the posterior surface of the lower third of the left shoulder during extension of the elbow joint with weights. Immediately after the injury, he noted pronounced swelling of the soft tissues in this area. He did not seek medical help; he independently applied dermal forms of NSAID ointments with minimal positive effect. I did not reduce physical activity. He began to notice weakness and lack of extension in the elbow joint.
He performed an MRI of the left elbow joint: a series of MRI images showed signs of separation of the triceps tendon from the olecranon process.
Given his young age and high level of physical activity, the patient was recommended for surgical treatment, refixation of the triceps tendon to the native attachment site using anchors with a double-row suture.
Classification
Conventionally, such injuries are divided by doctors into several main groups.
For example, a person may receive a splinter injury. Moreover, this could be a fracture with a fragment or an unstable elbow fracture.
In addition, the patient can also get a simple crack. A person can also get a fracture of the olecranon without displacement, with displacement of fragments, open or closed. The top, base, and middle of the process can also be injured.
Because of this, damage occurs:
- simple;
- oblique;
- transverse.
An injured person can also receive a fracture with elements of compression, in which a section of the cancellous bone is crushed.
Do not forget that the patient may be damaged:
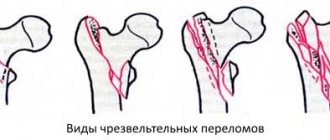
- 1 type. In this case, the patient receives a comminuted fracture of the olecranon of the first type without displacement of the fragments (1B) or a non-comminuted fracture (1A).
- 2 types. This is an injury in which fragments are displaced. Moreover, it is stable. A person may suffer a non-comminuted (2A) or comminuted (2B) fracture. With such an injury, the fragments move 2-3 mm apart from each other. You can move your forearm, because... There is no deformation of the collateral ligaments.
- 3 types. With such an injury, a person develops an unstable fracture with displacement of bone fragments. Such injuries are divided into two main types. A person can receive a non-comminuted (F) or fragmented (F) injury. This also includes subluxations and fracture-dislocations.
Medical reference books
Fracture of the olecranon
Epidemiology
An olecranon fracture is the most common injury in adults. In young people - as a result of high-energy trauma, and in older people - as a result of a simple fall.
Mechanogenesis of damage
This is a high-energy injury, more common in male athletes, as a result of hyperextension or excessive flexion of the forearm at the elbow joint. The direct mechanism of injury is a fall on the elbow joint, the indirect mechanism of injury is a fall on an outstretched arm, accompanied by a strong sudden contraction of the triceps, which can result in an oblique or transverse fracture. When these mechanisms are combined, a fracture-dislocation of the forearm at the elbow joint is possible.
Classification of fractures at the proximal level according to AO/ASIF
21-A extra-articular fractures. 21-A1 only the ulna. 21-A2 only radius. 21-A3 of both bones. 21-In the intra-articular one of the bones of the forearm. 21-B1 only the ulna. 21-B2 radius only. 21-B3 of one bone is intra-articular, the other is extra-articular. 21-C complex intra-articular of both bones. 21-С1 are simple. 21-C2 of one of the bones is simple, the other is comminuted. 21-C3 complex of both bones. The Mayo classification determines the stability of the humeroulnar joint, the degree of displacement of fragments, and the degree of fragmentation (see.
): ·
Type I
– fracture without displacement (A) or with minimal displacement (B), treatment is conservative.
· Type II
– fracture with displacement of the proximal fragment, but a stable glenohumeral joint.
— Type II A
– non-comminuted fracture, requires intense osteosynthesis with cerclage and wires.
— Type II B
– comminuted fracture, osteosynthesis with a plate is required.
· Type III
– the fracture is always unstable in the humeroulnar joint and always requires surgical treatment.
Diagnostics
In case of a fracture of the olecranon process, the displacement of the fragments is caused by the action of the triceps tendon. An unstable fracture is combined with damage to the coronoid process. The patient supports the injured limb with the opposite hand with slight flexion at the elbow joint. There is a lack of active extension in the elbow joint, pain, deformation and asymmetry of the elbow joint area.
Physical examination
Palpation reveals an obvious defect with retraction of soft tissues at the level of the olecranon. The patient cannot actively straighten the arm at the elbow joint as a result of damage to the extensor apparatus of the elbow joint. In comminuted fractures, as a result of high-energy trauma, damage to the ulnar nerve is possible.
X-ray examination
In standard two projections and oblique projection (Greenspan) (
). With the Greenspan oblique projection, the forearm is positioned in a neutral position, and the tube of the device is directed at an angle of 45° to the cephalic end. This projection allows visualization of the radiohumeral joint (the projection is described in the section on radial head fractures). A computed tomogram is performed for comminuted fractures with significant displacement of fragments during preoperative planning.
Treatment
Goal of treatment:
· restoration of articular surfaces, · preservation of the extensor function of the elbow joint, · prevention of the development of contracture,
Conservative Indications:
· no displacement of fragments, · displacement of fragments less than 2 mm, · slight displacement of fragments in elderly people with limited physical activity. Immobilization with a posterior plaster splint or orthosis in the position of flexion of the forearm at an angle of 90°, in a neutral position between pronation and supination (Fig. 2.89). On days 5-7, early dosed development of movements begins with mandatory repeated X-ray examination. After 3 weeks, the bandage is changed and more active movements are allowed, excluding flexion of more than 90°. Consolidation occurs after 6-8 weeks.
.
Surgical treatment Benefits
Restoration of the extension mechanism, early functional rehabilitation, rapid restoration of elbow joint function.
Disadvantages
Operative risk of anesthesia, soft tissue necrosis, infection, presence of a postoperative scar.
Indications Absolute:
· Pronounced displacement of fragments.
· Intra-articular fractures. · Open fractures. · When combined with damage to the neurovascular bundle, a revision of the damaged area is necessary. · Lack of effect from conservative treatment. · Displaced fracture of both forearm bones. · Segmental fracture. · Polytrauma. Relative:
- displacement of fragments more than 2 mm.
Contraindications
- Violation of the patient’s somatic status. — Soft tissue disorders (diabetes, vascular or neurological pathology).
Selecting a latch
1. Intramedullary fixation with a 6.5 mm cancellous screw; In order to achieve adequate fixation, the screw must pass through the medullary canal distal to the fracture site, in the presence of a large proximal fragment. This technique can be supplemented with fixation with a tensioned wire cerclage; 2. Tense osteosynthesis with wire with a combination of two Kirschner wires held in parallel. This prevents tensile forces and converts them into compressive forces (Weber osteosynthesis, see Fig.
), used for transverse fracture of the olecranon; 3. The plate and screw are used for complex fractures of the olecranon, Monteggia injuries, fracture-dislocations in the elbow joint, and oblique fractures. There is no fundamental difference between the installation location of the plate - on the rear and lateral surface (). 4. Bony osteosynthesis with a DCP plate. For complex fractures, combined with damage to the humerus trochlea. 5. Extrafocal osteosynthesis is used for open fractures.
Selection of fixation method according to AO/ASIF recommendations
· Bridge plate A1.3, B3.2, B3.3, B1, B3.3, C2.1, C3. · Compression plate A1.2, B3.1, B3.2, B3.3. · Compression plate and screw A1.2, B3.1, B3.2, B3.3. · Screw and protective plate A1.2, B3.1, B3.2, B3.3, B1, B3.1, C1, C3. · Restoration of triceps A1.1. · Tense osteosynthesis with wire B1, B3.1, C1, C2.2/3. · Fracture of the coronoid process C1, C2.1, C2.2/3, C.3.
Access
For the proximal part of the ulna, the dorsal () and lateral () approaches are preferable.
Rear access.
It begins a few centimeters proximal to the apex of the olecranon, goes around it somewhat medially and ends a few centimeters distally. Take care of the ulnar nerve, which is located behind the medial epicondyle of the shoulder. The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle is abducted more medially, and the ulnaris muscle is abducted more laterally.
Lateral access.
It begins 2 cm proximal to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
Continues across the elbow joint, above the head of the radius. Ends 5 cm distal to the elbow joint. Three transverse fingers distal to the head of the radius, inside the supinator muscle, is the posterior interosseous nerve, which must be protected throughout the procedure. Further access lies between the tendon of the olecranon muscle and the tendon of the extensor carpi ulnaris. NB
1. Full pronation of the forearm protects the posterior interosseous nerve during the approach. 2. Avoid opening the joint capsule too far anteriorly, since the radial nerve is located along the anterolateral surface of the elbow joint capsule.
Complications
· Infectious – 0%-6%. · Migration of fixative – 15%. · Ulnar nerve neuritis – 2%-12%. · Formation of heterotopic ossifications – 2%-13%. · False joint – 5%. · Loss of movement, especially extension, is about 50%.
Rehabilitation
5 days after the intervention, movements in the fingers of the hand begin, and after 12 weeks, regardless of the type of treatment, active exercise therapy of the elbow joint begins. After surgery, it is mandatory to use a posterior plaster splint (until the swelling subsides), with early dosed development on days 5-7.
Forecast
— When the olecranon is fractured, osteoarthritis occurs in 5% of cases (in 58-60% after surgical treatment).
Diagnostics with and without displacement
The injured person must be shown to a traumatologist.
Remember: only a doctor will be able to determine whether there is displacement of the fragments or not. Typically, an injury with displacement of fragments is diagnosed.
Why is it important to get a person to the emergency room on time? The fact is that after some time the patient will develop severe swelling, so it will be almost impossible to detect the retraction of the olecranon process.
The doctor must examine the person. Severe swelling of the soft tissues of the arm indicates a fracture. This is also evidenced by the retraction of the skin area. Additionally, the doctor can feel the problem area and determine the displacement of bone fragments located inside the joint. The victim will also have to undergo instrumental examination. He is given an x-ray in two projections. Usually, based on the image, the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Additionally, the patient may be referred to:
- MRI.
- CT.
Why should you turn to Scandinavian traumatologists?
The Scandinavia Clinic is equipped with modern tomographs that allow you to accurately diagnose a fracture and choose the most effective treatment tactics.
- Qualification of doctors
. Traumatologists with more than 5 years of experience will make an accurate diagnosis in one visit. - Loyal conditions of admission
. We accept out-of-town and foreign citizens, you can check with the operator for details. - Comfortable hospital
. The hospital is equipped with modern technology, there is Wi-Fi in the clinic. - No queues
thanks to standardized patient registration.
Conservative treatment
In case of minor injury, without displacement of bone fragments, the injured person is prescribed conservative treatment methods.
At the same time, doctors:
- Bend the injured limb at an angle of 50-90 degrees, apply a plaster cast to the arm. This is how the doctors immobilize her. Moreover, the plaster should cover the area from the shoulder to the hand.
- Manual reposition of bone fragments is performed. Usually it is carried out with a slight displacement. After repositioning, a plaster cast must be applied to the injured limb.
- Relieves a person from pain.
- Help the patient develop the damaged joint.
Mechanism of triceps brachii avulsion injury.
The most common mechanism of injury is eccentric muscle contraction, under conditions of functional overload, when the athlete either attempts to perform an exercise with excess weight, or against the background of significant muscle fatigue. In addition, injury often becomes the result of long-term microtraumatization, when tendon tissue is gradually replaced by scar or calcified. Since the injury is typical specifically for athletes who have high functional demands, the only treatment method is surgical, refixation of the tendon to its native attachment site.
Surgery
In case of a fracture of the olecranon process with displacement of bone fragments, the victim undergoes surgery.
Remember: the operation is performed within the first hours after admission to the emergency room. Otherwise, the bone is overgrown with tissue, and it will not be possible to correctly compare bone fragments.
Usually the injured person undergoes osteosynthesis.
With it, doctors connect bone fragments, fix them in the correct position until a bone callus forms. In addition, the victim undergoes osteosynthesis according to Weber. In this case, bone fragments are fixed with special titanium knitting needles and wire.
In case of a comminuted fracture with displacement and separation of the apex of the process of the ulna of the injured person, the fragments are fixed with a special titanium structure. It helps restore the integrity of the olecranon process and the articular surface of the bone.
After the procedure, a plaster splint is applied to the patient’s injured limb, the limb is bent at an angle of 60-90 degrees, and secured to a scarf sling. After rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a displaced injury and complete fusion of the bone (after 3-4 months), the plaster is removed.
Treatment of a fracture of the olecranon process of the ulna
Applying plaster
In case of a non-displaced process fracture, conservative treatment is prescribed. A plaster bandage is applied to the site of injury, which covers the third part of the shoulder (upper) together with the forearm (up to the wrist joint). The arm is bent at an angle of approximately 1200 and fixed this way.
For loose joints, the doctor prescribes movements from the first days, and the damaged area begins to be worked out after 2 weeks. To do this, temporarily remove the bandage and do careful extensions and return to the previous position. The plaster is then put in place.
Treatment occurs in the same way if there is displacement of the fragments, but only slightly. The hand is fixed in the position in which the fragments take their places. Complete restoration of bone tissue requires 3 to 4 weeks.
Surgery
If the fragments are severely displaced, surgery is required. It is used if there is a distance of 2 mm or more between the fragments or they are displaced to the side. Surgical intervention is also required for fractures with multiple fragments. After determining the type of injury, the most suitable treatment method is selected, in which it will be possible to begin movement in the injured area as early as possible. To treat a fracture, osteosynthesis is used, that is, the bones are fastened with two knitting needles and titanium wire. The operation can be performed as soon as the patient is admitted to the department.
After anesthesia, an incision is made over the damaged area. All blood clots and very small bone particles are removed through it. The fragments are adjusted relative to each other in the correct position using a single-tooth hook. Using a drill, two knitting needles are inserted. At a distance of at least 3 cm from the fracture, holes are drilled for pulling the wire holding the fragments together. The ends of the wire are twisted with pliers. No more than 2 cm of the length of the needles is left above the olecranon, the rest is bitten off. The ends are bent towards the bone.
The operated limb is secured with a scarf. After about 5 days, it is recommended to start moving your arm. Complete rehabilitation of motor ability occurs within 5 weeks.
Metal fasteners are removed under local anesthesia no earlier than after 3 months.
For fractures in which a Monteggia lesion is present, osteosynthesis is performed using a long pin. The head of the radius is pre-set.
In case of fragmentation of the olecranon process and separation of its apex, all fragments are removed, and the tendon stretch of the biceps is fixed. They are secured using sutures in the area of the ulna, in which holes are drilled specifically for this purpose. Fixing sutures are also made on the fascia and periosteum. After the operation, the arm is fixed for 3 weeks at an angle of approximately 1550. Then the recovery period begins.
On topic: 12 folk methods for home treatment
First aid for a fracture
Relatives of the injured person can help him.
They need to fix the injured limb so that it no longer causes pain to the injured person.
In doing so, they require:
- Examine the limb and determine its position. Remember: you cannot bend your arm.
- Place the injured person on his back, tie his straight arm to the body with a bandage, scarf, or scarf. This is how doctors will transport the patient to the hospital.
Remember: if the injured limb can be bent, then it must be placed in a position in which the patient will not feel pain.
You can also fix the limb with a special Kramer splint. In this case, the tire must be bent in a comfortable position. Additionally, you can use a board or plank. They are applied to the outer surface of the shoulder. A soft roller can be placed in the armpit and the injured limb can be tied to the body. Additionally, it can be secured with two scarves. One scarf can be tied to the body, and the second can be hung on the forearm to the neck.
Rehabilitation
A person who has undergone surgery recovers completely in 1-3 months.
But he definitely needs rehabilitation.
Remember: after the swelling subsides, the victim can do exercises to help develop the damaged joint.
Initially, he can make light extension and flexion movements with the forearm and contract the muscles.
Additionally, the patient will have to sign up for:
- Therapeutic baths.
- Acupuncture.
- Mud therapy.
- Paraffin wraps.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Massotherapy.
- Exercise therapy.
Also, a victim who has suffered a displaced fracture of the olecranon process will have to switch to proper nutrition during rehabilitation and recovery, apply an orthosis to the injured limb at home, take vitamins, anti-inflammatory medications, and calcium supplements.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures also help speed up the patient’s recovery process.
The victim can sign up for:
- UHF.
- Microwave.
- Procedures with electrophoresis.
Such procedures speed up the wound healing process, stop the inflammatory process, and activate the work of muscles and nerve endings.
If the victim has broken the styloid process of the ulna, then he simply needs to go to physical therapy. They will speed up the healing process of nerve endings.
Predisposing factors for triceps brachii avulsion.
According to world literature, abuse of anabolic steroids is the most common predisposing factor that can lead to tendon rupture, including the triceps tendon. Also, this group of patients is characterized by a national training regimen, when they often exceed their functional capabilities. Taking certain types of antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones, is also associated with a high risk of tendon damage. In addition to these risk factors common to all tendon injuries, there is also one that is specific to the triceps. It is olecranon bursitis, or olecranon bursitis. A long-term chronic inflammatory process in the area of the olecranon leads to inflammatory restructuring of the tendon, thereby increasing the risk of rupture.
Physiotherapy
During rehabilitation, it is very important to do gymnastics, because... it speeds up the patient's recovery process. Moreover, the exercises can be performed already on the 3-4th day, but under the supervision of an orthopedic doctor.
For example, if a person has broken the olecranon, then first he should work on developing his fingers, because The olecranon process is closely connected with the muscles responsible for the mobility of the fingers.
Remember: the load must be increased gradually.
At home the patient can:
- clench your fingers into a fist, clench an expander in your fist;
- roll a ball, ball, car on the table;
- work out with light dumbbells and weights. You can take dumbbells weighing no more than 2 kg;
- clasp your hands;
- Raise your clasped hands up.