What it is?
Degenerative-dystrophic changes are a complex of symptoms that occur in diseases of the spine caused by the same mechanisms.
The pathological process affects discs, vertebrae and ligaments, and is characterized by deformation, destruction and decreased tissue density. As a rule, such changes appear in older people due to the natural wear and tear of the body. However, in the presence of tissue dystrophy (impaired blood supply and metabolic processes), pathology can also develop in young people.
Picture of the course of the disease
Degenerative-dystrophic changes are characterized by compaction of the tissues of the spinal column , the formation of osteophytes, dehydration of the intervertebral discs, and a decrease in their width. The result is a decrease in neck mobility and flexibility, and the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Degrees and classification
Below are the types of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine in the cervical region
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine occur in the presence of the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis is the most common form of dystrophic changes. The disease is characterized by compression of the spinal column, a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc, its dissection and separation into parts.
- Spondylosis is a chronic degenerative pathology of the spinal column, accompanied by damage to the fibrous tissue of the intervertebral discs and the formation of osteophytes (overgrowth of bone tissue). The disease is usually found in elderly patients.
- Spondyloarthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic change in the intervertebral joints of the spine, which is accompanied by severe pain. Initial degenerative changes in this form of the disease progress independently or together with osteochondrosis.
Prevalence
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine are common and characterized by a chronic course. Most often they occur in old age due to the natural aging of the body.
How to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Treatment of exacerbations of cervical osteochondrosis should be comprehensive. In such therapy schemes, specialists can use both medicinal methods of relieving the symptoms of the disease, as well as physiotherapeutic techniques, massage, physical therapy, and the like.
Regardless of the method of influencing the diseased spine, all methods of treating osteochondrosis of the cervical spine have several goals:
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- restoration of lost sensitivity in different parts of the face and upper extremities;
- strengthening the muscles and ligaments that support the vertebrae;
- relief of local inflammation and reduction of tissue edema;
- elimination of the consequences of pinched nerve roots;
- prevention of progression of the pathological process.
As drug therapy for osteochondrosis, doctors often prescribe to patients drugs from the group of analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, B vitamins, glucocorticoids, and chondroprotectors. Therapeutic gymnastics and physiotherapy can achieve good results in treating the disease.
Surgical correction of disorders in cervical osteochondrosis is a last resort, which is used in the absence of effect from conservative treatment.
Risk factors, causes
Degenerative-dystrophic changes occur for the following reasons:
- unwanted stretching of the flexor muscles of the back caused by staying in a bent position;
- decreased muscle tone due to a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, and prolonged driving;
- the presence of abnormally formed vertebrae caused by a genetic predisposition.
Less commonly, changes may occur when:
- mechanical damage to the cervical spine (trauma);
- metabolic disorders in intervertebral discs;
- pathological changes in the cardiovascular system:
- hormonal disorders;
- poor nutrition;
- constant stress.
Consequences
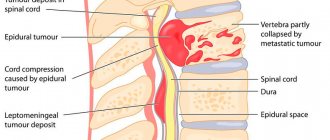
If changes in the spine are diagnosed, it is important to begin treatment as soon as possible. Otherwise, you may encounter complications such as scoliosis, protrusions, paresis, arthrosis, intervertebral hernia, osteochondropathy . Ultimately, all this can lead to disability.
Benefits of massage
For osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, massage helps to increase the tone of the muscle layer and eliminate pain. Today, experienced massage therapists use different massage techniques in their practice, but the most effective for osteochondrosis are:
- stroking to stimulate the upper muscle layers, which begins from the collar area, gradually moving to the area of the collarbone and armpit;
- rubbing, which helps improve blood flow and relieve tension;
- squeezing, as a method of influencing deeper areas of the skin, is carried out by grasping tissue across the neck;
- kneading, which is an impact on the deep layers of neck tissue and, if performed incorrectly, can harm the patient.
Only an experienced specialist should perform massage procedures. An illiterate approach to treatment can provoke an exacerbation of osteochondrosis in the patient and even the appearance of severe consequences.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
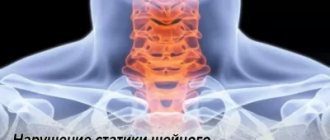
The first symptom indicating the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes is pain . It occurs in the neck area and can radiate to the shoulders and back of the head. With muscle spasm, the mobility of the neck is limited, which forces the patient to freeze in an unnatural position with his head tilted.
If there are problems in the neck, constant pain in the head appears. In addition, when the cervical vertebrae are damaged, vascular and neurological disorders appear (fatigue, poor coordination of movements, asthenia). The spinal canal in the neck area is quite narrow, so changes in the shape or height of the disc can be dangerous for the spinal cord.
Infringement of blood vessels and nerve roots is accompanied by:
- frequent headaches;
- dizziness (usually occurs in the morning);
- increased blood pressure;
- hearing loss, tinnitus;
- decreased concentration, memory impairment;
- impaired sensitivity of the hands and their numbness;
- blurred vision;
- nausea.
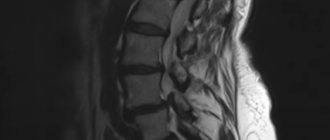
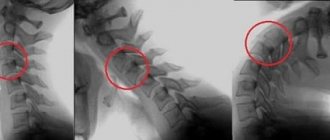
The presence of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine can be established using an X-ray examination. To clarify the nature of the lesion, a tomographic study (computed tomography or MRI) can be performed. .
Treatment
Modern medicine is not able to cure degenerative-dystrophic changes completely. All that can be done today is to slow down or stop the process, reduce or eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Degenerative changes in the spine are treated mainly conservatively. In this regard, therapy should be aimed at:
- restoration of intervertebral discs;
- reduction of pain;
- elimination of pinched nerves and arteries;
- increased joint mobility;
- strengthening the muscular system.
Treatment measures are prescribed after a full examination, and on an individual basis. A noticeable improvement can occur with complex therapy and strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
Drugs
Did you know that...
Next fact
Drug treatment of degenerative-dystrophic changes includes the use of the following groups of drugs :
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Designed to relieve pain, swelling, inflammation of soft tissues. They can be used in the form of tablets, intramuscular injections, medications for external use (gels, ointments). |
| Proteolytic plant enzyme |
| They reduce hernial protrusion, make the spine mobile and flexible, and the cartilage tissue elastic and resilient. Improves the shock-absorbing properties of intervertebral discs. |
| Antispasmodics |
| Relieves muscle spasms. They can be prescribed by injection (administered subcutaneously, intravenously, intramuscularly). The goal of this therapy is to improve blood circulation and relieve muscle pain. |
| Centrally acting muscle relaxants |
| Relaxes tense muscles and inhibits spinal reflexes, reducing pain. Allows you to improve the effect obtained from massage, physiotherapeutic procedures and manual therapy. |
| Chondroprotectors |
| Nourishes bone tissue and helps restore lost substances. They relieve the inflammatory process and prevent further development of the disease. |
| Vitamins |
| They improve blood supply, nourish nerve fibers, make cartilage tissue more elastic, eliminate inflammatory processes, strengthen muscles, regulate mineral, carbohydrate and protein metabolism. |
If the pain becomes acute and unbearable, the patient may be prescribed novocaine blockades . In this case, the sodium channels of the nerve endings are blocked, which leads to instant relief of pain.
Paravertebral blockade is carried out near the spine - the injection site can be subcutaneous tissue or muscle. Sometimes the injection is given into the area of a nerve root, spinal ganglion, or anterior branch of the spinal nerve.
Surgery
If conservative therapy does not bring the expected effect, the patient is prescribed surgery . It is carried out in several stages. First, doctors eliminate the pathological disorder, and then install special grafts to ensure immobility of the bone vertebrae.
Exercise therapy and massage
You can combat degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine with the help of physical therapy, swimming and other physical activity. It is important to understand that any exercises can be performed during remission , i.e. outside periods of exacerbation. It will not hurt to engage in exercise therapy for those who are predisposed to the development of spinal diseases.
You can relieve muscle tension during degenerative-dystrophic changes with the help of massage. This can be manual therapy, osteopathy, the classical method of exposure and even acupuncture. Doctors recommend 10 to 14 massage sessions every three or four months.
Video: “Exercises for the neck for degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine”
Treatment at home
It is better to treat degenerative-dystrophic changes using traditional methods. However, you can get rid of symptoms, such as neck pain, using folk remedies.
In particular, you can use the following recipes:
- Apply a compress of burdock, alder, cabbage or coltsfoot leaves to the affected area.
- Make warm lotions with medicinal plants such as chamomile, elderberry or horsetail.
- Add 10 drops of bay oil to 1 liter of heated water. Apply a cloth soaked in water to the affected area for 20-30 minutes.
- Grind young burdock root, pour boiling water (200 ml of boiling water per 1 tablespoon of root), leave for 2 hours. Drink the infusion three times a day after meals, half a glass. The recommended duration of therapy is 2 weeks.
Prevention
With age, the likelihood of developing degenerative-dystrophic disorders increases.
To prevent the development of diseases and maintain health, it is enough to follow the following recommendations::
- monitor your posture, incl. during “sedentary” work (the head and back should be kept straight);
- avoid staying in uncomfortable positions for long periods of time, do a warm-up and a break after every hour of working at the computer;
- do morning exercises regularly;
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine cannot be cured, therefore prevention at an early age is very important; giving preference to healthy foods;- stop smoking, reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- sleep on an orthopedic mattress or any hard surface, use low pillows;
- avoid hypothermia, increased physical activity, and heavy lifting;
- regularly visit the bathhouse/sauna to relax the neck muscles (a contraindication to visiting such establishments is the presence of hypertension);
- daily for 10 minutes. take a hot shower;
- walk, do yoga and exercise therapy, visit the pool;
- purchase special armchairs/chairs for the office and home that support the spine in an anatomically correct position;
- do not load the spine while playing sports;
- Do not make sudden bends or turns of the head.
- monitor your weight and prevent obesity.
After 40 years, metabolic processes slow down, so at this age it is recommended to take vitamin preparations enriched with phosphorus, magnesium, calcium and vitamin D.
Prevention methods
What can be done to minimize the risk of the disease returning? Any doctor will tell you that the only, but extremely effective preventive measure can be normalizing your lifestyle. Stop smoking and drinking alcohol; if this is not possible, then reduce the number of cigarettes and glasses of wine to a minimum. Review your nutrition system, eliminate junk food from your diet, give preference to fresh fish and meat, seasonal vegetables and fruits. Move more: cervical osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree occurs in those who neglect physical activity. Walk for at least half an hour at least once a day; if you have the time and opportunity, sign up for a pool or yoga class.