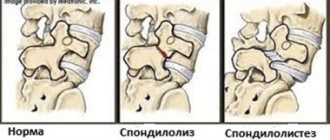
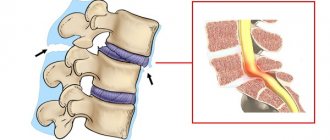
Retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebra in relation to an adjacent vertebra, but much less than subluxation. Usually we talk about vertebral retrolisthesis in cases where the vertebra is displaced back to the underlying vertebra. In the past, this clinical pathology was called retrospondylolisthesis.
Retrolisthesis, unlike anterolisthesis (or spondylolisthesis), is the displacement of a vertebra in the opposite direction in relation to another vertebra. Retrolisthesis is easily diagnosed on a lateral x-ray of the spine, especially if the patient is positioned correctly in a lateral position and without rotation of the trunk. But taking pictures of the patient in a supine position does not give a complete picture of the real biomechanical disorders due to vertebral retrolisthesis when the patient is in an upright position.
Retrolisthesis occurs mainly in the cervical and lumbar spine, but sometimes occurs in the thoracic spine.
Classification of retrolisthesis
- Complete retrolisthesis : The body of one vertebra is displaced completely posterior to both adjacent vertebrae
- Stepped retrolisthesis : The body of one vertebra is displaced posterior to the overlying vertebra and anterior to the underlying vertebra.
- Partial retrolisthesis : The body of one vertebra is displaced posteriorly in relation to the upper or lower vertebrae.
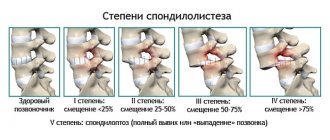
This classification does not give an idea of the size of the displacement and, therefore, in clinical practice, the classification of retrolisthesis is more often used based on the size of the vertebral displacement in mm, which makes it possible to determine the degree of stability of the motion segment. In addition, vertebral displacement is also classified as a percentage of the vertebral body.
1st degree – displacement up to 25%
2nd degree from 25% to 50%
3 degree from 50% to 75%
4 degree from 75% to 100%. But sometimes it is difficult to measure the degree of displacement using such a gradation of retrolisthesis.
Causes
Retrolisthesis occurs due to trauma and results in instability of the soft tissues that provide stability to the motion segment (ligaments, discs, muscles, tendons and fascia). Muscle spasm may also occur as a result of nerve dysfunction, which occurs due to the pressure of a misaligned vertebra on the nerve structures. In addition, a displaced vertebra can affect not only the motor and sensory nerve roots, but also the veins, arteries or lymphatic vessels that also exit the spine, which can lead to disruption of the supply of nerve tissue. Often, at the level of retrolisthesis, degenerative changes in the area of vertebral displacement are determined (osteophytes, disc damage, decreased disc height, disc herniation, disc protrusion). Retrolisthesis, at a minimum, places hyperstress on one disc and places intense stress on the anterior longitudinal ligament, annulus fibrosus, endplate cartilage, and capsular ligaments. Improper distribution of loads leads to excessive load on the facet joints and the development of spondyloarthrosis.
Tissues that are damaged during retrolisthesis:
- Ligaments – their function is to prevent excessive movement of the bones to which they are attached. Their function becomes insufficient during retrolisthesis.
- Discs - These are shock-absorbing pads between the vertebrae and prevent excess movement, as do ligaments. The discs provide movement of the motor segment (flexion, lateral flexion, extension, rotation). When a disc is damaged, conditions arise for an excessive range of motion in the motion segment.
- Fascia provides the muscles with the information they need to properly distribute loads.
- Muscle tone is necessary for proper posture and balance of the spinal column. Muscle tone is the result of a normally functioning nervous system, where subluxation is excluded.
- Vertebrae - If they move more than they should, especially backwards, they can cause direct compression on the nerves.
- Nerves can work normally only if there is no compression on them and play a trophic and coordinating role in the functioning of organs and systems. Life itself exists only thanks to nerve impulses.
- Joint stability. Joint stability is easily calculated by taking flexion and extension x-rays.
Prevention
Retrolisthesis of the spine, we already know what it is and how it threatens the patient. Now, to summarize, let’s look at prevention methods. Therefore it is necessary:
- First of all, eat properly and nutritiously.
- Also control your normal weight. This will certainly reduce the load on the spine.
- Perform regular exercises to strengthen your core muscles.
- Finally, watch your posture throughout the day.
- Yoga classes will be especially relevant.
- Regardless of the circumstances, do not lift heavy objects.
- Be less involved in bad habits. In general, get rid of them as soon as possible.
More information here
Symptoms
Retrolisthesis can manifest itself with various symptoms, which will vary in both severity and intensity. This occurs because retrolisthesis may have different effects on the nerves and mechanical factors affecting the joints of the spine.
Motion segment instability may be experienced as some discomfort, but can also lead to significant movement disorders throughout the entire spine. If changes in the joints of the spine occur during retrolisthesis, this can also lead to impaired range of motion. Pain can be the result of irritation of the nerve roots and depends on the degree of vertebral displacement and the presence of positional rotation of a particular vertebra. With retrolisthesis, as a rule, protrusion of the vertebra occurs (protrusion with subsequent rupture of the fibrous ring and the development of disc herniation). Such changes are not visible on radiography, but are clearly visualized on MRI. In the presence of severe retrolisthesis, a compressive effect on the spinal nerve structures and significant neurological symptoms are possible
What are the causes of retrolisthesis of the l2-l5 vertebrae? How to cure it?
You'll never guess: pain in the back or lower back that radiates to the legs or buttocks - is it osteochondrosis or something more serious? Could this signal a disease when it is urgent to see a doctor?
The reason for retrolisthesis is a fairly large load on the vertebrae, any injuries received, deviations from the norm or disorders of the spine, damage to ligaments, etc. All this can be interconnected, becoming the main cause of retrolisthesis. This is accompanied by many other symptoms, for example, sharp and terrible pain in the lower back with increased and heavy loads, as well as a decrease in sensitivity in the legs and groin area.
Treatment of retrolisthesis
Treatment of such vertebral deformity will depend on the cause of the disease, so they often resort to a complex combination of methods such as physiotherapy, physical therapy and surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment is resorted to in the case of: 2-4 degrees of retrolisthesis, with severe vertebral instability, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and rapid progression of the disease.
Physiotherapy is resorted to when it is necessary to focus on the restoration of the spine and the surrounding muscle corset. These methods of physiotherapy include: a special corset, manual therapy, acupuncture and spinal traction. We also do not forget about physiotherapeutic procedures.
Retrolisthesis of l5 vertebra
The manifestation of retrolisthesis depends on the area of the vertebral displacement. With any displacement, a person is worried about: pain in the lower back, which radiates to the leg or groin, spasm in the pelvis, fecal and urinary incontinence, weak sensitivity in the pelvic area, etc.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the strength of the displacement and whether soft tissue is involved. Such signs are characteristic of many pathologies that manifest themselves as pain in the lumbar region. And if the patient is bothered by these particular symptoms, he is referred to a vertebrologist or neurologist. Then the specialist will prescribe an examination, during which you need to take an x-ray.
Basic drugs that will be prescribed for retrolisthesis:
- Muscle relaxants;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mild analgesics;
- Hormonal (for inflammation) and strong painkillers.
- Vitamins.
Manual therapy and massage, spinal column straightening, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and laser treatment are mandatory.
The operation is not performed on everyone. Surgical intervention will be in cases where other methods do not work, there is a third or fourth stage of the disease, there is instability in the course of the pathology or its accelerated development, or the nervous system and soft tissues are affected.
As always, prevention is important to prevent the development of pathology.
- Avoid injury to the spine.
- Play sports and strengthen your muscles.
- Stick to proper nutrition.
- Don't forget about posture.
Vertebrogenic pathology
Retrolisthesis of the L5 vertebra is a type of vertebrogenic type.
Signs and symptoms of vertebral damage due to this disease:
- Characteristic pain in the lower back.
- Decreased sensitivity in the pelvic area.
- Paralysis of the muscles of the lower extremities.
- Incontinence.
Diagnosis and treatment of retrolisthesis of the L5 vertebra
Symptoms indicating the development of this pathology are just a reason to visit a doctor. It is necessary for a neurologist (or vertebrologist) to give a referral for an x-ray of the lower back. Pictures will be needed in two projections. Based on the obtained images and after examining the patient on a tomograph, he will be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
In case of this disease, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist and not engage in independent treatment. Because many patients go to chiropractors, apply ointments and hope that home methods will help them, but this is not the case. The condition may worsen.
For the first and second degrees of displacement, doctors recommend non-surgical methods, which involve restoring the supporting column. This treatment takes a couple of months. This includes drugs to relieve muscle hypertonicity, to combat inflammation and lower back pain, injections of potent painkillers, and others.
There are additional methods of therapy:
- Manual (as prescribed by a doctor);
- Wearing a corset;
- Physiotherapy;
- back massage.
Surgical intervention will be performed only in cases where compression of the spinal cord nerves increases, vertebral instability appears, and retrolisthesis progresses to the third or fourth degree. The goal of such an intervention is to eliminate displacement problems and return the spinal column to its physiological position. The period of complete recovery after surgery is 12 months.
Lumbar retrolisthesis
The lumbar spine includes the vertebrae: L1, L2, L3, L4, L5. They have increased resistance to physical stress. They are subject to the maximum depreciation load and so on. Any displacement of these vertebrae provokes a narrowing of the lumen of the spinal cord canal.
- Muscle weakness in the lower extremities;
- Feeling of numbness in certain areas;
- Legs do not obey, problems with movement;
- The appearance of parasthesia;
- Development of paresis or paralysis.
Treatment of vertebral retrolisthesis
Before treatment you need to be thoroughly examined. The doctor is required to determine the degree of displacement of the vertebrae and whether there are any complications. Should identify the potential cause of their loss of stability. Next, a treatment plan for retrolisthesis is developed.
This plan should include measures to restore the intervertebral joint, as well as drugs and complexes aimed at strengthening the paravertebral muscles. If possible, you need to start the process of regeneration of all tissues that are damaged.
Diagnostics
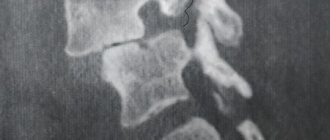
The diagnosis of retrolisthesis can be made even with the help of routine radiography, which allows one to determine the presence of posterior displacement of the vertebra.
Associated radiological signs include:
- Vacuum effect in the core of the pulpous intervertebral disc below retrolisthesis, which is usually a sign of rupture of the annulus fibrosus of the disc
- Disc height reduction
- Marginal sclerosis of adjacent vertebral bodies
- Osteophytes
- Spinal joint instability
Considering that with retrolisthesis, secondary damage to soft tissue structures occurs, in addition to radiography, an MRI study is necessary. MRI allows you to diagnose morphological changes in tissues such as discs, ligaments, spinal cord, and nerve roots. MRI results make it possible to determine more adequate treatment tactics and, to a certain extent, predict the development of the process.
If there are signs of nerve compression, it is possible to conduct an ENMG study, which allows you to determine the degree of damage to the nerve fiber.
— Buy a magnetic corset from an official seller, with delivery: 1290 rubles. (LINK) -
——————————————————————————————————————————
Causes of retrolisthesis.
Retrolisthesis can be caused by a spinal injury (for example, in an accident or during extreme sports). What is noteworthy is that the first symptoms of the disease can appear quite a long time after the direct injury to the spine. Athletes involved in sports in which the spine is regularly exposed to high loads are also susceptible to retrolisthesis. For example: weightlifters, wrestlers, ... Under such conditions, the articular tissue of the intervertebral discs is more at risk of structural changes. This may be a prerequisite for the occurrence of retrolisthesis.
Also at risk are people whose professional activities involve regularly lifting or carrying heavy objects (for example: loaders).
Elderly people often experience pathological changes in the bone and joint tissues of the spine. This can also lead to retrolisthesis.
Treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the size of the listhesis, and treatment can be either conservative or surgical.
Conservative treatment is effective for minor listhesis and is a combination of manual manipulation (repositioning, myofascial techniques) with exercise therapy, massage, and physiotherapy. Of great importance in the treatment of retrolisthesis is a sufficient supply of essential nutrients to the body, such as copper, manganese, zinc, vitamins, and glucosamine. Some effect is possible with weight loss, as the load on the damaged motor segment is reduced. Exercise therapy is of great importance in the conservative treatment of retrolisthesis. Dosed physical activity allows you to strengthen the muscle corset, restore range of motion and, thus, compensate for impaired biomechanics of movements in the spine.
Surgical treatment methods are indicated for severe retrolisthesis and the presence of persistent neurological symptoms, as well as for the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, and consist of fixation of the vertebrae.
What are the causes of retrolisthesis of the l2-l5 vertebrae? How to cure it?
You'll never guess: pain in the back or lower back that radiates to the legs or buttocks - is it osteochondrosis or something more serious? Could this signal a disease when it is urgent to see a doctor?
The reason for retrolisthesis is a fairly large load on the vertebrae, any injuries received, deviations from the norm or disorders of the spine, damage to ligaments, etc. All this can be interconnected, becoming the main cause of retrolisthesis. This is accompanied by many other symptoms, for example, sharp and terrible pain in the lower back with increased and heavy loads, as well as a decrease in sensitivity in the legs and groin area.
Treatment of retrolisthesis
Treatment of such vertebral deformity will depend on the cause of the disease, so they often resort to a complex combination of methods such as physiotherapy, physical therapy and surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment is resorted to in the case of: 2-4 degrees of retrolisthesis, with severe vertebral instability, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and rapid progression of the disease.
Physiotherapy is resorted to when it is necessary to focus on the restoration of the spine and the surrounding muscle corset. These methods of physiotherapy include: a special corset, manual therapy, acupuncture and spinal traction. We also do not forget about physiotherapeutic procedures.
Retrolisthesis of l5 vertebra
The manifestation of retrolisthesis depends on the area of the vertebral displacement. With any displacement, a person is worried about: pain in the lower back, which radiates to the leg or groin, spasm in the pelvis, fecal and urinary incontinence, weak sensitivity in the pelvic area, etc.
The intensity of symptoms depends on the strength of the displacement and whether soft tissue is involved. Such signs are characteristic of many pathologies that manifest themselves as pain in the lumbar region. And if the patient is bothered by these particular symptoms, he is referred to a vertebrologist or neurologist. Then the specialist will prescribe an examination, during which you need to take an x-ray.
Basic drugs that will be prescribed for retrolisthesis:
- Muscle relaxants;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mild analgesics;
- Hormonal (for inflammation) and strong painkillers.
- Vitamins.
Manual therapy and massage, spinal column straightening, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and laser treatment are mandatory.
The operation is not performed on everyone. Surgical intervention will be in cases where other methods do not work, there is a third or fourth stage of the disease, there is instability in the course of the pathology or its accelerated development, or the nervous system and soft tissues are affected.
As always, prevention is important to prevent the development of pathology.
- Avoid injury to the spine.
- Play sports and strengthen your muscles.
- Stick to proper nutrition.
- Don't forget about posture.
Vertebrogenic pathology
Retrolisthesis of the L5 vertebra is a type of vertebrogenic type.
Signs and symptoms of vertebral damage due to this disease:
- Characteristic pain in the lower back.
- Decreased sensitivity in the pelvic area.
- Paralysis of the muscles of the lower extremities.
- Incontinence.
Diagnosis and treatment of retrolisthesis of the L5 vertebra
Symptoms indicating the development of this pathology are just a reason to visit a doctor. It is necessary for a neurologist (or vertebrologist) to give a referral for an x-ray of the lower back. Pictures will be needed in two projections. Based on the obtained images and after examining the patient on a tomograph, he will be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
In case of this disease, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist and not engage in independent treatment. Because many patients go to chiropractors, apply ointments and hope that home methods will help them, but this is not the case. The condition may worsen.
For the first and second degrees of displacement, doctors recommend non-surgical methods, which involve restoring the supporting column. This treatment takes a couple of months. This includes drugs to relieve muscle hypertonicity, to combat inflammation and lower back pain, injections of potent painkillers, and others.
There are additional methods of therapy:
- Manual (as prescribed by a doctor);
- Wearing a corset;
- Physiotherapy;
- back massage.
Surgical intervention will be performed only in cases where compression of the spinal cord nerves increases, vertebral instability appears, and retrolisthesis progresses to the third or fourth degree. The goal of such an intervention is to eliminate displacement problems and return the spinal column to its physiological position. The period of complete recovery after surgery is 12 months.
Lumbar retrolisthesis
The lumbar spine includes the vertebrae: L1, L2, L3, L4, L5. They have increased resistance to physical stress. They are subject to the maximum depreciation load and so on. Any displacement of these vertebrae provokes a narrowing of the lumen of the spinal cord canal.
- Muscle weakness in the lower extremities;
- Feeling of numbness in certain areas;
- Legs do not obey, problems with movement;
- The appearance of parasthesia;
- Development of paresis or paralysis.
Treatment of vertebral retrolisthesis
Before treatment you need to be thoroughly examined. The doctor is required to determine the degree of displacement of the vertebrae and whether there are any complications. Should identify the potential cause of their loss of stability. Next, a treatment plan for retrolisthesis is developed.
This plan should include measures to restore the intervertebral joint, as well as drugs and complexes aimed at strengthening the paravertebral muscles. If possible, you need to start the process of regeneration of all tissues that are damaged.