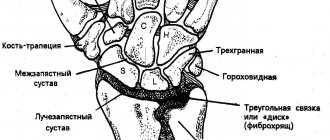
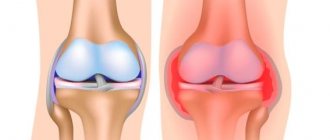
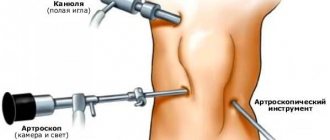
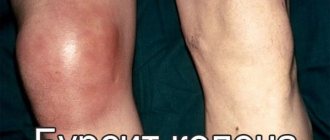
Ligamentitis of the ankle joint is a disease associated with damage to the ligaments and tendons. These tissues experience serious overload during walking and running. They ensure the stability of the position of all bones in the joint capsule. Therefore, if the integrity of the tendon and ligament fiber is damaged, there is a high probability of rapid destruction of the joint.
Most often, ankle ligamentitis develops in women over 35 years of age who are overweight, but do not refuse to wear high-heeled shoes. The combination of excess weight and improper foot position results in the ankle ligaments being constantly exposed to trauma. In their thickness, microscopic fibers rupture. At these points, the process of inflammation and scar formation begins. Gradually, the area of deformation increases, which worsens the physiological properties of the ligamentous tissue and provokes frequent inflammation. Clinical symptoms of chronic ligamentitis appear.
Ligamentitis of the ankle ligaments is dangerous because the ligament and tendon tissue is gradually completely destroyed. Serious complications may occur, such as divergence of the heads of the tibia and fibula, displacement of the talus and calcaneus, stretching of the joint capsule of the ankle, deforming osteoarthritis, rupture of the ligament and tendon apparatus.
It is advisable to carry out treatment in the early stages. In advanced cases, a surgical operation is indicated, during which reconstruction of the damaged ligament or tendon fiber is performed. Therefore, pay attention to the clinical signs described in this article. If you or your loved ones have them, immediately consult an orthopedist. The doctor will conduct an examination, make a diagnosis and prescribe effective conservative treatment.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with an orthopedist in our manual therapy clinic right now. Fill out the doctor appointment form located at the bottom of the page. The administrator will contact you and agree on a convenient time for the visit. The initial consultation is provided completely free of charge for all patients.
Causes
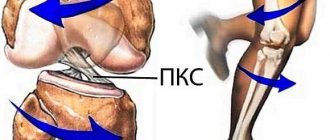
Any factors that negatively affect the ligaments and tendons can trigger the onset of the disease. The process usually begins after an injury. Ligamentosis of the knee joint is often recorded, because this joint experiences constant stress and is often damaged. Microtraumas received during excessive physical training, lifting and carrying heavy objects play a major role in the etiology of damage to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
Injury to the ligamentous-tendon apparatus provokes an inflammatory process, which often becomes chronic. But not only the knee is susceptible to this pathology. Bruises, dislocations, subluxations, sprains of any joints can lead to the development of the disease, especially if they are not treated on time.
The disease can develop at any age; it is most difficult to treat in older people, since the process occurs against the background of a slower metabolism and decreased immune defense, typical of old age.
The following factors contribute to the development of pathology:
- autoimmune disorders - especially rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- deforming osteoarthritis;
- diabetes mellitus, pathology of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels of the extremities;
- insignificant physical activity, which helps to reduce blood supply to muscle-joint structures;
- diet with insufficient intake of proteins, minerals and vitamins;
- hereditary predisposition to joint diseases;
- long-term use of certain medications.
Does joint instability exempt you from the army?
It is worth immediately highlighting the fact that the medical commission of the military registration and enlistment office does not consider isolated situations of displacement as a reason for enlisting in the reserves. Only those conscripted citizens whose disorder is congenital or chronic have the right to receive exemption from the army. In other words, if we are talking about dysplasia or joint instability.
Instability is a pathological condition when periodic displacement of the articular ends of the bone is observed. Signs of this condition depend on the type of joint affected.
However, there are also common features that are characteristic of the affected area:
- External deformation of the affected area;
- Inability to completely straighten a limb;
- Pain when trying to move a limb;
- Swelling;
- Crunching and clicking noises while driving.
Signs that are characteristic of a dislocated knee joint include lameness and, in advanced cases, curvature of the shape of the limb in the area of the knee joint.
The medical examination of conscripts with such a disease is carried out according to Article 65 of the Schedule of Diseases. The regulations on the military medical commission interpret the violation as non-conscription. Suitability category “B” or “D” is issued when taking into account the impairment of functionality.
During examination, specialists often evaluate these clinical expressions. But with the compensated form, detailed diagnosis is necessary, the use of advanced examination methods that will help determine the condition of the joint.
They will not take on service with total instability of any large joint. Here we can say that normal mobility of the joint is absent, the joint does not hold support. In addition, the service is contraindicated in case of stable contracture of the joint in a functionally disadvantageous position; there is a significant limitation of movements. In such cases, conscripts are issued fitness category “D”.
Category “B” is reserved for young people with joint instability:
- Instability of the shoulder joint in the presence of frequent dislocations (3 or more times per year);
- Instability of the patella in the presence of frequent dislocations (3 or more times a year);
- Stage 2 or 3 knee instability.
The disease schedule considers instability of all major joints, including the clavicle and patella. Dislocations of large joints fall under this category. If a young man has instability of the shoulder joint, then dislocations at least 3 times a year will be a good reason for exemption from the army. If less often, then another category will be created with which they can serve in the army with restrictions on the choice of troops.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ligamentosis of the knee joint are largely due to intra-articular hemorrhage and accompanying subcutaneous hematomas in the knee area.
Most often, cruciate ligamentosis is diagnosed, accompanied by the following pathological phenomena:
- knee pain of varying intensity, intensifying with light exertion;
- a decrease in the range of active and passive movements, especially evident in the morning and after rest;
- crunching when flexing and extending.
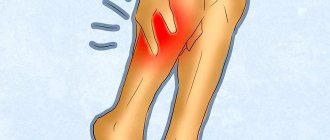
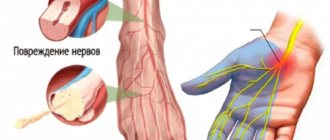
Ligamentosis of the ankle joint sometimes develops after a sprain of the ligamentous apparatus. Signs of pathology: swelling, decreased sensitivity and a crawling sensation in the ankle and lower third of the leg. When walking, a person notices rapid fatigue and begins to limp.
When the ligaments of the sole are affected, the pain increases while standing and when walking. They spread from the heel tubercle to the toes, often have a burning character, and are sometimes accompanied by itching.
Spinal ligamentosis is more often diagnosed in the areas that experience the maximum load - the cervical and lumbar. The main manifestation of the disease is pain, which subsides with rest and is provoked by bending, turning, and long walking.
Common manifestations of pathology of any localization are swelling and redness of the skin in the joint area, local pain, often aching in nature, aggravated by movement.
Which doctor treats ligamentosis?
If joint pain occurs, the patient should first consult a local physician. After laboratory and instrumental examination, the person is sent for treatment to an orthopedist, traumatologist or vertebroneurologist. Consultation with a rheumatologist or osteopath is often required.
Do they take you into the army with a torn cruciate ligament?
If a young man has a cruciate ligament rupture at the time of enlistment, then he is granted a deferment of 6 months. Temporary release from service is enshrined in Article 85 of the Schedule of Sicknesses. It is provided for the period of drug treatment or surgery and recovery after it.
If the injury has recovered, then, taking into account the condition of the conscript, the members of the commission make a decision on the conscription of such a young man. To understand in what options a conscript can count on a deferment or a reserve, you need to understand the special aspects of the disease: the impact of injury on the functionality of the body and the health of the young man.
If the cruciate ligament ruptures, surgery may be required, followed by a rehabilitation period. If the conscript is fired, then he will be sent to the ITU, and then disability. In this case, the conscript will be provided with a military ID with exemption. After 6 months, the fitness category from “G” changes to another and will depend on the results of the operation performed.
Diagnostics
The doctor will listen to the patient’s complaints, find out the circumstances of the injury, then perform an examination and prescribe the necessary instrumental examinations.
These include the following diagnostic measures:
- Ultrasonography. Detects an increase in connective tissue density in the joints most accessible to research. Using ultrasound, ligamentosis of the knee joint and damage to the shoulder are detected.
- Radiography. Detects ligament damage in the later stages of the disease. Ligamentosis ossificans is well diagnosed when the articular ligaments are compacted and deformed due to salt deposits. So, ligamentosis of the foot is determined - the plantar tendon is clearly visible in the picture.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. Visualizes the condition of ligaments and tendons in controversial cases. Using these methods, ligamentosis of the cruciate ligaments of the knee and other hard-to-reach formations, in particular the hip joints, can be diagnosed.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ligamentosis is based on the results of instrumental studies: ultrasound examination of the articular joints involved in the process, magnetic resonance imaging examination of the damaged ligamentous apparatus and articular joints, as well as x-ray examination.
These examinations make it possible to visualize the entire volume of structural transformations in the ligaments, determine the area of ossification and deposition of calcium salts, which in turn confirms the expected diagnosis.
Additionally, such examinations can make it possible to determine concomitant or causative pathological processes, the consequences of chronic injury to the articular joint and periarticular tissues, as well as the level of progression of the ligamentous process.
Treatment
Therapy for the disease consists of a set of therapeutic measures prescribed in accordance with age, health status and the severity of the pathology.
Treatment of ligamentosis is carried out with a certain frequency, since the pathology is considered chronic. The task of the doctor and the patient is to prevent exacerbations of the disease. But if a relapse develops, it is necessary to create rest for the affected joint.
For example, with ligamentosis of the shoulder joint, the joint is fixed in a physiological position using a special bandage, and at the same time, the load on the arms is eliminated - it is forbidden to carry heavy objects or perform physical work. For knee ligamentosis, treatment includes using an elastic bandage or knee brace to relieve weight on the leg when walking.
Medicines
The main goals of drug therapy are to relieve inflammation, reduce pain and swelling. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used: Diclofenac, Movalis, Nimesulide. The drugs are used intramuscularly or orally for a short course. Analgesics (Baralgin, Pentalgin) may be prescribed.
It is necessary to use chondroprotectors (Chondrolone), B vitamins (Milgamma).
As a rule, ointments or gels are used for local effects on the diseased joint:
- Dolobene.
- Voltaren.
- Emulgel.
- Dolgit.
Treatment of cruciate ligamentosis includes intra-articular administration of solutions of Hydrocortisone and Diprospan. The use of hormones has a lot of side effects, so it is carried out according to strict indications.
Surgery
The help of surgeons has to be resorted to in cases of massive ossification of ligaments and tendons. Ligamentosis of the cruciate ligaments of the knee joint especially often requires surgical intervention. In this case, an endoscopic method is used, which causes little trauma to the tissue. The ossified areas are removed and replaced with implants - artificial (fiberglass) or natural (parts of the patient's tendons).
After the operation, it is necessary to use fixatives recommended by the doctor, undergo courses of drug therapy, physical therapy, exercise therapy and massage. Gradually the functions of the joint are restored.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is used only as part of a comprehensive treatment. The effect is possible with long-term use in the early stages of the process.
The following witchcraft recipes enjoy a good reputation:
- inside - decoctions of elecampane root, St. John's wort, birch buds;
- externally - compresses of steamed oats and honey mixed with grated horseradish.
Shock wave therapy
With the help of this modern method of treatment, ossifications on ligaments are broken down, and the processes of regeneration of normal connective tissue are activated.
After a course of procedures, pain and joint stiffness are significantly reduced. As a rule, the sessions are well tolerated by patients.
Physiotherapy
Treatment is aimed at improving capillary circulation, normalizing metabolism, and activating lymph flow.
The following physiotherapeutic procedures are most effective:
- electrophoresis with solutions of anti-inflammatory, analgesic and vascular drugs;
- heat treatment using paraffin, ozokerite, mud;
- laser exposure;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation.
Physical training
A set of exercises is selected by the doctor in accordance with the patient’s condition. It needs to be performed regularly, but only when there is no exacerbation. The first classes are best conducted under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor.
Sudden movements and overwork are prohibited. The joints develop gradually; in a state of stable remission, elements of manual therapy are possible.
Therapeutic measures
The pathological process responds better to treatment the faster therapeutic measures are started, so even with a conservative method it is possible to eliminate the focus of degeneration at the initial stage.
Therapy for this disease forces doctors to take a comprehensive approach:
- Maximum physical unloading of the affected joint. It is recommended to limit any physical activity on the shoulder joint; sports activities and heavy lifting are contraindicated.
- Immobilization of the arterial joint. Limiting the performance of motor acts in the pathologically altered articular area helps prevent subsequent damage and will significantly speed up the recovery process. For this purpose, you should use an elastic bandage or special knee pads.
- Drug therapy. At the acute stage, NSAIDs should be prescribed, which have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Chondroprotectors and B vitamins are also prescribed to promote regeneration processes in tissues.
- Healthy diet. It will help restore chondral tissue and also improve overall health. It is recommended to exclude fatty, fried, salty foods, and alcoholic drinks.
- Exercise therapy. Doctors recommend regularly doing therapeutic exercises, which helps improve blood circulation, maintain the elasticity of ligaments, and relieve painful syndrome. All procedures are performed under the strict supervision of a doctor.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment. It includes laser therapy, ozone therapy, and mud applications.
Prevention
Dystrophic changes in the ligamentous joint apparatus can be prevented by following simple rules. Thus, ligamentosis of the hip joint is easy to prevent by avoiding chronic physical overload, carrying heavy objects, hypothermia, and extreme sports.
Injuries to the knee joint can be prevented by using knee braces and other braces to prevent injury and reduce the stress on the lower extremities during sports.
To keep ligaments and tendons healthy, the following preventive measures are important:
- a balanced diet enriched with minerals, vitamins and products containing collagen;
- body weight control;
- morning exercises, including warming up all joints, gentle stretching of muscles and tendons;
- timely treatment and treatment at the first signs of joint diseases.
The disease is chronic and prone to progression. Ossification of not only ligaments, but also muscles is dangerous; this leads to complete immobility of the joint. Timely treatment will stop the worsening of the pathology and help a person regain health and joy of movement.
Author: Olga Shchepina, doctor, especially for Ortopediya.pro
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your feedback about military service and joint instability in the comments, your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Vladislav:
There were problems with the joints, a diagnosis of joint instability was made, but the commission stated that such a disease was not on the list of diseases. They took me into the army and barely served. I advise guys to prove their illnesses, even in court.
Michael:
With such a diagnosis, I was not accepted into the army, but, frankly speaking, it would be better for me to serve in the army than to suffer from these joint pains like this.