Osteosynthesis of the jaw is a method of surgical treatment of bone fractures using special, most often metal, structures. Osteosynthesis surgery is performed if the fracture site cannot be secured with splints, and also when it is difficult to fix bone fragments. There are different methods of performing the operation, they can be used depending on the type of injury and its severity.
Osteosynthesis allows you to maintain the required level of blood circulation in the damaged bone, which means that such a fracture will heal faster. Not only the integrity of the bone is restored, but also its structure, and this will take only a few weeks.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to follow certain rules and monitor your well-being and the condition of your bone tissue. Violations of doctor's instructions can lead to pain and even loss of chewing functions.
Indications for osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis may be prescribed in the following cases:
- if there are not enough stable molars at the fracture sites;
- upon impact, the fragments moved significantly;
- broken jaw bone behind teeth. With such an injury, individual parts of the bone tissue are displaced;
- the injury occurred as a result of the development of inflammatory diseases that thin the bone tissue;
- in case of a fracture of the lower jaw, if too small or massive fragments have formed;
- if the branches and body of the jaw are incorrectly positioned relative to each other;
- it is necessary to perform reconstructive surgery or osteoplasty.
What happens after surgery
After surgery, the patient is monitored during the recovery phase, when he awakens from anesthesia. Exercise therapy is started soon after this to prevent ankylosis and reduce muscle loss.
The chosen osteosynthesis procedure and the individual healing process will determine whether the bone can be used as usual. A broken bone takes at least six weeks to heal; however, the overall process can also take several months. However, partial mobilization is usually possible quite early, and the patient can weight-bear the limb with the help of walking aids or crutches. Several factors determine whether osteosynthesis material can be removed if the fracture is completely healed. The material used (titanium) can remain in the body for life. These days, screws and plates are usually not removed unless there is a specific reason to do so.
In our clinic, you can find out the cost of bone osteosynthesis in consultation with a doctor; usually the price consists of the operation itself, preparation, anesthesia and subsequent rehabilitation. Our doctors have unique experience in treatment and rehabilitation; we can choose the most optimal correction method for you. You can make an appointment by calling the clinic or on the website.
Types of osteosynthesis
There are several methods of osteosynthesis; the doctor decides what type of operation the patient needs. Most often, surgeons combine several methods with each other to achieve better results.
Osteosynthesis of the jaw can be:
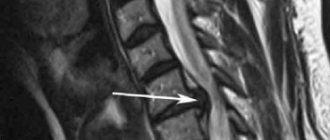
- Open. It is usually used for severe fractures. During the operation, soft tissue is cut and bone fragments are exposed. They are connected to each other and non-functional small fragments are removed, compressed soft tissues and fascia are released. However, with such an operation, there is still the possibility of tissue peeling off from the bone, then the callus at the fracture site will not be formed correctly. And this can affect the patient’s quality of life. In addition, stitches remain on the skin and paresis (decreased activity) of facial muscles is even possible. Depending on the type of fastening device, it is possible that the incision on the face will have to be made again to remove the fastener.
- Closed. The doctor combines bone fragments without cutting facial tissue;
- Focal. The fixing fastener is applied directly to the fracture site;
- Extrafocal. Fasteners are placed on top of the skin, above the fracture site.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation:
The patient remains in the clinic after the operation for 2-3 days. Already starting from 3-4 days, you can begin active recovery measures, including physical therapy, physiotherapy and massage.
On average, the recovery time after a minimally invasive operation performed at the ABIA clinic is 2-3 times shorter than after a classic open osteosynthesis operation. The absence of the need to wear a cast, as well as the possibility of a speedy return to work and active life, significantly improves the quality of life of our patients in the postoperative period.
The essence of osteosynthesis and what kind of procedure it is
With osteosynthesis, the doctor not only connects the fragments of the damaged jaw, but also securely fastens them with metal structures or glue.
Open focal osteosynthesis is carried out using:
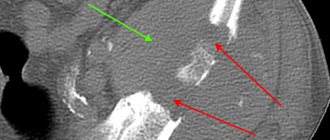
- Bone suture. If the lower jaw or cheekbone is broken and the injury is recent, it can be fastened with a bone suture. For this, stainless steel, titanium wire or nylon thread is used.
During the operation, the doctor dissects the soft tissues of the face and fixes the fragments with wire. If the fragments are connected using a bone suture, the patient retains chewing function and can continue to care for the oral cavity. This method is contraindicated if the fracture site is inflamed or the patient has an infectious or purulent bone lesion.
- Installation of periosteal metal mini-plates. This method has proven itself in the treatment of all types of jaw bone fractures, except those in which a large number of fragments have formed. In this case, it is enough to make an incision only on one side. The doctor aligns the fracture sites, applies mini-plates to them and screws them on. Nowadays, mini-plates are most often fixed inside the oral cavity.
- Fixation with quick-hardening plastics. It is practiced only for fractures of the lower jaw. After exposing the bone fragments, the doctor makes a bone groove and places a special fixing compound in it. Excess plastic is removed with a cutter, after which the wound can be sutured.
- Osteoplast glue. This composition for fixing bone fragments is made of purified epoxy resin with an organic antiseptic - resorcinol. After application, the glue hardens in 8-12 minutes and reliably fixes the combined bone fragments. Nowadays this method is rarely used.
- Metal staples. For osteosynthesis, staples made of nickel-titanium alloy are used. At low temperatures, the alloy becomes plastic and is easy to shape into the desired shape. Then, at room temperature, the staple regains its previous shape. During the operation, it is first cooled, then inserted into the prepared holes on the bone fragments. As soon as the staples warm up, they straighten and securely fix the fracture site. Metal staples are especially convenient for fixing a fracture of the angle of the lower jaw.
Closed focal osteosynthesis is practiced for healing fracture sites where bone displacement has not occurred. Methods:
- Installation of Kirschner spokes. The doctor inserts metal needles into the bone fragments using a surgical drill. For reliable fixation, the needles are fixed into each fragment to a depth of up to 3 cm. There is no need to dissect soft tissues; the operation is performed through the mouth. This is a low-traumatic practice, but wearing needles creates a lot of inconvenience for the patient.
- Applying a surrounding suture. Applicable when the fracture gap is displaced forward or backward along the jaw. In this case, the suture passes through the central part of each bone fragment. If there are a lot of fragments, the operation takes a long time, but this is one of the most reliable methods of osteosynthesis. It allows the patient’s jaws to be restored even after very complex injuries.
Removal of metal structures:
Surgical treatment at the ABIA clinic is performed using modern materials that are safe for health. However, in many cases, operating traumatologists recommend removing the fixation structure after healing of the fracture zone in order to exclude rare cases of the development of long-term complications. It is better to do this 8-12 months after osteosynthesis.
After removal of metal structures, soft tissue healing occurs quickly. The incision is made along the old scar, a cosmetic suture is applied, due to which the scar becomes almost invisible after healing.
Osteosynthesis using ultrasound
With the help of metal fasteners, the jaw bones can be fixed quite firmly. But during surgery, it is most often necessary to cut through facial tissue and the salivary glands or branches of the facial nerve can be damaged.
It is less traumatic to perform osteosynthesis using ultrasound. In this case, the bone-fixing devices can be inserted shallowly into the bone and a small amount of scars remains on the patient’s face.
The doctor uses low-frequency ultrasound on a titanium plate with spikes. A plate with holes for the dental bur is placed at the fracture site and adapted to the shape of the jaw. An instrument is then used to make shallow holes in the bone through the plate. After which low-frequency ultrasound vibrations are directed to the base of the spines. In this way, the spikes gradually sink into the bone tissue, reliably fixing bone fragments. In this case, an antiseptic solution is supplied through the instrument, which treats the wound.
The bone tissue around the spines becomes denser under the influence of ultrasound. This occurs due to the large contact area, reducing pressure on the bone due to the use of a spike and the internal compression force of the bone tissue.
Ultrasonic osteosynthesis can reduce the time of surgery and reduce the amount of postoperative trauma. The method gives fewer complications and provides a good cosmetic effect.
Osteosynthesis at the Miracle Doctor clinic
If such treatment is indicated for you, we recommend performing the operation at the Miracle Doctor clinic. We guarantee individual treatment taking into account the characteristics of the fracture, the condition of the bones and the general condition of the body.
- The low invasiveness of the techniques used allows for stable and functional osteosynthesis in the early stages after injury.
- The stability of osteosynthesis allows patients to be activated in the first hours after surgery, facilitating care, improving the course of a traumatic disease and reducing the risk of developing severe hypostatic complications.
- The use of minimally invasive biological osteosynthesis can significantly reduce the length of stay of patients in the hospital and significantly improve the quality of life of patients in the early postoperative period.
Affordable prices for osteosynthesis, an individual approach, highly qualified trauma surgeons, attentive and caring staff will help minimize the consequences of injury and restore confidence in recovery.
2.The essence of the method
Osteosynthesis refers to operative, surgical methods of treatment.
The primary tasks are antiseptic treatment, restoration of tissue integrity (including soft periosteal tissue, which is very important), but the main thing is reposition of bone segments and fragments, i.e. ensuring the relative spatial arrangement of bones and joints, which is provided for by the normal anatomy of the human body. In many cases, it is completely impossible to do this from the outside (for example, by repositioning and applying a plaster cast), just as it is impossible to ensure a stable, reliable, mechanically stable junction of separated segments - without which, in turn, the bones will either heal incorrectly or not heal at all. For the purpose of fixation, all kinds of artificial devices are used, the temporary implantation of which forms the fundamental basis of the osteosynthetic method. To date, a variety of designs have been developed - knitting needles, intraosseous pins, nails, screws, plates, screws, etc.
Such fixatives remain in the patient’s body for several months, sometimes up to a year or more, therefore, taking into account the risk of rejection, suppuration, and tissue degeneration, they must be made from structural materials with the properties of maximum biological inertness. Today these are mainly metal alloys (stainless steel, chromium, nickel, cobalt, titanium, molybdenum), but over time, in all likelihood, synthetic materials will be introduced, with properties approaching the characteristics of living tissues and therefore “invisible” to the immune system. systems, however, are much more durable.
Visit our Traumatology and Orthopedics page
Varieties
There are different ways to fix bone fragments:
- Internal osteosynthesis involves the presence of an incision. The surgeon gains access to the broken bone and performs fixation. To do this use: Screws. Used for fractures of short bones and long heads.
- Plates. They are screwed to the bone. They securely hold the fragments together, but they are not used in children, as they can damage the periosteum and disrupt bone growth.
- Pins and spokes. They are driven into the bone in a longitudinal direction.
- Wire, special threads. They are usually used to hold small fragments in place.
External transosseous osteosynthesis technique
An operation using a guide apparatus prevents the penetration of bone fragments into the tissue and does not impair the functioning of the joint. This allows you to speed up the restoration of cartilage and bones in the affected area. This operation is recommended for open fractures of the humerus and tibia, as well as for closed fractures of the tibia.
Note! The operation must be performed by an experienced expert, since different types of needles are used and it is necessary to correctly calculate the trajectory of movements and determine the design features of the device. Moreover, all calculations are made during surgery, so you need to act within a narrow time frame. A successful operation allows the patient to rehabilitate in just 20-25 days.
4. Indications and contraindications. Efficiency
The most common area of application of osteosynthetic methodology is the treatment of complex comminuted fractures of long bones, intra-articular fractures, as well as poorly healing or malunited fractures, when reconstructive intervention becomes the method of choice. However, osteosynthesis is actively used in many other situations: to eliminate developmental anomalies and acquired deformities in various elements of the musculoskeletal system, in maxillofacial surgery, etc.
The main contraindications include an infectious and inflammatory process in the wound area, severe osteoporosis, some diseases of the hematopoietic system and central nervous system, the patient’s serious condition with a large open wound or polytrauma, etc.
Efficiency. Possible complications
As stated above, osteosynthesis is a modern generally accepted method, it is used very widely throughout the world and continues to be improved. A fairly large array of medical and statistical data has been accumulated, and yet they should be averaged with a certain caution: too much depends on the timeliness of the intervention, the nature of the fracture, its location, the patient’s age, the quality of the implants and many other factors. An analysis of current domestic sources shows that in approximately 80-85% of cases it is possible to achieve results that are assessed by experts as excellent or good; the share of unsatisfactory outcomes accounts for about 2-4%.
It is noted that often removing the retainers turns out to be a more difficult task than installing them, so it is very important to observe optimal timing and follow well-established technologies, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the case.
Sometimes it is necessary to remove the fixators ahead of schedule (if there is a reasonable suspicion of a degenerative-dystrophic or atrophic process, if there is severe pain or other discomfort for the patient) or even on an emergency basis (for example, with the acute development of a purulent infectious-inflammatory process in the installation area, with instability and threat of displacement of the structure with the risk of damage to surrounding vessels, nerves, etc.). In other cases, on the contrary, the question of keeping the fixative in the body for life is considered, since this may be more expedient and safer (in the absence of complications) than exposing the patient to the risk of repeated surgical trauma.
1.General information
The term “osteosynthesis” literally translated from ancient Greek means the joining of bones; In English-speaking medicine, the synonym “internal fixation” is also common, which also quite accurately reflects the essence of this methodological direction in traumatological and orthopedic surgery.
Archaeological finds indicate that the first attempts to fix bones “from the inside” were made many centuries ago, in particular by healers of Central American cultures, and there is reason to believe that at least some such interventions were performed long before the patient’s death, i.e. . were carried out quite competently, ensuring intravital fusion and healing of fractures. The modern scientific paradigm of osteosynthesis dates its history only from about the middle of the 19th century. At the same time, by the turn of the 20th-21st centuries, this medical methodology was already so developed in all respects (theoretical, technical, technological, rehabilitation, etc.) that it confidently became the dominant or, as they say in medicine, the gold standard for the treatment of complex fractures. In this regard, it is necessary to note the generally recognized contribution of the Soviet and then Russian school to the development of the theory and practice of osteosynthesis (G.A. Ilizarov, M.V. Volkov, O.N. Gudushauri and many others).
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!