Salt deposition is what people often call arthrosis of the knee joint, or gonarthrosis. In fact, the cause of knee pain is not calcium salts at all, but changes in the structure of the cartilage. One way or another, you shouldn’t put it off until later, otherwise a slight stiffness in movements will develop into severe pain and complete immobility.
The knee joint is subjected to enormous physical stress in everyday life.
general information
The knee joint regularly experiences enormous stress. Walking, running, jumping, climbing stairs and simply standing - all this has an impact on the condition of cartilage. The processes of destruction and restoration are in constant balance, but if, under the influence of certain reasons, this balance is disturbed, the gradual development of arthrosis begins.
Initially, microcracks appear in the thickness of the cartilage, which help reduce its thickness in some areas. As a result, the load is redistributed on the contacting surfaces of the bones, which accelerates the pathological process. Gradually, a whole complex of changes occurs in the knee:
- thinning of cartilage until complete disappearance;
- changes in the composition and reduction in the amount of synovial fluid;
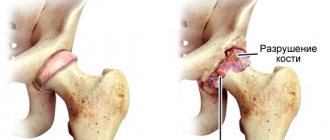
- damage to bones due to friction against each other;
- the appearance of bone protrusions (osteophytes) first along the edges of the joint, and then throughout its entire area;
- compaction of the joint capsule as a result of a chronic inflammatory process, which leads to joint stiffness;
- compensatory spasm of surrounding muscles.
Ultimately, the knee becomes significantly deformed and mobility is limited, leading to disability.
Depending on the location of the process, arthrosis of the knee joint can be unilateral and affect the right or left knee, or bilateral. In this case, both legs are affected.
Make an appointment
What should I do?
It is better to select a complex of drugs together with your doctor. It will probably include chondroprotectors with chondroitin and glucosamine. They are a building material for cartilage tissue, and also relieve inflammation, stabilize the condition of the joint and help reduce the amount of pain medication.
In the initial stages of arthrosis, intra-articular injections of a synovial fluid prosthesis, for example Noltrex, are indicated. While the cartilage is not sufficiently destroyed, this process can be stopped by restoring the fluid deficit. The gel is distributed inside and performs a shock-absorbing function. The joint stops hurting during movements, and most importantly, its degeneration stops.
After one or two Noltrex injections, painkillers will no longer be needed for a very long time.
2. Exercise through pain.
If the joint hurts, it means that the disease is in an acute stage. What it is - arthrosis or arthritis - the diagnosis will show. In any case, until the pain subsides, you should not load the joint. For such diseases, running, jumping, squats, intensive walking on uneven terrain, climbing hills and stairs, especially with heavy objects in your hands, are contraindicated.
Causes
Arthrosis occurs against the background of its damage due to increased load, inflammation, or against the background of congenital pathologies of the articular apparatus. The list of the most common reasons includes:
- knee injuries: dislocations, damage to ligaments and menisci, severe bruises accompanied by hemorrhage into the joint cavity, intra-articular bone fractures;
- increased load on the joint: professional sports, lifting weights, working in a standing position, wearing the wrong shoes, excess body weight;
- connective tissue pathologies: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis;
- congenital and acquired weakness of ligaments and muscles, including those associated with low physical activity;
- diseases or injuries of the musculoskeletal system, accompanied by increased load on the knee (flat feet, arthrosis of the hip joint, etc.);
- hormonal disorders, especially diabetes;
- metabolic disorders accompanied by salt deposition (gout);
- inflammation of the joint (arthritis) regardless of the cause;
- knee surgery;
- heredity.
How dangerous is the disease?
The danger of reactive arthritis is that it can develop into a long-term chronic recurrent disease that is difficult to treat.
Stages of ReA
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
The inflammatory process in the joints occurs in several stages:
- initial
- with an acute onset, general symptoms appear: fever, headache, malaise, as well as inflammation, swelling and tenderness of the joints; At first, the ankle joints and joints of the 1st toe are most often affected; - expanded
- asymmetrical damage to the joints of the legs (from bottom to top), starting from the ankle joints to the knees; pain appears in the lower back associated with damage to the joints of the spine, skin rashes, erosions on the mucous membranes, enlarged lymph nodes; with Reiter's syndrome - conjunctivitis and urethritis; - final
- with intestinal and nasopharyngeal forms of reactive arthritis, the inflammatory process ends after 3 months with recovery; in a subacute course, the process can last up to 6 months and also end in recovery; The urogenital form of ReA often occurs chronically.
Possible complications
Chronic reactive arthritis can cause lameness
Reactive arthritis should be treated as early as possible.
Prolonged inflammation can lead to chronic pain, especially in the heel, foot and toes, leading to lameness.
With a long chronic course of Reiter's syndrome, damage to the optic nerve and blindness is possible, as well as damage to the reproductive system and infertility.
What to do during an exacerbation
If the inflammatory process has taken a chronic, relapsing course, then it is necessary to carry out long-term treatment under the supervision of a physician. When the first signs of relapse of reactive arthritis appear, you should:
- limit physical activity;
- take a medicine from the group of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) - Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam; a tablet of any product can be taken orally, and a cream, gel or ointment with the same composition can be applied externally to the area of the affected joint;
- Urgently contact your doctor to prescribe adequate treatment.
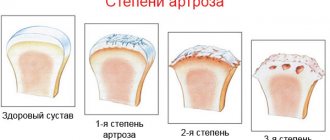
Degrees
Depending on the extent of tissue damage, orthopedists distinguish 4 degrees (stages) of arthrosis of the knee joint, which determine its symptoms:
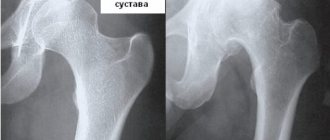
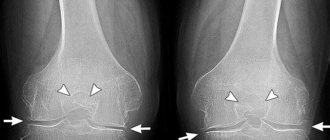
- grade 1: there are no symptoms, and minor abnormalities are found on x-rays;
- degree 2: the patient notes episodic pain during physical activity, when walking up stairs, squats, and standing for a long time; The images reveal a narrowing of the joint space and obvious foci of degeneration; initial manifestations of osteophytes or calcification of the lateral ligaments of the joint.
- degree 3: pain haunts the patient constantly, even at rest, walking without a cane is impossible; X-rays show a significant narrowing of the joint space, sometimes asymmetrical, due to damage to the menisci, signs of joint deformation, multiple, large osteophytes, bone growths;
- grade 4: movements in the joint are practically impossible, X-rays reveal complete destruction of cartilage and significant deformation of the articular surfaces of the bones, a large number of osteophytes; in severe cases, the bones fuse together.
Nutrition for deforming arthrosis of the knee
A healthy diet for deforming arthrosis of the knee joint includes dishes with a reduced content of trans fats and “fast” carbohydrates. Preference should be given to lean meat and fish, seafood and vegetables, steamed, wrapped in foil or stewed under a lid. Also useful are fruits, berries and drinks rich in antioxidants - wild plants, blueberries, lingonberries, cranberries, high-quality green tea and coffee. You can also eat whole grain porridge and legumes. But potatoes, white bread, sweets, processed foods, fast food and alcohol should be excluded.
If you are overweight with deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, consider low-carbohydrate diet options.
Symptoms
Symptoms of knee arthrosis are typical of a degenerative lesion. A person faces the following problems:
- pain at the initial stage manifests itself in the form of mild discomfort after climbing stairs, and then gradually increases; with severe damage, it becomes permanent and torments the patient even at rest;
- morning stiffness: occurs already in the early stages of development, at first lasts only a few minutes, then up to half an hour;
- crunching: occurs with the second and further degrees of damage, differs from physiological sound in sharpness and special tonality, and is also accompanied by pain;
- limited mobility: associated with the proliferation of osteophytes and increased bone friction; bending and straightening the knee is difficult and often accompanied by pain; in the final stages, the joint may become completely blocked (ankylosis);
- knee deformation: occurs due to changes in the shape of the contacting bones, bone growths and involvement of muscles and ligaments in the pathological process; when inflammation occurs, swelling of the tissues around the joint occurs;
- lameness: as arthrosis progresses, a person lame more and more; in the later stages, he is forced to use a cane or walker.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joint is carried out by an orthopedist-traumatologist. The following help to distinguish the disease from pathologies with a similar picture, as well as determine the degree of damage:
- interview and history taking: the doctor finds out the main complaints, the history of the development of the disease, learns about previous injuries, etc.;
- examination: the degree of knee mobility, tissue deformation, and pain syndrome characteristics are revealed;
- laboratory diagnostics: a general blood test reveals inflammation, a biochemical test reveals possible causes of problems;
- X-ray methods: X-ray and CT are the main diagnostic methods, allowing to detect typical signs of arthrosis: narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes, bone deformations;
- MRI: makes it possible to visualize soft tissues, assess the condition of muscles and ligaments;
- Ultrasound: assessment of the condition of muscles, tendons, joint capsule;
- joint puncture: allows you to take an analysis of the joint fluid, as well as insert a miniature camera to examine the cavity from the inside (arthroscopy).
If necessary, additional studies and consultations with specialists are prescribed.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
All treatment methods for arthrosis of the knee joint can be divided into three groups:
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical.
When a patient is diagnosed with stage 1-2 disease, a complex of medications and physical therapy is used, but if the lesion has become extensive, surgery remains the priority.
Drug treatment
Proper administration of medications can relieve pain, stop the inflammatory process if it exists, and also stop or at least slow down the destruction of cartilage tissue. The following groups of tools are used for this:
- anti-inflammatory (ibuprofen, ketoprofen, diclofenac, as well as their derivatives): relieve inflammation and relieve pain in the joint;
- hormonal (corticosteroids): prescribed when anti-inflammatory drugs are ineffective;
- antispasmodics (mydocalm and analogues): help get rid of muscle spasms and alleviate the patient’s condition;
- chondroprotectors (glucosamine, chondroitin and their combinations) stimulate the processes of regeneration of cartilage tissue;
- drugs to improve microcirculation (nicotinic acid, cinnarizine, pentoxifylline): improve the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the joint.
Depending on the situation, tablet, injection and local forms of drugs are used, intra-articular administration is allowed. Only a doctor is responsible for selecting medications, their dosage and frequency of administration. If used uncontrolled, many drugs can worsen the condition of the joint and also cause unpleasant side effects.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques are used to improve blood circulation in the joint area, increase mobility, and also enhance the effect of medications. The doctor may prescribe:
- shock wave therapy: ultrasound of a special frequency, helps eliminate osteophytes;
- magnetotherapy: exposure to a magnetic field, stimulating metabolism and regeneration processes;
- laser therapy: deep heating of tissues with a laser beam;
- electrotherapy (myostimulation): exposure of muscles to a weak electric current;
- electro- or phonophoresis: administration of medications (chondroprotectors or analgesics) using electric current or ultrasound;
- ozone therapy: introduction of a mixture of gases into the joint cavity.
Physiotherapy exercises and massage are also prescribed according to individual indications.
Basic modern techniques
Diagnosis of diseases of the knee joint, as well as their traumatic injuries, is aimed at visualizing its structures using several common methods, which include:
- Radiography.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasonography.
- Arthroscopy.
The choice of research method is determined by the results of a clinical examination, during which the doctor pays attention to the symptoms of the disease and the circumstances of the injury. The list of procedures and tests is also determined by the technical capabilities of the clinic.
Radiography
Surgery
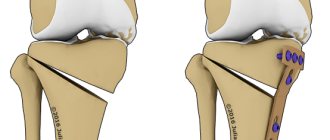
Surgical treatment of knee arthrosis is prescribed when other methods are ineffective. Doctors perform several types of operations:
- endoprosthetics: complete replacement of a damaged joint with a prosthesis;
- arthrodesis: fastening bones together to eliminate mobility (reduces pain and allows a person to lean on the leg);
- osteotomy: cutting one of the bones and placing it at the optimal angle to reduce the load on the joint.
Arthrodesis and osteotomy are used when it is impossible to perform endoprosthetics or it is necessary to postpone this operation for some time.
Make an appointment
Treatment methods for grade 1 osteoarthritis
The essence of the treatment of osteoarthritis at the very beginning comes down to the return of synovial fluid to its molecular composition. This way you can improve the nutrition of cartilage and restore the surface of bones. Once mobility is restored, pain and discomfort disappear and the patient recovers.
Complex treatment:
- Eliminate the causes of the disease, if possible. It is necessary to lose weight, improve nutrition, focusing on benefits and vitamins. Those who spend a lot of time on their feet are advised to change their lifestyle and monitor the alternation of work and rest.
- Restoring hormonal balance. If there is a suspicion that the cause of the disease is the influence of hormones, the rheumatologist sends the patient to an endocrinologist. Tests show where the imbalance is hidden, and, if possible, it is corrected with medications or nutrition.
The diet for osteoarthritis consists of low-carbohydrate foods. Protein, calcium and collagen are shown. Usually they recommend adding to the menu:
- Calcium: cheese, cottage cheese
- Protein: veal, white fish, beans
- Collagen: jelly, lentils
- Vitamins: fruits and vegetables
Prevention
To keep your knees healthy, you must adhere to the following rules:
- lead an active lifestyle, engage in amateur sports, walk more and do exercises;
- avoid stress and overwork;
- minimize the risk of injury;
- maintain weight within normal limits;
- eat properly and balanced;
- wear high-quality orthopedic shoes;
- Avoid putting excessive stress on your knees (heavy lifting, professional sports, prolonged work on your feet).
The same rules are relevant for those who already suffer from arthrosis, because following them helps slow down the development of the disease.
Diet
The condition of cartilage largely depends on the quality of nutrition. If there are signs of arthrosis, it is recommended to exclude:
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- excessively fatty and spicy foods;
- canned food and semi-finished products;
- products with artificial colors, preservatives, flavors.
The diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein, fatty acids (especially omega-3), collagen (found in gelatin, agar-agar). It is necessary to structure the menu in such a way as to prevent weight gain.
Glucocorticosteroids
If NSAIDs are insufficiently effective, as well as with synovitis, intra-articular administration of corticosteroid drugs is recommended -
Diprospan
Kenalog
Their administration quickly relieves pain and inflammation, but given that these drugs are hormones, their use is limited. It is believed that no more than 5 intra-articular injections are permissible with an interval of at least 5 days between them, after which it is necessary to refrain from administering them for several months in order to avoid the development of side hormonal effects and adrenal insufficiency.
Consequences and complications
Osteoarthritis of the knee joints develops very slowly, but if left untreated, this disease becomes the cause of serious and unpleasant complications:
- severe deformation of the joint and leg in general (associated with changes in the configuration of the knee, as well as restructuring of the muscle frame and curvature of the bones);
- shortening of the limb by grinding down the heads of the bones;
- ankylosis: complete lack of movement in the affected knee;
- damage to other parts of the musculoskeletal system due to improper load distribution (heel spur, arthrosis of the hip joint, pain in the spine).
To prevent these problems, it is important to undergo a timely examination by an orthopedist and follow his recommendations. Self-medication and addiction to folk remedies can cause a serious aggravation of the situation.
What is reactive arthritis (ReA)
The term “reactive arthritis” was first used more than 50 years ago to name arthritis that develops after yersiniosis in the absence of infectious agents in the joints. But after a few years, this name began to be associated with certain infections of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary organs and nasopharynx.
Currently, reactive arthritis is considered to be non-purulent inflammation of the joints, developing no later than 6 to 8 weeks after a urogenital, intestinal or nasopharyngeal infection. ICD-10 code M02.
Young men aged 17–40 years are more likely to get sick after suffering from sexually transmitted infections (women get sick much less often). In children, adolescents, as well as people of any age and gender, reactive arthritis can develop after intestinal infections, as well as infections of the nasopharynx.
The prevalence of ReA in our country among adults is about 43 per 100,000 population, among children - 99, among adolescents - 172. The incidence is growing, which is largely due to genetic predisposition, asymptomatic infections and untimely administration of adequate treatment.
There is also Reiter's syndrome, which develops after a urogenital infection and manifests itself in the form of three main symptoms: arthritis, conjunctivitis and urethritis.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
If your knee begins to crackle or ache suspiciously after physical activity, you should immediately make an appointment with an orthopedist. The Health Energy Clinic offers its patients the most popular and effective methods for treating the early stages of arthrosis:
- modern drug regimens for cartilage restoration and pain reduction;
- intra-articular administration of drugs for rapid pain relief;
- physiotherapeutic techniques;
- physical therapy under the supervision of an experienced instructor;
- professional massage;
- PRP therapy;
- injection of artificial synovial fluid to facilitate movement.
All methods of treatment and prevention are selected individually depending on the results of the examination.
General clinical recommendations
In the acute and subacute course of ReA, after a course of treatment, the patient should be under the supervision of a rheumatologist for six months with clinical and laboratory monitoring every 3 months.
In the chronic course of the disease, dispensary observation is longer with the prescription of courses of anti-relapse therapy until a state of stable remission appears.
After an illness, it is recommended to avoid heavy physical activity and strength sports. Swimming is a good way to restore joint function.
Persons with a genetic predisposition (presence of the HLA-B27 antigen) to reactive arthritis are recommended to have one proven sexual partner.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Advantages of the clinic
The Energy of Health clinic has modern equipment for diagnosing and treating a wide variety of diseases. We offer each client:
- comprehensive screening programs to identify various diseases;
- effective methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics;
- modern approaches to the treatment of diseases, including not only medications, but also physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage and diet according to indications;
- consultations of highly qualified specialists;
- flawless performance of medical procedures;
- comfortable conditions and maximum comfort within the walls of the clinic;
- reasonable prices for all services.
Health is the greatest value. We will help restore and strengthen it. Take the first step towards excellent health, sign up for an examination at Health Energy!
FAQ
Is reactive arthritis contagious?
No. But the urogenital infection that caused it can persist for a long time and be contagious.
Are there any peculiarities of the course, diagnosis, treatment in children?
In children, ReA is more acute and rarely becomes chronic.
What prognosis do doctors usually give?
The prognosis for reactive arthritis is favorable; in most cases, complete recovery occurs. But if left untreated, it becomes chronic with a long course and constant pain in the joints.
Reactive arthritis is a complex, incompletely studied infectious-allergic disease that mainly affects genetically predisposed people and requires timely and adequate treatment. It's not worth running.
But if you were unable to seek medical help in time, do not despair, modern technologies make it possible to provide assistance and relieve pain at any stage of the disease. The Paramita clinic (Moscow) will always help you.
Literature:
- Agababova ER, Bunchuk NV, Shubin SV, etc. Criteria for the diagnosis of reactive arthritis (draft). Scientific and Practical Rheumatology 2003;(3):82–3.
- Kovalev YN, Ilyin NI. Reiter's disease. Chelyabinsk: Option-book; 1993. 240 p.
- Zeidler H, Hudson AP. New insights into Chlamydia and arthritis. Promise of a cure? Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:637–44. doi:1136/annrheumdis-2013-204110.
- Ford D.K. Natural history of arthritis following venereal urethritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1953;12(3):177–97. doi: 10.1136/ard.12.3.177.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 10/13/2020 Date of update: 12/14/2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)