home
Treatment
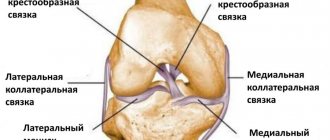
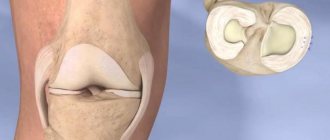
Knee-joint
Plasty of the cruciate ligament of the knee in case of rupture
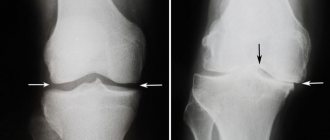
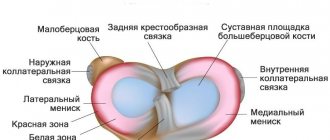
The knee joint has a cavity that houses strong collagen fibers that connect and stabilize two bones, the tibia and femur. These fibers are called the cruciate ligaments and are divided into the posterior and anterior ligaments. They solve important problems - they prevent the shin from moving inward and forward.
When jumping, hitting, turning the body with fixed limbs, the cruciate ligament is torn from the attachment point or ruptured. This type of knee injury is very common. According to statistics, the anterior ligament tears 15 times more often than the posterior one. Every year there are 30 such injuries for every 100 thousand people. They usually affect athletes (football players, hockey players, snowboarders, skiers) and dancers, with women 4 times more likely than men. The main danger of injury is that in 70% of cases it leads to damage to other elements of the joint - the internal meniscus, lateral ligaments, cartilaginous surfaces.
Degrees of ligament injury:
- microfracture – up to 10% of fibers are destroyed
- partial rupture – up to 50% of the fibers are damaged
- complete break
Typical symptoms of injury:
- pain
- hemorrhage, knee redness, swelling
- destabilization of the lower leg
- cracking sound when fibers break
- knee pain that gets worse with palpation
- difficulty flexing and straightening a joint
- swelling
- destabilization of the lower leg
Another common injury is a sprained cruciate ligament, which occurs when overuse occurs.
The main symptoms of a sprain:
Damage to the posterior ligament or sprain of the anterior ligament in the absence of destabilization of the joint can be treated conservatively. For more complex injuries, surgery is necessary. Plastic surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament will help restore the health of the joint.
Only a doctor can accurately classify the type of injury and prescribe treatment. In medical institutions, diagnosis of cruciate ligament rupture is performed during examination of the patient, motor tests, ultrasound, radiography, and MRI. Often victims go to the doctor late, considering the injury to be a simple bruise. This can lead to a worsening of the condition and the development of complications. If you suspect any ligament damage, you should consult a doctor.
Patients are often interested in how much a diagnosis will cost. This depends on the type of research chosen, the presence of additional injuries and concomitant diseases.
The main methods of treatment for ruptured cruciate ligament of the knee:
- conservative therapy for minor injuries;
- surgical reconstruction using arthroscopy - plastic surgery of the cruciate ligament of the knee joint.
For what diagnoses is surgery strictly necessary?
For a hip fracture, surgery is necessary the sooner the better, since this problem occurs in older people. If the operation is delayed, such patients are difficult to rehabilitate. With arthrosis, everything depends on how the patient assesses his condition, pain syndrome, and whether he is mentally ready to undergo surgery, regardless of what the doctor recommended. If you delay surgery for severe arthrosis, the remaining joints and spine suffer, and deformity appears. The sooner the patient undergoes surgery, the easier and faster the recovery.
What knee diseases can be diagnosed using arthroscopy?
- Inflammatory processes in the knee in acute and chronic form, including gonarthrosis.
- Deforming arthrosis.
- Rupture of the posterior or anterior cruciate ligament.
- Injuries and damage to the meniscus.
- Detection of fragments of torn cartilage (“articular mouse”).
- Baker's cyst.
- Fracture of the bones that form the knee joint.
- Displacement of the kneecap.
- Swelling of the synovial membrane.
- Articular cartilage defects.
- Arthritis.
- The presence of effusion inside the mobile bone joint (including with hemarthrosis).
Arthroscopy is also recommended if difficulties arise with making a diagnosis using other methods. Another indication is discomfort and pain after knee replacement or other knee surgery.
Arthroscopy is often ordered to determine the cause of knee pain.
Doctors performing cruciate ligament reconstruction:
Samilenko Igor Grigorievich
Traumatologist - orthopedist, doctor of the highest category
24 years of experience
Make an appointment
Marina Vitaly Semenovich
Traumatologist-orthopedist, head of the minimally invasive traumatology and orthopedics service
Experience 36 years
Make an appointment
Are there any contraindications
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive, but nevertheless surgical intervention that is not performed under the following conditions:
- if there is inflammation in the joint with purulent contents;
- in the presence of an extensive infected open wound;
- if the joint space is overgrown with high-density connective tissue, and movements in the knee joint are impossible for this reason;
- in case of serious condition of the patient.
There are also relative contraindications to arthroscopy, which remain at the discretion of the doctor. Sometimes the procedure is abandoned in case of violations of the tightness of the bone connection, in case of rupture of ligaments and joint capsule, as well as in case of heavy bleeding in the joint cavity.
Arthroscopy has absolute and relative contraindications - the decision remains with the doctor
Surgery on the ACL: types of plastic surgery, principle of execution
All types of plastic surgery in modern medicine are performed using arthroscopy with minimal trauma.
Experts choose closed surgery with general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. This eliminates damage to blood vessels, nerves and soft tissue, which minimizes blood loss during surgery.
Additionally, it is possible to avoid the appearance of large scars and scars, since incisions are made with a diameter of no more than 3-5 mm. An arthroscope is inserted into the incision, which displays a clear image on a screen using a miniature camera.
This allows the surgeon to see the treated area in detail and perform the work with maximum precision.
In what cases is endoprosthetics required?
Clear indications for knee replacement are the consequences of problems such as:
- post-traumatic arthrosis;
- rheumatoid polyarthritis;
- degenerative-dystrophic diseases;
- pathologically fused bones;
- tumor formations that interfere with the normal functioning of the joint;
- damaged ligaments of the knee joint with pronounced changes in the articular ends of the bones.
Often problems in the functioning of joints arise as a result of arthrosis, arthritis, gout, and frequent injuries. In these cases, the surgeon’s recommendation for endoprosthetics is also objective.
Autotransplantation
A part of the patient's tendons is transplanted, which the surgeon takes from the area of the patellar ligaments and tendons. A thin layer is cut off, which does not cause further discomfort to the person. When choosing this method, injured tissue is removed and replaced with healthy ligaments. The edges of the cut tendons are attached to the holes of the tibia and femur, after which they are stretched and fixed with biodegradable materials. After a few months, all materials become accustomed to the bone tissue. Due to the huge practical base and the high percentage of successful engraftment, specialists primarily give preference to autotransplantation.
Indications for surgery
Complete removal of the meniscus of the knee joint is inevitable if the diagnosis showed a rupture of a large part of the body or fragmentation of the cartilaginous layer. Fortunately, this happens extremely rarely. Organ-saving surgery, which is mainly performed, consists of partial removal of the meniscus of the knee joint, that is, resection of only the non-viable area. As for conservative medicine, it is used for minor fiber tears, microtraumas, structural degenerative-dystrophic changes, if they do not provoke pinching and joint instability.
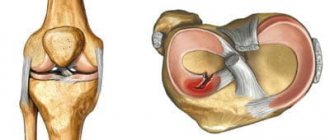
Types of meniscal tears.
According to doctors, patients do not always go to the hospital immediately, but years after they have experienced the injury. And what previously seemed like an ordinary bruise, over time leads to serious complications. Since the shock-absorbing pad does not have a sufficient network of blood vessels, there are practically none, some tears in certain areas cannot heal on their own - they must either be resected or stitched. Surgery on the meniscus, and it is reasonable to do it for fresh injuries, which increases the chances of full restoration of motor functions, has the following indications:
- the presence of a vertical break in the midline;
- transverse or longitudinal violation of integrity;
- flap (tongue-like) anterior tears;
- multiple bundles;
- separation of a fragment of cartilage from the main plate;
- pinched meniscus cartilage;
- highly fragmented structures;
- presence of cystic formations.
A removed meniscus in the hands of a traumatologist.
Loose meniscus pieces or torn pieces of cartilage that are constantly wedged between articulating bones are a real disaster for motor support functions and the health of the articular surfaces. Arthrosis is guaranteed if an operation to remove the meniscus of the knee joint, or rather its pathological fragments, was not performed in a timely manner. And neglected osteoarthritis is a direct road to disability. That’s why experts don’t advise tempting fate, but at least go to the emergency room first.
Attention! Internet sources often mention that they allegedly replace the meniscus of the knee joint, mind you, in passing and without any details. The scant information regarding the implantation of donor material or a meniscus implant simply means that such a technique has not yet received approval from orthopedic experts. Due to the insufficient clinical evidence base for its effectiveness, meniscal replacement, unlike knee arthroplasty, has not yet become widespread.
How risky is knee arthroscopy?
The operation is low-risk, but complications after such a diagnosis of arthrosis do occur. Among them are:
- increased bleeding, including inside the knee joint;
- wound infection after manipulation;
- breathing difficulties caused by anesthesia;
- allergies to anesthesia or medications injected into the joint;
- formation of a blood clot in the leg.
After arthroscopy, patients undergoing treatment for osteoarthritis sometimes complain of stiffness in the knee. Unfortunately, there are cases when, due to inept manipulation, cartilage, ligaments, menisci, blood vessels or nerve endings in the knee are damaged. To avoid this, you should undergo the procedure in reliable clinics.
Arthroscopy – jewelry work
How is recovery going?
Recovery from this minimally invasive procedure takes only a few hours. You can return home on the same day, and in some cases, a little later, within three days. To relieve pain, it is recommended to apply an ice pack to the knee, which will reduce swelling and reduce pain. On the first day, it is important to protect your leg from stress and provide it with complete rest. Also, to relieve swelling and pain, analgesics, manual or lymphatic drainage massage are prescribed, and anticoagulants are prescribed to prevent deep vein thrombosis.
A person can move independently without crutches on the second day. The stitches are removed after about two weeks. At your scheduled consultation, the surgeon will recommend a set of exercises. It will help strengthen your muscles and restore your range of motion.
How to prepare for surgery
The appointment of joint operations is preceded by a thorough diagnosis. It allows you to assess the degree of tissue damage and determine the severity of the pathology. During the procedure, the doctor gets an idea of the structural features of the joint capsule that will need to be taken into account during manipulations.
Previous diagnostics include:
- Ultrasound. Allows you to determine the presence of pathological changes in the ligamentous apparatus and cartilage tissue, determine the volume of synovial fluid and exudate.
- X-rays. Allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the diseased area, which is highly informative.
- Computed tomography (CT). Using a special tomograph, tissues are scanned layer by layer with small steps. CT allows you to obtain more than a hundred images that help assess the condition of each layer of tissue.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Like CT, this method allows you to take slice-by-slice images of the joint at a given step. But with MRI, the patient is not exposed to x-rays. Scanning occurs due to the influence of a powerful magnetic field on it.
To increase the information content, hardware research can be carried out with contrast. This is the name of the procedure for injecting a substance into a vein that penetrates through the blood into all tissues and increases the clarity and brightness of images. During a CT scan, the patient is injected with iodinated contrast agents, and during an MRI, gadolinium-based drugs are administered.
If you live in Moscow or the Moscow region, you can have joint surgery at our medical center. Prices for services depend on the complexity of the procedure. Surgeons perform intra-articular punctures of categories 1, 2 and 3. They are prescribed for the treatment of synovitis, bursitis, arthritis and other rheumatological pathologies.
Do I need special preparation for arthroscopy?
At your first appointment with your orthopedist, you will be told how to prepare for the procedure. The doctor will ask what medications you are taking and may make adjustments to them.
- It is recommended to stop taking aspirin and ibuprofen for several days or weeks before the procedure.
- You should not eat or drink for 6-12 hours the day before.
- If necessary, you will be prescribed additional pain medications.
How is arthroscopy used to determine the cause of knee pain? A practicing orthopedic surgeon-traumatologist tells and shows:
Complications after meniscus removal
Incomplete or total removal of the meniscus can have consequences, like any surgical intervention, although the likelihood of negative reactions occurring is low. According to statistics, about 90% of operations to remove the menisci of the knee joints predict a successful outcome without postoperative problems. Of course, with high precision of manipulation, compliance with asepsis and antisepsis during the procedure and proper postoperative care. But still, let’s announce possible complications:
- thrombotic formations in the operated limb;
- bleeding due to damage to blood vessels;
- injury to the nerve bundle;
- pathogenic infection inside a joint or in a surgical wound.
There is an opinion that a common consequence after meniscus removal is arthrosis. We do not argue, but it is also important to take into account the fact that total surgery, namely, it threatens the appearance of degenerative pathogenesis in 15 years, is a rarely used tactic, used exclusively in particularly difficult cases, as a last resort. For example, if the scale and severity of the lesion are not subject to corrective plastic surgery or partial resection of the meniscus of the knee joint, which is very rare.
Specialists always try to leave as much of a functional unit as possible, understanding that the biomechanics of the bone joint of the knee rests on it. Therefore, being guided by the fact that removal of the meniscus will provoke consequences in the form of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, and not going to the doctor, is a huge mistake. Serious osteochondral degenerations, plus atrophy of the thigh muscles, will definitely not take long to occur. And even simple defects in the collagen structures of cartilage left to chance, which at one time could have been completely cured conservatively, promise a similar outcome.
Valuable information! First of all, the operation saves the meniscus, which means that the pathological source that interferes with the normal interaction of the articular bones will no longer act on the knee. By eliminating the damaging factor, the likelihood of the formation of a degenerative-dystrophic focus in the structures of the bone joint is also reduced.
Recovery at home
It may take up to 3 months to fully recover from knee replacement surgery. Most people can return to normal activities within 6 weeks after surgery, but there may be some pain and swelling for up to 3 months, and scar tissue and muscle will still be healing over the next 2 years. Patients following knee replacement surgery can expect to engage in moderate exercise such as walking, swimming and cycling, but they should avoid extreme sports.
Types of meniscus repair
For meniscus injuries, several types of arthroscopic techniques are used:
- suturing;
- meniscus repair;
- partial resection of unstable meniscal fragments;
- total meniscectomy (complete removal).
Meniscus seam
Today, physicians prefer arthroscopic meniscal repair because it produces better clinical and radiographic results than partial and total meniscectomy. The integrity of the meniscus is restored by suturing or using plastic surgery. This operation allows you to stabilize movements in the joint and achieve uniform distribution of axial load on the articular surfaces of the thigh and lower leg. And this, in turn, reduces the risk of subsequent development of osteoarthritis.
On the other hand, with severe injuries it is not always possible to restore the integrity of the meniscus. Therefore, doctors often have to perform a partial resection or remove it completely. This produces less favorable results.
Review of Surgical Techniques
Surgery of the meniscus of the knee joint, which involves complete/incomplete removal, is called meniscectomy in orthopedics and traumatology. According to the method of creating access, the technique is classified into 2 types: open and closed resection of the meniscus of the knee joint.
The first type of procedure involves a cavity opening of the joint (incision length up to 8 cm) and manipulation through a completely open surgical field. Such outdated tactics are practically not used, because they are associated with significant intra- and postoperative risks. In addition, postoperative treatment of a removed meniscus after open radical surgery is long and very difficult for patients to tolerate.
The second option is based on the use of modern minimally invasive endoscopic technology – high-tech arthroscopy. The method makes it possible to productively eliminate a meniscal tear through 2-3 puncture punctures (5 mm in size), while the operation is characterized by reliable safety. The arthroscopic procedure today is the basis for the provision of highly effective and gentle surgical care to people with various meniscal injuries. Let's look at how arthroscopic meniscectomy works.
- Initially, of course, anesthesia is administered. The most common type of anesthesia for such a session is spinal anesthesia. Of course, a general anesthetic can also be administered. Even at the stage of preoperative preparation of the patient, the anesthesiologist takes care of the competent selection of the most optimal pain reliever.
- Next, the surgeon inserts into the joint through a miniature access a thin arthroscope tube equipped with a video camera, thanks to which the problematic component is displayed on the monitor screen in a greatly enlarged format. Then, through the same small incision, the non-functional fragment or the entire meniscus is removed using special microsurgical instruments. Note that replacing the menisci of the knee joints with donor material or a prosthesis is not practiced in this area.
- Non-viable tissues are removed through the outlet channel of the instrument. If the menisci are torn, surgery can help if you need to stitch the torn area. To do this, using a guide needle and special braided polyester threads, the doctor applies a strong longitudinal or transverse suture. At the end of all activities, the joint is sanitized (washed) in order to disinfect and thoroughly clean the cavity from small segments of cartilage.
Another example of a meniscus injury as seen through an arthroscope.
A minimally invasive operation, meniscal arthroscopy, has multifaceted possibilities. It is also used for detailed diagnosis of various knee pathologies. Today, arthroscopy is the most informative and 100% reliable way to determine even microscopic defects in hyaline and meniscal cartilage, ligaments, bones, condyles, bursae, capsule and other components of the articulation.
During the operation.
Modern medical technologies have undoubtedly reached the pinnacle of development, thanks to which many serious joint diseases requiring surgical intervention are treated safely, bloodlessly and relatively painlessly. Minimal trauma makes it possible to reduce the time of postoperative treatment of a removed meniscus and significantly minimize the likelihood of complications.