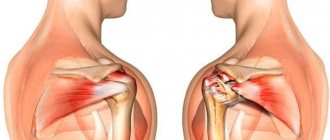
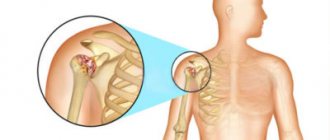
The glenohumeral joint is a ball-and-socket joint. This is one of the four joints that make up the shoulder complex. It is formed by the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. The glenohumeral joint is considered the most mobile, least stable and most susceptible to dislocation.
Movements in the glenohumeral joint
Planes in anatomy
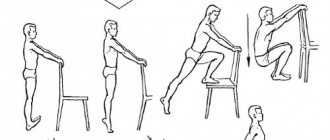
- Abduction (abduction) - raising the shoulder in the frontal plane.
- Flexion (flexion) - raising the shoulder anteriorly in the sagittal plane.
- Extension (extension) - raising the shoulder posteriorly in the sagittal plane.
- Internal rotation (internal rotation) - rotation of the shoulder inward (in the medial direction).
- External rotation (external rotation) - rotation of the shoulder outward (in the lateral direction).
- Abduction in the plane of the scapula is the elevation of the shoulder in the plane of the scapula, which is between the frontal and sagittal planes.
- Horizontal adduction is the inward movement of the shoulder in the horizontal plane (usually accompanied by some degree of shoulder flexion).
Procedure
The tomography procedure of the shoulder joint takes on average 20-40 minutes. The duration of the scan depends on the tomograph model. In the diagnostic room, the patient is placed on a tomography table. Then a special coil is placed over the examination area. The table is moved into the scanning part of the device and the screening procedure is started.
The main task of the patient during the examination is to remain completely still. This is largely a guarantee of quality research. The fact is that the tomograph is very sensitive to any movement. If the patient moves the shoulder during the scan, motion artifacts appear on the tomograms. They reduce the effectiveness of the study and the overall quality of diagnosis.
Questions about diagnostics
Dress code
You can enter the MRI room in any clothing that does not contain metal. When going to the clinic, it is best to wear loose, non-restrictive clothing without metal elements (zippers, rivets, hooks), in which you can lie comfortably. For women, we recommend bringing a T-shirt or not wearing a bra with metal wires or hooks.
Preparation
This tomography does not require any preparatory steps from the patient.
Is MRI harmful to health?
MRI is a completely harmless diagnostic method for the human body. This method of examination can be carried out at any age and for any disease an unlimited number of times, unless you have contraindications.
Contraindications
Some pacemakers and foreign objects in the body may pose serious limitations to tomography. In particular, cochlear implants, vascular clips, stents, heart valves and insulin pumps, pacemakers, neurostimulators, steel screws, staples, pins, plates, joint endoprostheses may be a contraindication to diagnosis. The patient must notify the radiologist about all implanted objects in the body. The diagnostician will be able, based on information about the composition and model of the implant, to assess the possibility of conducting diagnostics.
If you are having an MRI with contrast, be sure to report any allergies to medications or kidney problems. It is also necessary to inform the radiologist about a possible pregnancy.
Is it possible to do an MRI with braces and dental implants?
Dental implants and crowns are not a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic field does not have any negative effect on them. Fixed brace systems can produce artifacts on tomograms during MRI of the head. If the light effect is too strong, the doctor will stop the study and offer the patient alternative diagnostic methods.
Is the device noisy?
Any MRI machine in working condition makes noises reminiscent of tapping. The open tomograph is one of the quietest installations. The noise from its operation is significantly lower compared to closed tomographs. If the sounds of the operating unit cause you anxiety, you will definitely be offered special noise-canceling headphones.
What should I do if I have claustrophobia?
An open tomograph is the optimal solution for patients suffering from panic attacks in a closed space. It is open on the sides on three sides and does not create a claustrophobic feeling.
Can I take sedatives before an MRI?
If you are a little nervous, before the tomography you can take mild sedatives, for example, valerian, motherwort infusion or afobazole. Taking sedatives does not have a negative impact on the quality of MRI.
Why is it important not to move during the test?
Any movement during the examination reduces the quality of the resulting images. Multiple motion artifacts may appear on the images, and the MRI results will be uninformative.
Can I do the research with an accompanying person?
Absolutely yes. You can invite any accompanying person from among your family and friends to the MRI room. It is important that your companion does not have metal implants or artificial pacemakers in his body.
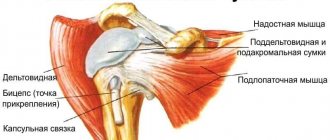
Joint capsule and ligaments
The joint capsule and ligaments of the glenohumeral joint provide passive support for the head of the humerus in contact with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
Capsule of the glenohumeral joint
Capsule of the glenohumeral joint
- Laterally, the capsule of the glenohumeral joint is attached to the anatomical neck of the humerus.
- Medially, the capsule is attached to the glenoid cavity and the articular labrum.
- When the arm is in a resting position, the lower and anterior portions of the capsule are relaxed while the upper portion is taut.
- The anterior portion of the capsule is strengthened by the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral (glenoid-shoulder) ligaments, which form a Z-shaped pattern on the capsule (some sources call this the articular-labial periarticular fibrous complex).
- The rotator cuff muscles strengthen the joint capsule superiorly, posteriorly, and anteriorly.
- Without ligaments and surrounding musculature, the joint capsule provides little support to the glenohumeral joint.
- According to some sources, the overall strength of the capsule has an inverse relationship with the patient’s age: the older the person, the weaker the joint capsule.
Indications
The shoulder joint is one of the most loaded joint systems of the musculoskeletal system. It is not surprising that regular stress on it can lead to degenerative pathologies and inflammatory diseases. If a person puts a lot of physical stress on his shoulder joints, their bone and cartilage structures begin to wear out quickly, and pain occurs. In addition, shoulder injuries are a common reason for visiting an orthopedist or traumatologist. In order to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the causes of shoulder dysfunction, the attending physician usually prescribes an MRI of the shoulder joint. The following symptoms may lead the patient himself to the idea that he urgently needs to undergo magnetic resonance imaging:
- pain and crunch in the shoulder;
- injuries in the shoulder joint, fractures;
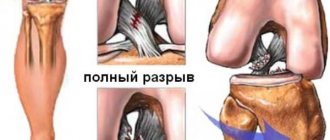
- ligament ruptures, periodic dislocations;
- swelling in the shoulder area;
- improperly fused bones, the presence of bone spurs;
- pinched nerves, tendons;
- visually noticeable tumor.
Initial appointment with an ORTHOPEDIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
Bursae of the shoulder joint
Bursae of the shoulder joint
The shoulder complex has many bursae, the largest being the subacromial bursa. It also includes the subdeltoid bursa as they are often continuous. The subdeltoid bursa allows the rotator cuff to slide easily under the deltoid muscle.
In order not to miss anything interesting, subscribe to our Telegram channel.
Blood supply
In addition to the main source of blood flow - the axillary artery, there are two auxiliary vascular anastomoses (circles) around the shoulder joint. The scapular and acromial-deltoid arterial circles are necessary for additional blood supply to the upper limb. This may be necessary if the axillary artery is damaged or blocked by atherosclerotic plaque.
Their essence lies in the formation of dense vascular networks in the thickness of the deltoid and subscapularis muscles. The vessels feeding these formations depart slightly earlier than the axillary artery. Therefore, if the blood flow through it is disrupted, then these plexuses will allow blood supply directly to the artery of the shoulder.
Since the vessels of these plexuses are small in size, they can provide normal blood flow only if the axillary artery is gradually damaged. Consequently, they will work effectively only with atherosclerosis of this vessel.
Muscles of the glenohumeral joint
Muscles of the shoulder complex
Flexors
- anterior portion of the deltoid muscle.
Extensors
- triceps brachii;
- teres major;
- posterior portion of the deltoid muscle;
- latissimus dorsi muscle.
Rotator cuff muscles
- supraspinatus muscle;
- infraspinatus muscle;
- teres minor;
- subscapularis muscle.
Internal rotators
- subscapularis muscle;
- teres major;
- latissimus dorsi muscle;
- pectoralis major muscle.
External rotators
- teres minor;
- infraspinatus muscle.
Abductors
- deltoid;
- supraspinatus muscle.
Adductors
- pectoralis major muscle.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that MRI of the shoulder is a safe diagnostic method, it is contraindicated in persons who have:
- metal objects in the body (shards, bullets, plates, staples);
- pacemakers, hearing aids and other electronic implants, the passport of which does not indicate o;
- Signs of inappropriate behavior of the subject (severe agitation, strange psychomotor reactions, panic);
- metal joint prostheses made of ferromagnetic alloys, such as steel;
- metal clips on vessels.
Metal elements used in modern orthopedics and surgery, in most cases, do not pose a danger during an MRI of the shoulder joint, but the patient must warn the doctor performing the procedure about the presence of any foreign objects in his body. The strong magnetic field of the tomograph can move them out of place and thereby damage surrounding tissue. Therefore, before a tomography, the radiologist may ask to see a certificate for a metal structure located in the patient’s body. After studying the data, he will assess the risks and make a decision about the safety of the study. If such documents are not available, it is recommended to undergo an X-ray examination before magnetic resonance imaging. It will show the presence of fragments, bullets or any other inclusions made of magnetic alloys in the body. Fillings and braces do not have a significant effect on the magnetic field of the tomograph and are not a contraindication to MRI of the shoulder joint.
Previous Next