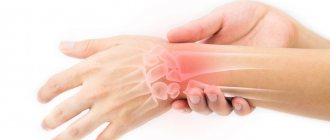
The human hand is one of the most functional elements of the body. It is difficult to imagine a full life without hands. The brush performs dynamic, touch and static functions. Despite its small size, it has a rather complex specific structure and consists of a bone frame, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, nerve fibers, etc. The ligaments of the hand are strong, elastic and dense formations of connective tissue that allow them to be fixed and held in a certain position. position of the joints, while providing them with the necessary mobility within the physiological norm. Ligaments also connect bones to muscles. The ligamentous apparatus of the hand provides elasticity and flexibility of the limb. Ligaments can withstand quite serious loads, but in cases of increased physical impact, various injuries are possible.
Types of damage
Ligament injuries in the hand occur in both adults and children. The reasons can be very diverse. These include household injuries (falling on an outstretched arm, which can be combined with dislocations and subluxations of the joints); sports injuries resulting from improper exercise or excessive stress on the hand. For children, ligament damage is common in cases where adults, without calculating their strength, lift or sharply jerk the child, holding him by the hands.
The most typical injuries to the ligaments of the hands can be considered:
- Sprains of the hand are injuries to nerve fibers and blood vessels at the microscopic level
- Rupture of the ligaments of the hand is a partial or complete violation of the integrity of the fibers. Less common is a complete separation of the ligament from the bone or with a fragment of part of the bone (then the ligamentous rupture is complicated by an avulsion fracture)
- Inflammatory processes occurring in the hands. These are the following diseases: peritendinitis (inflammation of ligaments and tendons), carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, etc.
Inspection
- We will begin the examination by collecting anamnesis. During this we want to know more about the origin of the injury and can already assess whether there are (according to the patient) any functional impairment. Have the patient describe the symptoms (the most common complaint is pain). It is also important to ask about expectations from therapy. You can gather information about previous injuries and any possible factors that may interfere with the healing process.
- After taking a history, you should examine the injured wrist, comparing it with the other wrist. A sore wrist may be swollen, red, warm, and painful to the touch.
- After completing the examination, you can palpate the wrist with all its structures. Most structures can be felt very well, but swelling and tenderness may interfere with this.
- After palpation, you should evaluate each joint for pain, abnormal movement, or crepitus.
- Physiological wrist movements can be examined using simple palmar flexion, dorsiflexion, radial and ulnar deviation tests.
- You should also test functional movement by allowing the patient to do things such as grasping, pinching, holding, and manipulating objects.
- When there is severe swelling, you can expect that even the simplest movements will be very painful for the patient.
- To test muscle strength, you can evaluate resistance movements. This is possible at the moment of flexion, extension, radial and ulnar abduction. Be careful as this can be very painful or even impossible for patients with severe wrist injuries where passive mobilizations are already painful and not fully feasible.
- Your test results, and therefore your functional impairment, will depend on the severity of your injury.
You can also do some more specific provocative tests to look for wrist injuries.
- Watson's scaphoid shift test.
- Lunate-triquetral ballot test.
- Extension of fingers against resistance.
- Mid-palm test.
- Distal radioulnar joint test.
- Stress test of the triangular fibrocartilaginous complex.
- Stress test of the triangular fibrocartilaginous complex with compression.
- Grip and rotation test.
These tests will give you more information about which ligaments are damaged and whether there is instability in the wrist.
Symptoms and location of pain
When sprains of the carpal ligaments, the following symptoms are observed:
- The occurrence of pain of varying intensity
- The appearance of puffiness and swelling of the hand
- The mobility of this part of the arm is limited
- When moving the hand, the pain increases
- A hematoma may appear on the injured area of the arm as a result of rupture of blood vessels
- With ruptures, the pain syndrome intensifies, a clicking sound is characteristic, and movements in the joint acquire an unusually large amplitude.
Symptoms of hand ligament injuries may vary depending on the location of the source of pain. For example, damage to the ligaments of the wrist, damage to the ligaments of the fingers and separately to the ligaments of the thumb are possible.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
If left untreated, sprains are complicated by acute and then chronic tendinitis. The pathology is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process with progressive dysfunction of the hand. Subsequently, the inflamed ligaments become ossified, that is, calcium salts are deposited in them. At this stage, a person is bothered by chronic pain and severe stiffness of the arm. It becomes impossible to cure the pathology conservatively.
In case of grade III sprains, the lack of medical care is fraught with irreversible loss of limb function. The victim loses the ability to perform certain movements with his fingers and hand. An operation performed untimely may not help correct the defect.
Diagnosis of ligament injuries
Diagnosis of sprains and ligament tears includes:
- initial examination by a doctor with a complete medical history of the patient
- x-ray examination
- ultrasonography
- magnetic resonance imaging.
The need to limit the load on the wrist
Applying an elastic bandage to the wrist is performed for preventive and therapeutic purposes.
Prevention:
- preventing damage to muscles, tendons, joints;
- reducing the risk of inflammation and irreversible changes in bone and muscle tissue;
- reducing discomfort when performing monotonous, monotonous work.
When treating chronic or acute diseases, such as arthritis and arthrosis, applying an elastic bandage to the wrist allows you to:
- reduce the range of motion of the joint, which helps reduce swelling and pain;
- prevent the development of pathological processes;
- speed up the recovery of the injured limb.
In addition, the bandage has a massage effect on the tissue, which improves blood circulation in the damaged area and promotes a speedy recovery;
Treatment options for hand ligament tears
For minor sprains and bruises, conservative treatment is prescribed. This is a set of measures that involves: drug treatment (taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, using chondroprotectors, ointments, taking vitamins); physiotherapeutic treatment (electrophoresis, laser treatment, magnetic therapy, wave therapy and other methods as prescribed by the doctor); appointment of massage treatments; applying a bandage that limits the mobility of the injured arm, etc.
In more serious cases (tears and ruptures of ligaments), the patient undergoes surgery in the hospital. The surgeon determines the optimal surgical option in each specific case, based on the patient’s diagnostic data. It consists of stitching torn ligaments, or removing inflamed parts of the ligaments, fixing tendons and bones. After surgery, the patient needs rehabilitation measures. To fully restore the functional ability of the hand, physiotherapy, therapeutic massage, exercise therapy, etc. are prescribed.
If you receive such injuries, you should not self-medicate and delay contacting a doctor. The sooner the correct diagnosis is made and the necessary treatment is prescribed, the more favorable the prognosis for the complete restoration of mobility and performance of the hand. Specialists from the Department of Hand Microsurgery of the Medical Center of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences are always ready to provide you with qualified assistance.
Physical therapy
Phase 1
First you have to follow the RICE algorithm:
- Rest: Stop using the injured wrist for 48 hours or until pain and swelling subsides.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a towel to the injured wrist (for about 15 minutes, several times a day for several days). Do not use ice for more than 20 minutes at a time!!! —— It is believed that cryotherapy allows you to narrow the superficial vessels, thereby reducing local blood flow and swelling. There is some debate about the effectiveness of cryotherapy, but most studies support the fact that cryotherapy has an analgesic effect. There are also indications that cryotherapy affects inflammation, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
- Compression: Apply an elastic compression bandage to your wrist. This should help drain fluid from damaged tissue. Start applying the bandage at the base of the fingers and stop just below the elbow, i.e. we move towards the heart. The wrap should be tight, but be careful not to restrict blood flow.
- Elevated position: Try to keep your wrist higher than your heart (as often as possible for two days). This will help fluid drain and reduce swelling around the wrist. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is also recommended.
In cases of severe injury, wrist immobilization may be recommended. In some cases, surgery may be required to repair a completely torn ligament.
How to provide first aid for sprains on the hands?
In such cases, the following methodology is used:
- The injured person must immediately immobilize the arm that was injured. For these purposes, you need to bandage your wrist with a plastic tourniquet or bandage. If you don’t have them at hand, you can use a handkerchief, a scarf, a piece of cloth, etc. The injured hand must be suspended.
- If the damaged joint is capable of actively bending and unbending, then to fix it, you need to use a homemade splint from any hard material at hand (slats, boards).
- It is recommended to apply a cold compress to the injured area. This temporarily relieves pain and swelling for the patient.
- When, in severe cases, the victim suffers from persistent, severe pain, it is advisable to give him an anesthetic, and if possible, then give him a pain-relieving injection.
- After this, the patient must be urgently transported to a trauma hospital. There doctors will prescribe him a special course of treatment. It includes the use of various special-purpose equipment and the patient undergoing physiotherapy courses.
2. Why muscle strain occurs
In the process of life, when we are awake, certain muscle groups are almost constantly working, making numerous contractions. For the most part, they are safe and do not lead to negative consequences. In this case, the muscles adjacent to the contracting muscle tissues are stretched. The elongation limit is quite high, but in extreme situations, during overloads or sudden movements, a mismatch occurs - adjacent muscles contracting simultaneously cause harm to each other. The muscles most often subject to excessive stretching are the back, neck, legs, and forearm. Regular training and warming up before heavy exercise can minimize the risk of such injury. Also important here:
- natural flexibility of the body and elasticity of tissues;
- general physical fitness;
- individual characteristics of the musculoskeletal frame;
- posture.
Factors and situations that increase the likelihood of getting a sprain are very diverse and sometimes unexpected:
- practicing sports involving monotonous movements (rowing, tennis), as well as contact team sports (football, basketball);
- long periods of static body position in an uncomfortable, monotonous position (sitting at a table, embroidering, painting and some crafts);
- sudden loss of balance, falling on ice, jumping over an obstacle/puddle/stream;
- sharp sudden cough;
- lifting weights without bending your knees;
- catching a thrown object (volleyball);
- inconsistency when performing heavy work with the participation of a partner.
Visit our Traumatology and Orthopedics page
How to apply
You can find out how to apply an elastic bandage to your wrist in each specific case by consulting with your doctor. Independent unskilled bandaging may not improve, but only worsen the situation and lead to more serious consequences. It is imperative to go to a medical facility if it is necessary to apply a bandage for medical reasons.
The general rules for applying an elastic bandage to the wrist are as follows:
- wrap the bandage around your wrist, starting from the inside;
- stretch the bandage diagonally across the outside of the palm, between the thumb and forefinger and back through the inside of the palm;
- wrap the bandage around the wrist and pull it in the opposite direction (along the inside of the palm, between the thumb and index finger) and through the outside of the palm back to the wrist;
- wrap your wrist and make several turns, partially overlapping the previous layer by at least half the width;
- secure the bandage.
It is also important to follow the following rules:
- the tension of the bandage should not be very strong, otherwise there is a high probability of disrupting blood flow in the affected area;
- The bandage should not be applied to swelling. To relieve swelling, you need to raise your hand up and hold it in this position;
- Bandage should be done from narrow to wide;
- There should be no folds or gathers, the bandage should not be twisted;
- Even tension should be maintained, otherwise the bandage will not hold well.
Preventive measures
Anyone may experience a situation where symptoms indicate a sprained arm, and treatment for such injuries is inevitable. But damage can be avoided if you follow safety rules in any situation: at home, at work, in the gym or just on a regular walk.
When performing sports exercises, you need to use special equipment. Extreme caution must be observed on the road, both as a pedestrian and when driving a vehicle.
You need to walk carefully in heels, as a careless fall can lead to dire consequences. If the activity involves lifting heavy objects, then movements should be light and smooth; sudden jerks increase the risk of injury.
Those suffering from excessive weight should reconsider their diet and try to lose a few extra pounds. Consume sufficient amounts of vitamins necessary to strengthen ligaments and the entire body as a whole.
The rules are quite simple, but if you don’t forget about them and adhere to the right lifestyle, you can avoid spraining your hand, which you won’t have to think about doing in such situations.
Diagnostic tests
Even if you have the slightest suspicion that a sprain has occurred in the palm of your hand, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible to make a diagnosis. Only a qualified doctor, after analyzing the mechanism of injury, will be able to determine the severity of damage to fibers and tissues.
If necessary, the doctor may also prescribe diagnostic measures:
- if there is a need to refute or confirm the presence of inflammation, then laboratory tests are carried out, namely: analysis of synovial fluid and a general blood test. They are prescribed when a sprain on the wrist is advanced and full treatment was not carried out immediately after the injury;
- radiography. It is prescribed as an independent examination or in combination with other procedures. Using an x-ray, the doctor determines whether a ligamentous joint has been damaged or a bone fracture has occurred. In some cases, an x-ray is enough to accurately diagnose and treat sprains of the wrist according to the correct scheme;
- ultrasonography. The procedure is absolutely harmless and at the same time highly informative. It is used both to establish a diagnosis and to analyze the effectiveness of the treatment process. Ultrasound scanning shows a complete picture of the condition of tendons, muscle tissue, joints and ligaments;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It allows you to see images of all layers of soft tissue from different angles. If we compare this procedure with an x-ray, it is much safer for the body in terms of radiation, so MRI is very often used to diagnose and monitor injuries in pediatric patients;
- arthroscopy. This procedure is minimally invasive; in terms of the nature of its implementation, it is equivalent to surgical intervention. The surgeon makes punctures in the skin and through them inserts a surgical instrument and a microscopic optical system under the epidermis. The event is carried out in cases where other methods cannot determine the causes of pain, or when conservative treatment does not provide the desired result.
These are the main diagnostic procedures that allow you to correctly determine the type and complexity of the injury, as well as correctly determine the method of further treatment.
Basic dressing methods
There are several ways to apply elastic fabric when stretched:
- Circular - the retainer is applied in such a way that each turn is applied 2 times at the same level, after reaching the damaged area, the retainer is used, the duration of wearing is 3-10 days, it should be removed to apply medications, change the bandage, and treat the wound.
- Spiral - also applied in a circular manner, in a beveled direction, the next layer overlaps the previous one by 2/3. Bandaging can be done from top to bottom or vice versa, the thickness depends on the tightness of the fit. Every two turns, the elastic bandage must be bent in the vertical direction; the duration of wearing is 1-1.5 weeks.
- Cross-shaped - the name corresponds to the shape and course of bandaging; in the process, elastic fabric is wound in the shape of the number 8. The first turns start from the top, from the area above the wrist, gradually descending to the back of the hand. After this, the dressing is performed obliquely to the joint, the manipulations are repeated until the hand is completely fixed. At the final stage, the specially bifurcated parts of the fabric must be connected (bandaged), the duration of wearing is 5-15 days. Removal of the elastic bandage is allowed if the limbs feel numb.