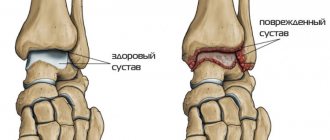
Coxarthrosis is deforming arthrosis of the hip joint. This is a chronic disease, which is characterized by degenerative changes in tissue and damage to cartilage. Symptomatically, coxarthrosis is determined by regular pain and deformation in the hip joint, and impaired mobility. The pathological changes are based on cartilage damage and the subsequent inflammatory reaction. With arthrosis, bone tissue changes. The lesion occurs locally, but may also involve other articular joints. The main group of patients are elderly people. Risk factors may include hereditary predisposition, large body weight, and previous trauma. People with this problem exhibit endocrine disorders and metabolic imbalances. But the main emphasis in treatment is on restoring the structure and functions of cartilage. Treatment of coxarthrosis is a long process, including anti-inflammatory therapy, the use of chondroitin and glucosamine preparations to replenish joint nutrition, exercise therapy and physiotherapy. To maintain joints at home, herbal treatment is recommended. A proper diet and moderate physical activity are extremely important.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
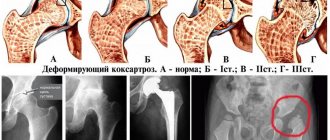
In coxarthrosis, articular cartilage is the first to undergo deforming changes. There are 3 stages of disease development. At the initial stage, there are no morphological changes in the tissues of the joint. Only his functional viability suffers. A person feels periodic pain in the joint area after physical activity, running, or long-distance walking. After rest, the pain disappears. In the second stage, the bone begins to deform. The naturalness of movements decreases sharply. The pain varies in intensity and often appears at rest. The third stage is characterized by chronic pain syndrome. Pain bothers patients day and night. Walking without a cane is difficult; a person is forced to bend his torso forward. Multiple growths appear on the articular bones.
The main symptoms of arthrosis include:
- morning stiffness;
- joint pain;
- difficulties in moving at a distance of more than 1 km;
- increased pain with prolonged sitting or standing.
Orthopedists call coxarthrosis one of the most common types of arthrosis. The risk group includes obese people, those engaged in heavy physical work, and the elderly. Lack of treatment leads to complete destruction of the hip joint, accompanied by unnatural mobility or complete immobility, as well as severe dysfunction of the lower extremities.
Lilac tincture
To prepare a miraculous pain reliever, you need the following ingredients: potatoes, black radish and a tablespoon of finely chopped parsley.
Mix everything, make a compress. For severe pain, use every 3-4 hours. You can also fill a two-liter jar with lilac flowers, add alcohol, and place in a cool, dark place for three weeks. It is recommended to rub the affected area every day, preferably before bed. Try this method: mix honey, iodine, glycerin and alcohol in equal proportions. Place the mixture in a dark place for 12 hours. Apply with light movements to the affected area from bottom to top, do not rub, and after the procedure, lie down for two hours. Store the mixture in the refrigerator. And as one of the options - bodyaga: mix 1 tablespoon of butter with this plant. Rub into the problem area before going to bed.
Valery DEMIDOV, Polotsk
Drug therapy
Treatment of coxarthrosis begins with limiting exercise. This is a long process that combines a variety of therapy methods: taking anti-inflammatory and painkillers, intra-articular injections, physiotherapeutic treatment and exercise therapy.
Features of treatment of coxarthrosis of 1, 2, 3 degrees:
- at the first stage, NSAIDs are prescribed to stop the inflammatory process; medications that normalize metabolic processes and analgesics are also needed; folk remedies are used in complex therapy;
- at the second stage of coxarthrosis, intra-articular injections based on hyaluronic acid are added to drug therapy, laser treatment, and electrical stimulation are performed;
- the third stage is treated conservatively and surgically, when it is impossible to cope without surgery, joint replacement is performed.
Drug treatment plays the biggest role. Without anti-inflammatory and supportive drugs, degenerative changes cannot be avoided and constant pain cannot be eliminated. Doctors prescribe pharmacological agents of various actions to alleviate the condition of patients during exacerbations.
- Drug treatment plays the biggest role. Without anti-inflammatory and supportive drugs, degenerative changes cannot be avoided and constant pain cannot be eliminated. Doctors prescribe pharmacological agents of various actions to alleviate the condition of patients during exacerbations.
- Muscle relaxants. Reduce the tone of skeletal muscles. The muscles relax, which reduces pain, and the person gets relief from pain. These drugs are contraindicated in patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
- Chondroprotectors. Symptomatic preparations containing collagen. Nourishes damaged cartilage and restores it. They supply the joint with collagen from the outside and stimulate its production by the body. Chondroprotective drugs are taken for a long time. Under the influence of these agents, tissue metabolism improves, and damaged cartilage gradually increases. In complex therapy, these drugs have undoubted benefits, especially at the initial stage of the disease. In case of chronic arthrosis, they postpone disability.
To stop the destruction of cartilage tissue and provide the joint with “lubrication,” injections are given with drugs based on hyaluronic acid and synthetic substances, the composition of which is similar to synovial fluid. They are highly compatible with human body tissues. They effectively stop the process of cartilage destruction and have an analgesic and chondroprotective effect. Synthetic substances contain silver ions, which provide an additional bacteriostatic effect.
Diagnostics
An orthopedic traumatologist is involved in identifying symptoms and selecting treatment. To make a diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease, he uses:
- survey: listening to patient complaints, identifying risk factors (injuries, diseases, heredity, etc.);
- examination: assessment of limb mobility, identification of areas of greatest pain;
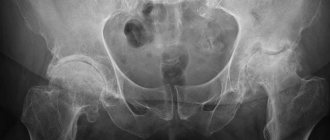
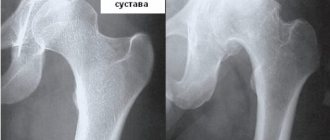
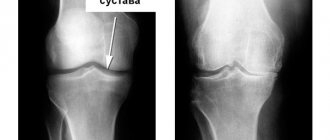
- X-ray: X-ray makes it possible to assess the condition of bones and cartilage, the size of the joint space, the presence and location of bone growths; to examine the necessary details more carefully, the study is supplemented by CT (computed tomography);
- laboratory diagnostics: a general blood test allows you to identify signs of an inflammatory process, a biochemical test allows you to note some risk factors, for example, the level of uric acid;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): allows you to evaluate the condition of not only bones and cartilage, but also soft tissues: bones, ligaments, muscles, joint capsule, etc.;
- joint puncture
If it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with other diseases, as well as evaluate concomitant pathologies, additional tests, instrumental examinations, and consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed.
Prosthetics
Endoprosthetics is a surgical method of treating the hip joint. When, as a result of coxarthrosis and dysplasia, irreversible consequences occur in the cartilage tissues, joint replacement is resorted to. As a result of the operation, it is possible not only to reduce constant pain, but also to restore function and mobility of the joint. Artificial joints are made of metal-polyethylene and ceramics. Fixation to living bone occurs in a cemented or cementless manner. Endoprostheses take root well and can last for decades. But in some cases, the prosthesis wears out quickly, and then repeated surgery is required.
How to understand that you have coxarthrosis
The bones of the hip joint are covered with articular cartilage, which provides soft gliding and helps distribute the load while walking. The joint fluid performs a shock-absorbing and nutritional function. With the development of coxarthrosis, the characteristics of the articular or synovial fluid change - it is no longer able to sufficiently lubricate the cartilage tissue. The cartilage dries out and becomes thinner - the bones of the joint begin to rub against each other and become deformed.
At different stages these processes are accompanied by:
- pain in the groin and thigh;
- pain when walking, rising from a chair or bed;
- crunching in the joint;
- limited mobility;
- slight limp due to atrophy of the thigh muscles.
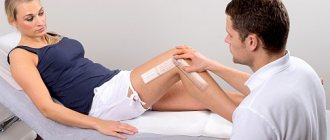
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint is carried out using complex measures, including physiotherapy. This area is associated with physical rehabilitation, supporting the body during the period of recovery and remission, and preventing exacerbations. Physiotherapy is provided by orthopedists, traumatologists, rheumatologists, massage therapists, and exercise therapy instructors.
The following methods are recognized as effective for the treatment of coxarthrosis:
- ultrasound therapy;
- laser therapy;
- inductothermy;
- massage;
- manual therapy.
With ultrasound therapy, high-frequency waves penetrate tissue and act like a vibration massage. They improve biochemical processes, prevent stagnation, and promote better absorption of medicinal substances. Ultrasound reduces the inflammatory process.
Laser exposure dilates blood vessels, stimulates lymph flow, inhibits inflammation, and heals tissue. The technique improves tissue trophism and helps preserve the structure and function of organs.
During inductothermy, the body is exposed to high frequency waves. The method is effective in the presence of any inflammation and pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Stimulates the immune system, relieves pain, and has a regenerating effect.
Massage can be hardware or mechanical. Contrary to popular belief, during a massage not only the superficial layer of skin and muscles is exposed. During the work of a massage therapist, reflex and humoral mechanisms of regulation of internal organs are activated. By combining a wide variety of massage techniques, the patient receives antispasmodic, tonic, lymphatic drainage and analgesic effects.
A chiropractor works on human bones and joints. It relieves tension from some areas, tones others, eliminates pain, and restores the functional viability of joints. First, the doctor uses diagnostic techniques, during which he determines the condition and capabilities of the muscles, ligaments, and joints. Then he moves on to treatment. Manual techniques are not used during exacerbations and complications.
Causes
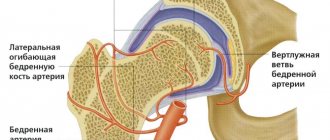
One of the common causes of arthrosis of the hip joint is mechanical damage, not only direct injuries, but also microdamages caused by the destructive effect of excessive loads on it. One of the most common causes of the disease is a fracture of the femoral neck. It extends from the femur at an angle of 120° and connects it to the head. The presence of osteoporosis significantly increases the likelihood of a hip fracture, but this type of injury can also result from a traffic accident, a fall from a height, an impact, etc.
A femoral neck fracture may be accompanied by aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, which will become a trigger for the development of degenerative changes in the joint. The presence of dysplasia or subluxation of the hip joint, ruptures of its ligaments, transcondylar fractures or fractures of the acetabulum also creates favorable conditions for damage to its structures. In such situations, post-traumatic arthrosis of the hip joint is diagnosed.
Often, post-traumatic arthrosis of the hip joint occurs in professional lightweight and weightlifters, parachutists, loaders, and speed skaters.
The development of arthrosis of the hip joint after injury is caused by a violation of the congruence (comparability) of the articular surfaces, a decrease in the quality of blood supply to the components of the joint and prolonged immobilization. As a result of prolonged immobility, not only deterioration of blood circulation in the fixed area occurs, but also shortening of muscles and a decrease in their tone. The likelihood of post-traumatic arthrosis increases significantly when treatment is inappropriate for the situation or untimely treatment, which leads to the persistence of defects of varying severity. Also, the risks of its development increase with excessively early loading of the joint and inadequate exercise therapy, including too intense, started late or, conversely, early.
Sometimes the disease occurs after surgical interventions on the hip joint due to the formation of scars and additional tissue trauma. Although in some cases surgery is the only way out to eliminate the consequences of the injury.
Excessive loads can also trigger changes in the hip joint, as they lead to microtrauma. Regular tissue damage activates the process of division of chondrocytes (cartilage cells). This is accompanied by an increase in the intensity of the production of cytokines, which are normally produced in small quantities. Cytokines are mediators of inflammation, in particular the cytokine IL-1 leads to the synthesis of special enzymes that destroy hyaline cartilage of the hip joint.
In addition, high loads can provoke microfractures of the subchondral plate. This leads to its gradual compaction and the formation of bone growths on the surface, called osteophytes. They can have sharp edges and cause further destruction of the joint and also injure surrounding tissue.
The subchondral plate is the outermost part of the bone in direct contact with hyaline cartilage.
In some cases, it is not possible to determine exactly what triggered the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the hyaline cartilage of the femoral head and acetabulum. In such situations, idiopathic or primary arthrosis of the hip joint is diagnosed.
Today it has been established that the tendency to develop it can be inherited, i.e. the presence of this pathology in close relatives significantly increases the chances of developing arthrosis of the hip joint. Presumably, it has polygenic inheritance, i.e. its development depends on the presence of many genes. Each of them individually creates weak preconditions for the development of the disease, but when they are combined, it becomes a matter of time, especially when leading a sedentary lifestyle and obesity or, conversely, heavy physical labor.
There is a theory that arthrosis of the hip joints is a consequence of the presence of a congenital or acquired mutation of the type II procollagen gene.
There is also secondary arthrosis of the hip joint, which develops against the background of concomitant diseases and age-related changes. But its features are discussed in more detail in a separate material “Coxarthrosis”.
The role of sanatorium treatment
For coxarthrosis, great importance is given to sanatorium treatment. Treatment and prevention institutions primarily use natural factors to support people with musculoskeletal diseases.
- Climatotherapy. These are terrain features, a combination of weather factors, sea water, sun, air. Climatic therapy helps recovery, prevents the development of exacerbations, improves the course of biological and physiological processes in the body. Ideal conditions for the treatment of arthrosis are created in areas with high air temperatures and large amounts of solar radiation.
- Healing mud. They vary in origin. There are peat, sulfide-silt, sapropel, hydrothermal. They are distinguished by high heat capacity. They contain mineral, organic, biologically active components that penetrate the skin and have a beneficial effect on the joints. Improve metabolic processes, reduce inflammation, normalize blood circulation.
- Mineral water. Contains microelements, dissolved salts, and biologically active substances. For diseases of the musculoskeletal system, mineral baths are indicated. The procedures increase mobility, tone, activate blood circulation, and improve metabolism.
- Phytotherapy. A method based on the use of medicinal herbs. Infusions and decoctions contain a large number of active substances that not only effectively support the sick body, but also have a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Treatment with natural factors in sanatoriums is combined with physiotherapeutic methods, physical therapy, dietary nutrition, and adherence to a daily routine. Sanatorium-resort programs are developed for all stages of joint diseases.
Physical activity
In recommendations for people with arthrosis, doctors advise limiting the load on their legs. It is worth stopping squatting, squatting, and being more careful when doing physical work in the house and in the garden. Do not strain the joint if pain is already felt (reduce the drastic load). It is especially worth excluding running and jumping. However, you won’t be able to do without gymnastics.
To make the joint function, you should do special exercises. A person with arthrosis is categorically not suitable for “young” gymnastics - at a fast pace, with increasing loads, with a high intensity of the entire session. For a sore joint, gymnastics should be done extremely slowly, smoothly, measuredly, until discomfort or pain appears. If there is pain, you should take a break.
Therapeutic gymnastics allows you to normalize the condition of the muscles, improve blood circulation in the joint, provide it with adequate nutrition, and remove decay and inflammation products. Gymnastics helps medicinal substances get into the diseased joint faster and begin their therapeutic effect. The most difficult task of physical therapy is to dose the load correctly. Too short a workout will not allow you to achieve a therapeutic effect. And excessive load will cause additional harm to the joint. Only the attending physician can give competent recommendations. They will depend on the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the disease in each specific case.
Is pain relief necessary?
If you suffer from coxoarthrosis, then you know what pain it causes. Unpleasant sensations increase with movement. Naturally, there is a desire to take a painkiller pill or use an ointment. But such measures are temporary. As for anti-inflammatory drugs, it makes no sense to take them for arthrosis, since this is not inflammation. All of these medications contribute to the development of the disease, creating the appearance of improvement.
We restore the natural production of periarticular fluid. This brings long-term effects.
Nutrition for coxarthrosis
There are many reasons for the destruction of cartilage. Great importance in the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint of 1, 2, 3 degrees is given to nutrition. Today the market is filled with products rich in preservatives. Attractive hams, smoked meats, and sausages that flaunt on the shelves contain a large number of specific components. The meat is treated with enzymes, active substances that speed up the production process and allow you to quickly obtain an attractive product. Preservatives increase the shelf life of any product: finished or raw, which cannot but be widely used among manufacturers.
When consuming food loaded with preservatives, a person receives excess salt, which retains moisture. Salt is retained and accumulates in the cartilage tissue, causing the normal functioning of the joint to fail. Such arthrosis is essentially a simple inflammation, which is perfectly treatable. And coxarthrosis, which arose against the background of metabolic disorders, metabolic failure, and intake of junk food, requires adherence to a diet. It is not necessary to strictly limit your food intake or give up a whole list of healthy foods. It is enough to follow simple rules:
- refuse any ready-made smoked meats from the store;
- eliminate the consumption of concentrated broths;
- According to the method of preparing dishes, give preference to boiling and stewing;
- completely eliminate salt consumption, do not buy salted fish, sausages, canned foods;
- consume no more than 10-15 g of animal fats per day, prepare meals with the addition of a variety of vegetable oils;
- monitor the calorie content of foods, give up so-called “fast” carbohydrates, sugar, and confectionery;
- exclude mayonnaise from the diet, season salads and sauces with low-fat sour cream;
- eliminate the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- limit consumption of fatty fish and caviar.
Instead of smoked meats, buy natural meat and chickens raised on farms by domestic producers. It is better to cook first courses in vegetable broths, without boiling vitamin-rich foods for several hours. The bouillon cubes popular today are almost 100% chemical. This is harm in its purest form.
You should not completely give up boiled meat. But it’s better to take pre-boiled lean pieces and put them in portions on a plate, and only then pour in the vegetable soup. Complete abstinence from meat is extreme.
An ancient recipe for maintaining strong bones and joints is jellied meat. Several decades ago, when little was known about artificial preservatives, this was justified. Now such a product can only increase cholesterol.
Fresh fish has not previously been treated with preservatives. But modern manufacturers have learned this too. Today, we can talk about the benefits of fish only if it came to the counter directly from a fishing trawler or was bought alive.
Only by changing the principles of nutrition can a person reduce suffering from deforming arthrosis. The diet should include a large amount of fresh vegetables, berries, herbs, and fruits. Low-fat dairy products, lean meats, and chicken are healthy. Rice, beets, potatoes, and watermelon help remove salt from the body. Once a week, it is recommended to arrange fasting days on kefir, cottage cheese, fruits, and herbal decoctions.
Treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint in the Solnechny sanatorium in Belarus
Treatment of coxarthrosis is one of the main profiles of the Solnechny sanatorium. Over many years of work at the institution, an impressive practical base has been developed for the management of patients with this type of illness. Within the framework of the sanatorium, a wide range of therapeutic and preventive measures are carried out in the direction of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The medical base is equipped with all the necessary instruments and equipment for the treatment of pathologies of the hip and other large and small joints. Specifically in this area, the following types of procedures are used: physiotherapy, massage, acupuncture, mud therapy, exercise therapy (including pool and swimming exercises).
Sanatorium Solnechny is the only one in the country that practices treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint through intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid. A rehabilitation treatment program for hip arthrosis has been successfully applied. See here .