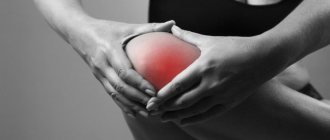
Meniscal injuries are one of the most common knee injuries. Most often it occurs in athletes and able-bodied people aged 18-40 years. The optimal treatment method for knee injuries is arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is less traumatic. The surgeon performs all manipulations through small incisions, under visual control (for this, an arthroscope with a camera is inserted into the joint cavity).
During the operation.
What is a meniscus?
Knee
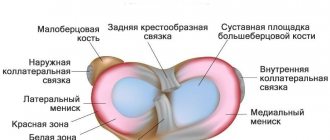
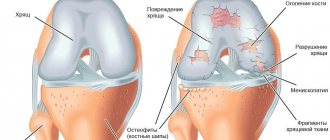
is a complex component of the musculoskeletal system, which is formed by the surfaces of 3 bones - the patella, the femoral condyles, as well as the sockets of the tibia and fibula. Since it can withstand significant loads caused by body weight, paired crescent-shaped cartilage components are located in the joint space. They are called the lateral (outer) and medial (inner) meniscus.
These components have a body (the wider part) and two horns (tapered parts that face forward and backward). Due to such anatomical features of structure and localization, these components provide shock absorption, strengthening and certain stabilization of the joint.
Causes
This injury can occur from falls, impacts, accidents and car accidents. Elderly people suffering from joint diseases, professional athletes, and people working in dangerous and difficult jobs are at particular risk. Excess weight and poor diet can also contribute to this injury.
You don't have to be in a serious accident to get a cracked knee; even a bad fall on a slippery floor can cause it. In addition, a crack in the meniscus can also be non-traumatic. People who are overweight and have sore joints can get this damage even when actively walking or squatting for a long time.
Mechanism
The pathogenesis of damage involves the implementation of several mechanisms, which include:
- Sudden excessive flexion, which causes stretching of the ligaments, as well as the cartilages themselves.
- Rotation (rotation) of the femur with the tibia fixed and vice versa.
- Bruise with a blunt object or a fall (quite often changes develop when falling on objects with sharp edges - the edge of a step, curb).
These damage mechanisms are more often realized in relation to the internal meniscus
. This is due to the fact that it is fixed more rigidly by ligaments, therefore, under any mechanical influence it practically does not move, which is accompanied by a violation of its integrity.
The outer cartilage is less susceptible to injury, since it has high mobility. A frequent variant of integrity violation is pathological changes in the properties of cartilage tissue, leading to a decrease in its strength.
Patella fracture
This is a more common injury. And not only athletes encounter it, but also teenagers, children due to their mobility, as well as older people, as they more often experience falls due to weakness in their legs.
The patella is the unprotected part of the knee joint . Therefore, it is susceptible to injury from direct impact. Therefore, the main causes of cracking of the kneecap is a fall on a bent knee. This part of the knee can also be damaged by a direct blow to the kneecap.
In this case, the location and direction of the crack can be very different. When the crack is horizontal, often part of the bone comes away completely, that is, it breaks off. With vertical cracks, parts of the kneecap diverge much less frequently. There is also a complex injury, when cracks literally spread out in different directions from the center of the patella.
Such knee injuries not only have characteristic symptoms, but are also perfectly palpable. The patient experiences pain as with any joint injury. But at the site of cracking, swelling appears, and a hematoma may appear. At the same time, the mobility of the leg is preserved, which allows the person to move.
The most reliable diagnosis in this case is considered to be x-ray . It is done in several projections at once. This pathology must be treated immediately. A common consequence of untreated injury is increased patellar mobility. This can lead to chronic instability and recurrent dislocation.
Therefore, if there is a crack in the patella, even a minimal one, it is undesirable to refuse a plaster cast. This part of the joint is quite mobile and it is problematic to immobilize it simply by bandaging or using an orthosis. However, tight bandaging is often recommended by doctors for such an injury.
Etiology
The causes of meniscal tears can be different; the most common triggers include:
- A person’s young age, as well as a life of high physical activity.
- Playing sports (amateurs or professional athletes) that are characterized by high mobility. These sports include football, volleyball, hockey, and athletics.
- Congenital defects of cartilage tissue caused by changes in certain genes that are inherited. In this case, a rupture can occur already in childhood, even in the absence of excessive physical activity.
- Acquired deterioration in the density of cartilage tissue, which is predominantly formed against the background of a decrease in its trophism and leading to degeneration. This provoking factor leads to pathological damage in elderly people after moderate loads on the legs.
- Long-term inflammation caused by specific (tuberculosis, syphilis) or nonspecific infections, as well as an autoimmune condition in which antibodies are produced to one’s own cells (rheumatoid arthritis).
Identification of provoking factors is carried out during a comprehensive examination of the person, which is required to select adequate therapy, as well as prevent changes in the future.
If your knee is cracked, what to do and what are the reasons?
After receiving an injury or experiencing unexplained pain in the knee joint, you should immediately consult a doctor to rule out a pathology such as a crack in the knee. To find out how dangerous such damage is, you need to find out the type of pathology, understand the principle and reasons for its occurrence and the possibility of complications in the absence of adequate treatment.
Classification
The choice of treatment method, namely surgical intervention or therapy without surgery, is made by the doctor based on the research conducted, as well as determining the type of injury in accordance with the modern classification.
The severity may be:
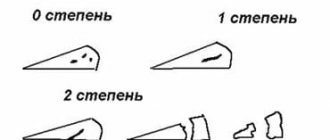
- Incomplete meniscal rupture
- injury or changes are characterized by the formation of a pathological focus that does not extend through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, therefore its shape and general anatomical structure are not disturbed. - A complete rupture of the meniscus
is a severe violation of integrity, accompanied by the spread of changes through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, disruption of the shape, as well as the frequent formation of a fragment that can displace and wedge into the joint space.
MRI is used to determine the extent of damage in modern medical institutions. Using this technique, the severity of damage is assessed according to Stoller, which implies 4 degrees of severity.
Based on the location of the damage, a rupture in the anterior or posterior (horn) area, body, or a combination thereof is identified. Also, after identifying the main etiological factor that led to the corresponding injuries, a pathological or traumatic rupture is determined.
Clinical picture
Damage to the cartilage of the knee joint after an injury is characterized by the appearance of quite characteristic symptoms. Among them:
- Pain that appears immediately after exposure to a traumatic factor. It is usually pronounced, localized on the outer or inner surface of the knee, and also intensifies when trying to perform movements in it.
- Decreased range of motion in the knee, the severity of which depends on the degree of damage. In the case of the formation of a cartilage fragment, a block of movements may develop, which is accompanied by intense pain.
- Signs indicating the development of an inflammatory reaction, which always accompanies changes in cartilaginous components. These include hyperemia (redness of the skin), swelling of the soft tissues with an increase in the joint in volume, as well as a local increase in temperature, manifested by the skin becoming hot to the touch.
Pathological changes, prolonged inflammation, as well as damage due to a congenital decrease in the strength of cartilage tissue are accompanied by a longer development of clinical symptoms. At first, pain may be absent or appear only during exercise. Then it intensifies and becomes permanent. Movements in the knee are accompanied by the appearance of “crunching” or “clicking” sounds.
Diagnostics
Only a qualified specialist can correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe adequate treatment, so immediately after an injury you should not delay, you must immediately take the patient to the emergency room. It is best to immobilize the limb, since knee injuries are often accompanied by a condyle fracture.
In the hospital, the doctor examines the patient, asks questions about how the injury occurred, what kind of pain is bothering him and in what place. During palpation, the doctor usually observes the mobility of the joint; when the meniscus is torn off, its displacement is felt. An experienced specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis at the first examination.
To confirm the pathology and to identify the location of the rupture, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations:
- Ultrasound examination of the knee joint;
- MRI;
- Laboratory research.
Often one ultrasound examination is enough, but to clarify some points, the doctor may also refer you for a tomography. Laboratory tests are always carried out before surgery, and with conservative treatment they help to identify the presence of an inflammatory process.
Study
Based on clinical manifestations, it is impossible to make a reliable conclusion about the nature and severity of changes. In modern clinics, before determining treatment tactics, an objective examination is required, including several basic methods of visualizing the components of the knee:
- X-ray
is a study that allows you to identify significant changes, in particular a complete rupture. To more accurately establish the localization of changes, a study is carried out in frontal and lateral projections. - MRI
is a diagnostically informative technique that involves performing layer-by-layer scanning with tissue visualization due to the physical phenomenon of resonance of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms. They are part of the molecules of organic compounds in a strong magnetic field. This study makes it possible to assess the severity of damage according to Stoller. This is necessary to determine further therapeutic tactics. - Computed tomography is a technique for layer-by-layer visualization of tissue. X-ray radiation is used for this. The method is very accurate and informative. It allows you to detect even minor traumatic or pathological injuries.
- Ultrasound examination is a diagnostic method characterized by the absence of radiation exposure to the patient’s body. It makes it possible to detect inflammatory changes and assess the volume of intra-articular fluid.
- Arthroscopy
is an innovative invasive technique characterized by direct visual examination of internal structures using an optical arthroscope equipped with a video camera and lighting.
Today arthroscopy
is not only a diagnostic research method. It has also become widespread for performing minimally invasive surgeries with minimal damage to healthy knee tissue.
Degenerative cracks in the knee
Hyaline cartilage and menisci can crack due to degenerative changes. This is a direct sign of developing arthrosis. There can be many reasons for this pathology.
But it is the lack of nutrition and moisture that leads to cracking. The patient may not even suspect that there are cracks in the cartilage of the knee, since in this case the pathology takes the form of minor mesh-type damage. Symptoms begin to appear during periods of exacerbation of the disease and in advanced stages of the pathology.
Usually these are starting pains in the knees, problems with motor activity. It is impossible to detect cracking of cartilage using x-rays. For cartilage structure disorders, it is better to do an MRI.
Restoring the integrity of cartilage during arthrosis is a complex and responsible process. First of all, the emphasis is on the use of chondroprotectors in combination with vitamin complexes and physical therapy. Injections of hyaluronic acid have worked well, after which the cartilage is covered with identical natural lubricant and it has the opportunity to regenerate.
When conservative methods do not produce results, various surgical corrections are proposed, which are often stimulating in nature. In the most difficult situations, with complete loss of mobility or threat of disability, the patient is offered prosthetics with full or partial joint replacement.
As you can see, there are quite a lot of situations when cracks appear. A crack in the knee joint is a diagnosis that requires clarification, since damage can affect various structures and have the most unexpected origin, which affects both diagnostic methods and treatment methods, prevention of relapses, and complications.
Principles of therapy
The choice of therapeutic tactics is made by the doctor individually for each patient. It is based on the results of a clinical examination and imaging techniques of the components and tissues of the knee. In modern medical institutions, therapeutic tactics include several main areas, which include:
- Therapy without surgery.
- Surgical intervention.
- Rehabilitation.
All stages of treatment are prescribed sequentially. Regardless of the main stage of therapeutic measures (surgery or conservative therapy), the final restoration of knee function necessarily includes rehabilitation.
Therapy without surgery
Any intervention involving tissue dissection is invasive, so modern traumatologists and orthopedists try to carry out treatment without surgery whenever possible. Conservative treatment is possible in certain cases:
- Diagnosed incomplete rupture with the absence of cartilaginous fragments.
- Localization of damage - due to certain anatomical features, an incomplete tear of the lateral meniscus of the knee joint is diagnosed; treatment in this case is possible without surgical intervention.
- The patient has absolute contraindications to surgery - usually conservative therapy is prescribed to elderly patients with pathological changes in the cartilaginous components.
Therapy without surgical intervention can be carried out in a hospital or on an outpatient basis, but only if the patient follows medical prescriptions in a disciplined manner.
Indications for meniscus arthroscopy
Arthroscopic intervention is indicated for serious injuries of the knee joint, when doctors suspect or have already discovered damage to intra-articular structures. Arthroscopy can be performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, it allows you to identify ruptures and tears of the menisci, damage to the cruciate ligaments, synovial membrane, articular cartilage, etc. In the second, it makes it possible to restore the integrity of the structures of the knee joint without opening the joint cavity and minimally injuring the soft tissues.
Arthroscopy is used for significant damage to the meniscus when conservative treatment is ineffective. If possible, doctors try to perform partial resection of the meniscus, plastic surgery, or suture. Total meniscectomy (complete removal) is used only in extreme cases. After all, complete removal of the meniscus leads to an increase in the load on the articular cartilage and further development of arthrosis. At the same time, plastic surgery and resection make it possible to preserve the functions of the knee and avoid degeneration of cartilage tissue after surgery.
Types of meniscus damage
General recommendations
Following general recommendations is a prerequisite for successful treatment, these include:
- Functional rest - during the entire stage of the main course of therapy, as well as partially during rehabilitation, the knee should not be subjected to stress. To ensure rest, a special motor regimen is used for the patient, and a tight bandage is applied to the joint using an elastic bandage or plaster splint.
- Diet – Dietary recommendations include eating high-calorie, highly digestible foods with sufficient fat, protein, carbohydrates and vitamins. Also, organic compounds that are directly involved in the synthesis of the intercellular substance of cartilage tissue must enter the body with food.
- Quitting bad habits - during the main course of therapy, it is advisable to give up smoking and drinking alcohol-containing drinks, since nicotine and alcohol are vascular toxins, they significantly slow down the processes of tissue regeneration (healing).
The implementation of such general recommendations (with the exception of functional rest) is desirable at the rehabilitation stage.
Drug therapy
In almost all cases of conservative treatment without surgery, medications of various groups are used. The most widespread are:
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs based on adrenal hormones and glucocorticosteroids. They are used in the development of a pronounced inflammatory reaction in the form of intra-articular, intravenous or intramuscular injections.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce the intensity of the process, the synthesis of mediators of the inflammatory reaction by cells of the immune system, thereby reducing the severity of manifestations. These drugs are mainly used in the form of injections or tablets for oral administration. Additionally, local therapy may be prescribed in the form of a cream or ointment.
- Chondroprotectors are a large group of medications, the active substance of which is the main structural component of cartilage tissue. These drugs have the ability to slow down degeneration processes, as well as restore damaged cartilage tissue.
- Vitamins are an essential component of drug therapy, helping to improve the course of metabolic (metabolic) processes in the body and accelerating healing.
Medicines are used over a long period of time, which is determined individually by the attending physician.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment involves the use of physical factors that have a therapeutic effect. Most medical clinics use procedures such as electrophoresis with topical medications, treatment with a magnet, ozokerite, and mud therapy.
They help reduce the intensity of inflammation and also accelerate the healing of damaged tissue. As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures are combined with the prescription of drug therapy.
Alternative Treatment
In modern traumatology and orthopedics, the acceleration of regeneration processes is carried out using alternative methods of non-surgical treatment. The most common of them is the introduction of platelet mass into the joint cavity. This is a suspension of platelets in a saline solution with a high content of growth factors. They are produced by formed elements of blood.
These compounds affect the functional activity of cells of cartilage, bone and connective tissue with an increase in the intensity of the process of synthesis of components of the intercellular substance. The duration, frequency of administration of biological drugs, as well as the dosage are determined by a medical specialist individually.
Recovery
After surgical or conservative treatment, rehabilitation is carried out, which is aimed at restoring knee function. This result is achieved through the use of special exercises with a gradual increase in the load on the joint. They enable the cartilage components to fully adapt and also prevent their re-injury in the future.
The duration of such measures may vary, depending on the nature of the damage, as well as the direction of the main course of therapy. It may only last a few months. In some cases, after open surgery, the rehabilitation period may exceed 1 year.
Forecast
The effectiveness of therapeutic measures depends on the severity of changes in the cartilaginous components of the knee and the condition of the patient’s body as a whole. Since incomplete rupture occurs quite often, conservative therapy is preferentially prescribed.
The disciplined implementation of medical prescriptions, including general recommendations, as well as the patient’s responsible approach to rehabilitation are the basis for obtaining a favorable result of the treatment.
No comments. You can be the first to leave a comment.
Cracked knee - types, symptoms and treatment
A cracked knee is a fairly serious injury that occurs when falling from a great height or receiving a strong blow. With such damage, a person feels severe pain and cannot move normally.
Many people do not consult a doctor on time when receiving this injury, and this leads to serious consequences - changes in joints and lameness. Proper and timely treatment will help avoid dire consequences, which is why you should not delay a visit to the doctor even for a day.