In orthopedics, knee joint distortion is a dangerous pathological position of the condyles of the tibia and femur, which can cause meniscal injuries, ligament ruptures and abrasion of the cartilaginous synovial layer. Distortion of the right knee joint often develops, especially in people who are actively involved in active sports. But distortion of the left knee joint is relatively rare; it is mainly a complication of traumatic damage to the ligaments, tendons and muscles in the knee area.
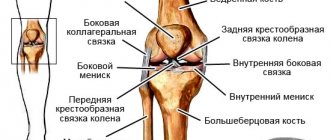
The anatomical structure of this bone articulation is very complex:
- it includes three bones (tibia, femur and patella);
- external cruciate ligaments (anterior and posterior) fix the joint in the corresponding planes;
- intra-articular ligaments (shin and tibia, arcuate and oblique) stabilize the position of the condyles of the tibia and femur relative to each other;
- the patellar ligaments fix this bone and limit forward mobility of the tibia;
- lateral and medial cartilaginous menisci are located between the condyles of the tibia and femur (they provide stability to the joint and protect the bony articular surfaces from excessive friction during walking and other movements;
- joint capsules (patellar, deep subpatellar, subcutaneous prepatellar, etc.) provide uniform distribution of shock-absorbing load; if they are damaged, bursitis develops.
The knee joint is large and bears the maximum physical, mechanical, dynamic and shock-absorbing load during walking and running. Even while standing, a person puts enormous pressure on all the tissues of the knee due to his body weight. Therefore, any increase in weight is considered potentially dangerous for the knee joint. This is a risk factor for the development of deforming osteoarthritis.
Distortion can develop not only when the ligamentous and tendon apparatus is damaged. A decrease in the height of the menisci, a violation of the position of the condyles of the bones, destruction of the bursae, a decrease in the intra-articular lumen due to degeneration of the synovial cartilaginous layer - all this can cause instability of the joint. But in most cases, knee distortion develops after an injury, such as a sprain or rupture of the cruciate or collateral ligament. A characteristic symptom is box syndrome. It is checked in a standing position. The doctor presses on the bone above the knee and it moves forward or backward.
Distortion can be primary acute - occurring immediately at the time of traumatic injury, and long-standing secondary (after scarring of the torn area of the ligament or tendon apparatus. In both cases, complex treatment is required. In most cases, this disease can be treated conservatively. To strengthen the joint, an individual complex of therapy is developed. The treatment is carried out by an orthopedist.
In Moscow, you can make an appointment for a free appointment with an orthopedist at our manual therapy clinic. The doctor will conduct a full examination and make a preliminary diagnosis. If necessary, he may prescribe additional examinations (MRI, CIT, radiography, ultrasound, etc.). After an accurate diagnosis is made, an individual course of therapy is developed for the patient. You can sign up for a consultation and learn about all the intricacies and prospects for treating knee distortion in your individual case.
Causes of knee ligament strain
Potential causes of the development of this pathology are injuries of various etiologies. At a young age, sprains and microscopic tears of ligaments and tendons predominate. At older ages, fractures and cracks of the tibia and femur come to the fore.
In old age, distortion of the knee joint ligaments develops against the background of general degenerative processes. In such patients, a complete absence of the synovial cartilaginous layer inside the joint capsule and excessive flattening of the medial and lateral menisci are revealed. Often, distortion contributes to the development of deforming osteoarthrosis (gonarthrosis). This disease interferes with normal mobility of the lower leg and leads to complete disability. In this case, surgery is required to restore the function of the lower limb.
Injuries to the ligamentous apparatus accompany the occurrence of distortion:
- at the initial stage, secondary instability occurs against the background of a traumatic accumulation of intra-articular exudate and capillary blood (ballotage of the patella and misalignment of the position of the femoral and tibial condyles occurs);
- at the scarring stage, an incorrect position of the bone heads is formed, which entails excess pressure on the medial and lateral menisci and joint capsules;
- secondary dislocation of all articular structural parts is formed;
- restructuring of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus occurs;
- the joint itself and its capsule are deformed.
Risk factors for the development of knee joint distortion are:
- excess body weight, which creates additional mechanical stress on the articular surfaces of the knee;
- maintaining a sedentary lifestyle with predominantly sedentary work and lack of regular physical activity on the muscles of the lower extremities;
- incorrect placement of the foot (flat feet or clubfoot), valgus or varus deformity of the foot or lower leg;
- destruction of the hip joint, in which shortening of the lower limb occurs, a change in the position of the femoral head in the cavity of the acetabulum;
- vascular pathologies (varicose veins of the lower extremities
- atherosclerosis, obliterating endarteritis, diabetic angiopathy, etc.);
- pathologies of the spinal column (spondylitis, spondyloarthritis, osteochondrosis, protrusion and hernia), leading to disruption of the innervation of the soft tissues of the lower extremities;
- heavy physical labor and inadequate loads (for example, at the beginning of the weightlifting process);
- smoking and drinking alcohol (causes the destruction of cartilaginous synovial tissue throughout the body);
- poor nutrition and insufficient consumption of clean drinking water during the day.
Main causes of distortion
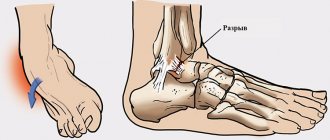
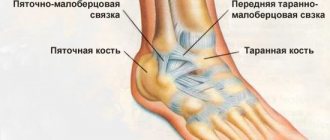
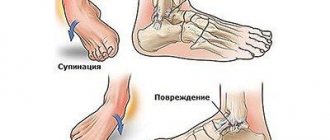
A strain, also called a sprain, almost always damages the outer ankle ligaments. The talofibular ligament suffers the most.
A person gets injured when, when tucking the foot, the sole bends too much. An acute pain syndrome appears in the ankle area. Common causes of distortion are presented in the table.
Table 1. Common triggers:
| Cause | Description |
| Persons whose weight exceeds 90 kg are at risk of getting distortion. |
| Distortion is often observed in professional athletes and people leading an active lifestyle. |
| Persons carrying a weight of more than 50 kilograms are at risk of getting distortion. |
| Teenagers are at risk. |
| Distortion occurs when wearing high-heeled shoes. |
Common symptoms
The main symptoms are swelling and pain
Signs of distortion depend on the degree of injury. More detailed information can be found in the plate.
Table 2. Main symptoms of ankle distortion:
| Stage of damage | Symptoms |
| 1 degree of distortion | A slight swelling appears. Painful sensations appear while walking, as well as when palpating the joint. Joint functions are not impaired. |
| 2nd degree of distortion | The size of the swelling is growing. Hemorrhage spreads along the outer surface of the foot. The painful sensations intensify. The person has difficulty moving. Joint functions are partially impaired. |
| 3rd degree of distortion | The swelling is visible to the naked eye. The hemorrhage spreads to the plantar part of the foot. The pain is so severe that the person is deprived of the ability not only to walk, but also to make other movements with the injured limb. |
Symptoms of distortion of the capsular and ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint
Distortion of the ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint can occur suddenly after traumatic exposure or develop over several months. The first option is more typical of young people who receive knee injuries during work or active sports. They immediately develop a characteristic clinical picture:
- acute pain in the knee area;
- dense pronounced swelling of soft tissues and their hyperemia;
- pain on palpation;
- You can’t step on your foot;
- the patient feels instability in the position of the bones in the knee;
- there is a subjective sensation of displacement of the condyles of the tibia and femur relative to each other.
In older people, distortion of the capsular ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint develops gradually and is most often associated with age-related degenerative dystrophic changes. This is the destruction of the intra-articular synovial layer of cartilage, as a result of which the joint space decreases and the free volume of the joint capsule increases. It ceases to fix the condyles of the tibia and femur. They begin to move freely relative to each other.
Then the destruction of the medial and lateral menisci begins. Due to the high degree of distortion, the joint capsules can be systematically damaged, which causes the development of chronic traumatic bursitis.
With chronic distortion of the knee joint, the clinical picture is as follows:
- a feeling of instability in the joint (looseness, laxity);
- constant twisting of the leg when walking;
- pain in the knee area and below the knee;
- pain on palpation;
- when trying to shift the bones, they may yield to the movement of the doctor’s hand to the left, right, back or forward (depending on which of the ligaments is damaged);
- decrease in the amplitude of mobility in relation to the physiological volume (flexion and extension of the leg) due to the development of secondary ankylosis and cicatricial deformation of the ligamentous apparatus.
The severity of the disease is determined by how damaged the ligaments, tendons or joint capsule are. With partial stretching, the first degree is established, with a small tear - the second. The third degree is a complete rupture of the ligament, tendon or joint capsule, resulting in absolute instability of the knee.
For differential diagnosis, an x-ray is prescribed. It allows you to exclude fractures and cracks of bones, dislocation, and the development of deforming osteoarthritis. Then a puncture of the knee joint is performed. This procedure is both therapeutic and diagnostic. Using a large needle, fluid is taken from the joint capsule. If there is blood in it, then rupture of soft tissues or damage to the periosteum is excluded. If the synovial fluid is transparent, then deformation of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus and damage to the white zone of the meniscus are excluded.
If it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, an MRI examination is prescribed. Based on its results, an accurate diagnosis can be made. In complex cases where surgery is expected to be required, the patient is prescribed arthroscopy. It allows for differential diagnosis and at the same time performing the necessary amount of surgical intervention in order to eliminate the detected defect of the ligament or tendon apparatus.
Causes of pathology
The main predisposing factors to the development of knee joint distortion are:
- Excessive physical activity.
- The effect of mechanical stress on the limb.
- Various injuries, severe bruises, falls, as well as dislocations and subluxations of the knee joint.
- The mechanism of the disease is that one segment of the limb performs motor activity, while the other remains in a calm state. And depending on the sharpness and strength of the movement, various degrees of pathology appear.
Treatment of knee joint distortion
Surgery for knee distortion may only be necessary if a complete tear of the cruciate or collateral ligament is detected. These tissues do not have their own vascular network and usually do not grow together. If they are completely ruptured, plastic surgery is recommended. The operation is performed 5-6 weeks after the injury.
In case of partial rupture or any other pathologies, treatment of distortion begins with eliminating the negative influence factor. The doctor collects anamnesis and excludes potential causes of distortion.
Then an individual course of treatment is developed using conservative methods using manual therapy. In our clinic we use the following techniques:
- osteopathy and massage can restore blood microcirculation, accelerate the process of tissue regeneration, increase the elasticity of muscles, ligaments and tendons;
- laser exposure stimulates the process of tissue renewal at the cellular level, removes excess scar tissue, etc.;
- therapeutic exercises and kinesiotherapy increase the level of availability of nutrients during diffuse exchange with muscles, strengthens the muscles of the lower extremities;
- physiotherapy allows you to improve the cellular balance and condition of all tissues in the lesion;
- reflexology (acupuncture) triggers natural tissue regeneration by using the body's hidden reserves.
Other treatment methods
Also, joint distortion suggests:
- undergoing physical therapy;
- use of folk remedies;
- undergoing physical therapy.
Note! If the ligaments are torn, surgery is prescribed.
Undergoing physical therapy
Baths with herbal infusions help
On the 3rd day after immobilization, the patient is prescribed:
- medicinal baths with herbal infusions;
- paraffin applications;
- ozokerite applications.
To speed up the healing process, the doctor may recommend that the patient undergo sessions of magnetic therapy, thermo or electrotherapy, as well as acupuncture.
Surgery
If conservative methods fail to stop further instability, the doctor resorts to surgery
Most often, the patient is prescribed arthroscopy. In this case, a thin tube equipped with a video camera is inserted into the joint. This way, a specialist can assess the degree of ruptures and detect bone fragments. Reconstruction is carried out by suturing the ligaments.
Physical therapy exercises
When the acute symptoms of ankle distortion decrease, the patient is prescribed gentle exercise therapy.
Therapeutic gymnastics helps strengthen muscles. The damaged joint is stabilized, which helps prevent relapses. The most effective exercises are presented in the table.
Table 6. The best exercises of therapeutic gymnastics:
| Exercise | Description |
| It is recommended to walk in a circle. You need to step on the outer part of the foot first, then on the inner. The duration of the exercise is 5-7 minutes. There should be no pain when performing it. |
| Having stood on the bar, you need to rise to the maximum on your toes, and then carefully lower yourself onto your heels. All movements should be slow and smooth. The number of repetitions is 10-12. |
| Circular movements with your fingers are recommended. First you need to rotate your fingers clockwise, then counterclockwise. The optimal position is sitting on a chair. |
| Promotes a rapid increase in metabolism in soft tissues. The healing process is faster. The first procedures should be carried out by a specialist. Then you can move on to self-massage sessions. |
Note! All exercises must be performed regularly.
The use of folk remedies
For minor injuries, it is allowed to resort to traditional medicine. The best recipes are presented in the table.
Table 7. Folk remedies for distortion:
| Means | How to cook | How to use |
| The sponge dissolves in heated water. When the medicine acquires a mushy state, it can be used. | The product is gently rubbed into the damaged area. It is best to do this procedure before going to bed. Bodyaga allows you to relieve pain and remove swelling. It is advisable to use this product 3-4 times/7 days. The course of treatment is 1-1.5 weeks. |
| For this, raw potatoes are used. The tuber needs to be peeled and grated on a medium grater. Mix with 1/2 onion and 150 grams of fresh white cabbage. | The compress is applied overnight. The damaged limb should be wrapped in woolen cloth. You need to repeat the procedure every other day. The duration of the course is 10 days. |
| Chop 1 onion, add 0.5 teaspoon of sea salt, mix well. | It is recommended to place the potato-onion mixture on several layers of gauze, squeeze, and apply to the damaged area. The compress helps relieve swelling and remove excess fluid. |
Note! Folk remedies are used only as prescribed by a doctor. The cost of not following this recommendation can be very high.
DISTORTION
Distortion (lat. distortio curvature) - stretching, partial rupture of the ligamentous apparatus of the joint.
Distortion refers to closed joint injuries and occurs due to the indirect application of a traumatic factor during sudden and sharp movement in an increased volume or direction unusual for a given joint. More often, one of the limb segments acts as a lever, to which force is applied, for example. own body weight, and the other segment of the limb at this moment is in a strictly fixed position. With this mechanism of injury, the ligamentous apparatus of the joint perceives a large load, and the degree of damage to the ligaments depends on the size of the cut - from simple stretching with partial rupture of fibers to complete rupture, often with separation of bone tissue at the site of attachment of the ligament.
The lateral ligaments of the joints are most susceptible to distortion, since their range of motion is, as a rule, always insignificant. D. occurs predominantly in large joints, especially the lower limb - the knee and ankle, less often in the joints of the upper limb - the elbow and wrist. D. is a common type of household and sports injury.
The main cause of D. is the twisting of a limb during an awkward movement, for example, a foot or lower leg on a slippery surface, a forearm or hand when falling on an outstretched arm.
D. is accompanied by damage to small nerves and vessels with moderate hemorrhage into the surrounding soft tissues and the joint cavity with the development of hemarthrosis (see) in cases of simultaneous damage to the joint capsule.
Clinical picture
D. is characterized by swelling of the tissues of the damaged joint, most pronounced in the area of the affected ligament, pain on palpation, active and passive movements, as well as instability of the joint.
The diagnosis can only be made after x-raying the joint to rule out other injuries. In particular, to avoid complete rupture of the ligaments, photographs are taken with forced adduction or abduction of the limb. Sometimes a contrast study of the joint helps. D. should be differentiated from joint bruise, complete rupture of ligaments and fracture.
Distortion of the cervical spine in children
According to statistics, distortion of the cervical spine is diagnosed in almost 10% of children admitted to traumatology departments with spinal column injuries. In most cases, the functionality of the spine is slightly impaired. It is extremely rare that the injury is complicated by ligament rupture, which is accompanied by a sharp limitation in the range of motion.
Among the reasons for the development of such a disease in a child are sharp turns of the head, injuries received while jumping on a trampoline and while swimming, significant physical activity, as well as direct blows and jolts to the head and neck area.
A sprain of the cervical ligaments manifests itself as pain that intensifies when turning, tilting the head, and the development of swelling and hyperemia in the neck area. First aid is complete immobilization, for which the child is placed on a flat, hard surface, and a cushion is placed under the cervical region. After this, the patient must be urgently taken to a medical facility to clarify the diagnosis and provide adequate care.
Treatment
The damaged joint is immobilized. Depending on the location of D., various types of soft bandage bandages are used for immobilization; in severe cases, splint or circular plaster bandages are used. Immobilization lasts from 1 to 3 weeks. depending on the location and degree of damage. If hemarthrosis is present, joint puncture and removal of escaping blood is indicated.
After cessation of immobilization, massage, physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises are performed to restore the function of the damaged joint. To reduce hemorrhage and swelling and relieve pain, bandages, novocaine blockades, ethyl chloride, cooling lotions or ice packs and cold water are used. The limbs are given an elevated position.
Sometimes after Distortion, instability of the joint persists for quite a long time, which is associated with weakening of the ligamentous and muscular apparatus. In these cases, the joint is strengthened by bandaging with an elastic bandage or elastic cuffs. Massage of adjacent muscles and special gymnastics are also used. D. individual joints - see articles on joint names (eg, Ankle joint, Knee joint, etc.).
Bibliography: Dubrov Ya. G. Manual on traumatology, M., 1973, bibliogr.; Kaplan A. V. Closed injuries of bones and joints, M., 1967, bibliogr.; Mironova Z. S. and Kheifets L. 3. Prevention and treatment of sports injuries, M., 1965; Odinov D. E. and Shabanov A. N. Outpatient surgery, M., 1973, bibliogr.; Watson-Jones R. Bone fractures and joint damage, trans. from English, M., 1972.
E. Ya. Dubrov.
Source: Great Medical Encyclopedia (BME), edited by Petrovsky B.V., 3rd edition
Recommended Articles
Source
First degree treatment
Finalgon
At the first degree of damage to the ligamentous apparatus, limb immobilization is prescribed. After it, on the 3rd day, warmth is recommended using medicinal baths using paraffin, medicinal herbs and other components. Warming ointments are also prescribed to the patient. Among them the most popular are:
- Finalgon is an excellent ointment with a pronounced warming and anti-inflammatory effect. Helps accelerate blood circulation, reduces pain and swelling by dilating blood vessels. It is also capable of restoring the structures of damaged muscles and tissue. The therapeutic effect occurs within 25 minutes.
Contraindications for use are children under 12 years of age, pregnancy, breastfeeding, intolerance to components and application to an area where there is a violation of the integrity of the skin.
Capsicam
- Capsicam is a popular analgesic and warming ointment. It has an irritating effect, which causes the blood vessels to dilate, blood flow accelerates and pronounced signs of distortion are reduced. The therapeutic effect of the product occurs half an hour after rubbing into the affected area and lasts for 6 hours.
It is prohibited to use the ointment for children, pregnant and lactating women, people with hypersensitive skin, those who have intolerance to components and impaired integrity of the skin.
- Arthro-Active is a universal ointment that is excellent for treating various joint diseases and ligament damage. It has a pronounced warming, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and decongestant effect. Helps improve blood flow, motor activity and increases regenerative abilities.
Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity.
Complete restoration of the function of the knee joint and fusion of the ligaments occurs after 14 days. Also, in case of severe inflammation and pain, anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed and the use of vitamin complexes is recommended.
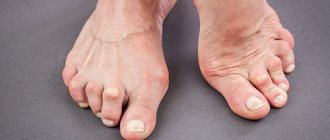
What is curvature of the knee joint?
Crooked knees are one of the most common orthopedic diseases. Because of it, the gait changes and clubfoot appears. There is constant pain in the knees. Simple walks bring discomfort and fatigue. Mild deformation does not cause pain during normal life, and is purely aesthetic in nature.
When deformed, the knee moves inward or outward, which leads to rotation of the femur and lower leg, a change in the angle of support and curvature of the leg bones. Doctors distinguish two types of deformity:
- valgus - the knees turn inward, the silhouette of the legs looks like the letter X;
- varus - the knees move outward, the legs resemble the letter O.
Causes of knee deformity
The disease can develop at different stages of life: before birth, during childhood and in adulthood. A congenital anomaly of the shape of the knees occurs if the mother during pregnancy:
- there was poisoning with toxic substances,
- there were frequent stressful situations,
- antibiotic treatment was present,
- there were problems with the endocrine system.
If the child was born healthy, then he has a chance of developing joint deformities in the following cases:
- with a lack of calcium and vitamin D in food,
- with excess body weight,
- against the background of chronic or congenital diseases of cartilage and bone tissue,
- with long-term restriction of movement,
- when trying to learn to walk too early.
Due to lack of nutrients, bones and cartilage become softer and more fragile. If a child gets up early on legs that are not yet adapted to support his weight, then the joints will inevitably become bent.
An adult has several ways to acquire this disease:
- displaced leg fractures,
- ligament rupture and dislocation of the same knee several times,
- damage and diseases of cartilage tissue.
Of course, if there is a lack of vitamins and minerals in the diet, problems with the knees will also appear in an adult. However, in already developed joints the risk of serious curvature is much lower than during growth.
How to diagnose and treat?
The doctor will see severe deformation of the knee joint during a visual examination. To do this, he will measure the distance between the ankles (for valgus deformity) or knees (for varus deformity) in a relaxed state. If he suspects a pathology, he will prescribe a full examination of the knees and pelvic bones:
- x-ray,
- ultrasound diagnostics,
- MRI of leg joints,
- CT scan of the pelvis and knees.
In rare cases, in advanced stages of the disease, it is necessary to take photographs of the lumbar and sacral spine.
If the disease appears after an injury or the development of joint pathologies, doctors will have to work with the primary disease. Here you may need pictures of the spine, general and biochemical blood tests, as well as studies of synovial fluid.
Treatment for deformity includes physical therapy and massage, the use of orthopedic shoes, light physical therapy, and diet changes. Chondroprotectors and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. In a severe stage, the curvature is corrected surgically.
It is necessary to get rid of the disease-cause, since curvature of the legs will lead to serious consequences. The structure of not only the lower extremities, but also the entire body is disrupted. Deformation of the knee joint has many consequences: from flat feet to scoliosis and serious curvature of the spine. Pain in the knees and lower back will increase over time, and rapid fatigue and fatigue will develop when walking.
Prevention of curvature of the knee joints
In children
The first prevention should be carried out by the mother: she should carefully monitor her diet and medication intake during pregnancy. If possible, you should spend this time in a clean area, and not in the city center. Any interaction with toxic substances: paints, solvents, insecticides should be avoided.
In the first years, the child should receive a sufficient amount of calcium and vitamin D, and regularly be in the fresh air. You should not restrict his movements or, conversely, try to sit him up or put him on his feet before he is ready to do it himself. If he has a congenital tendency to weak joints, he should be observed by a specialist. Perhaps he will advise correction of nutrition or physical activity.
In adults
It is enough for an adult to lead a healthy lifestyle, regularly do at least light exercise, eat well and wear comfortable shoes. Protect yourself from injuries and treat infectious diseases in a timely manner.
To prevent the development of an existing deformity, follow your doctor’s recommendations: take prescribed medications, use orthopedic shoes, and engage in physical therapy. Be sure to monitor your diet to ensure it contains enough vitamins and minerals. These actions will not only help with joint problems, but will also relieve many other unpleasant symptoms.
And don’t put off visiting a doctor if you or your child experience knee pain and a change in gait. Deformation of the knee joint is much easier to treat at the initial stage, when the problems are still almost invisible.
Source