Worms can affect not only the gastrointestinal tract, but also other organs. Parasites in the joints are quite common and lead to joint inflammation. It is difficult to diagnose helminthic infestation, because the symptoms resemble other diseases. The consequences of infection can be very serious. The most common problem is rheumatoid arthritis, which is difficult to treat. The risk of its occurrence increases if antihelminthic therapy is not carried out.
Parasites, having entered the human body, move throughout it and can be temporarily or permanently localized in the joints.
Types of parasites that affect joints
Helminths can affect joint conditions directly or indirectly, that is, through disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Helminths can get into joints by moving through the blood or lymph. It should be remembered that there are not only joint pains from worms, but also from parasitic microorganisms and fungi. List of parasites that affect joints:
- Giardia;
- roundworms;
- hookworms;
- trichinella;
- pork tapeworm;
- leishmania;
- chlamydia;
- sarcocysts;
- piroplasmids;
- trypanosomes;
- cryptosporidium;
- cysticercosis.
There are many ways of infection:
- unwashed hands, dirty water, dirty fruits, berries, vegetables;
- bites of insects and lice, fleas living on domestic animals;
- household items, bed linen, towels;
- animal fur, on which parasite eggs can be viable for 6 months;
- dust, air;
- poorly cooked meat and lard, fish;
- feces;
- contact with an infected person.
Prevention of infection
To prevent worms and their larvae from entering the muscles, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- drink clean water;
- consume products that have undergone high-quality heat treatment;
- wash your hands thoroughly;
- fight blood-sucking insects;
- Avoid visiting areas where there remains a high risk of infection.
Parasites in the muscles can cause serious complications, including death. Therefore, if suspicious symptoms appear, you need to consult a doctor, get diagnosed and begin treatment as quickly as possible.
Symptoms of infestation
To understand why joints hurt, you need to analyze all the symptoms. If the pain is caused by helminthic infestation, then the following signs are observed:
- allergic skin reactions, itching, redness, rash;
- gastrointestinal disorders - diarrhea, constipation, bloating, heartburn, abdominal pain;
- increased body temperature, weakness, dizziness, nausea.
Specific symptoms include: muscle pain. Parasites that live in joints damage it and muscle tissue and reduce local immunity. The joint becomes weak and loses functionality. The trigger for the development of the disease is considered to be local autoimmune reactions of weakened immunity, which damage their own tissues.
Only through a comprehensive examination can parasites be detected in the joints.
Parasites that can live in muscles
Parasites that can live in human muscles include:
- pork tapeworm larvae;
- Guinea worms;
- filariae;
- trichinella;
- spirometers.
The main route of infection is nutritional. This means that worm larvae enter the body through the digestive system.
Pork tapeworm and its larvae
Pork tapeworm causes taeniasis. Worms parasitize in the small intestine of the patient, but during vomiting their larvae are thrown into the stomach. Of these, oncospheres are released, which migrate through the human body with the bloodstream, settling in the muscles and other internal organs. This disease is called cysticercosis.
A person becomes infected with pork tapeworm by eating pork meat that has not been heat-treated. Sometimes worm larvae enter the body through water or with dirty hands. An infected person poses a danger to others, as he is a source of infection.
Guinea worm
Guinea worm is a round thread-like worm that causes a disease called dracunculiasis. Parasites settle in intermuscular tissue and subcutaneous tissue. The disease is manifested by fever, skin rash, joint pain, and swelling of the affected area. 8-10 days after the first symptoms appear, the worm emerges on the surface of the skin. This process is accompanied by severe pain.
Most often, parasites settle in a person’s legs, in the area of the legs and ankles.
Less commonly, they are found in the arms, back, abdomen, buttocks and other parts of the body. Infection occurs by ingesting water that contains cyclops guinea worm larvae. They reach the muscles through soft tissues, penetrating into them through the intestinal wall.
Filaria
Filaria are nematodes that parasitize the muscles and lymphatic system. The disease is accompanied by fever, lymphostasis, skin rash and itching. As it progresses, the patient develops elephantiasis in the extremities, and the eyes may be affected. Complications of untreated parasitic infestation often include heart failure and the formation of an intermuscular abscess.
Filaria are carried by blood-sucking insects. A person becomes infected when bitten by mosquitoes, horseflies or midges.
These muscle parasites can exist in the human body for more than 20 years.
Spirometer
Spirometra is a worm that causes a disease called sparganosis. People become infected by eating contaminated water or eating the meat of infected snakes, frogs or birds.
The infection manifests itself through allergic reactions and muscle pain. They will be concentrated in the area where the parasite settles. Most often they live in the muscles of the limbs, although cases of damage to the lungs, brain, heart, and bladder are known.
Trichinella
Trichinella is a roundworm that causes a disease called trichinosis. Its distributors are wild boars, rats, pigs, bears and other animals that live in the wild. A person becomes infected by eating raw, smoked or salted meat. Trichinella lives in the human intestines, and their larvae are spread throughout the body through the bloodstream. They are encapsulated in muscles, where they can remain viable for about 10 years.
Trichinella in muscles
Joint diseases caused by helminthic infestation
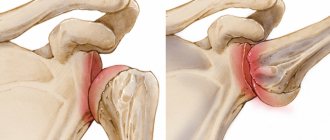
Helminths cause destructive changes in joints directly or indirectly. Parasites, being in the intestines and releasing toxic substances into the blood, cause inflammation. This leads to arthritis. The disease occurs in both old and young people. Arthritis also occurs after infection with parasitic protozoa - amoebas, blastocysts.
Arthritis caused by parasites is called rheumatoid or parasitic. Rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints of the fingers, toes, knees, ankles, and ankles. In this disease, cells of the immune system destroy joint tissue, mistaking them for foreign. This is caused by toxins produced by parasites that accumulate in the serous fluid. Gradually the joint loses its mobility, which leads to disability.
Parasites located in the joints provoke pain, weight loss, and fluctuations in body temperature.
Symptoms
The disease initially leads to destruction of the joints of the hands and wrists. Inflammations can occur on both hands at the same time. Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis:
- weight loss, weakness, fatigue;
- general body temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- pain and stiffness, especially in the morning and evening;
- reducing pain when moving.
There are a number of features of parasitic or rheumatoid arthritis that distinguish it from ordinary diseases:
- parasite eggs, entering the joint, attach to tissues or remain in the serous fluid, which leads to chronic inflammation;
- allergies develop, plaques and rashes appear in the area of inflamed joints;
- the spine is affected.
Attention, echinococcosis!
The beginning of February this year turned out to be hot, especially for Russian infectious disease specialists. An outbreak of a dangerous disease, echinococcosis, among students of the Suvorov School became the subject of heated discussion for medical theorists, a cause for concern for thousands of Russians and fertile ground for the emergence of myths about routes of infection and prognoses of parasitosis. What kind of disease is this, how can you get it, and is it true that echinococcosis is similar to malignant neoplasms? Let's figure it out.
Echinococcus and man
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease. Its causative agent is the larval stage of the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. According to statistics, about 1 million people suffer from echinococcosis at any given time (1). Cases of the disease are recorded in almost all corners of the globe, including in Eurasia.
The development cycle of echinococcus includes a change of two hosts. A person becomes an intermediate host of echinococcus and does not affect its circulation in nature, being a biological dead end.
The source of infection for humans are infected animals that are the definitive hosts: wolves, dogs, and less commonly cats.
Their intestines are parasitized by mature worms, which are small cestodes about 3-6 mm long. It consists of a head, neck and three segments, one of which contains the uterus. It contains from 400 to 800 eggs, inside each of them there is an embryo - an oncosphere. Mature segments of the worm, filled with eggs, are excreted in feces and, when released into the environment, become sources of disease for intermediate hosts, including humans.
How to diagnose?
Diagnosis is quite difficult, because having discovered arthritis, many treat it rather than anthelminthic therapy. For accurate diagnosis, 3 methods are used:
- Stool analysis can detect parasites in the body, but this method is not accurate enough because not all parasites are excreted from the body in feces.
- Vegetative resonance testing is based on the ability of each living organism to create vibrations. Parasites are no exception, so measuring vibrations in the body can provide a more accurate answer to the presence of helminths.
- An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test allows you to determine special antibodies that are released during parasitic infection, for example, Giardia causes the production of IgM type antibodies.
Diagnostics
If parasitic infestation is suspected, the patient should be referred to an infectious disease specialist. The doctor will perform a physical examination and then order laboratory tests. Blood sampling and ELISA can be performed. This serological method allows the detection of antibodies to a specific parasite. In some cases, an instrumental examination is performed, for example, ultrasound of soft tissues, abdominal organs, joints.
Sometimes interviewing the patient helps to suspect a parasitic infestation. The doctor clarifies which countries or endemic areas the patient has visited, as well as what exotic foods he ate.
Treatment of parasitic arthritis
The approach to treating the disease should be comprehensive and depend on the type of parasite. Antihelminthic therapy, which should be prescribed by a doctor depending on the type of helminth, will help relieve joint pain due to worms. But the drugs have a number of contraindications. For example, drugs against Giardia disrupt the hematopoietic process. Antibiotics are used for parasitic protozoa.
Depending on the type of parasite, the appropriate tablets and additional methods for cleansing are determined.
If getting rid of parasites was successful, then you need to cleanse the body of toxic products of their vital activity. To do this, you need to take sorbents, do cleansing enemas and drink herbal infusions, for example, from wormwood or oak bark. It is necessary to improve immunity. Treatment for parasites in joints lasts an average of a month.
It is necessary to restore the mobility of damaged joints. For this purpose, local therapy, medications and folk remedies are used. They can enhance each other's healing effects when used correctly. Local therapy includes:
- corticosteroids, which are administered intra-articularly;
- local cooling or cryotherapy;
- gels and ointments;
- laser therapy.
A whole range of folk remedies against arthritis is offered. The main components are cinquefoil and juniper. They need to be taken all the time, other components, alternating, every 3-4 months. The following means are also used:
- tincture of maclura;
- "Todikamp" - kerosene tincture of green walnuts;
- Dioscorea Caucasus;
- rock oil;
- tincture of aconite;
- tincture of marsh cinquefoil;
- elderberry syrup;
- ointments from eucalyptus and St. John's wort, ointment from maclura, ointment from cinquefoil - externally.
Timely initiation of treatment guarantees complete recovery within 6 months.
Treatment
Medicines and surgery
Treatment depends on the type of parasite that has settled in the human body. You can deal with worms and their larvae in the following way:
- To combat filariasis, a course of Ditrazine is prescribed.
- Rishtas go out into the water. When the head of the worm appears, it is removed by wrapping it in gauze. If the parasite ruptures, surgical intervention is necessary. Drugs for treatment: Metronidazole or Thiabendazole. Taking them allows you to destroy the worm and make it easier to remove it from the muscles. If bacterial complications develop, antibiotics are prescribed.
- Treatment of cysticercosis requires surgery to remove the pork tapeworm larvae. Be sure to prescribe medications for worms, for example, Niclosamide or Praziquantel.
- Treatment of trichinosis is carried out with the use of Albendazole.
- Spirometers must be surgically removed from the muscles. If surgery is not possible, then intravenous administration of Novarsenol is prescribed.
In parallel with the main therapy, efforts are directed towards eliminating pain, removing intoxication from the body and relieving allergic reactions.
How to get rid of parasites using traditional methods
Folk remedies against parasites are not able to help completely remove them from the body, but they can be used as auxiliary methods of treatment. For this purpose, pumpkin seeds can be used, which are consumed on an empty stomach in an amount of 100 g. The diet includes cranberry juice, garlic, sauerkraut brine, dill and caraway seeds. You should practice folk remedies on yourself with caution and only after consulting a doctor.