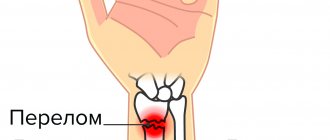
A false joint or pseudarthrosis is actually a section of bone formed after an injury as a result of incorrect fusion of fragments with unusual continuity, which is characterized by the appearance of pathological mobility in this section. Pseudarthrosis after a fracture is diagnosed in approximately three percent of clinical cases. Less commonly, pseudarthrosis is congenital.
Most often, traumatologists have to deal with pseudoarthrotic formations on the radius, tibia or ulna. Sometimes in clinical practice there are also false joints of the femur (femoral neck), false joints of the rib, and other tubular bones. If such a pathological connection cannot be corrected, over time it will transform into more complex pathologies and sooner or later will cause a person’s disability.
Causes of formation of false joints
The formation of a false joint during a fracture is associated with a disruption of the process of normal bone fusion, when the defect between its fragments is replaced by connective tissue with an altered structure. Among the most common causes of this pathological condition, experts identify:
- the distance of bone fragments from each other, which prevents their normal fusion;
- bone chips falling between the two broken ends of a bone;
- placing increased intensity loads on the bone during the formation of callus;
- suppuration at the site of a bone fracture or impaired blood circulation.
Frequent causes of pseudarthrosis during conservative treatment of fractures are decisions to remove the plaster cast prematurely. Sometimes the cause of the formation of pseudarthrosis is nerve damage, diseases of the endocrine organs, deterioration of calcium absorption, metabolic problems, severe blood loss during a fracture, or shock conditions.
Danger of condition
Acquired false joints are parts of bone, the space between which is filled with connective tissue. After some time, the ends of the fragments will become covered with cartilage and become more mobile. Articular cavities will form in the area of the voids. They will be filled with synovial fluid. If the pathology is congenital, then there is bone tissue that is only partially formed.
Detecting the problem is not so easy: the symptoms are mild or may be completely absent. Congenital pseudarthrosis is detected when the baby learns to walk. Acquired forms where there was a fracture. Palpation is usually painless, but loading causes pain.
Why is a false joint dangerous? Its fragility, inability to withstand the usual loads, which is fraught with repeated fractures.
Signs of a pseudarthrosis
All types of false joints are characterized by the presence of a common sign of pathology - unusual mobility in a certain area of the bone. Symptoms in the acquired form of the disease are mild or may be absent altogether until the false joint of the bone develops consequences.
In addition to pathological mobility, the formation of a false joint during a fracture is accompanied by the appearance of pain under axial loads on the damaged bone. The congenital variant of pseudarthrosis makes itself felt as soon as the child begins to walk. This pathological condition interferes with the normal development of the baby and has a more pronounced clinical picture than post-traumatic disorder.
General information
A false joint is a pathological variant of fusion (consolidation) of bone fragments, which occurs in approximately 5% of patients; it can be detected after twice the average period normally required for the complete formation of a callus , and the features of consolidation are also not detected on x-rays.
Pathology manifests itself in the form of unusual mobility and broken continuity of the bone, up to the “dangling” version. Pseudarthrosis or pseudarthrosis ( ICD 10: M84.1) includes a whole sympathocomplex, manifested by pain and the inability to perform functions of the injured limb. Pathology is most often a complication of a fracture and causes morphological transformations and radiological signs of deterioration of osteoreparation .
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the doctor is guided by the clinical examination of the patient and the presence of the main symptoms of pseudarthrosis or complications of a pseudarthrosis. Pathology can be confirmed by X-ray examination, during which the following is determined:
- absence of callus, which should connect bone fragments;
- fusion of the bone marrow cavity;
- smoothing the ends of bone fragments.
In doubtful clinical cases, the specialist may suggest that the patient do a computed tomography scan at the site of the suspected development of a pseudarthrosis.
Causes
The causes of pseudarthrosis can be general and local. General etiogenesis is associated with a decrease in the reactivity of the body, metabolic disorders and reparative processes of bone regeneration, these include:
- endocrinopathies;
- intoxication;
- dystrophy;
- vascular diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- tumor cachexia;
- rickets;
- pregnancy;
- multiplicity of combined injuries.
Local causes most often include:
- intrauterine disorders of bone formation and instability of osteosynthesis;
- in approximately 42%, defects occur after surgical interventions, for example, as a result of unstable fixation or resection of fragments during surgical treatment;
- in 32% of cases, malunion occurs due to an error in conservative treatment: when plaster immobilization was not carried out thoroughly, overextension occurred in skeletal traction, interposition of soft tissues occurred, for example, if plaster casts were frequently changed or bone fragments were displaced under them;
- in approximately 18%, the cause of pseudarthrosis is local disturbances in the blood supply in the area of bone fragments and suppuration as a result of inadequate surgical treatment of an open fracture, violations of asepsis , traumatic surgical technique, closing the wound with a skin flap and its excessive tension, ineffective drainage of the wound or non-use of antibiotics ;
- an insignificant percentage - 3.3% is due to the likelihood of postoperative treatment errors in the form of short-term insufficient immobilization for osteosynthesis, repeated, unjustified or untimely attempts to reduce fragments, early removal of the transosseous fixation device, too early loading, etc.
the patients’ obesity, lack of periosteum, insufficient blood supply, diabetes , pregnancy , radiation sickness , general exhaustion, severe anemia , hypoproteinemia and vitamin deficiency .
Treatment of pseudarthrosis in Naberezhnye Chelny
Treatment of a pseudarthrosis should be carried out exclusively by an experienced and qualified specialist after a competent diagnosis of the pathological condition. Therefore, if you suspect a problem at the site of a former fracture, you must contact a competent orthopedic traumatologist who can recognize pseudarthrosis and prescribe the patient the necessary examinations to confirm the diagnosis.
Today, for the effective treatment of false joints of bones, surgical techniques are used using Ilizarov apparatuses for intensive osteosynthesis of the damaged area. If such a technique does not bring the expected result, then doctors resort to bone grafting as a more complex method of treating pseudarthrosis.
In the case of a congenital defect, children are prescribed surgical correction or a set of physiotherapeutic procedures. More detailed information about physiotherapeutic treatment of pseudarthrosis can be found here.
Treatment
The method of surgical treatment is selected based on the results obtained from x-ray examination. In some cases, there are contraindications to surgical intervention, then conservative treatment is carried out using special support devices, massage, and physiotherapy. In addition to the general condition of the patient, the time that has passed since the day of the fracture is also taken into account, whether the femoral head is viable, what part of the neck remains intact, and how significantly the greater trochanter and diaphysis of the femur have shifted upward.
Surgical treatment comes down to several options:
- Reconstruction using autograft . This method is suitable for people who have preserved the femoral head, minor destruction of the femoral neck, and a slightly upward displacement of the greater trochanter. During the operation, the fragments are freed from fibrous formations, the surfaces of the bone fragments are “refreshed” by cleaning. Next, a rod that performs a conductive function is threaded through the greater trochanter, the fragments are reduced, and the wire is advanced into the femoral head. The position of the rod is determined using x-rays. The graft is taken from the tibia and, using a pre-made tunnel, is passed through the trochanter, neck and head. The joint is fixed for 2-3 months. If the fusion is successful, then further restoration occurs with the help of an orthopedic device. After six months, it is possible to use the operated leg.
- Open reduction , intra-articular osteosynthesis using a nail. During the operation, the capsule is incised, all scar tissue is removed, the fragments are combined and fixed with a three-blade nail. If necessary, additional traction with a wire is applied, and bone grafts are used. Elderly patients often have to create an artificial ankylosis by driving the nail through the head of the joint and the acetabular cup.
- Reconstructive surgery . It is used for complete resorption of the femoral neck, destruction of the head and significant displacement of bone fragments. In this case, the neck and also the head are recreated by transplanting cartilage to the trochanteric end, the femur, and the remaining part of the neck. During the reconstruction process, metal caps and other devices are used.
In some cases, the above methods are ineffective, the fusion process does not occur, and inflammation and suppuration begin.
Especially if the operation was performed on an elderly person, when slowed metabolic processes no longer provide nutrition to the joints and bones. The issue is resolved by hip replacement. After which the patient’s normal mobility is restored. Modern implant models reduce the risk of inflammation and rejection to a minimum. Not all clinics can guarantee a positive result from endoprosthetics, especially when it comes to older people. In Europe, the percentage of successful operations is very high, so many who have the opportunity seek treatment there. The best combination of price and quality is the Czech Republic. , which has long-term strong ties with leading orthopedic clinics in this country, organizes treatment and rehabilitation for patients from the Russian Federation. Reviews after endoprosthetics speak for themselves.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after surgical treatment of false joints is recommended to begin within a few days after surgical correction. To prevent the formation of contractures, the patient is prescribed an individual complex of physical therapy using the most effective exercises in this case. Magnetic therapy, UHF and other physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect on the process of normal healing of the defect and restoration of bone structure.
The clinic of restorative medicine in Naberezhnye Chelny employs professional doctors who are able to provide a truly effective range of services to eliminate problems with false joints of bones. Our specialists are known for their attentive attitude towards patients, extensive experience in the field of traumatology and rehabilitation, and the use of exclusively modern and effective techniques.
All information about the cost of treatment can be found by following the link, by calling +7 (8552) 78-09-35, +7 (953) 482-66-62 or by visiting the clinic in person.
Classification
There are many classifications of false joints depending on various factors of their division into types. For example, if the cause of origin is taken into account, the condition may be congenital, pathological and traumatic, resulting from a non-gunshot or gunshot wound. Whereas, depending on the unfolding clinical and radiological manifestations, a false joint occurs:
- forming - that is, occurring after the expiration of the period normally required for healing of an ordinary fracture , characterized by the presence of pain at the fracture sites, as well as during palpation, a distinct “gap” and periosteal callus at the fracture site can be detected on the radiograph;
- “ tight ” or in another way – fibrous – outwardly reminiscent of slit-like, which is characterized by the formation of tissues that are rough and fibrous in nature between the edges of the fragments, while there is no pronounced pathological mobility (no diastasis), and a thin lumen is visible on the x-ray;
- necrotic - develops after gunshot wounds that affected not only the bone, but also its blood supply; also at risk are fractures that are considered predisposed to necrotic processes in the bones - fracture of the femoral neck , transverse fracture of the neck of the supracalcaneal bone, transverse fracture of the middle part of the scaphoid, they may have aseptic necrosis of the edges, freely lying in the middle of the fracture, or necrosis associated with fragments;
- in the form of bone regenerate - more typical for the tibia as a result of insufficiently strong fixation, elongation of segments or excessive stretching;
- true neoarthrosis - most often affects single-bone segments with pathological mobility, the fragments undergo grinding, one becomes spherical in shape, and the second - cup-shaped, between them there is a space that is filled with liquid, a capsule is formed similar to an articular one, since there is a covering of fibrous with islands of hyaline cartilage, the process can occur against the background of a defect in the bone substance.
The false joint may be uncomplicated or have purulent complications , which can be infected , with fistulas , while purulent discharge, the presence of sequesters or foreign bodies that support the purulent process are detected, for example, during injury, fragments of projectiles, metal clamps, etc. can get into the wound .d.
Depending on the degree of osteogenic activity of the pathological process, changes can be normotrophic , atrophic and hypertrophic , when a false pseudojoint is formed as a result of the proliferation of bone tissue at the edges of fragments. It is usually inactive, but the vascular network of the surrounding tissues is preserved. People who have frequent axial loads are at risk. In addition, the process can be avascular - when the blood supply is impaired and poor bone formation occurs against the background of osteoporosis of the fragments.
According to topographic descriptions, pseudarthrosis usually occurs in the bones of the forearm, hips, wrist, foot, jaw, etc.
Congenital pseudarthrosis
In addition to the acquired complication of healing fractures and other injuries, pseudarthrosis can be congenital - in approximately 0.5% of people. Most often it affects long tubular bones, such as the tibia, and manifests itself with mobility along the diaphysis. The pathology is based on a defect in skeletal ossification - fibrous dysplasia .
Congenital pseudarthrosis of the bones of the left leg
The problem can only be solved surgically with the use of bone grafts. It can be identified already at the stage of learning to walk and other movements, since the limb has abnormal mobility and bends in the wrong place.
Pseudarthrosis after femoral neck fracture
A fairly common case among all diagnosed examples of pseudarthrosis is failure of fusion after a femoral neck fracture. It has complex consequences and significantly reduces the quality of life, because symptoms include progression of lameness, shortening of the limb, wasting of soft tissues, and limitation of movements during abduction of the limb. Axial loads cause cephalad displacement of the femur. Ununited fractures and secondary static deformations lead to pelvic distortion, curvature of the spine and equinus position of the foot.
False joint of the forearm
The severe condition of pseudarthrosis of the radius can be complicated by chronic dislocations and displacements of the heads of the bones of the forearm. To solve the problem of the bone apparatus, a consultation of doctors and the development of a step-by-step treatment strategy are usually required. Initially, it is important to align the bone axis and perform distraction, which can be quite painful and require additional anesthesia.
It is important to seek help promptly if you suspect a false joint, because it affects the ability to fully work with your arm and limits movement. Patients may have problems with self-care and work activities.
Neoarthrosis
The most common type is transverse sacral neoarthrosis of the spine. The formation of false joints occurs in pathological conditions occurring between the spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae or involving the lateral masses of the sacrum. The reasons are the contact of these structures, trauma, their friction, destruction of the soft tissues located between them, including ligaments, dysplastic enlargement against the background of spinal curvature and a significant decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs.
Neoarthrosis of the spine can cause overload conditions and arthrosis . In the case of a bilateral process, they speak of articular sacralization of the transverse processes, but most often the pathological process is unilateral. In this case, patients complain of lower back pain ( lumbodynia or lumboischialgia ), do not tolerate static loads well, it hurts them to turn or bend over, and sometimes even palpation leads to severe discomfort.
Reasons for development
Pseudarthrosis of the femoral neck is more often expected after a fracture in women aged 60-80 years, which indicates the significant role of disorders of calcium metabolism and blood circulation of the femoral head. However, young people of both sexes are not immune from it either.
Provoking factors are considered:
- Lack of timely treatment.
- Wrong choice of treatment method.
- Fibrous osteodysplasia and osteomalacia.
- Chronic diseases.
- Metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus).
- Osteoporosis.
The mechanism of formation of a pseudarthrosis is that any of these or other disorders disrupts normal osteogenesis (bone formation): instead of bone, fibrous tissue develops.
Surgical methods for the treatment of false joints of the forearm bones
Due to the rapid development of mechanization and automation of production, the increase in the number of vehicles, the nature and severity of injuries has changed, and the number of complex, multiple and combined injuries has increased. One of the severe and frequent complications after fractures of the diaphyseal bones of the forearm are non-unions, fractures and false joints, accompanied by contractures in nearby joints and long-term disability of patients [1,5]. False joints of the forearm bones are the most severe and common complication of fractures of this segment. Pseudarthrosis of the forearm bones in the practice of reconstructive surgery, according to various authors, accounts for 20-25% of all pseudarthrosis of long tubular bones [3] and 53.5% of fractures of the upper limb bones [1]. The incidence of formation of pseudarthrosis of the forearm bones after fractures of the diaphyseal parts of the forearm bones ranges from 13.2 to 29.8%, and disability reaches up to 21.1-40% [2]. With open fractures of the bones of the forearm, false joints form two times more often than with closed ones, and three times more often if the fractures of the radius and ulna occur at the same level [3]. According to a number of authors [4,8], in isolated fractures, healthy bone prevents complete contact of fragments of the broken bone, which often leads to nonunion. According to its anatomical structure, the forearm is a complex segment of the upper limb, in which two equal-sized bones, muscles and neurovascular bundles are located close to each other. If, when one of the bones of the forearm is damaged, the other acts as a spacer, then when both bones are damaged due to multidirectional traction of the muscles, significant displacements of fragments occur with pronounced deformation of the forearm. Under the influence of contractions of various muscle groups, mixing of fragments occurs, both in length and width, as well as rotational mixing, which complicates the reduction of fragments and their immobilization during conservative treatment. These circumstances lead to repeated repositions, and surgical interventions are highly traumatic. Considering that the neurovascular bundles run along the bones, neurocirculatory disorders are pronounced, which is of no small importance in the development of various complications. They are often combined with ruptures of the bursal-ligamentous apparatus of nearby joints, the interosseous membrane, and damage to muscles, blood vessels, and nerves. Underestimation of these injuries and incorrect choice of treatment method subsequently leads to severe anatomical and functional disorders and ultimately disability of patients [5-7].
The purpose of the study is to improve the results of surgical treatment of ununited fractures and false joints of the forearm bones by developing and introducing new methods of stable functional osteosynthesis with the introduction of a solution of cucumazim and bone marrow.
Materials and methods of research. Our report is based on a study of the results of treatment of 64 patients with pseudarthrosis of the diaphysis of the forearm bones who received treatment from 2009 to 2012 in the Department of Adult Traumatology of the Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Of these, 41 were men, 23 were women. The vast majority of patients were aged from 18 to 60 years.
Table 1. Distribution of patients by age.
Rice. 1. Distribution of patients by age.
In 35 patients, pseudarthrosis were localized in both bones of the forearm, of which: 10 - in the upper third, 17 - in the middle third, 8 - in the lower third. Isolated localization of pseudarthrosis in the radius was observed in 14 cases: 3 in the upper third, 7 in the middle third, 4 in the lower third. False joints of the ulna were found in 15 patients: 3 of them in the upper third, 8 in the middle third, 4 in the lower third. All the patients we observed were disabled. All patients underwent radiography in two standard projections and in these patients additional ultrasound Dopplerography was performed, in 41 of them X-ray densitometry was performed. 25 patients underwent additional ultrasound examination (US), 12.5% of patients underwent multislice computed tomography (MSCT). The operations were performed as planned for all patients. We have proposed a method for treating false joints of the forearm bones. The essence of this method is the use of the proteolytic enzyme cucumazim and bone marrow. Cucumazim is a natural sum of proteolytic enzymes (papain, chymotrypsin, and proteinase III) isolated from the milky juice of the papaya melon tree (Carica papaya). The drug has proteolytic activity. The action is due to the proteolytic enzymes included in its composition.
Technique of operation. With the proposed method under general anesthesia for accelerated fusion of bone fragments, including preliminary implementation of the correct orientation of bone fragments with correction of the axis and elimination of segment shortening under conditions of stable osteosynthesis, the introduction of a drug that accelerates bone regeneration into the area of the false joint, and into the area of the false joint one day before operations, cucumazim is administered at a dose of 50 proteolytic units (PU). The next day after the administration of cucumazim, under sterile conditions under general anesthesia, with the patient in the supine position, an Ilizarov apparatus is applied to the damaged segment. After this, the area of the iliac crest is treated with alcohol and iodine, a thick syringe needle is inserted into the thickness of the iliac crest and a mixture of bone marrow in a volume of 2 ml is taken. The collected bone marrow is injected into the area of the pseudarthrosis under aseptic conditions. The injection of red bone marrow into the area of the pseudarthrosis leads to the formation of a hematoma rich in calcium, which accelerates the regeneration of bone tissue at the site of damage. After this, an aseptic bandage is applied to the damaged area around the needles of the Ilizarov apparatus and to the injection sites of the needles. The introduction of cucumazim (of plant origin) helps to increase chondrolytic, fibrinolytic activity and accelerates the fusion of fragments. The introduction of a mixture of bone marrow taken from the iliac crest, which has a maximum calcium content, helps to improve the healing of bone fragments. The application of the Ilizarov apparatus increases the stability of fixation of bone fragments.
Results and its discussion. From the next day, distraction with the Ilizarov apparatus begins, which helps to increase the hematoma. After achieving the required distraction, radiography is taken in two projections; if there are residual displacements, compression is performed using the Ilizarov apparatus. Long-term results were studied in 40 patients over a period of 1 to 3 years. A good outcome was noted in 75% of cases, satisfactory in 22.5%, unsatisfactory in 2.5% of patients (in one patient no signs of regeneration were noted).
Clinical example. Patient U.U., 29 years old, medical history No. 1756, admitted on March 19, 2012. Diagnosis: Pseudarthrosis of the upper third of the ulna on the right, healing fracture of the middle upper third of the radius. Within 15 months. was treated to no avail. There is atrophy of the muscles of the right forearm, range of motion in the elbow joint: flexion 70º, extension 160º. One day before surgery, cucumazim 50 PE was injected into the area of the pseudarthrosis to soften and lyse the connective tissue.
Rice. 2. Radiographs of patient U.U.: a – upon admission, pseudarthrosis of the upper third of the ulna on the right; b – a treatment process: fixation of the forearm with the Ilizarov apparatus; c – after removal of the Ilizarov apparatus.
On March 21, 2012, an operation was performed and an Ilizarov apparatus was applied, consisting of 3.5 rings, with the distal fragment fixed by two rings, the proximal fragment by 1.5 rings. Stable fixation has been achieved. After which the patient was injected with bone marrow taken from the iliac crest in a volume of 2 ml. On the fourth day, after the pain subsided, distraction began until a diastasis of up to 1 cm appeared between the fragments in the area of the pseudarthrosis. An X-ray image was taken, and then a stage of compression was performed until the ends of the bone fragments were joined. 60 days after surgery, the range of motion in the elbow joint was 90º. Fixation with the device was carried out within 150 days. After removal of the Ilizarov apparatus, physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy were prescribed. After 5 months after surgery, the range of motion was 120º. There is no pain in the fracture area.
Conclusions. Thus, our observations show the effectiveness of transosseous compression-distraction osteosynthesis using the proteolytic enzyme cucumazim and bone marrow of plant origin in the treatment of false joints of the diaphysis of the forearm bones.
Clinical manifestations
The symptoms of pseudarthrosis of this localization can be vague. Patients can even walk on crutches. Externally, noteworthy:
- Shortening of the leg from 1 to 5 cm or more.
- Deformation of the injured limb.
- Impaired limb support.
- Atrophy of regional muscles (gluteal, femoral).
The professionalism of doctors, the modern equipment of the orthopedic department of our clinic and an individual approach to each patient help to identify pseudarthrosis in the early stages and apply the necessary method of surgical treatment (osteosynthesis or endoprosthetics).
When adjacent departments are not affected, restoring health is much easier.