How to determine dysplasia
Dysplasia in newborns can be diagnosed in the maternity hospital. At the same time, the baby will receive the necessary help.
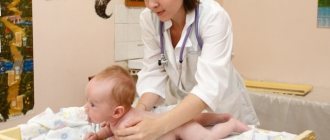
Pediatricians will determine the degree of joint mobility in the child. In normal condition, the baby's legs are spread 180 degrees .
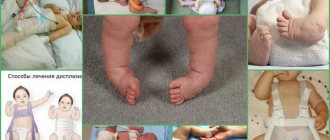
A more accurate diagnosis can be made using ultrasound . The disease can be identified by the following symptoms:
- The diseased leg will be shorter.
- There may be a fold on the thigh, or folds on the buttocks are located asymmetrically.
- If you bend the leg, you hear a clicking sound.
Children under one year of age who are already walking may experience swaying when walking. To make walking easier, the baby can stand on his toes.
When the joints are immature, no symptoms are observed.
Underdevelopment of joints in children is diagnosed in 10% of cases. Incomplete formation of the joint structure is a congenital defect. Dysplasia can be grades 1 and 2 – subluxation, and grade 3 – dislocation.
If the disease is diagnosed before six months, then with proper care it goes away by one and a half years. When the diagnosis is made later, treatment may be complicated.
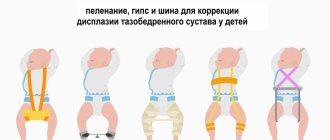
An effective orthopedic method is wide swaddling, which ensures that the legs are in the anatomically correct position.
The attachment of the joint in the central part of the acetabulum contributes to the overgrowth of the joint with ligaments. At the same time, he stops moving.
Indications
Dysplasia often results from pathologies during childbirth - subluxations or breech presentation. To understand whether such a deviation is present in a baby, it is enough to visually examine his legs and hips.
Signs of dysplasia:
- with dysplasia in these places, the folds are not distributed symmetrically;
- the baby's legs are of different lengths;
- Often a head tilted to the side or a curved back when lying down are also signs of dysplasia.
When a baby exhibits motor activity, one leg is less mobile. Sometimes you can hear a soft click in the hip joint. The baby’s constant desire to walk on his toes is also a clear sign of dysplasia. In the future, if no measures are taken, the child will develop a “duck” gait and spinal curvature.
General characteristics. For dysplasia, the nature of the inferiority of the hip joint. It is congenital and caused by abnormal development of the fetus. During childbirth, this leads to dislocations and subluxations of the femoral head.
The ligaments and muscles of such a baby are very weak and are not able to cope with the loads that befall them. This is why it is so difficult for the joint to lock into the acetabulum.
The main therapy is precisely aimed at reducing pressure and helping the skeleton develop correctly. Wide swaddling is the fixator that holds the joint in the cavity. It is recommended to use it for up to 4 months.
Types of swaddling
There are several types of swaddling.
Here they are:
- Natural wrapping or open wrapping is used when diapers are not used. In this case, panties with diapers, rompers and blouses are used. This assumes complete freedom of movement for the baby. Psychologists do not recommend using this method at first, as it may cause some anxiety.
- With loose wrapping, the lower limbs are wrapped and the upper limbs are left free.
- Pediatricians do not approve of tight swaddling, as this method inhibits the development of motor functions.
- Wide swaddling is even called therapeutic. It is used as a preventive method and to correct problems with the hip joint.
The last type of swaddling can be used even for completely healthy children.
Necessary equipment
To properly wrap the baby, the mother will need thin flannel diapers, which are used to wrap the baby’s legs in the hips and lower back. For children over 1 month old, it is recommended to use a Frejka pillow for wide swaddling: the device is located between the thighs and allows you to maintain the correct position of the legs.
For fixation, you can sew a special cover with side ties, shoulder straps and a thick insert.
Cloth diapers
For wide swaddling, several diapers made of soft natural fabric are used. Cotton, chintz, flannel, flannel, cambric are suitable. Before wrapping your baby, you can put on disposable diapers or make reusable cloth ones.
Panties are sewn from the cut; Velcro or fabric ties are needed to secure them. The necessary devices can be purchased in children's specialized stores, pharmacies, and ready-made products are also sold there.
Case
It can be made from flannel fabric folded in several layers. The design has an elongated rectangular shape with sewn ribbons, with the help of which the product is secured at the waist. The wide swaddling product itself is placed between the baby's legs.
Freyka's pillow
This is a soft orthopedic device that holds the legs in an abducted position. It is recommended to use the bandage in the first 1–3 months; less often, treatment is continued for up to a year. Pillows are sold in different sizes, which allows you to choose the right option for each child. When purchasing the product, you should take into account the distance between the popliteal fossae, which is formed when the limbs are fixed in the correct position. The device must be worn constantly; it is removed only during changing clothes, water procedures, and massage.
Why do you need wide swaddling?
Wide swaddling is a universal method that is used for joint problems. When using this technique, the legs are spread apart and bent, which allows you to maintain a natural position.
At the same time, the joints develop fully. The method protects against the development of pathologies such as dislocation or subluxation.
You can see how swaddling is done correctly in the video at the end. To get a complete picture of the procedure, you should read the reviews. To do this, you need to go to a special thematic forum.
Diagnosis and treatment
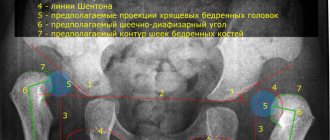
To confirm the visual impression, the baby is subjected to a hardware examination. It is with its help that a more accurate diagnosis can be made.
Ultrasound. An ultrasound examination will accurately determine pathology, if any. This diagnostic method is used as a control option, periodically checking how the hip joints develop.
X-ray. As additional confirmation, X-rays are used. It is recommended for children over 3 months of age, but in severe cases it is also prescribed for newborns who have not yet reached 4 weeks of age.
They resort to wide swaddling without waiting for the results of hardware diagnostics. There are already enough visual signs of developmental pathology. If severe deviations are detected, a Freik pillow, panties and Pavlik stirrups are used.
It is important to know about dysplasia in children. To understand how serious this problem is, you should read the following information:
- dysplasia is not uncommon. It occurs in 20% of newborns;
- Children with a pure breech presentation are most often at risk;
- more than half of all children suffering from dysplasia are first-born. At the same time, there are more girls than boys, as this is due to the characteristics of the body;
- Babies born to older people are at risk of developing dysplasia. Exactly the same as premature babies weighing up to 2.5 kg.
Any serious illnesses during pregnancy, poor environment, heredity and poor nutrition are all factors that can lead to the development of this pathology.
How to do wide swaddling
For dysplasia, special gymnastics and massage are indicated, but at other times the child should remain with his legs fixed. Before you begin the procedure, you need to familiarize yourself with the following important rules:
- Before swaddling, check your baby's position. It should be on a flat surface where there are no bulges or folds. You can use a changing table or wrap it on the sofa.
- Use natural fabrics that allow the skin to breathe. You can choose flannel, knitwear, calico or chintz. The fabric must be washed and ironed on both sides.
- To avoid overheating or hypothermia, it is necessary to choose the right diapers, undershirts and rompers.
Everything you need for the procedure. These are several diapers, diapers and a flat surface.
Let's look at how to do the wide swaddling procedure step by step:
- One diaper needs to be folded so as to form a rectangle shape with a width of 15-20 cm. Spread the baby’s legs and place the folded fabric between them.
- Fold the second diaper like a scarf and wrap it around the baby's hips. Fix the legs at right angles.
- The third diaper should be used to wrap the baby below the waist.
- Pull the legs with the bottom of the diaper so that the baby cannot bring them together.
The child's legs must be fixed at right angles to the body. This swaddling is especially effective at first, when the joints are not fully formed. If you can’t use diapers, you can purchase special panties. With enough skill, you can get by with diapers.
To do this, you need to take two square cuts with dimensions of 80*90 cm, as well as one - 80*120 cm. With this wrapping, you can use either a homemade diaper from diapers or a purchased one.
How to properly swaddle a baby in this way?
To do this, you can use one diaper, two, or three. It is also possible to swaddle your baby using a diaper. This is how babies are swaddled to prevent diaper rash, developmental disorders of the hip joints, etc.
First way
It is suitable for a calm baby. You can also swaddle him while he sleeps.
To do this, a rectangular diaper needs to be spread on a hard surface. Then fold it in half. Open one pocket to form a triangle. Then the middle part of the diaper is bent and folded into a rectangle. This creates a diaper. It is used for swaddling the baby.
It's done like this. The baby needs to be placed in a diaper. Move the legs apart to form a 90-degree angle. Wrap both legs of the baby in a diaper, place the middle part between them and bend it up so that the folded rectangle is between them.
To prevent such a diaper from immediately unraveling due to the child’s movement, you need to put sliders on it, or swaddle it on top. To better master this technique, you can watch a special video about wide swaddling with a diaper.
Second way
It will require two diapers. One of them needs to be taken more, the second - less. The first, large diaper should be spread on a flat surface. Roll the second one into a rectangular roller.
The baby lies down on the spread diaper. Between the legs, bending them slightly, place a cushion from a smaller diaper. Wrap the baby's body on both sides. Having grabbed the lower part of the diaper, also place it between the legs and secure the ends around the waist.
It is imperative to remember that you should use only high-quality diapers, preferably cotton, soft, non-irritating to the baby’s skin and absorbing liquid well.
Using this method, it is possible to both correct deformities of the hip joints and prevent irritation and diaper rash. Much fewer disposable diapers will be required, which naturally reduces costs significantly. It’s easier and faster to teach a child to ask to go to the potty.
Third way
You need to use three diapers for it. The essence of the technology itself is this.
The first diaper should be folded into a triangle. Then place the child on it so that the middle (right) angle is under the legs.
Fold the second diaper into a rectangle (its width is approximately 20 cm). After this, pass between the legs. Then the corner of the first one is grabbed and also threaded between the legs, and the ends are wrapped around the hips, after which they are secured to the belt.
After this, a third diaper will be required. With its help, the baby’s body is wrapped, and the first two diapers are securely fastened. Then its lower edge is attached to the belt near the navel.
In cases where a diaper is used, a diaper folded into a rectangle is not needed. The diaper itself will play its role.
Using spacers
Wide swaddling is an effective method, but if the process is started, do not panic.
There are special spacers that allow you to properly fix the joints.
Here are some of them:
- Freyka's pillow is made in the form of panties. At the same time, the baby’s legs are supported in an extended position.
- Pavlik stirrups are a wide belt with devices for fixing the legs.
- The Vilensky splint should be worn around the clock. It is fixed on the hip joint. There are devices with different sizes.
Such spacers are used when dysplasia has developed into complications.
With any degree of dysplasia, do not despair. With the right approach, everything can be cured. If you consult a doctor and begin full treatment, you can cope with the problem.
And wide swaddling will be a reliable method for problems with hip joints in toddlers.
The goal is proper development of the joint
Hip dysplasia occurs in 54% of infants; in another 12-15% of infants, this pathology is detected by the 6th month. Since the problem is serious, treatment must be carried out immediately.
The main principle of treatment is to spread the child’s hips to the sides; regular diapers will help with this first, then, if the problem goes away slowly, more stringent treatment measures will be applied. The so-called “frog” position limits the child’s mobility, but at the same time ensures the normal formation of cartilage tissue.
Interesting! Parents should not be afraid - the “frog” position for babies is the most comfortable and natural.
Principles of medical support for children with connective tissue dysplasia
Connective tissue dysplasia (CTD) is not an independent nosological entity, but a heterogeneous group of connective tissue disorders of a polygenic and multifactorial nature, combined into phenotypes based on common external and/or visceral signs. DST is based on various defects in the formation of collagen and elastin fibers, as well as the basic substance of connective tissue, resulting from a genetic predisposition, the implementation of which largely depends on the influence of environmental factors [1–3]. It is the “omnipresence” of connective tissue that determines the variety of clinical manifestations when its development is disrupted. Contributions to this diversity include various metabolic disorders (dyselementoses, secondary mitochondrial deficiency), lability of nervous processes, autonomic dystonia, and psychoemotional disorders characteristic of children with CTD [4–6].
According to ICD-10, DST can be classified as class XIII (diseases of musculoskeletal and connective tissue). A detailed diagnostic algorithm is presented in the Russian recommendations “Hereditary and multifactorial connective tissue disorders in children. Diagnostic algorithms. Tactics of conducting”, published in a number of scientific and practical journals in Russia [6–8]. These recommendations should help not only pediatricians, but also doctors of various specialties in identifying children at risk of developing CTD and its early detection, which is the key to timely prevention or treatment and rehabilitation measures. Treatment and rehabilitation measures aimed at correcting connective tissue disorders should be carried out systematically and over a long period of time, be comprehensive and individually selected. This is only possible if the doctor is able to convey to the patient and his parents the essence of the pathological process in the connective tissue in order to convince them of the need to follow the recommendations for a long time.
Important components of the program of treatment and rehabilitation activities for children and adolescents with CTD are non-drug effects and medications.
Non-drug correction methods
Non-drug methods such as a nutritious diet and organization of a daily routine are of undoubted value.
Children with DST are recommended to eat foods rich in protein (meat, fish, squid, beans, soy, nuts), with individually selected dietary supplements containing essential amino acids (lysine, arginine, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, valine). Food products must contain a large amount of macro- and microelements, vitamins, unsaturated fatty acids necessary for normal collagen synthesis. For patients without pathology of the digestive system, it is advisable to include in the diet several times a week strong broths, jellied dishes of meat and fish containing a significant amount of chondroitin sulfates.
It is necessary to clearly organize the daily routine with alternation of work and rest. Daily exercise, walks in the fresh air, short rest during the day and a good night's sleep are required. Some children are also advised to take a nap during the day, especially if the workload at school is quite significant. In the morning, it is advisable to take a contrast shower, in which case it is enough to pour cool water over your feet. In addition to morning exercises, during the day, when the child is resting, you can perform the “bicycle” exercise for 5–10 minutes while lying on a hard surface. Any physical activity should alternate with rest, and it is advisable that during rest the child either lies down or sits with his legs raised, which helps improve blood circulation in the lower extremities.
The doctor should help in selecting the optimal motor mode, avoiding physical inactivity, on the one hand, and overload, on the other. However, these simple activities from the point of view of implementation often turn out to be unrealized due to the lack of preparation of parents and children for their implementation. This requires training for both. Such training is possible not only during an individual conversation between the attending physician and the child and his parents, but also through the reading of specially prepared lectures and conversations for a group of children with CTD, in which the importance of following dietary recommendations is explained in an accessible and visual form. It is possible to conduct group training for patients in day hospitals, clinics, rehabilitation centers, as well as in health centers for children, which are now centers for promoting a healthy lifestyle.
If there are no contraindications to playing sports, then the child can do it, but not professionally. Swimming has a good effect, relieving the static load on the spine. Skiing, cycling, measured physical activity on exercise machines and exercise bikes, measured walking, hiking, badminton, and table tennis are recommended. It should be borne in mind that systematic physical activity increases the adaptive capabilities of the cardiovascular system.
To improve muscle trophism, all children with CTD are prescribed therapeutic massage (course - 15–20 sessions). The area to be massaged is mainly the spine and cervical-collar area (segmental massage). For pain in the joints or legs, a limb massage is indicated.
The success of rehabilitation measures largely depends on the correction of autonomic disorders, which are detected in the vast majority of patients with DST, in which, in addition to medications, dosed physical training, physical therapy, and elements of classical kinesiotherapy are used. However, each of these methods has its limitations, since often their use does not fully take into account the patient’s physical qualities, the type of autonomic regulation, emotional and personal psychological characteristics. At the same time, psychological deviations are also typical for children with DSD, which is due to a whole range of reasons and, first of all, the nature of autonomic regulation. Therefore, in the rehabilitation program for such patients, we propose to include psychophysical training sessions, consisting of dynamic aerobic exercises, isometric exercises and a self-regulation session in a state of relaxation [10]. Psychophysical training harmonizes the emotional sphere, providing children with vagotonia with a reduction in personal anxiety, increasing mental activity and performance, and in children with sympathicotonia it reduces aggressiveness, impulsiveness, and reactive anxiety. The number of classes is determined individually. As the parameters of autonomic homeokinesis stabilize, psychophysical training should move into the category of a health-improving technique, and the regularity of classes is important.
Drug therapy
Since genetically determined changes in connective tissue are accompanied by metabolic changes in its structural elements, pathogenetic drug therapy should be of a replacement nature and carried out in the following areas:
1) stimulation of collagen formation; 2) correction of disorders of the synthesis and catabolism of glycosaminoglycans; 3) stabilization of mineral metabolism; 4) correction of the bioenergetic state of the body; 5) stabilization of peroxide oxidation processes.
To stimulate the process of collagen synthesis, it is recommended to use lysine, carnitine, vitamins C, E, group B, microelements (magnesium, copper, zinc, manganese, etc.). The use of vitamin-mineral complexes is rational.
The most widely used drugs in this area are levocarnitine and magnesium preparations. Levocarnitine (Elkar) is a natural substance related to B vitamins. Levocarnitine is involved in metabolic processes as a carrier of fatty acids through cell membranes from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria, where these acids undergo an oxidation process with the formation of a large amount of metabolic energy (in the form of ATP). The drug is approved for children from birth and has different dosage forms (30% solution for dosing in drops for children of early, preschool and primary school age and in syrup for children of senior school age). Dosage: children from 0 to 3 years old - 8-10 drops of solution per day, from 3 to 12 years old - 27-40 drops per day, from 12 years old - 5 ml of syrup per day. The course of treatment is 1 month.
The use of magnesium preparations in combination with a magnesium fixative - vitamin B6 (Magne B6) is indicated. For children over one year old (weighing more than 10 kg) in the form of a drinking solution in a daily dose of 10–30 mg/kg (1–4 ampoules). Orally for adolescents, 2 tablets or 1 ampoule 2-3 times a day. Precautions: in case of associated calcium deficiency, it is recommended to saturate the body with magnesium before starting calcium therapy. Course - 4–6 weeks.
Correction of disorders in the synthesis and catabolism of glycosaminoglycans is carried out by prescribing chondroprotectors, which are involved in the regulation of chondrocyte metabolism and suppression of the synthesis of enzymes that damage articular cartilage. These include chondroitin sulfates, glucosamine sulfate, and combination drugs that contain a combination of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate.
Chondroitin sulfate (chondroitin sulfate, Structum) is a high-molecular glycosaminoglycan, participates in the synthesis of collagen, the construction of the basic substance of bone and cartilage tissue, slows down bone resorption, helps reduce calcium loss, accelerates the process of bone tissue restoration, inhibits degenerative processes in cartilage tissue, and also normalizes metabolism in hyaline tissue. Used in children over 15 years of age, 1 g per day in 2 divided doses. Capsules are taken orally with a small amount of water. Course duration: 3 months.
For external use for joint pain, a combination drug is indicated, including chondroitin sulfate and dimethyl sulfoxide (Chondroxide). Dimethyl sulfoxide additionally has an anti-inflammatory effect, has the ability to penetrate cell membranes, and improves the transport of drugs through the skin. The ointment is applied to the affected area 2 times a day for 2–3 weeks.
Glucosamine sulfate (DONA, glucosamine sulfate) is a physiological substrate for the biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid, glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans of articular cartilage. Initiates the process of sulfur fixation during the synthesis of chondroitinsulfuric acid, helps normalize calcium deposition in bone tissue. Glucosamine is essential for collagen synthesis and cartilage repair. Indicated for children over 12 years of age in the form of tablets or sachets once a day for 6 weeks. In some cases, a longer course is prescribed. Repeated course of treatment - no less than after 2 months.
In addition, there are a large number of other drugs containing chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride. For example, Teraflex, approved for use from 15 years of age, contains 400 mg of chondroitin sulfate and 500 mg of glucosamine hydrochloride in 1 capsule. Dosage - 1-2 capsules per day for 2-3 months.
To stabilize mineral metabolism, primarily phosphorus-calcium, vitamin D2 preparations are used, and, according to indications, its active forms: alfacalcidol (alpha-D3-teva, Oksidevit), as well as calcium preparations with vitamin D (Calcium-D3 Nycomed, Calcium D3 Ultra). Thus, Calcium-D3 Nycomed is a convenient form for children; it contains 1250 mg of calcium carbonate, which is 10 times more digestible than calcium gluconate, and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) in a dose of 200 IU. This ratio is optimal. For children 3–5 years old, the drug can be prescribed 1/2 tablet once a day, for 5–12 years old - 1 tablet once a day, for children over 12 years old - 1 tablet 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 1 month. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated 2–3 times a year.
Vitamin and mineral complexes are also prescribed.
Correction of the bioenergetic state of the body is carried out by prescribing drugs that stimulate the production of ATP: inosine, ubidecarinone, levocarnitine, succinic acid preparations.
In addition, therapy is indicated aimed at stabilizing the processes of lipid peroxidation, which contributes to the inhibition of free radical oxidation, improvement of tissue respiration, rapid removal of peroxides and toxic oxygen radicals, for this purpose beta-carotene is used in combination with vitamins C and E (Vetoron), ubidecarinone , lipoic acid, omega-3, etc.
Courses of metabolite therapy should include 1-2-3 drugs, and their duration should be at least 1-2 months. The number of courses is 2–3 times a year, depending on the severity of CTD.
Clinical examination
The nature of dispensary observation and clinical and instrumental examinations of patients with DST is determined by the severity of the disease (Table).
Thus, medical support for children with CTD, including the diagnosis of this condition, the organization of preventive, treatment and rehabilitation measures, is a difficult, but very important component of the work of a pediatrician, since CTD is widespread in the pediatric population, prone to a progressive course, significantly worsening the quality children's lives. Detection of CTD is of great importance not only for assessing the child’s health status, but also for the prevention of possible diseases associated with CTD, their rational treatment and prevention of possible complications. Patients with DST require long-term and systematic correction of disorders in the connective tissue, combining both medicinal and non-medicinal methods of influence.
Literature
- Kadurina T. I., Gorbunova V. N. Connective tissue dysplasia: a guide for doctors. M.: ELBI, 2009. 714 p.
- Arsentyev V. G., Baranov V. S., Shabalov N. P. Hereditary connective tissue diseases as a constitutional cause of multiple organ disorders in children: monograph. St. Petersburg, 2013. 44 p.
- Strelkov N. S., Kildiyarova R. R., Sharaev P. N., Ishmamedov I. L. Connective tissue in children with pathology: monograph / Ed. R. R. Kildiyarova. Izhevsk, 2011. 210 p.
- Ivanova I. I., Gnusaev S. F., Koval N. Yu., Gerasimov N. A., Soldatova I. A. Metabolic aspects of undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia in children // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics. 2012. T. 57. No. 4–1. pp. 103–111.
- Tvorogova T. M., Vorobyova A. S. Undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia from the position of diselementosis in children and adolescents // Russian Medical Journal. 2012. T. 20, no. 24. pp. 1215–1221.
- Georgieva E. N. Kalmykova A. S., Minaev B. D. Psycho-emotional characteristics in adolescents and young people with connective tissue dysplasia syndrome of the heart // Bulletin of the Volgograd State Medical University. 2009. T. 29, No. 1. P. 70–72.
- Kadurina T. I., Gnusaev S. F., Abbakumova L. N. et al. Hereditary and multifactorial connective tissue disorders in children. Diagnostic algorithms. Lead tactics. Project of Russian recommendations // Pediatrics. Journal named after G. N. Speransky. 2014. T. 93, No. 5 (Appendix 1). 38 p.
- Kadurina T. I., Gnusaev S. F., Abbakumova L. N. et al. Hereditary and multifactorial connective tissue disorders in children. Diagnostic algorithms. Lead tactics. Project of Russian recommendations // Medical Bulletin of the North Caucasus. 2015. No. 1 (37). pp. 5–35.
- Abbakumova L.N. et al. Hereditary and multifactorial connective tissue disorders in children. Diagnostic algorithms. Lead tactics. Russian recommendations // Pediatrician. 2021. T. 7, no. 2. pp. 5–39.
- Nezhkina N. N., Vorobyova E. V., Kuligin O. V., Chistyakova Yu. V. The use of psychophysical training in the correction of neurocirculatory dystonia in adolescents // Bulletin of the Ivanovo Medical Academy. 2010. T. 15, No. 2. P. 54–55.
V. V. Chemodanov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor E. E. Krasnova1, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education IvSMA Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Ivanovo
1 Contact information
Principles of medical support for children with connective tissue dysplasia / V. V. Chemodanov, E. E. Krasnova For citation: Attending physician No. 11/2018; Page numbers in the issue: 66-69 Tags: metabolic disorders, correction, collagen, elastin