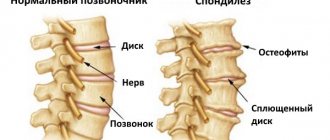
Arthrosis of the spine (spondyloarthrosis) is a chronic form of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the articular cartilage of the spinal column, characterized by thinning of the cartilage and proliferation of bone tissue in the vertebral joints. Many people think that the spinal system does not have joints, but consists only of vertebrae and intervertebral discs, which they are greatly mistaken. The central axis of the musculoskeletal system, or the spine, also has so-called facet (facet) joints. They are formed by the ends of the articular processes (facets) of two adjacent vertebrae and are concentrated between the superior process of the lower vertebra and the inferior process of the upper. The articulating surfaces of bones are covered with smooth, slippery and elastic cartilage.
The functional significance of such joints is enormous: they ensure normal flexion and extension of the spine, and also limit the degree of load on the spinal column, protecting it from excessive movements and instability. Degenerative-dystrophic processes that affect the important cartilaginous covering lead to its destruction, thinning and abrasion, as a result, deformations, increased friction of the articular bone elements and overload of the corresponding section. The problem is complicated by osteophytes, which are spine-like bone growths that arise along the edges of the articular area under the influence of heavy mechanical load.
This disease is dangerous because degeneration extends not only to the cartilage, but to all components of the joint: capsule, synovial membrane, ligaments, subchondral bone and even muscles. According to statistics, about 40% of people suffer from spinal arthrosis. Approximately 55% of cases of facet joint degeneration occur in the cervical region, about 30% in the lumbar segment, and the remaining 15% in the thoracic region.
The main category of patients are people over 45 years of age, who are most vulnerable to pathology due to the biological aging of the body. Those who constantly experience heavy physical activity or, on the contrary, lead a sedentary lifestyle are also predisposed to the disease. Excess body weight, a history of autoimmune diseases and injuries, structural anomalies of the spinal structure can also become provocative factors in the initiation and progression of degenerative-dystrophic pathogenesis in the joints of the spine.
There is one pattern: moderately active and not overweight people suffer from such diseases much less often.
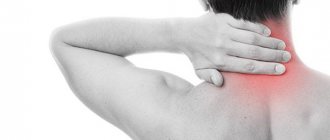
Arthrosis phenomena are accompanied by local pain and stiffness of the back or neck, depending on the location of the problem. It is extremely important to promptly detect the development of a dysfunctional process and begin treatment immediately. Otherwise, severe complications will follow, due to which the quality of life will significantly suffer, and the person will become disabled. It is not possible to completely cure the disease conservatively, but well-chosen therapy will slow down or stop negative phenomena. In advanced cases, orthopedic surgery may be required.
Symptoms of spondyloarthrosis
In the early stages, it is quite problematic to determine arthrosis of the facet joints between the sacral and lumbar segments without appropriate diagnostic equipment. Manifestations of early pathogenesis are not constant and pronounced, so a person usually does not perceive the first messages from a problem area as a disease. And the first sign is a feeling of heaviness in the lumbar region.
Heaviness occurs during active physical labor, a long stay in a motionless position, for example, when you have to stand or sit for a long time. As a rule, people attribute such an unpleasant phenomenon at the level of the sacral and lumbar regions to simple fatigue. But it is advisable to start treating the disease right at the stage of its inception. With moderate and severe forms, treatment is by no means an easy task.
Over time, arthrosis deformans begins to progress, new symptoms appear, which are more disturbing and bring a lot of suffering. One of the main signs of lumbosacral arthrosis is pain. It concentrates on a limited area of the lower spinal column. Then the person begins to understand that he is seriously ill, which forces him to seek help from a medical institution. Let's summarize what has been said and add something new regarding the clinical symptoms of lumboarthrosis.
The lumbar type of pathology is expressed:
- stiffness, limited motor potential of the lower back;
- pain in the sacrolumbar region of varying nature and intensity, most often aching;
- increased pain factor during lateral, anterior, posterior bending of the body, turning to the sides, rotation;
- pain after prolonged physical activity, a prolonged state of immobility (in case of non-advanced pathology, the pain subsides after rest; in case of serious degeneration, it is persistent, regardless of the load);
- local stiffness, while at the initial stage it appears in the morning, as soon as the patient gets out of bed, but after about 30-60 minutes everything goes away;
- sometimes a crunch in the lower back at the moment of making any movement;
- muscle tension at the location of the problem joint;
- local swelling and swelling of soft tissues;
- in severe cases, inability to sit down or get up from a sitting position on your own;
- fatigue, general malaise, and in rare cases, fever.
It is worth noting that a complicated disease, albeit in rare cases, can affect the sensitivity and strength of the lower extremities. A person may feel numbness, weakness in the feet, legs, pain in the legs or buttocks, although a similar picture is more typical of intervertebral hernias.
As you can see, the list of symptoms is quite extensive, and each of the listed signs can be attributed not only to this disease, but also to many other abnormalities of the musculoskeletal system, including internal organs. For example, the lower back may hurt due to poor functioning of the kidneys, intestines, etc. Therefore, it is important to undergo a high-quality examination to make sure that the problem lies precisely in the intervertebral joints, and not in any other element of the ridge or internal organ.
Thoracic spine (dorsal)
The thoracic spine is loaded to the least extent, which explains the smallest number of cases of arthrosis of the joints in this segment. The presence of pathogenesis may be indicated by symptoms such as stiffness, pain in the chest and ribs, and less often in the area of the shoulder blades. Due to muscle tightness and attacks of pain, it is difficult for the patient to bend over, turn around, and even breathe.
- In the initial period, symptoms in the thoracic region predominantly occur during prolonged physical work, prolonged sitting, or after sleep. But as soon as a person rests or disperses, the discomfort stops.
- As the disease progresses, breathing becomes impaired; when inhaling/exhaling or coughing, acute pain occurs in the sternum. Attacks with serious deformities are protracted and intense, often permanent.
- A person in bed cannot find a comfortable position to ease the severity of severe pain. You can more or less tolerate it lying on your side, but lying on your back or stomach is very difficult.
- At the beginning of the pathology, unpleasant symptoms can be muffled by external means and drugs for internal use from the NSAID series. But the further the stage, the stronger the effect of painkillers decreases significantly, as well as any other means of conservative therapy.
The structure of the spine.
It is of paramount importance to clearly establish what is causing the symptoms and recommend treatment only on the basis of reliable diagnostic data.
The point is that such symptoms are common to many diseases. Often people perform treatments that do not correspond to the true diagnosis. The pain syndrome is often localized in the area of the pancreas, stomach, heart, liver, and lungs.
So, someone is unsuccessfully struggling with heart disease, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, etc. But in reality, the emphasis should be on restoring the intervertebral joints of the spine. Or, on the contrary, you might think that it’s all about problems with the spinal system, but in fact it’s a pre-infarction condition or pneumonia. Do not joke with any discomfort that appears in the chest, either in the back or in the front, or in the shoulder blade or along the upper line of the abdomen. Go to the hospital immediately, only experienced medical specialists can make the correct diagnosis!
Attention! You should know that the lack of proper therapy for the dorsal form of arthrosis can actually lead to damage to nearby organs. Particularly dangerous is the pathology of the coronary vessels of the heart, as a result of which myocardial infarction can occur.
Costotransverse type of arthrosis
In the thoracic region there are costotransverse and costovertebral joints, which form the connections of the thoracic vertebrae with the ribs. These two types of formations are mechanically interconnected and therefore cannot work without each other. The costovertebral joint and the transverse costal joint perform the same function: raising and lowering the symmetrical arcuate bones that form the rib cage. This specificity of the articular apparatus of the spinal column is characteristic specifically of the thoracic region.
A little anatomy.
Each of the presented joints can suffer from degenerative-dystrophic pathogenesis. Although it is worth noting that articular lesions in this spinal region are very rare, since the thoracic segment is powerfully strengthened by the muscular-ligamentous complex. They develop more often in older people, mainly women.
As for clinical manifestations, in the previous paragraph we have already talked about the nature of the dorsal type of the disease. Let us recall one distinctive feature: pathological signs are predominantly concentrated in the region of the ribs and the upper part of the abdominal wall. If the disease is severely neglected, dangerous complications may follow: severe depression of the respiratory center and serious disorders of the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of “uncovertebral spondyloarthrosis of the cervical spine” is made by a neurologist
using the following diagnostic studies:
- radiography in two projections to identify defective changes in the structure in the bone canals;
- CT - a computer research method reveals the smallest changes in the cervical region;
- magnetic resonance imaging (this method is characterized by the ability to visualize changes in joints and bone growths);
- radioisotope survey;
- angiography;
- diagnostic blockade.
Osteoarthritis of the facet joints
Destruction of the matrix of the cartilaginous surfaces of the cervical joints is the most common type of spinal arthrosis, and one of the most severe. This subtype of the disease is also called uncoarthrosis or cervical osteoarthritis. The pathology develops over a long period of time and may not manifest itself at first. But a progressive osteochondral deformation, causing compression of the cervical-vertebral nerve roots, veins and arteries, and autonomic plexuses, will certainly show itself as a variety of neurological symptoms. So, destructive processes in the articular cartilages of the neck may be indicated by:
- limited mobility of the head and painful condition in the cervical region with an uncomfortable posture, prolonged immobility, turns and tilts of the head;
- the appearance of a specific sound when moving the head (crunching, clicking);
- local muscle tension in the projection of the damaged element;
- tinnitus and a feeling of loss of balance;
- shooting into the scapuloclavicular triangle;
- deterioration of vision, hearing;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- arterial hypertension;
- numbness in various parts of the upper extremities and other types of paresthesia;
- pain in the neck, head, shoulder girdle, arms, less often in the sternum (sometimes the pain imitates a heart attack).
Naturally, each person will have their own set of symptoms, but all patients will have one common problem - loss of mobility of the cervical segment. The worst thing is that without adequate and timely therapy, the deformed bone bodies can grow together, and the motor abilities of the neck will then be completely blocked. Among other things, due to an illness that affects any level of this department, blood supply and nutrition to the brain can be seriously disrupted.
Contraindications to physical therapy
Complex exercise therapy for cervical arthrosis is not always permitted. Here are the main contraindications:
- period of exacerbation of cervical arthrosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- if there is an aneurysm of the heart and aorta;
- the presence of acute infectious diseases;
- benign or malignant neoplasms;
- arterial hypertension;
- severe form of diabetes mellitus;
- threat of bleeding;
- tachycardia and arrhythmia;
- myopia.
Principles of treatment
Therapeutic goals for spondyloarthrosis of the facet joints include eliminating pain, maintaining cartilage and bone vertebral structures, and normalizing muscle function. Thus, the most important goal will be achieved – improving the patient’s quality of life. Since this disease is chronic, that is, it is impossible to completely get rid of it, a specialist develops a system of treatment and preventive measures that is optimally suitable for a particular case, aimed at achieving remission of the processes of degeneration and dystrophy in the affected segment.
The basic algorithm for the treatment of all joints and the spine is based on the use of medications, physiotherapy and exercise therapy procedures, and diet. All activities must be carried out comprehensively, in regular and complete courses throughout life. This is the only way to achieve lasting positive dynamics in the treatment of a serious illness. If a conservative approach does not help, surgical intervention methods are used. Below we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the table, which clearly presents all the principles of treatment of spondyloarthrosis.
| Methods | Examples | Benefit |
| Drug treatment | Non-steroidal painkillers (external and internal) | They relieve pain, relieve swelling, and eliminate inflammation in the affected area. |
| Vasodilators | Improves microcirculation in tissues, blood flow, lymphatic drainage. | |
| Muscle relaxants | Help relieve muscle spasms and tension (relax tense muscles). | |
| Chondroprotectors (effective in the early stages) | They provide necessary nutrition to cartilage, resist degeneration of healthy tissues, and increase joint mobility. | |
| Corticosteroid injections into the spine (only for strict indications) | They have a long-term anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. | |
| Physiotherapy | Magnetotherapy | Relieves pain, activates blood flow, stimulates interstitial metabolism, fights inflammation. |
| Reflexology | Strengthens blood circulation at the local level, normalizes tissue metabolism, reduces pain and inflammation. | |
| Ultraphonophoresis | Activates blood flow to the diseased area, reduces inflammation, accelerates cell regeneration. | |
| Physiotherapy | A specially selected set of exercises | Strengthens the musculoskeletal corset, increases the endurance of muscles and ligaments, restores motor-support functions, posture and gait, develops the sore area (exercises should not harm the problem area!). |
| Diet | Increasing the diet of vegetables and fruits, limiting salt and sweets, eliminating harmful fats and alcohol, etc. | It allows you to enrich the body with useful microelements and vitamins, which will help normalize metabolism both in the body as a whole and in osteochondral tissues. It will help you lose weight and relieve the spinal column from increased axial load. |
| ethnoscience | Natural plant-based tinctures, rubs, ointments, compresses, etc. | Traditional methods serve exclusively as a complement to the main treatment. They act purely symptomatically, giving a superficial, weakly expressed effect. |
| Surgery | Facet rhizotomy (denevration of the FS) | Causes regression of pain syndrome due to the destruction by high-frequency currents of nerve endings that send pain impulses to the brain. |
| Implant surgery | An artificial implant replaces a worn-out non-viable component of the spine, thereby achieving stabilization and restoration of mobility at a problematic level. |
Today, in different parts of the world, there are many clinical and rehabilitation centers that offer treatment for problems of the musculoskeletal system and spine using a variety of productive methods and technologies. But, perhaps, none of the famous countries can compare with the level of development of orthopedics and traumatology with the Czech Republic.
Here, treatment is carried out only by world-famous specialists who have extensive practical experience and a huge store of medical knowledge, who are fluent in all modern tactics of minimally invasive spinal surgery and joint replacement, and conservative therapy for arthrosis. In this country, the prognosis for a favorable outcome after any type of treatment process is the most promising - from 95% to 100%.
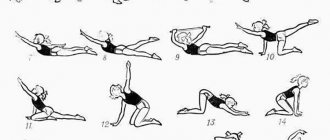
Spinal gymnastics
Orthopedists and traumatologists emphasize that regular performance of special therapeutic and preventive exercises plays a leading role in spinal arthrosis. An individually developed set of exercises for a particular department can significantly improve blood flow in the affected area, activate the nutrition of depleted tissues, establish the delivery of important substances for reparative and regenerative functions, normalize motor capabilities, and strengthen the muscles responsible for the functioning of the intervertebral joints.
Exercises for the cervical region
Exercise therapy for the cervical region is intended for people who are familiar with the feeling of stiffness in the neck and slight dizziness when moving their head. You cannot work on this part of the body at a time of exacerbation of pain and severe swelling. When you have uncovertebral arthrosis, you need to do exercises especially carefully, gently and calmly, avoiding sudden movements and jerks. This complex is also often recommended for osteochondrosis of the corresponding localization.
- Clasp both hands in your fingers. Place the inside of your palms on your forehead. Perform pressure for 5-7 seconds with the frontal surface on the palm, while creating a strong barrier with them, as if preventing the head from moving forward. You should feel the back of your neck muscles tighten. Number of repetitions – 3-5 times.
- Now we do the same, but from the back of the head. That is, we apply a closed lock of hands to the back of the head, and apply backward pressure with the head. We create a reliable barrier with our hands, not allowing our head to lean back even a millimeter.
- Now we place one palm on the side of the head and carry out the same resistance to the movement of the head, but to the side. We carry out similar actions on the opposite side. For all recommendations on time and frequency of repetitions, see exercise. No. 1.
- Slowly lower your head down, trying to reach the jugular fossa with your chin. Pause after reaching your destination for a few seconds, then calmly return back, while throwing your head back to the maximum you can. Don't force anything! Repeat the exercise 5 times.
- Press your chin to the front wall of your neck. Make turns to the right and left in this position (slowly!). The total number of turns is 10 times. It is also recommended to make regular right-hand and left-hand turns 5 times on each side, keeping your head level. But make sure it doesn't fall down and keep your shoulders straight.
- Tilt your head back, lower it towards your shoulder, trying to touch it with your ear. Do this on the right and left sides for a total of 10 exercises.
It is very important that your physical recovery takes place under the watchful supervision of a professional exercise instructor, orthopedist and physiotherapist. You can’t just take the first example of exercise you come across from the Internet and start doing it; physical therapy is prescribed by a doctor! Along with exercise therapy, the patient’s balanced diet plays a leading role, which will help compensate for mineral and vitamin deficiencies and reduce body weight.
In addition, keep in mind that you are advised to undergo treatment in sanatorium medical institutions 1-2 times a year. Within the Russian Federation, sanatoriums in Karelia have proven themselves well, offering a wide range of procedures for high-quality restoration of the musculoskeletal system.
Rules for doing it at home
Performing exercises for the prevention and treatment of cervical arthrosis requires knowledge of important rules. They must be followed to get the maximum effect from therapeutic exercises:
- Exercises are prohibited during periods of exacerbation of cervical arthrosis. This is dangerous to health and can lead to increased pain and complications of the disease.
- Pain and discomfort are not acceptable during exercise. If pain occurs regularly, stop performing the problematic task and consult a doctor.
- Keep your posture straight during classes, this will allow you to improve the effectiveness of the exercises.
- Perform all movements smoothly, slowly. The main task is to tone the muscles, and sudden movements can cause harm, lead to muscle injury and aggravate the situation.
- It is recommended to conduct the first lesson in a medical institution where there is a vertebrologist. He will show you how to perform the movements correctly.
- Most of the exercises are basic, but the complex includes individual exercises for each patient with different loads, so the treatment method is prescribed and developed exclusively by the doctor.
- You need to exercise regularly, several times a day. Prolonged physical activity is not recommended; the maximum duration of the complex for cervical arthrosis is 20 minutes.
- Classes begin with a minimum load, but gradually increase it with each training session.
- Before starting the exercises, be sure to do a warm-up to warm up the necessary muscles and relieve their stiffness. You can take a warm shower and massage the cervical area.
Exercise therapy for the lumbar region
This is the second most common type of pathology after uncovertebral osteoarthritis. Let us give an approximate complex of exercise therapy used for this type of disease.
Complex No. 1.
- Hang on the horizontal bar for 1 minute.
- Take a standing position, hands on your belt. Smoothly alternate bending of the body, first to the sides, then forward/backward (8-10 times).
- We do not change the IP. We carefully perform alternating movements of the pelvis back and forth (10 times for each direction).
- Get on all fours, resting on your forearm. Bend your back up, head down. Stay in this position for 5 seconds, return to i. p. (do up to 10 times).
- Lie on your back. Pull your bent knees to your chest one by one, helping with your hands. To do this, you need to grab your knee with both hands and pull it up. Do 10 repetitions for each leg.
We emphasize that in the acute phase, maximum immobilization of the diseased area is necessary, so consult a doctor to receive competent recommendations regarding the mode of physical activity.
Causes
Among several causes of uncovertebral spondyloarthrosis, there are two fundamental ones: congenital and acquired.
Injuries
The main cause of the disease is spinal injury resulting from a fall, accident or impact.
Hereditary predisposition to joint diseases
This disease can be transmitted genetically over several generations. Most often it is transmitted from father to son or from mother to daughter. There are also cases of transmission of the disease through generations.
Presence of congenital anomalies of the cervical spine
These diseases include Klippel-Feil syndrome, cleft of the posterior arch of C1, damage to the atlas and other defects.
Incorrect posture, damage to the hip area, flat feet
All these factors entail curvature of the spine, which can cause uncovertebral spondyloarthrosis.
Training complex for thoracic localization
Exercise therapy warm-ups will allow you to strengthen this part of the spinal column, increase and maintain its mobility, forget for a long time about excruciating pain in the shoulder blades, sternum and ribs, and restore the functionality of the internal organs.
- Stand straight, feet together. As you inhale, raise your arms up and slowly bend back; as you exhale, lower your arms and at the same time bend forward, rounding your back. Repeat 10 times.
- Sit on a chair, cross your arms behind your head. Inhaling, bend your back backwards, spreading your elbows as far apart as possible. As you exhale, we return back, relaxing our elbows (8 repetitions).
- Kneel down, rest on the palms of your straightened arms. Arch your back downwards, opening your chest as much as possible, and hold in this position for 3 seconds. Then bend your back upward, holding for the same amount of time. Perform alternate bending-bending 7 times for each task.
- Lie on your stomach, arms bent, palms at shoulder level. Straightening your upper limbs, raise your body. Standing on straight arms, smoothly arch the spine, pulling your chest forward (5-7 times).
- Starting position – lying on your stomach, upper limbs located along the body. We tear our shoulders off the surface, raise them to such a distance from the floor as your physical fitness allows (5-7 repetitions).
What type of doctor performs the operation?
A very important element for the employees of the Gelenk Klinik orthopedic medical center in Germany is the close connection between doctors and patients. This means that your attending physician will take care of you from the day you take your medical history until the operation itself. This way, you will have a contact person who understands your situation and can answer all your questions at any time. The Gelenk Clinic's specialist in the treatment of back pain and spinal surgery is the experienced neurosurgeon Dr. Bian Ganepo.