A disease such as arthrosis of the facet joints of the spine can rarely be found in a patient’s outpatient chart. It is quite difficult in differential diagnosis. Therefore, in case of characteristic jadoba, the doctor prefers to diagnose the familiar osteochondrosis. In fact, arthrosis of the facet joints is a pathology that, with proper examination, can be detected in 70% of modern urban residents who have crossed the age line of 45 years. And after reaching the age of 60 years, arthrosis of the facet joints occurs in 95% of the examined patients.
The development of the disease is due to a number of reasons. Among the most common negative influence factors, doctors cite excess weight, a sedentary lifestyle and lack of regular physical activity on the muscular frame of the back.
Regular attendance at manual therapy sessions allows not only to avoid the development of arthrosis of the facet joints of the spine, but also to restore the natural mobility of the spinal column to a physiological extent at any age. If you have back pain with limited range of motion, a feeling of stiffness in the morning and rapid fatigue of the muscular frame of the spine, then we invite you to a free initial consultation at our manual therapy clinic. We see experienced vertebrologists, neurologists, osteopaths and chiropractors. The initial appointment for each patient is provided completely free of charge.
During the initial free consultation, the doctor examines the patient, establishes a preliminary diagnosis, and gives individual recommendations for further diagnosis and treatment.
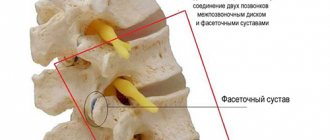
Facet joints of the spine and their facets
To understand the essence of this pathology and the factors of its development, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the basics of anatomy. The spinal column is a flexible structure that provides not only support for the entire body, but also flexibility and mobility of the torso. Due to the special structure of the spine, a person can make body turns, bends in different directions, twisting and a number of other active movements.
The spinal column consists of:
- vertebral bodies with spinous processes;
- intervertebral discs, consisting of cartilage tissue and ensuring uniform distribution of shock-absorbing load;
- uncovertebral joints;
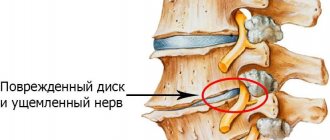
- facet joints with pronounced process facets.
It is the facet joints that provide attachment of the spinous processes to each other. And due to this, it becomes possible to make various movements with the body and head.
Normally, the facet joints of the spine are covered inside with a cartilaginous synovial layer. A dense joint capsule ensures stability of the facets. And synovial fluid creates ideal conditions for the heads of bones to glide easily during various movements.
The facets of the facet joints have a certain structure that prevents their rapid destruction during injury. But with prolonged exposure to excess body weight or curvature of the spinal column, these bones quickly collapse and become deformed. It is for this reason that people who are used to slouching and holding their back unevenly suffer from crunching and pain with any movement. This indicates that the facets of the facet joints of the spine are destroyed. If complex treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease quickly progresses and leads to impaired mobility.
The blood supply to the facet joints and their structural parts (cartilaginous, synovial, connective, bone tissue) is carried out through diffuse exchange with the surrounding muscles. To do this, the muscular frame of the back must be subjected to constant physical activity. During muscle fiber contraction, fluid is released, which is absorbed by the cartilaginous structures of the joints and intervertebral discs. If the muscles do not work, then diffuse metabolism is disrupted.
The process of dehydration of cartilage and synovial tissue begins. This becomes the beginning of a destructive process. At first, tight mobility is observed, then, as the cartilaginous layer thins and the bone tissue is exposed, it begins to crack and fill with deposits of calcium salts.
Methods of treating the disease
Therapy for arthrosis of the facet joints of the spine involves eliminating pain and preventing further tissue damage. Patients are advised to wear rigid fixation corsets to ensure optimal load distribution. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to reduce the intensity of pain. Muscle relaxants are used to relax muscle muscles and relieve painful spasms. High clinical effectiveness is characteristic of NSAIDs in the form of ointments and gels:
- Voltarena;
- Fastuma;
- Apizarthron;
- Indomethacin;
- Ketoprofen.
After their local application 2-3 times a day, pain, swelling, and hyperemia quickly disappear. If NSAIDs are ineffective, hormonal drugs are included in the therapeutic regimen, especially when acute inflammation in the joints is detected. The duration of glucocorticosteroid therapy is determined by the doctor, but treatment rarely lasts more than 3-7 days due to the pronounced side effects of these drugs.
| A group of drugs for the treatment of arthrosis of the facet joints | Pharmacological action of drugs |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Ibuprofen, Ortofen, Meloxicam, Ketoprofen) | Stop the inflammatory process, eliminate swelling and pain |
| Glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Triamcinolone, Kenalog) | Have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, decongestant, analgesic effect |
| Medicines that improve blood circulation (Curantil, Pentoxifylline) | Normalize microcirculation, stimulate blood supply to damaged tissues with nutrients and biologically active substances |
| Chondroprotectors (Teraflex, Structum, Dona, Glucosamine Maximum, Chondroitin-Acos) | Prevents further destruction of joints, and exhibits analgesic and anti-edematous activity when taken over long periods of time. |
If conservative therapy does not produce the desired result, the patient is prepared for surgery. It involves installing special implants between the affected vertebrae. Often, doctors immediately insist on surgical intervention, bypassing a course of medications. In such situations, it is worth listening to their recommendations, since arthrosis of the facet joints progresses rapidly.
Degenerative changes of the facet joints
Chronic degenerative changes of the facet joints begin at a young age. During puberty (12–16 years), hormonal changes in the human body begin. If during this period a teenager leads a sedentary lifestyle and does not force his back muscles to constantly “work,” then the excess amount of hormones starts the process of destruction of cartilage tissue. This can only be avoided with regular physical activity in accordance with the age-related recommendations of physiologists.
At an older age (approximately 25–27 years), an age-related restructuring of the configuration of the spinal column occurs. the process of fusion of the sacral vertebrae begins. This reduces the shock-absorbing capacity of the spinal column, which gradually provokes the destruction of its facet, uncovertebral and facet joints.
Degenerative changes lead to the development of arthrosis, osteoarthrosis or spondyloarthrosis. X-rays, CT or MRI will help establish an accurate diagnosis.
Causes and provoking factors
In addition to natural aging, the development of arthrosis is caused by frequent and prolonged stress on the spine - excess body weight, heavy lifting, grueling sports training. Doctors include in this group a violation of the relationship between the anatomical structures of the spinal column. Such congenital anomalies cause a redistribution of the load on other joints, which leads to their gradual destruction. The following pathologies in the structure of the spine are especially dangerous:
- lumbarization - partial or complete separation of the first sacral vertebra from the sacrum;
- sacralization - complete or partial fusion of the fifth lumbar vertebra with the sacrum;
- violations of joint tropism - asymmetrical arrangement of facet joints;
- improperly formed vertebral arches;
- violation of the attachment of arches to the vertebral bodies.
Many people are not even aware of the abnormal structure of their vertebrae. This is clarified when diagnosing already developed arthrosis or when undergoing a regular medical examination. In a person with such congenital anomalies, the load on the lumbosacral spine increases, causing rapid wear of the joints.
The disease can develop after severe trauma to the spine (fracture) or frequent microtrauma, for example, when lifting and carrying heavy objects. Especially often, post-traumatic arthrosis of the facet joints is diagnosed in untrained people who decide to actively engage in sports. The following factors can provoke degenerative-dystrophic pathology:
- posture disorders;
- sitting for a long time;
- flat feet;
- diseases caused by metabolic disorders.
The sacrolumbar spine experiences increased static loads. Therefore, often simultaneously with arthrosis, other pathologies localized in this area are detected - osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis.
Hypertrophy and deformation of facet joints
Based on the results of an MRI examination, hypertrophy of the facet joints is often detected, which is a direct clinical sign of the development of the initial stage of arthrosis or spondyloarthrosis.
Spondyloarthrosis of the facet joints begins with primary dehydration of cartilage tissue. Then the thinning of the synovial layer begins. As a compensatory reaction, hypertrophy of the facet joints begins, which means a total uniform growth of bone tissue in the form of deposition of calcium salts.
Such deformation of the facets of the facet joints is considered an irreversible process, since there are no pharmacological drugs that would be able to return the physiological shape of the facets after their hypertrophy. In fact, at the initial stage it is possible to reverse this pathological process. For this purpose, manual therapy techniques are used:
- massage and osteopathy restore microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the area of tissue damage;
- reflexology starts the process of tissue regeneration by using the body’s hidden reserves;
- Therapeutic gymnastics and kinesiotherapy ensure uniform development of the muscular frame of the back, due to which the diffuse nutrition of all cartilaginous tissues of the spinal column is completely restored.
If you require treatment for arthrosis of the facet joints, then you should not resort to the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They effectively relieve pain and stiffness of movement only in the early stages of the disease. Then their effect is completely neutralized and the patient requires injections of corticosteroids. These drugs also have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. However, they have an unpleasant side effect - they wash away calcium from bone tissue and provoke the development of osteoporosis. With arthrosis of the arcuate joints, this is fraught with acceleration of the process of destruction of bone tissue and loss of performance.
Diagnostics
At the initial stage of diagnosis, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, performs an external examination, and studies the anamnesis. Pathology may be indicated by previous trauma, chronic diseases of the joints - rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis, gout. A history of diabetes mellitus and thyrotoxicosis is also a clue. The clinical picture of damage to the facet joints is similar to the symptoms of many diseases of the musculoskeletal system - osteochondrosis, radiculitis, intervertebral hernia. Therefore, differential diagnosis is required using instrumental studies:
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography;
- ultrasound examination.
Arthrosis and osteophytes on x-ray.
X-ray images are the most informative. They clearly show changes in the structure of joints characteristic of arthrosis - narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes, subluxations and microcracks. The patient is prescribed a laboratory blood test to determine the level of uric acid, fibrinogen, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Biochemical examination of punctate allows one to determine the presence of infectious agents in the cavity of the facet joints.
Signs of arthrosis of the facet joints of the cervical and thoracic spine
Anatomically, the facet joints of the cervical spine can be classified as a flat type of structure. They are susceptible to destruction in the horizontal plane. The maximum physical load is placed on them when performing various movements. Deforming arthrosis of the facet joints of the cervical spine begins with long periods of static load:
- working on a computer;
- night rest in an uncomfortable position;
- wrong type of pillow for sleeping;
- the impact of the kinetic force of inertial movement during emergency braking while a car or train is moving;
- injury to the neck and surrounding muscle tissue;
- poor posture.
The facet joints of the thoracic region also have a flat horizontal structure. since this section does not have great mobility, arthrosis of the facet joints of the thoracic region rarely develops. But this disease causes severe pain and complete loss of mobility.
The main clinical signs of facet joint arthrosis include the following manifestations:
- pain in the affected area with irradiation along the radicular nerves (for example, with degeneration of joints in the cervical region, pain can spread through the arms, and if the process is localized in the lumbosacral region, through the legs);
- stiffness of movement in the morning and after a long period of being in one body position;
- crunching in the spine or clicking when performing certain movements;
- paresthesia, numbness, a tingling or crawling sensation in those parts of the body that are innervated by the radicular nerves located in those sections where the facet joints of the spine are destroyed.
When such signs appear, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis as quickly as possible, establish an accurate diagnosis and begin comprehensive treatment. For diagnosis, it is recommended to first carry out an x-ray examination. The photographs may show degenerative changes in bone tissue and narrowing of joint spaces. If radiographic images are not informative, the patient is recommended to undergo an MRI examination. In this case, the doctor has the opportunity to assess the condition of all structural parts of the spinal column.
It is important to exclude the possibility of developing ankylosing spondylitis - with it, the clinical manifestations are similar to spondyloarthrosis of the facet joints of the spinal column. But a blood test for rheumatic tests will allow for a correct differential diagnosis. The fact is that the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis differs radically from the treatment of this disease.
Diagnostic methods
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor is obliged to conduct an examination of the patient, which will confirm the presence of pathology. First, the patient's complaints are collected and examined. During them, the following factors are taken into account:
Arthrosis of the sacrococcygeal joint
- increased pain during physical activity or sudden movements;
- crunching sounds when bending the lower back or tilting the head;
- stiffness in movements after waking up;
- limited mobility in the lower back, neck and limbs.
To exclude other diseases when determining a clinical diagnosis, a rheumatologist may prescribe a number of additional examination methods. Among them, the most effective are:
- clinical blood test;
- X-ray diagnostics;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Carrying out these research techniques makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis. This also allows the doctor to prescribe the most effective course of therapy.
X-ray allows diagnosis in most cases
No ads 1
Treatment of arthrosis of the facet joints of the lumbar spine
Arthrosis of the facet joints of the lumbar region, as well as the thoracic and cervical ones, is easily treated with conservative treatment in the early stages. Unfortunately, with severe deformation of the structural parts of the joints, it will no longer be possible to completely restore the layer of cartilaginous synovial tissue. But it is possible to restore at least partially lost mobility to the back.
We recommend starting treatment for facet joint arthrosis at the stage of primary clinical signs. To do this, it is advisable to contact a chiropractor or osteopath. A vertebrologist also treats this pathology. These specialists have sufficient knowledge and experience to develop individual treatment for facet joint arthrosis.
Osteoarthritis of the facet joints of the lumbar spine is characterized by the fact that pain increases rapidly. With total damage to the joints, a person quickly loses his ability to work. Painful sensations occur even in a lying position, in the evening and at night.
Correctly developed treatment allows you to restore mobility and relieve pain. Complex therapy begins with traction traction of the spinal column. This procedure allows you to restore the anatomical structure of the facet bone articulation. then an individual course is developed, which may include manual therapy, osteopathy, massage, reflexology and kinesiotherapy. A properly developed complex of therapeutic exercises can prevent the risk of relapse of the pathology in the future.
It is important to follow all recommendations of your doctor. Sign up for a free initial consultation with a vertebrologist at our manual therapy clinic. You will be given individual recommendations for diagnosis and treatment.
Characteristic features of the disease
Arthrosis of the facet joints of the lumbar spine is a polyetiological disease, that is, its development can be caused by numerous external and internal unfavorable factors. Arthrosis is diagnosed in 90% of cases in patients over 50-55 years of age . At this age, recovery processes slow down significantly. With the development of destructive pathology in the body of a young person, chondrocytes begin to be produced to eliminate damage to cartilage and bone tissue. In old age, this process slows down and is aggravated by insufficient production of collagen and elastin.
CT.
But the disease has become “younger” and is now often found in people under 30 years of age. Rheumatologists, vertebrologists, and orthopedists associate this with a sharp decrease in motor activity and a sedentary lifestyle. Young people who prefer to spend time at the computer often suffer from back pain that precedes arthrosis of the facet joints.
Spondyloarthrosis - symptoms and treatment
The prognosis of the disease depends on its identified form and stage. At earlier stages of damage, a significant restoration of the motor functions of the intervertebral joints and relief of pain is possible. Stage IV is considered irreversible, so the main task in this case is to stop further structural destruction and form adaptive functioning mechanisms to maintain the patient’s ability to work and everyday activities.
Prevention of spondyloarthrosis primarily consists of:
- conducting regular medical examinations of the spine;
- maintaining physiological body weight;
- rational professional and everyday motor mode;
- eliminating physical overload (including sports);
- regular physical activity (adequate fitness programs with an instructor);
- timely qualified treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Nutrition for spondyloarthrosis, as well as for most other diseases, should be balanced and as natural as possible. Since most people suffering from spondyloarthrosis are overweight, a review of food preferences should be aimed at less calorie foods. In general, it is necessary to remember a fairly simple rule of all dietary programs for weight loss: the amount of energy expended must be greater than the amount of energy consumed.
The widespread recommendation of many specialists to “monitor your posture” in this disease certainly has a right to exist, but the practical effectiveness of such a recommendation is often reduced to zero. Even a relatively healthy person is not able to observe his back position during the day due to numerous professional and everyday distractions. Moreover, a patient with spondyloarthrosis will not be able to monitor his posture, since he strives to take the most painless position.
The formation of the most physiological posture occurs through regular exercise therapy (fitness rehabilitation) with a qualified instructor for at least six months. During this period, the most adequate paravertebral muscle tone is formed, which makes it possible to give the spine the most physiological position without attention control.
Fitness rehabilitation programs should be an integral part of the treatment of patients with spondyloarthrosis. Under the supervision of the attending physician, an individual set of therapeutic exercises is selected taking into account the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient. Early initiation of correction of movement disorders and training in the correct movement pattern contributes to faster recovery of working capacity.[1][7][9]
Treatment of spinal arthrosis with a therapeutic plaster NANOPLAST forte
In the therapeutic treatment of deforming arthrosis of the spine, the therapeutic plaster NANOPLAST forte is very effective. The NANOPLAST forte patch allows you to relieve pain and inflammation, improve blood circulation in the affected area. Depending on the severity of the disease, NANOPLAST forte can be used both in monotherapy and in complex therapy.
When using the patch in complex therapy in combination with NSAIDs, analgesics, antispasmodics, the patch helps reduce the dosage and shorten the time of use of these drugs, which are unsafe for the body.
When treating deforming arthrosis of the spine, the therapeutic plaster NANOPLAST forte is applied to the disturbing area, avoiding the front surface of the neck, especially the area of the carotid arteries and lymph nodes, as well as the heart area.
A course of treatment of 9 days or more is recommended. It is usually recommended to use the patch in the morning for 12 hours, but it can also be used at night.
High efficiency, unique composition, long-term (up to 12 hours!) therapeutic effects, ease of use and affordable price make NANOPLAST forte the drug of choice in the treatment of spinal arthrosis.
Read more about NANOPLAST forte
Treatment of deforming arthrosis of the spine
Treatment of deforming arthrosis of the spine is mainly conservative. The following methods can be used:
- anti-inflammatory therapy (NSAIDs) - for severe pain;
- centrally acting muscle relaxants - for severe muscle spasms;
- chondroprotectors (drugs that help slow down the degeneration of cartilage tissue);
- acupuncture;
- therapeutic exercises, incl. visit to the swimming pool
- special massage
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
On the recommendation of a doctor, orthopedic collars or corsets are used to help maintain the spine in the desired position.
The NANOPLAST forte therapeutic plaster showed very good results in the treatment of spinal spondyloarthrosis.
Exercise therapy for the lumbar region
This is the second most common type of pathology after uncovertebral osteoarthritis. Let us give an approximate complex of exercise therapy used for this type of disease.
Complex No. 1.
- Hang on the horizontal bar for 1 minute.
- Take a standing position, hands on your belt. Smoothly alternate bending of the body, first to the sides, then forward/backward (8-10 times).
- We do not change the IP. We carefully perform alternating movements of the pelvis back and forth (10 times for each direction).
- Get on all fours, resting on your forearm. Bend your back up, head down. Stay in this position for 5 seconds, return to i. p. (do up to 10 times).
- Lie on your back. Pull your bent knees to your chest one by one, helping with your hands. To do this, you need to grab your knee with both hands and pull it up. Do 10 repetitions for each leg.
We emphasize that in the acute phase, maximum immobilization of the diseased area is necessary, so consult a doctor to receive competent recommendations regarding the mode of physical activity.