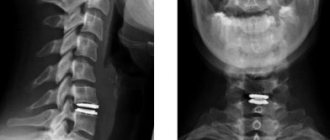
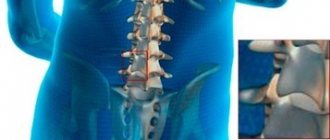
X-ray (x-ray) of the lumbosacral region is an available method for studying the condition and presence of pathological changes in this part of the spine. The diagnosis itself is completely painless, practically safe and allows you to see even the most minimal damage or manifestations of pathologies.
X-ray appointment
An X-ray of the lumbosacral spine is performed within 1–2 minutes, and the process itself does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient. Using modern equipment, radiation exposure is reduced to a minimum. The result is printed on a special film, which allows the doctor to see even the smallest details and features. Instrumental research is prescribed in the following cases:
- Suspicion of injury or fracture.
- Rachiocampsis.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Malignant processes in the vertebrae.
- Any pathological processes in bone tissue.
- Numbness of the limbs, chronic lower back pain.
- Diagnosis before surgery.
- Congenital anomalies.
Carrying out the procedure for preventive purposes is not recommended, since the study is quite harmful. In one session, the body absorbs as much rays as from all household appliances in a year. Modern devices cause less harm, and the results obtained can be obtained on a special electronic medium.
How is the examination carried out?
X-rays of the sacral region are usually taken in direct and lateral projections. This is enough to visualize structures and examine their condition. To begin the diagnosis, the patient is asked to lie down on a special table. When performing an x-ray of the sacrum, a picture is also taken of part of the spine in the lumbar region
and
coccyx
. This allows you to determine whether there are problems with the vertebrae, their size and condition, since the sacrum often hurts due to diseases of the neighboring vertebrae. The sacral x-ray procedure itself takes very little time. You will need to spend about five minutes in the office, after which the patient will be asked to wait outside the office while the doctor draws up a report. An important advantage of the procedure is that it does not require surgical intervention in the body and does not cause any discomfort.
Preparatory procedures
Despite the simplicity of the procedure, preliminary preparation for x-rays of the lumbar region is almost always required. It will increase the information content of the result, as it will eliminate the presence of shadows or darkening from gases and feces. Therefore, each patient is recommended to prepare thoroughly for the procedure.
You can do this as follows:
What is better - X-ray or MRI of the spine?
- In a few days, remove from the menu any foods that cause fermentation and contribute to the formation of gases. It could be legumes, cabbage, baked goods, white bread, carbonated drinks, milk.
- Before the study, refrain from eating. It will take 7-8 hours to give it up. Therefore, it is advisable to sign up for a session in the morning, just to skip breakfast.
- Do not drink water 2 hours before the x-ray. In case of severe thirst, no more than 100 ml is allowed.
- Do several cleansing enemas. For them, clean boiled water at room temperature is used. The volume is selected based on the patient's configuration. This will need to be done in the evening before the lumbar x-ray and immediately in the morning, 3 hours before the procedure.
- To quickly remove food residues, the diet for three days should include light, easily digestible foods. Additionally, it is recommended to drink Festal, Mezim or activated carbon.
- People prone to constipation are advised to completely abandon solid food a few days before the procedure and give preference to juices, teas, and broths. For constipation and a body weight of more than 80 kg, you will additionally need to drink a laxative, for example, Fortrans or Duphalac.
People suffering from chronic flatulence will need to start preparing 3 days in advance and strictly follow the diet recommended by the doctor. And you will also need to take carminative medications. This will reduce the accumulation of gases in the intestines and will not affect the information content of the resulting image.
The enema is done in compliance with the established technology, since there is a high risk of damage to the integrity of the intestine
No ads 1
Preparation the day before the examination
Preparation for an x-ray begins several days in advance, but it is most important on the day of the procedure. You will need to come to the office on an empty stomach, regardless of the appointed time. Therefore, many advise signing up for the morning hours. In the morning you need to follow the following rules:
- Completely avoid breakfast, coffee, tea or even juice.
- Drink a bag of laxative if there are more than 6 hours before the appointed time or give a cleansing enema.
- Give up bad habits, do not smoke on the day of the event.
- Drink 15 drops of valerian tincture or other sedative to reduce possible stress.
- Take water and food with you so that you can eat immediately after the procedure if it takes place in the afternoon or evening.
- Before undergoing the examination, you must remove any jewelry, especially piercings.
Preparatory procedures are extremely important when examining the lower back or lower back. The described measures will make it possible to more effectively cleanse the intestines of the accumulation of gases and feces, improve visualization, and increase the accuracy of diagnosis.
[node:field_similarlink]
How to do a cleansing enema correctly?
The information content of the resulting image directly depends on the correctness of the procedure performed. The process itself involves the introduction of warm water or herbal infusions into the rectum in order to cleanse it of feces. Using laxatives alone is not enough, as there may be solid residues left in the intestines that have not been eliminated naturally. To perform an enema you will need a bulb, Vaseline and clean warm liquid.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Lie on your back in a comfortable position, relax your stomach as much as possible.
- Check the tip for chips or sharp protrusions. They can injure the mucous membrane when administered. The surface must be perfectly smooth. It is better to avoid using damaged devices.
- Lubricate the tube with fat and insert it to a depth of 10 cm; no discomfort should be felt.
- Squeezing the bulb should be slow and even so that the solution gradually enters the rectum.
- After complete administration of the liquid, the tip is carefully removed.
- Wait for natural bowel movements.
The technique is quite simple, and you can handle it yourself at home. If preparation for a lumbar x-ray is carried out in a hospital, then the process is supervised by medical personnel. Instead of a pear, they can use an Esmarch cup, in which case the technology will be slightly different.
An x-ray allows a doctor to determine the condition of a person’s spine
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
X-rays for fractures or diseases of the sacrum are the main diagnostic method. This is due to the fact that such a procedure is very informative and accessible. The study allows you to determine the condition of the sacrum. However, x-rays involve irradiation of the body. Of course, radiation exposure standards are not exceeded, but x-rays cannot be taken more than once a year, and this may not be enough to control the disease. In addition, CT and MRI are more informative and will allow you to examine not only bones, but also soft tissues. At the same time, MRI
completely safe.
Features of the procedure
Depending on the expected diagnosis, the doctor in the prescription indicates the position that the patient will take in the process. This will allow you to take pictures in different planes. In the case of x-rays in the lumbar region, two projections are used: frontal and lateral. They are represented, in turn, by the following variations:
- Front. It involves placing the patient with his back to the device tube and facing the fluorescent screen.
- Rear. The patient is positioned facing the X-ray tube and with his back to the screen.
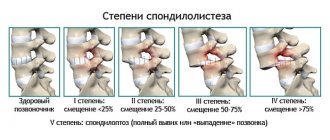
Additionally, oblique projections can be performed to identify vertebral displacements, since the lower back is a fairly mobile area. In this case, the patient is positioned at an angle of 45 degrees to the protective screen. A certain position of the body increases the information content of the image and allows the doctor to accurately diagnose the pathology, its stage and degree of development.
No ads 2
Pathologies of the sacroiliac joint
In the presence of pathology of the sacroiliac joint, the patient always feels pain in the back, which can radiate to the legs or spread higher up the spine. To eliminate pain, and most importantly, the cause of its occurrence, it is necessary to correctly determine the group of pathology.
Inflammatory – infectious and non-infectious
Among the main inflammatory processes that can negatively affect the functioning of the SIJ are:
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- pyogenic flora.
The proportion of disturbances in the functioning of the SIJ of infectious origin is quite small. Treatment consists primarily of eliminating the primary infection.
Degenerative (osteoarthritis of the SIJ)
The most common cause of pain in the SIJ area is osteoporosis or joint dysfunction. Arthritis of the SIJ can be caused by diseases such as psoriasis, Reiter's syndrome or ankylosing spondylitis.
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction (SIJD)
SIJ dysfunction most often develops in older people due to abrasion of tendons and ligaments. DKPS can also develop in pregnant women, in this case the pathology is explained by the hormonal effect on the connective tissue of the semi-joints themselves and their ligamentous apparatus. Women with this diagnosis may be contraindicated for natural delivery, that is, it is preferable to perform a cesarean section (as prescribed by the attending physician).
Injuries (pelvic fractures, rupture of SIJ ligaments)
Pain in the SIJ area can also be of traumatic origin. Pathological childbirth, road accidents, falls from height, sports injuries. All this can cause deformation of the sacroiliac joint, pinching of nerves in this area, displacement or destruction of bones, and so on.
Functional tests
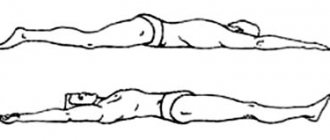
X-rays with functional tests are prescribed if it is necessary to study the condition of the most mobile parts of the spine - the lumbar and cervical. The main indications for it are acute, sharp pain. Usually several photographs are taken at once in different projections, the position of the body will change:
- Fetal position. The patient lies on the couch on his side, his head is placed on his arm bent at the elbow, his knees are pulled up to his stomach. When extending, one arm rests against the edge of the table, the other is located behind the head, while lumbar lordosis is preserved.
- Sitting. The patient needs to sit upright, cross his arms, clasping his knees with them, placing his elbows on his hips, and his body tilted forward. When changing, the head is tilted back and the maximum deflection of the ridge is made
- Standing. You need to stand sideways to the device, while bending forward as much as possible, try to reach your palms to the floor, without bending your knees. After changing the position, the spine extends as much as possible, while the hands are clasped behind the head.
Functional tests are carried out not for everyone, but for a specific group of patients, depending on the availability of indications for them. They are carried out in an X-ray room, all actions are corrected by the employee, so there is no need to memorize all the provisions in advance.
How is an X-ray of the sacroiliac joint done?
It is quite simple to describe how an x-ray of the sacroiliac joint is taken - the patient is placed on his back on the work table of the x-ray machine. Then they point the scanner at the area of interest (pelvic area) and take a picture, this takes 2-3 seconds. The patient must remain still during the scan. There is no pain. To take a lateral view, the patient needs to turn over on his side.
After this, the photograph is developed and a description is made of it.
Contraindications
Not everyone can have an X-ray of the lumbar region; it is contraindicated for some patients. This group includes small children, pregnant and lactating women, and overweight people. Manipulation is especially dangerous in the first trimester, when all the organs and internal systems of the embryo are formed. Children under 15 years of age are recommended to use a protective film during the procedure if there is no alternative to diagnosis.
It is also not recommended for people suffering from neurological pathologies or mental disorders. It should be noted that the radiation received during operation of the device does not accumulate, so there is no point in taking any measures to remove it.
X-ray is the most informative, painless and inexpensive way to find out about the condition of the musculoskeletal system. It is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor in a district clinic or hospital. In this case, you do not need to pay for the procedure if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy with you. In private medical centers, the referral service is not required, but it is not provided free of charge. In the case of examining the lumbar region, special preparation will be required to increase the information content of the image.
Contraindications to undergoing the study
Like any other study, X-ray diagnostics has certain contraindications. It is highly not recommended for women to have X-rays during pregnancy, since irradiation of the fetus can lead to serious pathologies in development, fetal death, and premature birth.
Women during pregnancy (if urgently needed) are recommended to undergo an MRI - this method is both safe and more informative.
Women of childbearing age are recommended to undergo X-ray diagnostics of this part of the spine in the first two weeks after the end of menstruation - in order to avoid a situation where the woman does not yet know about pregnancy, and thereby avoid possible exposure of the fetus.
Among the contraindications, it is also worth mentioning the recent presence of X-ray diagnostics using barium suspension.