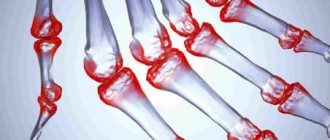
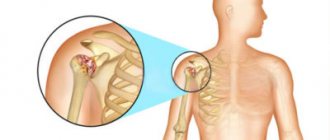
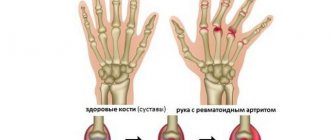
Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide are the main marker of rheumatoid polyarthritis in the early stages. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic disease characterized by predominant damage to the joints and quickly leading to disability if not diagnosed in a timely manner. As a result of disruption of the immune system, the body produces antibodies to the body's own cells and tissues, including proteins of the inflamed joint membrane containing citrulline. Immune complexes lead to joint damage (destruction and erosion). First of all, the small joints of the hands, feet, wrists and ankles, as well as the elbow and knee joints are affected; their damage is often symmetrical. In severe cases, other organs and tissues are involved.
Clinically, RA is manifested by pain in the joints, swelling and deformation, redness in the joint area, increased local and general temperature, and impaired motor activity. The hallmark symptom of rheumatoid arthritis is morning stiffness. If it lasts for a long time, there is a disturbance in movement in the joint up to complete immobility.
When RA is suspected, rheumatoid factor (RF) and C-reactive protein (CRP) are routine diagnostic tests. But these tests are not always informative; the levels of these indicators also increase in other autoimmune diseases.
The production of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide begins 1–2 years before clinical manifestations and is characteristic primarily of RA, so ASCP is a highly informative and accurate test for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis, allowing not only to make an early diagnosis and prescribe timely treatment, but also to differentiate between erosive and non-erosive arthritis. form of the disease. A high level of ASCP is associated with an erosive form that is more aggressive in its course, but it is not informative in assessing the effectiveness of treatment. To diagnose rapidly progressing forms of rheumatoid arthritis, an additional marker is used - antibodies to citrullinated vimentin (anti-MCV), which allows monitoring of therapy.
References
- Rheumatology: National Guide / ed. E.L. Nasonova, V.A. Nasonova. – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. – 720 p.
- Clinical rheumatology (a guide for practitioners) / ed. Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Professor V.I. Mazurova. – St. Petersburg: Foliant Publishing House LLC, 2001. – 416 p.
- Clinical manual for laboratory tests / Ed. WELL. Tiitsa. – M.: Unimed-press, 2003. – 942 p.
- Journal "Handbook of the head of a clinical diagnostic laboratory" No. 6, 2010. Modern laboratory diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
- EUROIMMUN Medizniche Labordiagnostika AG. Anti-CCP ELISA (IgG). 2009 (instructions for determining the ACDC).
- Anti-CCP antibody testing as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Oxford Journals Medicine QJM: An International Journal of Medicine Volume 100, Issue 4 Pp. 193-201.
Cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
The ACCP test is one of the newest methods for diagnosing and analyzing the course of rheumatoid arthritis. To diagnose the disease, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital determine the concentration of two antibodies in the body: ACCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies) and RF (rheumatoid factor). Analysis of ACCP for rheumatoid arthritis gives an accurate result. Decoding the test allows you to determine the pathological process at an early stage. Rheumatoid factor is quite specific. Its reliability is determined largely by the duration of the disease.
Determining ACCP in rheumatoid arthritis in 70% of patients allows us to identify the disease at the initial stage, in the absence of visible symptoms. The analysis reveals the stage of disease progression in 79% of cases. The accuracy of the results is 98%. The study predicts how the disease will develop. This provides an opportunity to start and carry out adequate therapy in a timely manner.
The need for early diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common chronic autoimmune disease, which is expressed by inflammation in the joints and the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in them, and extra-articular manifestations of the disease. When joint tissue is damaged, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Joint pain;
- Swelling and redness of the skin in the area of the diseased joint;
- Movement restrictions;
- Impaired limb function;
- Morning stiffness.
As the disease progresses, inflammation of the joint progresses. This leads to the development of deformities and limitation of movement. At an early stage of the pathological process, there is a need for differential diagnosis of the disease. The rheumatologist pays attention to the typical symptoms of arthritis, the development of inflammatory joint damage, rheumatoid factor and the presence of ACCP. Early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis allows you to prescribe optimal treatment and prevent joint destruction. Severe cases of the disease are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council of the Yusupov Hospital. Professors and doctors of the highest category take part in its work. Leading rheumatologists collectively develop patient management tactics.
Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide, anti-CCP
Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide, anti-CCP
- a highly specific marker of rheumatoid arthritis.
Detection of anti-CCP allows diagnosing diseases in the early stages. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
is the most common chronic systemic connective tissue disease of an autoimmune nature, in which the joints hurt, swell, lose mobility and become deformed. This disease is characterized by inflammation of the synovium, which spreads symmetrically from small to large joints. Initial symptoms of the disease include painful swelling of the joints of the fingers with loss of joint flexibility in the morning. This disease may have extra-articular manifestations. Early diagnosis and prompt initiation of appropriate therapy are critical to disease outcomes.
ACDC
- belong to anticitrullinated antibodies. The description of citrulline-containing autoantigens characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis has become one of the most important discoveries of rheumatology in recent times in the field of serological diagnosis. Citrulline is not a standard amino acid included in proteins during their synthesis; it is formed as a result of subsequent modification of arginine. The process of citrullination is observed during natural physiological and pathological processes and plays a role in the processes of cell differentiation and apoptosis. Citrullinated antigens were discovered during the search for antigenic targets of antikeratin antibodies, a specific marker of rheumatoid arthritis detected by immunofluorescence on tissue preparations.
Antikeratin antibodies recognize only citrullinated forms of the filaggrin protein, which is part of keratin. Among the possible inducers of the formation of antibodies to citrullinated peptides in the mechanism of development of rheumatoid arthritis, citrullinated fibrin, which accumulates in large quantities in the inflamed synovium, is considered. Citrullinated antigens of synovial tissues include citrullinated vimentin. During the development of methods for determining antibodies to citrullinated antigens, it was shown that the use of synthetic cyclic forms of citrullinated peptides provides greater test sensitivity compared to the use of linear peptides. Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide are currently recognized as an informative serological marker of rheumatoid arthritis.
Using a serum ACCP threshold of 5 U/mL, the clinical sensitivity of the test (assessed by the rate of false negative results in the group of patients with rheumatoid arthritis) was 70.6%. The clinical specificity of the test (assessed by the frequency of false positive results) was 99.5% in the group of healthy people and 97.3% in the group of patients with diseases other than rheumatoid arthritis (ankylosing spondylitis, autoimmune thyroiditis, Crohn's disease, dermatomyositis, infection Epstein-Barr virus, Lyme disease, osteoarthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, polymyositis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis, scleroderma, Sjogren's syndrome, SLE, ulcerative colitis).
ACCPs are predominantly of the IgG class, and their specificity for RA is about 97%. They are detected at very early stages of the disease. Patients with antibodies to CCP develop more severe joint damage. Antibodies to CCP have higher specificity compared to RF (anti-CCP - 97%, RF - 63%). ACCP can be found in 30% of cases of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (rheumatoid factor negative).
Anti-CCP is advisable to use in the early diagnosis of arthritis and for the purpose of prognosis of recently developed rheumatoid arthritis (ACCP is more associated with progression and erosive arthritis than rheumatoid factor). The use of ACCP for monitoring the activity of the process is not recommended (no correlation with activity markers, including ESR, CRP, has been identified). The test results should be assessed in conjunction with anamnesis and clinical observations, including instrumental examination data.
Limits of determination: 0.5 –1200 U/ml.
Indications:
- early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (advisable in combination with rheumatoid factor);
- diagnosis of seronegative (for rheumatoid factor) forms of rheumatoid arthritis;
- for prognostic purposes in newly developed rheumatoid arthritis.
Preparation
It is recommended to donate blood in the morning, between 8 am and 12 pm. Blood is taken on an empty stomach or 4–6 hours after the last meal. It is allowed to drink water without gas and sugar. On the eve of the examination, food overload should be avoided.
Interpretation of results
Units: IU/ml
Reference values: 0.00 - 20.00 IU/ml.
Increasing values:
- rheumatoid arthritis (clinical sensitivity - 70.6%, overall specificity - 98.2%);
- in some cases of other connective tissue diseases, especially SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus).
Preparing for the analysis of ACDC and conducting the study
In order to obtain test results that correspond to reality, the patient is advised to follow the following rules:
- Since the analysis is done on an empty stomach, the last meal should be 8-12 hours before blood sampling;
- You are not allowed to drink liquids during the day;
- On the day of collection of biological material, you should not smoke;
- On the eve of the study, do not drink alcohol.
To conduct the test, the nurse draws blood from a vein, observing the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. Serum is extracted from it and used for analysis. When conducting the study, the cytofluometry method is used: the serum is illuminated with a laser. The nature of the beam scattering allows us to determine the content of ACCP in the serum.
Decoding helps the rheumatologist create an effective treatment plan. At the end of therapy, doctors prescribe a repeat test, the results of which must correspond to the norm. If this does not happen, treatment is continued until the result is positive.
In order to undergo examination if you have signs of rheumatoid arthritis, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital at any time of the day, regardless of the day of the week. You will be scheduled for an appointment with a rheumatologist at a time convenient for you. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe a comprehensive examination. Analysis for ACCP for rheumatoid arthritis is included in the diagnostic program.