Numbness is an unpleasant sensation that most often occurs in the fingers or toes, but can affect any part of the limb. If numbness occurs, you should consult a neurologist. Initially, such sensations may be transient - arise and pass on their own, but over time, these sensations can intensify to such an extent that it is sometimes impossible to fully distinguish between cold and hot. Numbness is usually accompanied by tingling, burning or a feeling of tightness, and is accompanied by weakness, awkwardness, and pain.
Of course, numbness is an unpleasant sensation, but not so painful as to prompt a person to immediately consult a doctor with this complaint. Another thing should alert you: numbness is always a signal that there are serious problems with innervation in the body. That is, numbness is a signal that you urgently need to see a neurologist. You should be especially wary if, in addition to numbness, there is pain, awkwardness, weakness, inability to distinguish cold water from warm water, and impaired coordination of movements. In this case, visiting a neurologist absolutely cannot be postponed.
In essence, numbness is a violation of sensitivity (impaired perception of pain, temperature of objects or touch). This indicates damage to a nerve or an entire nerve bundle. That is, this situation is a direct indication for a thorough examination by a neurologist.
Why does my leg go numb?
Physiological reasons
Short-term numbness of the leg occurs when the blood vessels are compressed against the background of an uncomfortable position of the limb. In representatives of professions associated with prolonged standing and walking, slight numbness of the feet and legs appears towards the end of the day, due to overwork. The symptom is combined with pain, heaviness, and distension. It is detected among hairdressers, salespeople, and waiters.
Neuropathies
In patients with mononeuropathies, one limb is involved in the pathological process. The localization and extent of the zone of numbness in neuropathy are determined by the affected nerve trunk:
- Sciatic nerve.
The posterior surface of the lower leg and some areas of the foot become numb. Sciatica is detected. - Femoral nerve.
The numbness zone covers the lower 2/3 of the front surface of the thigh, the entire anterior inner surface of the lower leg. - Tibial nerve.
Sensitivity is impaired along the entire posterior surface of the leg, in the lower third of the segment it spreads laterally. - Peroneal nerve.
The lateral surface of the lower leg suffers. - External cutaneous nerve of the thigh
. Numbness occurs along the outer side of the thigh, then spreads to the front surface.
Extensive sensory disturbances are detected in patients with lumbar and sacral plexitis. The area of numbness may vary depending on the predominant damage to certain nerves. When disorders predominate at the lumbar level, hypoesthesia is detected mainly along the anterior surface of the leg, at the level of the sacrum - along the posterior surface.
Polyneuropathy
In polyneuropathies, decreased sensitivity is often preceded by paresthesia and hyperesthesia. Numbness covers both legs in a “sock-like” manner and gradually spreads proximally. Combined with muscle atrophy and gait changes. Common variants of the disease are alcoholic and inflammatory polyneuropathies (including CIDP), neuropathy of pregnancy.
People with insufficient functions of internal organs develop metabolic neuropathies. Pathology is detected in cases of damage to the liver, kidneys, and severe diabetes mellitus. In addition, multiple nerve damage occurs in systemic vasculitis, neuroAIDS, neuroacanthocytosis, and other diseases.
Numbness of the leg
Dorsopathies
Lumbar dorsopathies are a heterogeneous group of diseases of the spine and surrounding tissues, accompanied by numbness, weakness in the legs, cramps, constant or periodic pain in the lower back, radiating to the lower limb. Hypoesthesia is caused by radicular syndrome, myelopathy. Observed in the following cases:
- Degenerative lesions
: osteochondrosis, disc protrusion, intervertebral hernia, Schmorl's hernia. - Spinal deformities
: kyphosis, lordosis, scoliosis. - Spondylopathies
: spondylosis, spinal stenosis, spondylitis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, neuropathic, traumatic spondylopathies.
Restless legs syndrome
The pathology is accompanied by numbness, itching, paresthesia, and attacks of involuntary motor activity. Symptoms decrease or disappear with movement, intensify at rest, especially at night. Both legs are involved, and asymmetrical lesions are less common. Numbness first occurs in the lower legs. Subsequently, hypoesthesia and other discomfort spread to the feet and hips.
Other nervous diseases
Damage to the pathways or corresponding centers in the brain leads to numbness in one or both legs. The symptom is detected in diseases such as:
- Cerebral circulation disorders.
One arm and one leg are affected. In a transient form of the pathology, hypoesthesia persists for several minutes or hours, then disappears without a trace. With a stroke, numbness is permanent. - Disorders of the spinal circulation
. In the chronic form (myelogenous intermittent claudication), numbness and weakness of the legs occur in attacks and disappear after rest. Spinal stroke is accompanied by rapidly increasing symptoms. Along with numbness, paresis or paralysis and dysfunction of the pelvic organs are detected. - Multiple sclerosis.
The clinical picture is polymorphic. Numbness, paresthesia, muscle weakness can be detected in the upper and/or lower extremities. Subsequently, spastic paresis, ataxia, and hyperkinesis develop.
Traumatic injuries
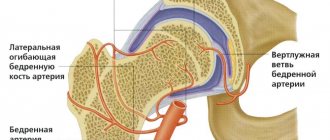
The most serious cause of numbness in the legs is spinal cord injury. Hypesthesia or complete loss of sensitivity is combined with paresis and paralysis. The cause of the violation of the integrity of the peripheral nerve is injury to the area of the buttock, thigh, and lower leg. Damage from bone fragments during fractures is rare. The zone of numbness coincides with that of mononeuropathy of the corresponding nerve.
With positional compression syndrome, a rapid increase in edema, and some other conditions, myofascial compartment syndrome may develop, accompanied by intense pain and subsequent numbness of the leg distal to the site of injury. The cause of numbness after applying a cast is an increase in swelling. To prevent complications, cutting of the bandage is required.
Vascular diseases
In obliterating diseases of the peripheral arteries (endarteritis, thromboangiitis, peripheral atherosclerosis), Mönckeberg arteriosclerosis, numbness is localized mainly in the feet. Atherosclerosis of the abdominal aortic bifurcation is characterized by widespread hypoesthesia of the legs, swelling of the feet, and trophic disorders.
Acute occlusion of the arteries due to obliterating pathologies and some other diseases of the cardiovascular system is manifested by sudden numbness, pain, paresis, and in the absence of treatment - necrosis of the distal parts of the limb. Pain, cramps, numbness in the legs at night are detected with subcompensated and decompensated varicose veins and occur against the background of chronic venous insufficiency.
Other reasons
Temporary or permanent numbness of the legs can be observed with the following pathologies:
- Hypovitaminosis
: beriberi, pellagra, hypovitaminosis B12. - ODS diseases
: osteitis deformans. - Cardiovascular pathologies
: vegetative-vascular dystonia. - Emergency conditions
: solvent poisoning. - Parasitoses
: filariasis. - Mental disorders
: senestopathies, hysterical neurosis.
Ultrasound of blood vessels of the lower extremities
Thigh numbness
Most often, loss of sensation in the lower extremities is a consequence of problems with the spine. The prerequisites for this are:
- radicular pinching;
- vertebral displacement;
- tunnel syndrome (compression of nerve fibers);
- intervertebral hernia;
- disc protrusion.
Other possible sources of symptoms:
- inflammation of the sciatic nerve;
- high loads on the ankle;
- post-traumatic syndrome;
- problems with the femoral head.
Diagnostics
The nature of the pathology causing leg numbness is determined by neurologists. Patients with vascular damage require consultation with a phlebologist or vascular surgeon. The specialist determines the history of the disease, evaluates the appearance of the lower limb, determines pulsation in the arteries, identifies swelling, signs of inflammation, and trophic disorders.
A neurological examination involves determining reflexes, sensitivity, and muscle strength. The additional examination program may include the following procedures:
- Electrophysiological studies
. To clarify the level, severity and extent of nerve damage, electromyography and electroneurography are performed. - Radiography
. Indicated for injuries, suspected nerve compression by a tumor, inflammatory infiltrate, bone growths. - Sonography
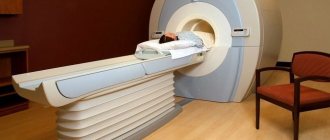
. Doppler ultrasound and duplex scanning are used for arterial lesions and varicose veins. The techniques allow one to assess the speed and nature of blood flow, determine changes in the diameter of blood vessels, and the presence of collaterals. - MRI and CT
. Recommended for patients with suspected injuries or diseases of the central nervous system. They are prescribed at the final stage of the examination to clarify the nature, size and location of the pathological focus. - Laboratory research
. Produced to clarify the diagnosis of hypovitaminosis and parasitosis. Allows you to assess the severity of dysfunction of the body in case of poisoning.
Numbness in the calves as a result of a lack of microelements
If your leg goes numb from the knee down at night, while doing physical exercises or walking, you can assume a lack of microelements:
- calcium (accompanied by mild cramps);
- potassium (leads to heart rhythm disturbances and high blood pressure);
- magnesium (combined with increased irritability, nervousness);
- B vitamins (manifested by weakening of memory, attention, imbalance in the functioning of the central nervous system).
Treatment
Pre-hospital assistance
If your legs become numb due to overload or vascular disease, it is recommended to limit the amount of time you stay on your feet, take regular breaks, wear comfortable shoes, and avoid hypothermia. Patients with radicular syndrome are advised to reduce the load on the back, use painkillers and local warming agents.
In case of traumatic injuries, immobilization is required, and sometimes a bandage and anesthesia are required. Signs of circulatory problems in the spinal cord or brain are an indication to immediately call an ambulance.
Conservative therapy
For polyneuropathies, treatment of the underlying pathology is required. Patients with neuropathies, plexitis, and radicular syndrome are prescribed anti-inflammatory, vasodilator, painkillers, and vitamins. Persistent pain syndrome that is not relieved by analgesics is an indication for therapeutic blockade. Patients are referred for physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, exercise therapy, manual therapy, and acupuncture.
The treatment program for vascular pathologies includes antispasmodics, antithrombotic therapy, and vitamin therapy. Acute occlusion is eliminated using anticoagulants and thrombolytics. For severe pain, blockades are performed. Ozone therapy is performed as part of physiotherapeutic treatment. ILBI, hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Hydrotherapy provides a good effect.
Surgery
For pathologies accompanied by numbness of the leg, interventions such as:
- Traumatic injuries
: suturing or plastic surgery of the nerve trunk, decompression of the spinal cord and fixation of fragments in spinal cord injuries. - Neuropathies
: decompression, isolation of the nerve from the adhesions, excision of a benign neoplasm. - Lesions of the central nervous system:
removal of hematomas and herniated discs, vascular surgery to restore blood supply to nerve structures. - Vascular diseases
: removal of blood clots from arteries and venous trunks, bypass surgery, stenting and arterial replacement, various options for phlebectomy.
Factors influencing the manifestation of symptoms
The nature of pain and the factors causing unpleasant symptoms may vary. For example, if pain occurs due to problems in the spinal region, a person will suffer not only from numbness of the limbs, but also back pain. With multiple sclerosis, coordination and orientation in space are impaired.
A person feels an unpleasant tingling and pain throughout the body. In patients with chronic numbness, unpleasant sensations occur when there is a sudden change in weather, an uncomfortable position, or even stressful shocks.