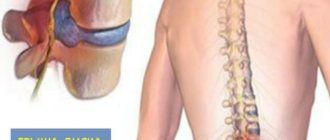
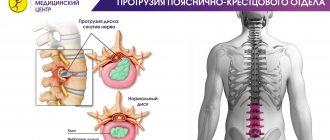
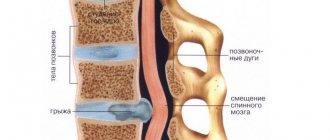
Dorsal protrusion of the intervertebral disc is a protrusion of cartilage tissue towards the spinal canal, accompanied by pinching of nerve endings and the occurrence of severe pain in the spine. Often, pathology is not an independent disease, but occurs as a complication of osteochondrosis and serves as a harbinger of intervertebral hernia. Dorsal protrusion is considered a dangerous condition. The protrusion gradually increases in size, leading to the complete destruction of one or more vertebrae, damage to the spinal cord, and partial or complete paralysis. In the absence of timely treatment, a completely healthy person slowly but inevitably turns into a disabled person.
If you have back pain, do not delay and immediately contact the doctors at Elena Malysheva’s clinic. Experienced doctors will provide quick and timely assistance, determine in which vertebra the protrusion has occurred, and select an individual treatment regimen taking into account the degree of vertebral destruction and the tendency to progression of the pathology.
Causes
Malnutrition of the discs is associated with a change in the functioning of the tissues surrounding the spine, from which, and not through the vessels, the intervertebral discs receive the necessary nutrients. Accordingly, protrusion of the cervical vertebrae occurs due to metabolic disorders in the cervical spine. A serious role in this is played by the hereditary factor, which determines the structure of the spine, the composition of cartilage tissue, and the state of the circulatory system. Also among the causes of the disease are:
- disruption of internal organs;
- hormonal pathologies;
- metabolic disease;
- age-related changes;
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, rheumatism, scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis);
- incorrect posture;
- neck injuries;
- lack of physical activity;
- lack of nutritional intake of vitamins and minerals necessary for the structure of cartilage tissue.
Danger of protrusion of the cervical spine segments c3-c4, c4-c5, c5-c6, c6-c7
Protrusion of the discs of the cervical spine is a classic pathology in people who spend a long time at the computer. This is due to the increased load on the lower segments of the neck during prolonged flexion.
Causes of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
Cervical discs normally compensate for the load on the upper part of the spine and prevent the vertebrae from shifting. When exposed to provoking factors, they begin to crack and lose their functional properties.
The cause of damage to the intervertebral discs most often lies in impaired blood supply and lack of nutrients (degenerative changes). These substances enter the intervertebral discs not from blood vessels, but through penetration (diffusion) from other tissues.
Initially, the nucleus pulposus begins to lose water, which leads to a loss of shock-absorbing function of the spine. Against this background, the cartilage tissue gradually begins to crack and at a certain moment the fibrous ring, which holds all the internal structures, ruptures.
The result of the process is disc protrusion at C5-C6, C6-C7 and other levels, which usually does not manifest itself as pain. It can only be accompanied by a feeling of slight discomfort, so it does not alarm the person. The main causes of bulging intervertebral discs in the cervical region:
- Metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes);
- Traumatic spinal injuries;
- Diseases of internal organs;
- Pathological changes in the vertebrae with osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis;
- Osteoporosis (loss of bone structure);
- Incorrect posture.
After degenerative-dystrophic changes, the second most common cause of prolapse of intervertebral discs in the C4-C5, C5-C6, C6-C7 segments is a change in posture. If, due to the nature of his profession, a person is forced to spend a long time with his head bowed, he is at increased risk.
Initially, the pathology affects the C6-C7 level, which accounts for the maximum shock-absorbing load when tilting the head; the C3-C4 segment is affected last. Thus, the progression of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine occurs from bottom to top.
Symptoms of protrusion in the cervical region
Protrusion of C5-C6 and C6-C7 in the initial stages is not accompanied by pain. Only with posterior protrusion can there be compression of the nerve roots, which is accompanied by local pain in the neck. The greatest danger is compression of the vertebral artery, which occurs when the vertebrae are displaced due to prolapse of the intervertebral discs. The artery delivers blood to the structures of the brain. When it is compressed, symptoms appear:
- Dizziness and headaches;
- Irradiation of pain to the area of the arms and lower extremities;
- Blood pressure surges;
- Numbness of hands;
- The appearance of aching pain in the upper extremities in bad weather.
Let us recall that protrusions of the cervical spine for the most part occur without clinical symptoms, and therefore are not detected in the early stages. However, the progression of this disease into a hernia can only be avoided if it is detected and treated in a timely manner.
Complications with protrusion of intervertebral discs
In most cases, cervical protrusion is not accompanied by serious complications. However, this level of the spine is quite vulnerable to many diseases. Against the background of instability of the cervical vertebrae, hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of brain cells may occur with periodic loss of consciousness.
If in other parts of the spine prolapse of intervertebral discs up to 4 mm does not cause serious complications, then in the cervical spine protrusion up to 3 mm at the levels C5-C6 and C6-C7 can lead to paralysis of the upper limbs and stroke (bleeding in the brain). The ligaments around damaged vertebrae and intervertebral discs become actively inflamed, which provokes cervical radiculitis (sharp pain in the back of the head when bending the head or raising the arms up).
Complications of the pathology also depend on the type of protrusion:
- Posterior circular protrusion;
- Uniform or circular protrusion;
- Foraminal-circular hernias.
- The posterior circular protrusion is directed to the region of the spinal canal. Complications of the disease can only be avoided if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Disc damage at the C4-C5, C6-C7 level often turns into an intervertebral hernia. If compression of the nerve roots occurs, pain occurs in the neck area.
Compression of the vertebral artery is accompanied by a disruption of cerebral blood supply with damage to the center of defecation and urination. The prognosis for a person in such a development of events is extremely unfavorable.
Basic principles and methods of treatment It is better to treat prolapsed discs in the cervical spine in the early stages. Basic principles of therapy for C3-C7 protrusion:
- Elimination of the cause of the disease;
- Taking measures to prevent further deterioration of the situation;
- Maximum exclusion of clinical manifestations of intervertebral disc prolapse.
The complexity of therapy lies in the need to treat a whole range of diseases. The most dangerous condition is vertebral instability. If it is localized at the level of C6-C7, there is a high probability of spinal cord compression syndrome. With it, a person often loses consciousness during intense physical activity or tilting the head. However, the above situation with vertebral instability occurs only in 5% of people.
If a prolapsed disc is detected at the C5-C6 or C6-C7 level in a timely manner, it can be quickly prevented. To effectively treat pathology, it is necessary to use combined regimens. They must take into account the pathogenetic links of the process, the characteristics of vertebral syndrome (manifestations of pathology at the level of the spine), and methods for eliminating compression of the nerves.
Pathogenetic therapy involves influencing factors that lead to changes in the vertebral disc segment (VDS). Principles of pathogenetic therapy:
- Means for normalizing blood and lymph circulation (andecalin, aminophylline, dihydroergotamine);
- Introduction of local anesthetic drugs into the affected area of the PDS;
- The use of ascorbic and glucuronic acid preparations to relieve inflammation and restore the structure of cartilage tissue;
- Correction of venous blood supply (escusan, glivenol, troxevasin);
- When the fixation properties of the articular-ligamentous apparatus of the SMS are weakened, measures are taken that are aimed at stabilizing the spinal segment.
In case of severe local pain in the C4-C5, C5-C6 and C6-C7 segments, bed rest and means to accelerate the repair of cartilage tissue are prescribed:
- Vitreous body;
- Rumalon;
- Phibs;
- Polybiolin;
- Potassium orotate.
If protrusion of C3-C6 is accompanied by severe pain, as well as displacement of the vertebrae (instability), it is necessary to use stabilizing corsets that will support the cervical spine in the correct position. It is better to choose models that can correct the displacement of the vertebrae (rigid). They must be prescribed by a doctor.
Neck bandages are also used when there is no favorable prognosis for the disease. Thus, protrusion in segments C4-C5, C5-C6, C6-C7 is a dangerous pathology in advanced cases. To cure it quickly, it is necessary to identify the disease in the early stages.
Symptoms
The spinal canal is narrow, so protrusion of the cervical spine, unlike protrusions in other parts of the spine, appears quite early. In this case, the patient experiences:
- pain in the neck and shoulders;
- stiffness when bending and turning the head;
- frequent headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances in the form of floaters and dark spots before the eyes;
- irritability;
- tingling in the hands, numbness and tremors in them;
- surges in blood pressure.
Diagnostics
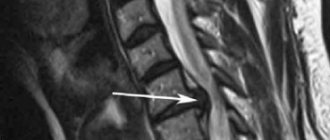
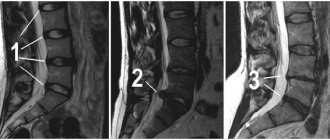
If the above symptoms occur, you should urgently visit a neurologist. Having suspected protrusion, he will refer the patient, first of all, to an x-ray. This simple and inexpensive examination will show whether there is a pathology, after which its examination is most effectively carried out using magnetic resonance imaging. It will provide comprehensive information about the size of the protrusion, the direction of the disc exit, the condition of the vertebrae and surrounding tissues. Myelography (x-ray examination using a contrast agent) and computed tomography are also considered informative methods. They are prescribed as needed as additional studies.
To identify the causes of the disease, you may also need to take a biochemical blood test, which will show the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and the degree of absorption of substances important for cartilage tissue. If you suspect hormonal diseases, you will have to do a separate blood test.
Why does disc protrusion occur?
The structure of the disc is complex in itself and this contributes to both serious injuries and chronic microtraumas, especially with prolonged curvature of the spine, or in case of heavy physical activity. An even more important role is played by the constant aging process, the main degenerative factor of which is dehydration - a decrease in the water content in the disc.
This results in limited elasticity, inability to absorb and compensate for pressure on the spine. Separately, it should be noted atherosclerotic damage to the vessels that supply tissues with oxygen and essential nutrients.
Another key point is changes in the collagen structure of the peripheral part of the disc - the fibrous ring, which violates its integrity and leads to distortion of its supporting functions. As a result, the distance between adjacent vertebrae narrows, the tone of the surrounding muscles and ligaments changes, the mechanics of small joints between the vertebral joints are disrupted, and secondary complications occur. Whether disc protrusion will appear at all, at what age degenerative changes will occur and how pronounced they will be, is determined by genetic predisposition and lifestyle.
Risk factors associated with degenerative disc changes include:
- smoking, which contributes to a dehydrating effect in the body;
- excess weight and obesity increase the mechanical load on the spine;
- intense physical labor;
- static loads that contribute to the curvature of the spine (work sitting/standing in the same position);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- congenital or acquired abnormalities of the spine (for example, scoliosis);
- systemic diseases affecting the spine.
Treatment
- When treating protrusion in the neck area, it is important to immobilize this part of the spine, for which special fixing collars are used.
- Drug therapy helps relieve pain, inflammation and swelling. To improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors, drugs that stimulate blood circulation, and vitamins are prescribed.
- Massage, physiotherapy, and a special set of exercises play a big role in restoring the spine. They help improve nutrition of the intervertebral discs, relax and stretch the spine.
Types of protrusions
Classification of protrusions is carried out in accordance with their location and nature. Depending on them, it is customary to distinguish the following main types of protrusion:
- dorsal - deservedly considered the most dangerous, characterized by localization in the spine towards the spinal cord canal;
- circular - is the most common and is characterized by a uniform protrusion of the disc in a circle with a chronic course and an increase in neurological clinical manifestations;
- median - not very common; characterized by a protrusion directed into the center of the spinal cord canal; is dangerous due to its clinical manifestations that are hidden for the time being.
Prevention
You can avoid changes in the intervertebral discs by following simple rules:
- strengthen the neck muscles;
- avoid sudden movements;
- maintain correct posture;
- eat rationally, take additional vitamin and mineral complexes if necessary;
- control chronic diseases, avoiding complications.
Considering that protrusion occurs more often with age, doctors recommend that all people over 40 years old undergo regular preventive examinations of the spine.
How to diagnose
Diagnosis is carried out through examination and questioning of the patient, after which the doctor refers the patient to an MRI or CT scan. The first procedure is considered the most informative and safest, since there is no irradiation of the body. Based on the results of the tomography, it will be possible to obtain images of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Having assessed their condition and position, the neurologist
will be able to diagnose diffuse protrusion of the C5-C6 disc or any other.