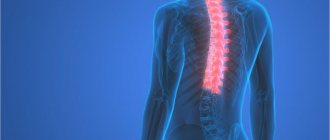
Protrusions of the thoracic spine most often occur in the area from the collarbone to the end of the chest. There are 12 vertebrae in this zone, and between them there are intervertebral discs. When they are damaged or inflamed, back pain occurs, which spreads to the chest and ribs. The condition is accompanied by muscle spasms, tingling, and numbness. Similar symptoms are typical for diseases of the abdominal cavity and sternum, so it is important to correctly diagnose the pathology and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Causes
Protrusions of the thoracic region occur due to the destruction of the walls of the intervertebral discs. This happens when their trophism is disrupted. In the thoracic spine, pathology is least often detected, since it is the least mobile and least susceptible to stress.
Among other reasons, doctors identify:
- sudden injuries caused by blows, falls, accidents;
- improper performance of physical exercises, in particular a combination of bending and twisting;
- genetic factors;
- chronic diseases of the spine: scoliosis, osteochondrosis;
- posture disorders;
- constant sitting;
- sudden movements;
- lack of nutrients.
Protrusions of the thoracic region are most often diagnosed in middle-aged and older patients, which is explained by age-related changes.
What is protrusion of the thoracic spine
The thoracic spine is formed by 12 vertebrae, between which lie layers of cartilage - intervertebral discs. As a result of age-related changes and the negative effects of a number of factors, degenerative-dystrophic changes begin to occur in them, that is, their surfaces wear out, their height decreases, and the elasticity of the fibers decreases. In such cases, osteochondrosis is diagnosed, which, if left untreated, leads to the formation of protrusion, and subsequently intervertebral hernia.
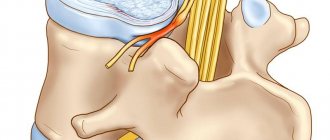
Intervertebral discs are responsible for shock absorption of the vertebral bodies during movements, providing flexibility and mobility of the spine. Therefore, the occurrence of pathological changes in them never passes without a trace for a person. Each intervertebral disc has a nucleus pulposus and an annulus fibrosus.
The nucleus pulposus is a jelly-like or gelatinous mass that is concentrated in the central part of the disc. It is surrounded by a fibrous ring formed by numerous elastic fibers that intertwine in 3 directions.
When walking or performing other movements, the intervertebral discs are compressed and their surfaces are worn out. When the load is removed, the disk expands and regeneration processes begin in it. Normally, the rate of disk destruction and recovery is the same. But under the influence of high loads or age-related changes, degeneration processes occur faster than the disc has time to recover. Gradually, this leads to dehydration of the cartilage, which normally consists of more than half water, and a decrease in the elasticity of the fibers that form the fibrous ring.
Therefore, when the disc is compressed during various movements, microscopic ruptures occur in them. Gradually they increase and eventually, in the most weakened place, a number of fibers of the fibrous ring are torn. The nucleus pulposus fills the resulting void. This is called intervertebral disc protrusion.
In this state, the annulus fibrosus still retains its integrity from the outside, but under the influence of pressure from the nucleus pulposus, the shape of the disc changes. At the site of prolapse, it protrudes outward, which creates the preconditions for compression of surrounding tissues, including the spinal roots.
Since the thoracic spine has low mobility, protrusions in its discs form quite rarely. More often the cartilaginous layers of the lower, i.e. 10, 11, 12, vertebrae are affected.
If at the stage of protrusion formation you do not intervene in the pathological process and do not begin complex treatment, over time the fibrous ring will not withstand the loads created during movements and physical work and will ultimately rupture at the site of protrusion formation. As a result, the nucleus pulposus will have the opportunity to come out, which will already be considered a true hernia. Such a contented state is dangerous, since the hernia, if left untreated, constantly increases in size and can compress not only the spinal roots, but also the spinal cord itself. The consequence of such processes can be severe neurological disorders, including paralysis and disability.
In the most advanced cases, part of the nucleus pulposus can separate from the maternal intervertebral disc and “travel” along the spinal canal. In such situations, they speak of the formation of sequestration, which is an indication for emergency surgery. Otherwise, a sequestered hernia can injure the nerve roots in any part of the spine, impinge on the spinal cord and lead to irreversible consequences.
Symptoms of protrusion
Symptoms of protrusions depend on the location of the damaged discs. In some cases, the pathology does not bother the patient until the formation reaches a significant size.
Patients report pain in the back and shoulder blades, spreading to the arm, abdominal organs and sternum area. It can be felt on one side of the spine or on both. The pain intensifies during heavy lifting, coughing, twisting, bending, and movements in which the arms are held in front of the body. If the patient experiences compression of the root, numbness and tingling of the limbs are noted. Patients note increased discomfort in the morning.
Protrusions are accompanied by muscle spasms. It is difficult for the patient to sit, stand, or bend, especially if the damage to the roots is extensive.
Some patients with protrusion of the thoracic spine may experience shortness of breath, increased blood pressure, headache, and nausea. Doctors have recorded cases of partial paralysis of the arms.
Protrusions in the thoracic region lead to weakening of the abdominal muscles.
Benefits of doing exercises
Moderate dosed loads on the back muscles during gymnastics can be a good addition to the treatment of protrusion using conservative methods. The thing is that during training, more blood will flow to the back muscles, and accordingly, the nutrition of the intervertebral discs will improve.
As a result of daily training you will be able to achieve:
- returning mobility to the affected area;
- pain relief;
- eliminating stiffness in the back;
- elimination of edema.
The exercises are chosen by the doctor, since each case of the disease is individual.
Diagnostics
Protrusions of the thoracic region are most often found in an advanced state. Patients in most cases self-medicate, thinking that they have problems with the heart or lungs. They go to the doctor in case of severe pain, when the protrusion has reached a significant size. The most important thing is to start therapy before a hernia forms.
Protrusions of the thoracic spine are diagnosed after a complete examination of the patient. A neurological examination is of great importance. Diagnostic methods used include CT, MRI, CT myelogram, electromyography, and x-ray. Of these, MRI is considered the most informative; the rest play a supporting role and are used to establish the cause of pathology or detect complications. Cardiac abnormalities resulting from protrusion are shown by an ECG.
A patient with suspected thoracic protrusion is also referred for a blood test. Indicators such as ESR, C-reactive protein, calcium and phosphorus concentrations, as well as hormonal levels are examined.
Treatment
Treatment for protrusion of the thoracic spine depends on the severity of the disease. In most cases, medication is sufficient for recovery. Patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and medications to relieve muscle spasms. However, they only relieve symptoms without eliminating the causes of the pathology. It is also necessary to take into account that long-term use of such medications is unacceptable due to adverse reactions.
For minor pain, mild analgesics are sufficient, but if they do not help, then prescription drugs are prescribed. If there is no improvement from medication, epidural injections are given directly to the problem area. They relieve pain instantly. The effect of drugs with this method of treatment is longer.
Patients with protrusion are advised to spend more time resting and change body position more often. It is prohibited to perform circular movements, turns and bends of the body. To reduce the load on the spine and eliminate postural disorders, patients can wear a corset.
Positive dynamics with protrusion of the thoracic spine are possible only through physical therapy exercises, which helps strengthen the muscle corset. Exercises are selected individually for each patient, with an emphasis on stretching. Sudden movements in case of damaged discs are excluded.
Physiotherapeutic procedures can eliminate pain and reduce inflammation of the nerve roots. Recovery of the spine is accelerated by magnetic therapy, cryotherapy, and laser treatment of protrusion of the thoracic spine. These procedures are effective only in the initial stages of protrusion.
The most effective exercises for protrusion
Therapeutic exercise is one of the components of complex therapy. Its appointment must be subject to the following rules:
- Classes are allowed only during the period of remission.
- The exercises should be selected by a specialist; before performing them, the patient must carefully study the technique, following the instructions presented in the photo or video.
- During training, it is necessary to avoid pain. If they occur, the activity must be stopped.
- All movements of the patient should be smooth and slow, sudden jerks should be avoided.
- Visualizing a positive effect plays an important role in achieving the goal. While performing the exercise, the patient is advised to imagine how the size of the protrusion decreases, the normal structure of the cartilage tissue is restored, and the spine becomes strong and flexible.
A selection of exercises for thoracic protrusion
The following exercises are safe and effective:
- Starting position - feet shoulder-width apart, feet parallel to each other, arms raised up. The patient's gaze is directed straight ahead. Technique: while inhaling, the patient needs to stretch upward with the tips of his fingers until a feeling of tension in the thoracic vertebrae occurs. At the height of inhalation, hold your breath for a few seconds, then exhale and slowly return to the starting point. Repeat 7-10 times.
- The exercise is performed from a sitting position on a chair. The back is straight, the arms are connected to each other at the back of the head. As you inhale, you need to bend your back, pointing your elbows back. Hold in the maximum possible extreme position for a few seconds. As you exhale, return to the starting point. The number of repetitions is 5-10 times.
- Starting position: lying on your stomach. Palms rest on the floor at shoulder level. As you inhale, you need to slowly straighten your arms, lifting and bending your upper body. At the extreme point, linger for a few seconds, then slowly lower to the starting position. The number of repetitions is no more than 5 times.
- Starting position: lying on your stomach. While inhaling, the patient raises the upper body and legs, thereby creating a deflection of the spine. The hands remain on the floor. In the extreme position, you should linger for 3-4 seconds and smoothly lower to the floor. Number of repetitions - up to 10 times.
- Starting position: standing on all fours. As you inhale, a deflection of the back is created, and as you exhale, the spine rounds. The number of repetitions is 8-10 times.
Typically, when there is protrusion of the thoracic region, therapeutic exercises are carried out according to the principle of circular training. Each exercise is performed a certain number of times, a short pause is made, after which everything is repeated again. One training complex contains no more than 5 circles.
Exercises in the gym
When conducting classes outside a medical institution, control over the exercises should be carried out by an experienced instructor. It is necessary to monitor the load and monitor the correct technique.
Training should be aimed at correcting poor posture, reducing excess weight, and increasing muscle endurance. At the same time, a nutritional plan may be recommended to help achieve recovery.
When working out in the gym, experts advise avoiding the following exercises:
- leg press from a lying position in a machine;
- flexion and extension of the legs in the simulator (if the technique is performed incorrectly, the exercise can be an additional damaging factor);
- lifting legs in the simulator;
- swing your legs;
- horizontal pull-down from a sitting position;
- pull to the chest of the upper block;
- bench press;
- hyperextension.
The effectiveness of yoga for protrusions
Yoga is often used as exercise therapy. The benefits of her practices include gentle relaxation of the back muscles, which helps relieve painful symptoms, partially restore cartilage tissue, and reduce the size of the protrusion.
In addition to its positive effect on the spine, yoga helps relieve nervous tension and improve mood.
Kinesitherapy
One of the methods of physical therapy is kinesitherapy. It is a combination of different types of physical training - active and passive.
Active exercises involve the patient performing the exercises themselves. You can conduct such classes at home, in the gym, or in the pool. During passive training, movements are performed by a specialist. The patient is at rest.
Alternative technique S.M. Bubnovsky
In the interpretation of Dr. Bubnovsky, kinesitherapy is carried out through overcoming pain. In his opinion, this helps the patient to fully feel his body, which contributes to the rapid recovery of the affected part of the spine. Mandatory conditions for such training are:
- control of the exercises by the instructor;
- strict adherence to technique;
- compliance with safety rules.
Other methods of treating protrusion
In the early stages of development of the pathology, the patient's condition improves by treating the spine using manual therapy. The technique allows you to restore the mobility of the spine and prevent the formation of a hernia.
For spinal protrusions, patients are recommended massage sessions, but they should be carried out by experienced specialists with medical education. The procedure is performed only after the pain disappears and the patient’s inflammation subsides.
The following actions are prohibited during massage with protrusion of the thoracic region:
- tapping;
- twisting;
- indentation;
- use of warming ointments during the session;
- impact directly on the spine.
Unpleasant sensations and pain during the session are a signal to cancel the massage procedure.
Pain during protrusion is reduced thanks to acupuncture, which stimulates active points and eliminates inflammation of the roots.
When there is protrusion of the thoracic region, it is very important to improve posture in order to reduce the load on the back and eliminate existing defects.
Surgery
In most cases, protrusion can be cured with the help of medications and physical therapy. If patients do not improve, surgery is recommended for patients.
Indications for surgery are:
- increasing muscle weakness;
- nerve damage;
- increasing radicular pain;
- numbness of the limbs.
Surgical methods are selected taking into account their invasiveness. One of the least dangerous interventions is endoscopic decompression. It is performed under local anesthesia using a laser and endoscope.
If the protrusion is caused by a pinched nerve by an intervertebral disc, part of it may need to be removed. For this purpose, endoscopic foraminotomy is performed. The operation is also minimally invasive and takes place with virtually no blood loss. All microsurgical instruments are inserted through the endoscope tube. After the procedure, loss of mobility is eliminated.
In cases where microsurgery is not required or is contraindicated, percutaneous laser decompression is recommended. This method involves inserting a puncture needle into the affected area.
Sometimes intradiscal electrothermal therapy is prescribed, carried out by introducing an electrothermal catheter into the affected area. The operation is carried out under X-ray control. Thanks to this intervention, the discs are heated and compacted, freeing the nerve roots. The patient is under local anesthesia. The only unpleasant moment after electrothermal therapy is severe pain for 2 days. 2 months after the procedure, it is recommended to begin light physical exercise.
Selective endoscopic discectomy is also considered minimally invasive. With this intervention, a needle is brought to the affected area, through which the endoscope is then guided. The procedure can be performed in conjunction with laser decompression. As a result of this operation, the patient immediately ceases to feel pain and can get back to his feet within 2 hours. The technique is often used for professional athletes.
Symptoms
When a disc bulge occurs, symptoms will directly depend on the location of the disc bulge (protrusion) and the soft tissue structure. Symptoms can range from mild to moderate discomfort if the disc is the only structure involved or can be more severe. These symptoms may include:
- Pain in the upper back or pain radiating to the chest or epigastrium.
- Sensory changes such as numbness or tingling if there is root compression.
- Muscle spasm and changes in posture in response to injury.
- Loss of range of motion, inability to bend, stand up straight, or sit
- Sitting and bending may be difficult if the protrusion is large. Often the patient will be in an unnatural position and have difficulty finding a comfortable position.
- The patient may be asymptomatic if the disc does not put pressure on sensitive soft tissue structures.
Prevention
After surgery, the patient must undergo a course of rehabilitation, otherwise he may experience a relapse of the disease. During this period, it is useful to do swimming, yoga, Pilates, and walking. Exercises must be systematic and performed in compliance with the biomechanics of movements.
Therapy for thoracic protrusion should be comprehensive and include taking medications in parallel with physical activity. In the initial stages, the pathology is easily treated. With a more extensive formation, it takes several weeks just to eliminate the pain. Normalization of the spine takes months. If you follow your doctor's recommendations and exercise regularly, the prognosis is favorable. Even after surgery, the patient’s motor activity is not impaired.
Exercises in the gym
This type of training can be aimed at stretching the muscles and increasing the space between the vertebrae. Do the following:
- find a board that is attached at an angle of 30 degrees, put your hands through the straps, lie on your stomach and hang with your whole body;
- hang on the wall bars, holding the crossbar with your hands, which you can reach with your arms outstretched;
- Lie on your stomach on a soft support and hang your arms and legs down.
When stretching, you should not feel pain, otherwise it will mean that you are damaging the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
Benefits of MBST Therapy
Thanks to MBST therapy, blood circulation improves, regeneration increases and muscle tension decreases. The main advantage of the technique is the absence of adverse reactions and contraindications. This procedure is not dangerous for the patient and allows you to cope with the disease without the use of chemicals.
In just 10 sessions, you can eliminate negative symptoms and cope with the cause of thoracic protrusion. It is MBST therapy that will allow you to avoid surgical intervention and help completely restore the thoracic spine.