In recent years, obstetricians and gynecologists have been paying particular attention to scoliotic disease. There are good reasons for this. At the II International Interdisciplinary Congress “Problems of Reproduction: Innovative Technologies in Reproduction”, which took place in Minsk at the end of April 2021, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of BelMAPO, Ph.D. Marina Tesakova devoted her report to the problem of scoliosis during pregnancy, indicating the extreme relevance of the topic. We have collected the most important points of the speech for our readers.
What is scoliosis
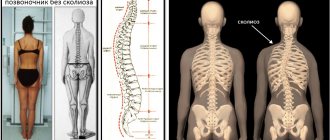
The lateral curvature of the spine, in which it takes a C- or S-shape, is called scoliosis. In this case, not only the spinal column is bent, but also the location of the vertebrae changes, they scroll in relation to each other.
With serious deformities, scoliosis is noticeable even to non-professionals.
In a patient with such a back deformity:
- shoulders are at different heights;
- the gap between the calmly hanging arms and the torso varies;
- The ribs unfold and a rib hump is formed.
In the initial stages, the body compensates for the deformation by curvature of other parts. But as the disease progresses, it becomes noticeable.
Causes of scoliosis
The causes of scoliosis in all groups of the population (not only pregnant women) include the following:
- idiopathic scoliosis is the most common; the exact reasons for its development are unknown, but there is an assumption that a mutation in the gene is responsible for its formation;
- congenital deformation of the vertebrae and other vertebral structures;
- as a manifestation of any neurological disease;
- as a consequence of a birth injury to the spine;
- as a consequence of poor posture (connective tissue dysplasia).
Planning pregnancy with scoliosis
At the planning stage, it is necessary to understand how severe the curvature is. The degree of scoliosis affects the management of pregnancy. To clarify the diagnosis, an x-ray or MRI is done.
With scoliosis of degrees I and II there are no functional disorders in the functioning of internal organs . But the condition of women with stage III or IV scoliosis should be assessed by an orthopedic surgeon , gynecologist and therapist. The decision on the possibility of self-carrying a pregnancy is made taking into account the condition of the woman’s internal organs.
It is necessary to understand that with severe deformations, the location of the heart muscle and lungs shifts. This leads to disruptions in their work. During pregnancy, the load on organs and systems increases, this can cause a threat to the life of the mother and fetus.
Pregnancy contributes to spinal deformation even in healthy women
The patient must understand that severe scoliosis can cause uterine displacement. Because of this, problems arise with conceiving a child and bearing it.
Even in the initial stages of scoliosis, patients sometimes experience pain . Their appearance is associated with an asymmetric load on the back muscles, ligaments, and joints. When pregnancy occurs, the situation will worsen.
Therefore, experts recommend trying to normalize your back condition as much as possible before pregnancy. After all, changes in hormonal levels after conception can only worsen the general condition. The cartilage in the intervertebral discs becomes more elastic, so with a weakened muscle corset, the likelihood of disease progression increases.
Video: “Scoliosis”
How does pregnancy proceed with stage I scoliosis? Consequences
Pregnant women with scoliosis need to regularly visit an orthopedist. In the initial form of scoliosis, the angle of deviation of the spine does not exceed 10°. An orthopedic surgeon may suspect the development of such a pathology during an examination. The diagnosis is confirmed using X-rays and MRI. From the outside, the curvature is almost invisible.
But during pregnancy, a woman with scoliosis should visit not only a gynecologist, but also an orthopedic surgeon. After all, an increase in static loads on the spine, which cannot be avoided, can lead to rapid progression of curvature.
Due to the weakness of the muscle corset, in some women scoliosis goes from stage I to stage III within 9 months.
The likelihood of negative consequences of pregnancy and childbirth is minimal . Exceptions are those cases when women do not pay due attention to disease prevention and spinal deformity increases during pregnancy.
How does pregnancy proceed with stage II scoliosis? Consequences
An orthopedic surgeon diagnoses stage II scoliosis in cases where the angle between the curved areas is 10-25o . At the pregnancy planning stage, consultation with an orthopedic surgeon is mandatory. Indeed, at this stage the patient already begins to experience characteristic symptoms in the form of minor pain and increased fatigue.
The tactics of pregnancy management for scoliosis I and II are practically no different. Women are recommended to perform gymnastic exercises, which are necessary to strengthen the muscle corset.
Wearing a bandage becomes mandatory . Also, if necessary, the doctor selects a corset, with the help of which the spine is held in the correct position. The duration and frequency of wearing it is determined by the surgeon.
How does pregnancy proceed with stage 3 scoliosis? Consequences
Women diagnosed with stage III scoliosis are treated very carefully during pregnancy. After all, the likelihood of complications increases significantly. This diagnosis is made in cases where the angle of curvature is in the range of 26-50o .
Scoliosis causes such unpleasant symptoms:
- pain in the spine;
- displacement of internal organs;
- weakness, fatigue;
- general deterioration in health;
- the appearance of problems with the functioning of the heart and lungs.
With curvature of the pelvic area, the likelihood of pregnancy is noticeably reduced, because the uterus can be displaced to the side. If pregnancy occurs, the load on the spine increases.
This increases the likelihood:
- the occurrence of intervertebral hernias;
- the appearance of cracks (microcracks) in the vertebrae;
- displacement of discs between vertebrae;
- pinched nerve roots.
It is advisable to correct the situation before pregnancy . If conservative methods are ineffective, surgery is performed.
If pregnancy occurs against the background of stage III scoliosis, then the woman should make the decision to bear a child taking into account the opinion of a gynecologist, therapist, or surgeon. After all, there is a high probability of health problems for the woman and child. Due to the incorrect location of the mother's internal organs, the load on the cardiac and respiratory systems increases.
Physical activity is absolutely contraindicated for pregnant women with scoliosis. With grade III scoliosis, stress on the spine is completely prohibited. You cannot bend over or lift heavy objects (even a weight of 5 kg can be critical). Any seemingly insignificant load (cleaning, washing by hand) can lead to irreparable consequences - injury to the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
Cracks appear in the bone tissue , and their contents come out into the spinal canal, forming hernias. They affect nerve endings and cause severe pain.
Having decided to carry the pregnancy to term, a woman must be prepared that the pain will only intensify, and the load on the heart and lungs will increase many times over. After pregnancy, the condition may worsen significantly.
Regular exercise, using bandages and corsets can help ease the condition a little. Such women are advised to sleep on a hard board.
How does pregnancy proceed with stage IV scoliosis? Possible consequences
Did you know that...
Next fact
The diagnosis of IV degree scoliosis is established in cases where the curvature is more than 50° . Even non-specialists can see the deformation; the costal hump is clearly visualized. In this condition, the internal organs are usually significantly displaced, and the shape and structure of the pelvic region is also disrupted.
Women experience:
- constant pain;
- malfunctions of the respiratory system;
- heart and circulation problems;
- disorders of the reproductive system.
Getting pregnant at this stage of scoliosis is problematic. If fertilization has occurred, then the tactics for managing pregnancy at stages III and IV are practically no different.
Women are often hospitalized. In a hospital inpatient setting, the load on the back is noticeably reduced (there is no need to do ordinary household chores), and the woman spends most of her time lying down. In addition, the hospital provides medical support for the condition of the heart, circulatory and respiratory systems.
The likelihood of spontaneous abortion at any stage in severe forms of scoliosis increases. Therefore, it is impossible to ignore the need for regular visits to a gynecologist, orthopedist and neurologist specializing in problems caused by spinal diseases. .
Stages of scoliosis
There are 4 stages of scoliosis: Stage 1 – curvature of no more than 100, visually invisible, diagnosed during an X-ray examination. Not life threatening.
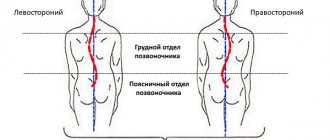
Stage 2 – the curvature reaches 250, changes are visually visible in the form of: different shoulder levels, asymmetry of the shoulder blades, different waist triangles. This degree can easily be treated in the form of massage, physical therapy, and wearing a corset.
Stage 3 – there is a clear progression of the disease, the angle of curvature of the spine reaches up to 500. Changes in the form of protruding ribs (formation of a rib hump) and torsion of the spine are visually visible. Correction of this stage is possible only with the help of complex surgery.
Stage 4 – curvature of more than 500. No conservative treatment methods will have an effect in this situation, only complex surgical procedures.
Elimination of the consequences and symptoms of scoliosis during pregnancy
You can minimize the load on your back and prevent complications from occurring through massage, self-massage and special exercises.
When pregnancy occurs, women are advised not to forget about the need to perform therapeutic exercises . Most exercises for scoliosis are allowed for pregnant women, because there is no strong strain on the muscles when performing them. In most cases, these are static exercises designed to stretch and strengthen the muscle corset. Regular exercise can prevent the condition from getting worse.
Doctors recommend wearing special belts and corsets , with the help of which the process of spinal deformation is stopped. It is also useful to visit the pool: intensive swimming is not advisable; it is better to do special gymnastics for pregnant women in the water.
You can also look for chiropractors who specialize in pregnancy. They can help relieve the condition, reduce pain and prevent further progression of the disease. If it is not possible to receive help from a specialist, patients are allowed to do regular self-massage. A woman can independently rub tight spots (those areas of muscles in which pain is felt).
The role of osteopathy in the treatment of scoliosis in pregnant women
In the presence of scoliosis, the most effective and painless treatment method will be osteopathic. What is its essence? Osteopathic techniques are aimed at relaxing muscles, relieving their tone, normalizing blood circulation in the spine and pelvic organs, and eliminating tension in the pelvic floor ligaments. The necessary preparation of the birth canal is carried out to ensure the smooth passage of the fetus and reduce injuries to a minimum.
Of course, severe bone deformations cannot be eliminated, so the risk of the child receiving a birth injury still remains. Therefore, after birth, the baby will need to be shown to an osteopath during the first month of life. This is simply necessary to eliminate possible dysfunctions that could harm the child’s health. The mother herself also needs to continue treatment, because... after childbirth, the ligamentous apparatus is softer and can contribute to the progression of scoliosis.
Childbirth with scoliosis and delivery methods
Women with degree I deformity are allowed to give birth independently . There are no restrictions. But usually before giving birth you need to take a certificate in which the orthopedic surgeon will indicate the stage of scoliosis.
In the first two stages of scoliosis, childbirth occurs naturally; in stage II, most women are allowed to give birth on their own. But their health status must be previously assessed by a specialist. After all, some may experience complications, in which case independent childbirth is not recommended. In patients with scoliosis, intervertebral hernias form during pregnancy. If present, natural childbirth can only worsen the woman’s condition.
Women with grade III scoliosis are not recommended to give birth naturally; a planned cesarean section is more often performed . After all, there is a possibility that the reaction of the pelvic ring will be difficult due to the immobilization of the lower part of the spine. Although some women decide to give birth on their own.
When diagnosed with stage IV scoliosis, doctors often recommend a cesarean section . Although, in the absence of contraindications from an orthopedist, neurologist and vertebroneurologist, women are allowed to give birth naturally. For many, due to scoliosis III, IV, the shape of the pelvis and its location change, so normal delivery becomes impossible.
Video: “Exercises for pregnant women”
Genetics of scoliosis
The first information about scoliosis as a pathology of the spine, and attempts to solve this problem using methods of external influences - fixation, traction - were described by Hippocrates. And even then, when we had not even heard of genetics, it was noted that scoliosis has a clear tendency to be inherited through the female line.
“Signs of the disease are noticeable in the daughter, but the causes should be sought in the mother.” (Hippocrates, 5th century BC)
Today, this fact has statistical confirmation: for every 6 girls with scoliosis, there is only 1 boy.
At the end of the last century, after conducting numerous and large-scale studies, scientists confirmed a fact that was disappointing for women. A girl born from a mother with a spinal deformity has a 20 times higher risk of scoliosis than a child born from a mother without such a pathology. According to Russian scientists, every 3rd woman with scoliosis gives birth to a child with the same pathology, and its course will be more aggressive.
But the end to genetic research has not yet been reached. Why are girls and women more susceptible to scoliosis? Are there specific genes that are responsible for the development of spinal deformities? Scientists have yet to find answers to these and many other questions.
In our country, the prevalence of the female population in this pathology is higher than world statistics: 1:8. These are the data from the Republican Scientific and Practical Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics. The first manifestations (onset) of the disease occur during the period of active growth: from 6 to 16 years. Spinal deformities are observed in 55 thousand children and adolescents in this age group. In approximately 10 thousand, scoliosis has an active manifestation, and accordingly, they receive treatment: conservative or surgical. A progressive form of scoliosis was noted in 5 thousand people. And mostly these are girls (more than 4 thousand), that is, potential future wives and mothers. It is for this reason that the problem of scoliosis is of particular relevance for specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.
Prevention of scoliosis
Preventive methods are aimed at regular monitoring of posture and correction of the position of the spinal column:
- examination by an orthopedist at least 2 times a year;
- playing sports;
- avoiding excessively high load on the spine;
- symmetrical load on muscles;
- fight against injuries.
Parents and teachers should pay special attention to the child’s posture when sitting at a desk or computer.
Scoliosis is a treatable disease. In the early stages, the pathology is easy to eliminate. It is only important to diagnose spinal column deformity in a timely manner. The SM-Doctor clinic employs doctors with extensive practical experience who will help you accurately establish a diagnosis and select treatment. Timely prevention allows you to avoid serious complications.
Diagnostics and diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of scoliosis begins with an examination and collection of anamnesis of the patient for further development of a treatment plan. The doctor will ask the child and his parents when and where spinal curvatures were discovered, whether the patient had previously sought medical help, and whether any treatment was prescribed. The doctor also gets acquainted with the patient’s medical record; it is important to determine if there are indications for surgical treatment of scoliosis.
As a result of collecting an anamnesis, a competent specialist is able to determine at what stage the disease is, whether it is progressing, and select the optimal treatment methods. When making a diagnosis, an important role is played by the age at which the peak of the disease was diagnosed.
Early diagnosis
When treating scoliosis, early diagnosis of the disease is important. Parents should constantly examine the patient's back to quickly detect any abnormalities. The lack of symmetry should be alarming. Pay attention to:
- The shoulder blades are deflected in an unnatural position;
- The head is tilted to any side of the pelvic axis in relation to the normal position;
- Shoulders or hips are not at the same height;
- Curvatures in the waist area;
- Asymmetrical arrangement of any paired body parts.
If you notice any of the above problems in yourself or your child, make an appointment with a podiatrist without delay. Timely treatment means no dangerous complications.
Stages of patient diagnosis
The main task of the attending physician before treatment is to establish why the patient began to develop scoliosis and at what stage the disease is currently located. As part of the primary diagnosis, the following activities are carried out:
- Questioning the patient, finding out the main complaints about his state of health. Most often, patients complain of severe pain in the thoracic or lumbar spine, cosmetic defects and severe deformities. The specialist determines the nature of the pain and the presence of other medical pathologies that could cause scoliosis.
- Thorough examination of patients. The orthopedist carefully examines the condition of your back. The patient must be referred for consultation to a neurologist to make a more accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Basic methods for diagnosing scoliosis
To make a final diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment for scoliosis, the following methods of diagnosing the body are most often used:
- Physical examination of the body. It consists of a visual examination of the spine and identification of curvatures in all planes. The patient needs to completely undress to the waist, bend his body forward, and try to reach the floor with his fingertips. In this position of the body, all deformations become invisible to the naked eye. The specialist also checks how symmetrically the body moves, the patient’s muscle strength and reflexes, and joint mobility.
- Scoliometer examination. A special device determines the position of the vertebrae, the angle of deviation of the spine from the normal position, and the severity of the hump in the area of the ribs. A distinctive feature of the method is that deformations can be detected without x-rays.
- X-ray. Radiation makes it possible to identify hidden deformations that have not yet manifested themselves. X-rays are also taken during the treatment of scoliosis to monitor the patient’s current condition and the effectiveness of treatment and prevention measures taken.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. It is mainly prescribed to patients who consult a doctor already at an advanced stage of the disease, when there is a risk of pinching and damage to nerve fibers.
The type of treatment for scoliosis is selected depending on the angle of deviation of the spine from the normal position, the degree of curvature, and the stage at which the disease is at the time of contacting a medical specialist.
Diagnosis of scoliosis
A pediatrician, pediatric surgeon, or orthopedist can diagnose scoliosis in a child.
To do this, the doctor will examine the child in a standing, sitting and lying position. A scoliosisometer is used to determine the extent of the disease. In difficult cases, doctors recommend x-rays of the spinal column. For a detailed examination use:
- CT and MRI;
- myelography;
- computer optical topography.
When scoliosis is complicated by diseases of the internal organs, they resort to cardiography, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, and consultations with specialized specialists are indicated.
How to protect yourself and “facilitate” the process of childbirth with scoliosis?
It doesn’t matter how the baby is born, what matters is his and your health!
By following simple recommendations, you can help yourself fulfill your dream of motherhood and avoid painful consequences:
- try to identify scoliosis at the stage of pregnancy planning and undergo a course of treatment;
- while waiting for the baby, wear a bandage that takes the pressure off your back;
- go in for swimming – it “unloads” your back and strengthens your muscles;
- follow the recommendations;
- listen to your body and pay attention to its “signals”.
Scoliosis, for women, cesarean, natural birth
Contraindications to natural childbirth and possible complications
One of the main contraindications to natural childbirth is narrow and skewed pelvic bones due to curvature. It’s easy to guess that with this position of the bones it will be quite difficult to cope with the loads on your own, and there is absolutely no point in overstraining the muscles and spinal column with scoliosis, so in such situations, it’s definitely a cesarean section. In addition, expectant mothers with this form of curvature have an increased risk of “passing on” scoliosis to the child.
It is also worth choosing a CS if scoliosis progresses during pregnancy. If the degree of curvature has increased significantly, then it will be much safer for mother and baby to choose a “cesarean section”. The least dangerous of the possible consequences of EP when the disease worsens is chronic back pain, which is not at all beneficial for a young mother. The worst consequences are irreversible changes in the spine (the need for surgical treatment), disability.
III and IV degrees of scoliosis are a contraindication to natural childbirth. Obstetricians often disagree with this fact and recommend that patients cope on their own, however, orthopedic surgeons have a different opinion and strongly recommend choosing the least traumatic method for the spine.
Possible complications during natural childbirth with scoliosis:
- deterioration of posture, progression of the disease;
- chronic pain;
- long and difficult labor with a risk to the child’s health (especially with curvatures of the lower spine);
- the appearance of visible cosmetic defects.