The main condition for the treatment of bone and joint injuries is to ensure complete fixation and immobilization without loss of comfort for the patient. The use of an orthosis for an ankle fracture instead of a cast creates all the conditions for effective regeneration of damaged tissue.
The ankle is constantly exposed to high loads, since it is it that distributes a person’s weight, helping to maintain stable balance. When regularly engaging in active sports, as well as during heavy physical activity at work, a person creates conditions for various ankle injuries. These can range from minor sprains and dislocations to serious cracks and fractures. As a result, in order not to get out of the usual rhythm of life, a person needs to have a way to quickly get back on track. This effect is provided by modern orthopedic orthoses. However, doctors often resort to traditional methods of treating injuries. The most common of these is gypsum.
Using an orthopedic orthosis for an ankle fracture instead of a cast can significantly reduce swelling of the affected joint, relieve mechanical stress and provide comfort during rehabilitation, which is often unattainable with a conservative approach.
Rigid orthosis for fixing the ankle joint
Important to remember! The use of orthoses for the treatment of injuries of various etiologies must be coordinated with a qualified orthopedist or other experienced physician. Don't do home therapy.
Description of the device
Fixed ankle splint
An ankle joint orthosis is a product in the form of a boot or sock that completely replicates the anatomical structure of the leg. Often the patient's fingers remain exposed. The main function of the ankle brace is to provide rigid fixation of the damaged area in the required position. There are also options when the work of the joint is partially limited. The degree of fixation depends directly on the conditions of the pathology. Manipulations with securing the orthosis are carried out thanks to adjustable Velcro, laces, belts or other components. The types of fasteners are determined by the model of the device.
The main design features of ankle orthoses are ease of use, absolute hypoallergenicity and the ability to allow air to pass through. This provides comfort and significantly accelerates the healing of injured tissue, eliminating the risk of developing concomitant pathologies.
Product classification
Depending on the type and severity of the pathology, the following types of orthopedic ankle orthoses are distinguished:
- Preventive. Designed to prevent joint injuries during heavy physical activity. Also prescribed to patients with an individual predisposition to ankle injuries.
- Functional. This type of orthosis is necessary for people with changes in the structure of the joint that cannot be corrected. Wearing a functional bandage compensates for the deficiency, ensuring normal motor activity.
- Treatment and rehabilitation. They are used to treat various ankle injuries caused by both mechanical factors and various diseases.
Standard ankle brace
Materials for the manufacture of orthopedic ankle braces can be either soft and elastic (cotton or synthetic fabrics) or hard (metal, medical plastic, wood). Depending on the therapeutic task facing the attending physician, the required degree of orthosis rigidity is selected. Based on this criterion, the following types of products are distinguished:
- Ankle brace. Serves as a support for the ankle and joint during sports or heavy work. Acts as a preventative device.
- Soft bandage. Most often presented in the form of an open-toed sock made of synthetic or cotton fabric. Used for sprains, minor bruises, arthrosis and arthritis.
- Bandage of medium hardness. Made from elastic materials. Equipped with various fasteners (cords, Velcro, belts). It may include several plastic or metal inserts, but is not an orthosis, as it is made primarily of elastic materials. Prescribed for more severe injuries of the ankle joint.
- Rigid orthosis. It is a boot with elements made of medical plastic (cellacast, turbocast) or metal, with internal elastic inserts. The bandage is also equipped with several types of adjustable fasteners to ensure the desired level of fixation. Wearing a rigid orthosis is indicated for patients with severe ankle injuries, as well as as a rehabilitation aid after surgical procedures.
- Joint splints. It has the shape of a boot made of medical plastic with an internal soft layer. A special feature of this device is the complete fixation of the ankle joint from the ankle to the end of the foot. Providing immobility has a positive effect in the treatment of pathologies such as ankle fractures, joint displacement or ligament rupture. Splints also help patients get back on their feet during the postoperative period.
Medium hardness bandage installed on the leg
Another criterion for classifying these orthopedic products is the type of their manufacture. In this case, the following types are distinguished:
- Serial. They are assembled models sold in regular pharmacies or specialized orthopedic stores. They have a fairly low cost.
- Modular. Devices of complex design that are assembled directly on a person’s leg in a medical facility or in an orthopedic salon.
- Individual. They are made to order from a plaster cast of the patient’s legs, taking into account all preferences. Their price is often high, but at the end you get an absolutely customized product.
Soft bandage model option
Important! The selection of an effective orthopedic bandage depends on the type of pathology and the individual structural features of the patient’s joint and is carried out exclusively by an experienced traumatologist or orthopedist. Self-medication is fraught with irreversible consequences.
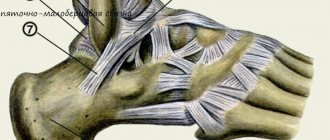
Ankle joint
Before moving on to the therapeutic indications and methods of using the bandage, it is necessary to understand the structural features of the ankle joint.
The main elements that provide stability and motor function are ligaments. Anatomically they are divided into three types:
- ligaments of the tibiofibular joint;
- external side;
- deltoid (inner lateral).
Ligaments securely connect all the bones of the ankle and foot and distribute the load between them. This allows a person to maintain balance and perform various types of physical activity.
However, the ankle is often subject to various injuries, the causes of which can be both external physical factors (bruises, sprains, fractures, dislocations) and consequences caused by diseases.
Each type of lesion requires an individual approach for effective therapy. The sooner the doctor makes the correct diagnosis and prescribes treatment, the faster the joint will return to normal. After all, ankle injuries completely knock a person out of the natural rhythm of life and increase the risk of developing associated negative health consequences.
Structure of the human ankle joint
Application of plastic plaster
Immobilization with plastic plaster in the clinics of JSC Family Doctor
Turbocast plastic gypsum is a low-temperature thermoplastic. When heated to 60-100° C, the material becomes plastic. In a few seconds it cools down to 35-45° C on the surface, which makes it possible to apply a bandage to the body. If necessary, it can be reheated - this allows you to set the required shape of the orthosis in accordance with your clinical situation. Within 6-8 minutes, Turbocast hardens, turning into a strong, rigid structure.
Immobilization with plastic plaster in Moscow is carried out by traumatologists from the Family Doctor clinic network.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Indications for use
The main condition for the treatment of injuries to the ankle joint is complete immobility, rest and removal of all stress. Another important factor is the creation of comfort and the ability to tailor the therapeutic device to each patient individually. Thus, the use of an orthosis for an ankle fracture instead of a cast, as well as for the treatment of other ankle lesions, is a priority.
The therapeutic use of the orthosis is indicated for the following conditions:
- sprains, complete or partial ruptures of the Achilles tendon and ligaments, accompanied by pain;
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- congenital ankle dysplasia;
- rickets;
- partial or complete paralysis of the ankle after a stroke;
- instability of the joint caused by various factors in the development of the body (obesity, deformation of the toes, flat feet);
- recovery period after ankle surgery;
- rehabilitation after injuries (fractures, cracks, dislocations).
Also, the use of an ankle orthosis is indicated for people involved in active sports and heavy physical work as a preventative measure.
Important! If you suffer any ankle injuries, you should seek immediate medical attention. Timely provision of therapy reduces the risk of complications and helps accelerate regeneration.
Derotation boot for fracture: types
By degree of fixation:
- rigid fixation
- semi-rigid fixation
At the location of the fracture:
- derotational boot for femoral neck fracture
- with a fracture (injury) of the leg
Derotational boot with rigid fixation - ensures complete immobility of the limb, excluding rotation around an axis not only in the ankle area, but also in the area of the knee and hip joints, which is so important in case of a femoral neck fracture
Derotational boot with semi-rigid fixation - provides moderate fixation. Fixation is ensured by stiffening ribs inserted into the boot (usually 4 of them) and lacing. Lacing is necessary to provide the desired level of tension, according to the individual anatomical features of the leg. You can walk in this boot. The main goal is to prevent rotation of the joint around its axis. Indications for a semi-rigid derotation boot: ankle fractures, arthrosis, arthritis, damage to ankle ligaments, as well as conditions after surgery and as an adaptation after removing a plaster cast.
Contraindications
The variety of medical orthoses allows you to select the necessary device for each person individually, which distinguishes them from classic plaster or bandage dressings. These products are successfully used both in high-performance sports and in everyday life.
However, despite a number of significant advantages, the use of orthoses is not always justified. For example, for open fractures accompanied by bleeding, the use of this type of bandages is contraindicated. In this case, the best option would be to turn to classic plaster. But after a while, the application of an orthosis will be a priority, since the fusion of the bone structure will take place faster in an adjustable bandage.
Correct selection of product
It should be remembered that the choice of orthopedic device for the treatment of ankle injuries determines the speed and effectiveness of treatment. That is why it is necessary to approach the choice of product as responsibly as possible. The main criterion for selecting an ankle orthosis is the size of the leg. However, if when choosing a device it is too tight for you, do not rush to go for a larger size. In this case, it is worth stopping at this model. This is due to the fact that a properly selected orthosis should tighten the ankle as much as possible to ensure fixation and immobility.
Orthopedists most often understand foot size as a combination of the following factors:
- patient's daily shoe size;
- ankle coverage;
- ankle coverage;
- boot coverage.
Remember! Choosing the right ankle orthosis is possible only in the presence of the attending physician. When selecting, all factors of the course of the disease and the characteristics of the patient’s body are taken into account. The wrong choice of product is fraught with many irreversible consequences.
Ankle injuries: new orthoses versus old casts
“I slipped, fell, woke up - a cast...” Everyone knows that a broken leg is rigidly fixed in a cast for several weeks. But not everyone knows that several years ago orthoses appeared in Russia, which allow patients after a fracture to walk almost immediately without crutches.
Vasily Aleksandrovich Shurov, a traumatologist-orthopedist and chief consultant for orthopedic products at Medi, talks about new methods of treating ankle injuries
Ankle is a joint connecting the lower leg and foot. It plays an important role when walking, carrying out the so-called roll - the redistribution of weight from the heel to the forefoot. The ankle bears the entire weight of the body, so it is very strong and inactive, it has a powerful ligamentous apparatus.
- Since it is so durable, it probably rarely gets injured?
Vice versa. The ankle joint is constantly under very heavy loads. Especially in winter when it’s icy, when it’s very easy to twist your leg. Those with a strong ankle get off relatively easily - with a simple sprain.
- What stretches?
Ligaments: their elasticity is impaired, micro-tears occur, if blood vessels rupture, a hematoma can form. The leg swells, it hurts so much for several days that it’s difficult to walk, but then everything goes away. More complex ankle injuries: broken ankles, torn ligaments, severe sprains.
- You can’t do without the help of a doctor...
If the ligaments are torn, surgery is necessary. The torn ligament must be stitched, and then the joint must be fixed with a plaster cast or a dynamic orthosis. If several ligaments are torn at the same time, a dislocation can occur - this is a very unpleasant injury in which the affected leg does not function at all until the dislocation is set.
- What if the bone is damaged?
Most often, if the leg “tucks” unsuccessfully, the outer ankle breaks. Here, too, rigid fixation will be required for a period of three to six weeks. Then the person will have to undergo long-term development of the ankle joint.
— Vasily Aleksandrovich, you said that a diseased joint can be fixed either with a plaster cast or a dynamic orthosis. What is a dynamic orthosis? Alternative to plaster?
Yes, this is a very interesting development, which in the West at one time made a revolution in traumatology. A dynamic hinge orthosis is a device for fixing the site of injury, much more comfortable than a cast. The main advantage of orthoses is that they allow you to adjust the degree of fixation, which means they can be used effectively at different stages of treatment.
- How is that possible?
At the initial stages of treatment, the orthosis is set to complete immobilization and works like a plaster, reliably fixing the site of injury. Then, during the recovery process, his mobility gradually increases. All hinged structures are designed for multi-stage long-term rehabilitation, thus, when wearing an orthosis, gradual development of the damaged segment occurs.
It is very important that orthoses allow the patient to almost immediately engage in physical activity and maintain muscle tone. This means you won’t have to learn to walk again, like after a cast. In addition, it has been proven that if the area of injury is carefully loaded, then blood flow and trophism in it improves - everything heals much faster.
— What do such orthoses look like?
The German company Medi has an ankle orthosis called medi WalkerBoot. WalkerBoot orthoses are professional orthopedic products. The orthosis looks like a boot, the sole of which has a special rocking shape, due to which a roll from heel to toe occurs, as during natural walking. In this case, the weight is not concentrated at one point, so the patient can begin to walk almost immediately. If, in case of a complex ankle injury, a plaster cast is applied, then the person will be deprived of this opportunity; he will have to move on crutches without stepping on the sore leg.
Agree, it is much more pleasant to walk in an orthosis than in a cast with crutches. Do not forget that the orthosis can always be carefully removed in order, for example, to wash the leg. This trick won't work with plaster.
— How long ago have such orthoses appeared?
Orthoses appeared in Russia less than ten years ago. Even earlier, in some institutes that dealt with prosthetics and orthotics, there were workshops that made such orthoses on an individual order, but only a few could take advantage of this.
- And in the West?
In the West, this trend has been around for over a hundred years, so the technology has been worked out to the smallest detail. Today, they produce a wide variety of orthoses; you just need to choose the right one. And this kind of ready-made orthoses are suitable for 95% of consumers.
- This is a lot, but what about the other five percent?
If the anatomical features of the ankle and the degree of injury do not allow the use of a ready-made orthosis, it is necessary to either make it custom-made or use plaster. I’ll say right away: for complex combined injuries, an orthosis is not recommended. But in all other cases, its use makes life much easier for the patient.
— Orthoses are produced by various companies. What to choose?
In terms of functionality, products from foreign companies are much better than domestic ones. I don’t want to offend anyone, but Russian manufacturers of orthoses, as a rule, try to make their products “to suit the West.” But since they do not have patents, their cuts are similar to Western ones only in appearance. Cheap, but not very high quality. And the same orthoses from the German company Medi have everything patented: special hinges, especially strong alloys, breathable materials that allow air to pass through well, but at the same time have increased strength.
Considering that in case of a complex ankle injury, an orthosis must be worn constantly, the conclusions suggest themselves.
— Who should select an orthosis? Attending doctor?
It's not always the same. Sometimes the hospital itself has a place where you can choose the necessary orthopedic product together with your doctor. But most often the doctor simply writes out a prescription for an orthosis. By the way, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that it is better to purchase orthoses in special orthopedic salons, and not in pharmacies. An individual approach is important here: you need to take measurements, select the right product, try it on, figure out how to use it correctly. This requires time and highly qualified sellers.
— Let's return to Russian realities. Let's say a person breaks his ankle and ends up in the emergency room. How can he convince the doctor to give him an orthosis instead of a cast?
I don't think there will be any problems with this. Now there are fewer and fewer traumatologists who are new to this technique. Orthoses are gaining popularity and are beginning to replace the good old plaster cast. Once at the emergency room, simply ask the doctor if he thinks it is possible to use an orthosis for this injury. But, in general, it is the doctor who is responsible for the patient’s health, so if he says that in this case it is more advisable to put on a cast, it is better not to argue with him.
As an advertisement
Application
Option to wear a cotton sock under an orthosis
For various ankle fractures, doctors first turn to traditional plaster casts. However, this is justified only at the initial stage of therapy. In the future, it is extremely necessary to switch to an orthopedic bandage. However, the transition time is individual for each patient and it is not possible to unambiguously determine the period.
The same can be said about the operating time. Depending on the type of injury and the abilities of the human body, wearing an orthosis can be either permanent or periodic.
A few minutes after putting on the brace, the patient may experience pain in the ankle and notice reddish spots at the site of the injury. Such reactions often pass quite quickly. However, in case of long-term observation of the above effects, you should contact an experienced specialist. Such reactions can occur due to incorrect selection of the product or incorrect adjustments.
It is recommended to wear high cotton socks under the device, especially if you are wearing a metal or plastic orthosis. This is due to the fact that hard devices can rub the patient’s leg and also cause skin irritation in case of intolerance to the material.
Remember! Only the attending physician can tell you how long to wear the device and whether it should be used. It is strictly prohibited to independently adjust the therapy process.
We treat fractures without plaster
The practice of restoring broken bones using plaster has been used in the world for a long time. But it turns out that plaster has a more convenient alternative - plastic orthoses, and they recently appeared at the Istochnik clinic. Let's find out why doctors and patients often choose plastic!
"Cheap and cheerful"
In 1811, Russian surgeon Karl Giebenthal first used plaster to fix a fracture. A little later, in 1847, another famous Russian doctor, Nikolai Pirogov, created a “stick-on dressing,” using first starch, then colloidin, gutta-percha, and finally gypsum to harden the material. Pirogov’s bandage has “survived” to this day. Gypsum is an inexpensive material, so from an economic point of view it is still profitable to use it for medical purposes.
But for a patient who has to walk in a cast for weeks and months, such a bandage is completely uncomfortable. It is heavy, often puts too much pressure on the fixed area, is afraid of moisture and is quite fragile. Under the cast, diaper rash and bedsores may appear, the skin itches, and swelling occurs. Plus, the bandage sometimes prevents you from taking a high-quality x-ray. A person with a plaster cast wants only one thing: to get rid of it as soon as possible, to scratch himself properly and wash himself calmly.
Plastic help
Now imagine that the doctor offers you material with which you can take a shower, go to the pool, or put on your favorite clothes even after a fracture. If necessary, you can even remove and put the bandage back in place. This is not science fiction: these are thermoplastic orthoses.
“Such orthoses are used for various fractures of the limbs, as well as during rehabilitation after dislocations, bruises, ligament ruptures, carpal tunnel syndrome and some other injuries,” says Ivan Anatolyevich Gromov, sports medicine doctor, head of the center for traumatology, orthopedics and sports medicine at the Istochnik clinic. — The orthosis is 10 times lighter than plaster, which makes the plastic structure convenient for treating patients, especially small children. Some people also like that they can choose different colors of the material.
The orthosis is simple and comfortable
Orthoses for fixing broken limbs are made from polyurethane foam. Depending on the complexity of the fracture, making an orthosis can take from a few minutes to 1.5 hours. Everything happens in the presence of the patient. The plastic is heated to 60-70 degrees Celsius and then applied to the affected area. The procedure is comfortable for the patient: the temperature of the plastic when applied is about 40 degrees Celsius. The doctor models the design so that the orthosis accurately follows the contours of the body and fits well to the surface.
After about 6-8 minutes, the plastic will harden and turn into a durable structure. The bandage is secured with Velcro strips or zippers. But if necessary, the material can be reheated and remodeled.
Lightweight and very durable thermoplastic does not injure the skin; there is no need to place additional pads under it. The brace is not afraid of moisture, so if there are no contraindications, you can go with it to the beach, shower or pool. The design fits tightly to the limb, maintains blood flow and muscle tone. This means that healing will be faster than with a regular plaster cast.
The plastic orthosis is easily removable: a convenient option for physiotherapy or hygiene procedures. The orthosis is then put back on and fastened.
— Modern thermoplastic orthoses have become a complete replacement for plaster. They allow the patient to undergo treatment and rehabilitation of injuries, slightly changing their usual lifestyle. Now the installation of plastic orthoses is available to patients of the Istochnik clinic,” summed up Ivan Gromov.
Advantages and disadvantages
Modern orthopedic orthoses prevail over casting and bandaging in almost all criteria. Among the positive aspects of using bandages are:
- reduction or complete elimination of pain and swelling in the affected area;
- strengthening ligaments, tendons and muscles;
- ensuring joint stabilization;
- relieving mechanical stress on the injured area;
- expanding opportunities for physical activity during rehabilitation;
- comfort of use;
- tightening adjustment.
Classic casting brings a lot of inconvenience to the patient and does not allow the doctor to carry out therapeutic manipulations over the affected area during treatment. At the same time, the use of bandages does not provide the proper level of fixation, which is also a significant drawback.
However, as mentioned above, the use of orthoses in the case of open bleeding ankle fractures is unacceptable, which is a certain disadvantage of this device.