Is a bandage needed after surgery?
The postoperative effect of the bandage lies in the external pressure that the Intex elastic belt exerts on the abdominal area after surgery and childbirth. Wearing a bandage after surgery : - Reduces the load on the postoperative wound, preventing the sutures from coming apart. — Improves blood circulation in the area of the postoperative wound, accelerating the formation of fibrin fibers. A durable scar is formed, eliminating the formation of a hernia - protrusion of internal organs through the scar area. — Provides external pressure on the postoperative suture, orienting fibrin fibers in the correct direction. This prevents the appearance of overgrown keloid scars. – Supports abdominal muscles weakened after surgery, helping the patient maintain a slim figure. — Fix internal organs in the correct position. This reduces the risk of the kidneys descending into the pelvic area.
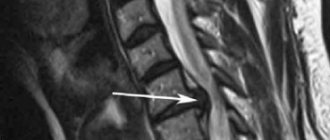
Rehabilitation after removal of herniated discs
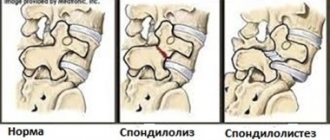
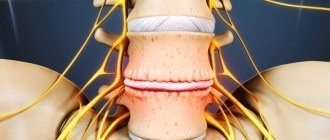
Today, there are many methods of surgical and microsurgical removal of intervertebral hernia. Medicine does not stand still and is constantly finding new methods, means and tools to reduce the invasiveness (penetration into the body through incisions in the skin) of spinal surgeries. After some manipulations, patients are discharged from the hospital within 3-5 days. However, no matter how short the postoperative period, one should not expect that the functions of the spine will be completely restored after a week.
After any surgery (for example, abdominal surgery), patients are advised to have a certain period of rest. A distinctive feature of hernia removal and other spinal surgeries is that there is practically no rest period and dosed physical activity is introduced from the second day of treatment. In many ways, the success of surgical treatment depends on the completed course of rehabilitation measures, as well as on the perseverance and patience of the patient himself.
Types of surgical treatment of the spine
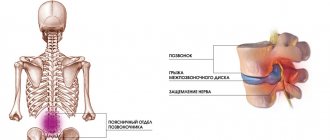
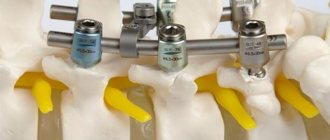
The classic methods for removing an intervertebral hernia are considered to be discectomy (removal of all or part of the intervertebral disc) and laminectomy (excision of part of the bone tissue of a vertebra with a hernia, osteophytes, scars, etc.).
Both operations are performed under general anesthesia and require a working trepanation window (tissue incision) ranging in size from 4 to 10 cm. Surgical manipulations are completed by layer-by-layer stitching of all dissected tissues. This is followed by a long recovery period; adverse reactions, complications and relapses are possible.
Microsurgical or endoscopic operations are considered more gentle, they reduce trauma to soft tissues when accessing the spine and avoid many postoperative complications. They are carried out using specialized instruments under constant monitoring of the operation using X-ray machines or microscopes.
They can be performed under local anesthesia and require only several small skin incisions up to 2 cm in length. In a similar minimally invasive way, hernia hydroplasty, laser or nitrogen excision is performed.
Postoperative period
Many patients who have undergone surgery to remove a herniated disc, having gotten rid of pain and feeling relief, think that the treatment is over. This is due to the elimination of compression of the nerve roots, the removal of swelling and inflammation of the soft tissues, and the emergence of a certain motor freedom. However, this is only the beginning of the main therapy and recovery period.
There is no single program for restoring the body after surgery. The choice of health-improving measures is carried out jointly by a neurosurgeon, neurologist, orthopedist and rehabilitation specialist individually for each patient. This takes into account: the type of surgical intervention, the postoperative and general health of the patient, the individual characteristics of the body (age, weight, condition of muscle structures, concomitant and chronic diseases, etc.).
In the postoperative period (up to 2 weeks), drug therapy continues, aimed at eliminating residual pain, neurological manifestations and general strengthening of the body. For many patients, early activation in combination with brace therapy is recommended. If necessary, wearing a corset can be extended to 2-3 months, but always in combination with dosed physical activity. Exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures are gradually being introduced, but direct impact on the operating area has not yet been carried out.
The recovery period lasts approximately 2 months after surgery. It helps to stabilize the health status, reduce some motor restrictions and adapt to the patient’s self-care in everyday life and society. During this period, it is recommended to wear a corset no more than 3 hours a day, but all physical activity or housework must be done in it.
It is undesirable to be in a sitting position for a long time, or to travel on public transport while sitting or riding a bicycle. Lift weights carefully (weighing no more than 5 kilograms), watch your posture and try not to make sudden bends or twists with your entire body, especially in combination with lifting weights.
Rehabilitation period
The rehabilitation period lasts from 2 months to several years, and sometimes lasts a lifetime. The measures taken are aimed at restoring the natural biomechanical functions of the spine, strengthening the musculoskeletal system, removing restrictions on motor abilities and returning the patient to a normal quality of life.
At this stage, it is recommended to monitor your daily routine, exercise and rest regime, and control your body weight. At least once a day you need to give the spine a complete unloading in a lying position for 20-30 minutes. The position in which maximum relaxation of the back is achieved is selected by the attending physician.
It is extremely undesirable to lift weights weighing more than 8 kg, to remain in static and/or incorrect positions for a long time, or to take long trips in transport. In addition, you should avoid hypothermia of the back and entire body, physical activity without pre-warming, possible injuries, falls, jumps from heights, nervous shock and stress.
Rehabilitation activities
- Drug treatment, as a rule, ends in the postoperative period, but may be present if all the consequences of the operation have not yet been eliminated (inflammation, swelling, spasm of muscle tissue). If necessary, for general strengthening of the body, vitamin complexes, calcium supplements, sedatives or B vitamins are prescribed to eliminate neurological manifestations after compression of nerve roots and blood vessels.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, mud applications, etc.) are designed to improve blood circulation, strengthen muscles and ligaments, relieve inflammation, swelling and pain of soft tissues.
- Physical therapy from the first days of the postoperative period is a key point in rehabilitation therapy. Sets of exercises are selected according to the patient’s condition and are aimed at restoring and strengthening muscle tone, increasing the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus, improving blood supply and nutrition of body tissues. In addition, swimming is considered the most effective method of treating and preventing spinal diseases, giving full load to all muscle groups.
- Mechanical unloading of the spine (kinesitherapy, hydrotherapy), soft and hardware traction (traction). For such procedures, special exercise machines, baths, and swimming pools are used, where you can completely relax the muscles and at the same time stretch the spine, which relieves the load on the discs. This frees up space for the disc to straighten out and move into its natural position, the spine is aligned, and its flexibility, mobility, and range of motion increases.
- Massages, acupuncture and other manual procedures resemble physical therapy in their healing properties. They should be used with extreme caution in the early postoperative period and directly in the area of pathological damage to the spine.
- It is recommended that all patients undergo specialized health resort treatment at least once a year and undergo a full range of orthopedic procedures. It will not only improve your physical health, but will also have a positive effect on your mental mood.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
How to choose a postoperative abdominal bandage?
What postoperative bandages are considered high quality? The postoperative bandage should fully relieve the postoperative suture and support the abdominal muscles, be comfortable to wear and not cause allergies. The postoperative Russian Intex bandage fits tightly to the abdomen, easing the load on the scar and abdominal muscles. The belt is made of durable, non-allergenic materials (latex, polyester, polypropylene - can cause allergic reactions of an individual nature), therefore it has a fine texture that allows you to wear the belt discreetly under clothing.
How to choose a corset
The attending physician determines which spinal corset for a hernia the patient needs to purchase. The doctor determines the degree of rigidity and height of the back brace. When purchasing, you need to pay attention to the following:
- a good fit to the back should be ensured;
- the product must fully correspond to the curves of the body;
- fasteners should adjust the degree of tightening;
- Manufacturing materials must be of high quality and pleasant to the body.
When choosing, you should be careful and follow all doctor’s recommendations. A tight orthopedic product can crush internal organs and impair blood circulation.
Wearing a corset is not the main treatment. This orthopedic product helps alleviate the patient’s condition as part of complex therapy.
How to choose a postoperative bandage?
In order to select an Intex bandage, you need to take two measurements (in cm): waist circumference and hip circumference. Then you need to compare the measurements with the tabulated intervals. Let's assume that your waist is 76 cm and your hips are 105 cm. These measurements fit into the intervals corresponding to size 3 (M).
The width of the postoperative bandage depends on the location of the scar. A belt with a width of 22 cm is suitable for people below average height, 30 cm - for people above average height. By average we mean a height of 175 cm for a man, 165 cm for a woman.