The list of ailments of modern man is increasingly headed by back pain. The situation is aggravated by the fact that it is not always possible to determine the cause of pain, and some changes may generally be asymptomatic. And when a person pays attention to the problem, irreversible changes have already occurred.
Common causes of diseases of the thoracic spine can be hernias, muscle spasms or joint dysfunction. Every year the number of people diagnosed with osteochondrosis, scoliosis, and kyphosis is growing. How do these diseases develop and can their occurrence be prevented? What exercises help relieve pain and correct posture? These are the most common questions about back pain that will be covered in this article1.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine: causes
Osteochondrosis is a term used to describe a wide range of skeletal lesions in humans and animals. This disease is most common in children and adolescents, and in animals - fast-growing horses, dogs, pigs and chickens. During the development of osteochondrosis, the blood supply to the bone is interrupted, resulting in localized necrosis. In the development of the disease, nutritional, hereditary, endocrine factors, as well as biomechanical effects and disturbances in the blood supply of growing cartilage, play an important role.
Osteochondrosis is accompanied by pain associated with the localization of bone damage. Some types of the disease, depending on the location of the skeletal lesion, may be accompanied by swelling, lameness, curvature or kyphosis of the upper spine.
Osteochondrosis can be divided into three groups:
- Spinal: Scheuermann-Mau disease is a curvature of the thoracic spine.
- Articular osteochondrosis: Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (avascular necrosis of the femoral head), Keller disease (aseptic destruction of the tarsal or navicular bones of the foot), Panner disease (osteochondritis dissecans of the head of the elbow) and Freiberg disease (osteochondropathy of the head of the second or third metatarsal bone of the foot) .
- Non-articular osteochondrosis: Sever's disease (calcaneus or heel) and Kienbock's disease (hand), as well as conditions not always characteristic of osteochondrosis, such as Osgood-Schlatter disease (a tubercle on the tibia) and osteochondritis dissecans2.
Osteochondrosis can occur in any part of the spine: in the cervical region (osteochondrosis CS), in the thoracic region (osteochondrosis TS) and in the lumbar region (osteochondrosis LS).
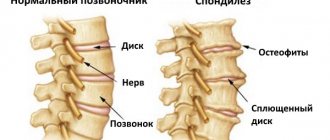
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is associated with wear and changes in the intervertebral disc. These fibrous rings are located between the vertebrae and act as shock absorbers during impacts. Due to strong pressure, the discs become deformed and lose their ability to regenerate. This results in the formation of bone spurs that can cause pain and severely limit the mobility of the spine.
Intervertebral discs, like other parts of the body, are subject to natural wear and tear. However, there are a number of factors that accelerate this process:
- Excessive physical activity, heavy lifting.
- Intervertebral disc infections.
- Herniated intervertebral discs.
- Spinal fracture.
- Scoliosis, pelvic displacement.
- Excess weight.
- Diabetes.
- Smoking.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is difficult to diagnose independently. To prevent the development of the disease, you should pay attention to the following manifestations:
- pain in the cervical and shoulder regions, in the area of the shoulder blades;
- tension and pain in the lower back and spine;
- a state of prolonged fatigue, apathy, drowsiness;
- numbness of the upper extremities (fingers, hands and arms);
- difficulties in flexing and straightening limbs;
- short-term loss of orientation when turning the body and head;
- nausea, dizziness, loss of balance;
- noise in ears;
- sharp pain with normal movements 3.
How to choose the right Gleason Loop?
You can buy the Glisson Loop from us, in the pharmacy chain, or make it yourself. The sources contain information about the technique of making the simulator. When choosing a product, you need to pay attention to the following features:
- size - the hood itself and the fastenings should not squeeze either the head or the neck;
- fasteners must be strong;
- material – you should also pay attention to the material of the product – the fabric should be soft, but have moderate compression.
Your attending physician will help you choose a Glisson loop. The first classes are necessarily carried out with the participation of a physiotherapist or a doctor in a therapeutic exercise room. In the future, you can perform workouts at home. The important thing here is to make sure that the bar or attachments through which the load passes can support the person's weight.
The spine experiences enormous stress every day, which is why it is so important to maintain its health. To prevent complications such as intervertebral hernias, protrusions and vertebral wear, it is necessary to ensure sufficient blood circulation in the structures of the cervical and thoracic regions. The Gleason loop is aimed at the treatment and prevention of spinal diseases. In addition, the simulator relieves pain, increases the effectiveness of basic therapy, and prevents premature surgery. Do not self-medicate at home - it is important to consult a doctor!
A set of exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Serious degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs require observation and treatment. Sometimes surgery may be necessary. If you start doing exercises for the thoracic region at the first signs of osteochondrosis, other measures may not be necessary. Gymnastics significantly improves the mobility of the spine, stretches the muscles of the thoracic region and normalizes muscle tone.
To relax and stretch the back muscles, exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis will help:
- Stand up straight and place your palms on your waist. Turn your shoulders to one side and the other. Try to fix the pelvis in place. Perform 10 turns in both directions.
- From the previous position, begin to squeeze your shoulder blades together, pushing your chest forward. Then round your back and squeeze your shoulders as much as possible. Perform 10 shoulder movements forward and backward.
- Lie on your back and place your fists behind your back above your waist. Stay in this position for 10-15 seconds, then remove your hands. Round your back, lower your chin to your chest and clasp your head in your hands. Stay in this position for 15 seconds. Do 5-10 reps.
- Sit on a high-backed chair and lower your arms along your body. Inhale and place your hands behind your head. Slowly move your body back and press your shoulder blades toward the back of the chair. Exhale and return to the starting position. Repeat five times.
- Place your hands on your shoulders and tilt your head alternately to the right and left shoulder. Do 10–15 reps on each side.
Exercises are best done in the morning or during the day. After eating, at least one hour should pass. In the evening, you can do 1-2 exercises so that the effect of gymnastics does not interfere with sleep.
Exercises for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can be performed in any order, but it is best to start and end the practice with the simplest ones. To enhance the effect, you can repeat the complex twice. All actions should be performed smoothly, without haste, avoiding sudden movements. If turning, bending or bending in any way causes severe pain, do not force it. Eliminate painful movements from the complex.
Thoracic osteochondrosis in an advanced form can lead to compression of the intercostal muscles and breathing problems. Exercises for the thoracic back relieve tension and return vital body functions to normal:
- In a standing position, raise your arms up. Grasp your left wrist with your right hand and lean to the right. Pull your left arm in the direction of the tilt and increase the stretch of the pectoral muscles on the left side of your body. Hold the pose for a few seconds. Straighten up and repeat the exercise on the other side. Do 5-8 bends in each direction.
- Sit on a chair and wrap a long towel around your chest. Grasp the left end of the towel with your right hand and the right end with your left hand. Exhale slowly as you pull off the towel. Then release the pressure and inhale. Complete 5 reps.
- Get on your knees and place your hands on the floor. Inhale, arch your back and lift your head. As you exhale, round your back and lower your head down. Do 10 reps.
Exercises for the chest muscles can be combined with a complex to work the back muscles. The sequence of exercises can be any, but it is advisable to perform the most difficult ones in the middle of the lesson.
The question often arises about whether it is possible to perform exercises for pain in the thoracic spine. It depends on the intensity of the pain and its duration. Severe pain will most likely prevent you from exercising. Prolonged pain is an indicator of serious disorders, such as an inflammatory process or a pinched nerve. It is best to consult a doctor and identify the cause of the pain.
Yoga helps relieve painful tension or get rid of osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine. Asanas make you feel better, and their regular practice allows you to forget about pain and medications. This effect is achieved due to the fact that the load is evenly distributed along the spine. This improves blood flow, strengthens the back muscles and relieves symptoms of osteochondrosis. Yoga activates all the body’s resources, since during practice it is necessary to monitor the correct execution of asanas and breathing.
The result of spinal traction
The complex effect allows you to get rid of functional blockades in the intervertebral joints in just one procedure. The position of the vertebrae is restored, the distance for the intervertebral disc increases, and the pressure inside the intervertebral discs decreases.
In total, this gives a greater chance of correcting the main problem of the intervertebral discs—reducing the prolapsed hernia. Massage with traction on the spine helps relieve symptoms of compression of the spinal nerve roots.
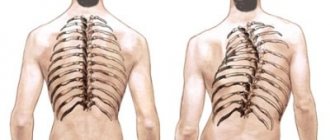
Kyphosis and scoliosis of the thoracic spine
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine to the left or right, as well as around its axis. Most often, the disease develops in children from 9 to 14 years old, during puberty. In most cases, scoliosis develops gradually and painlessly. Sometimes mild to moderate scoliosis can develop unnoticed. If scoliosis is mild, it does not require treatment. In difficult cases, treatment includes special gymnastics, back bracing, or surgery to straighten the spine.
The curvature in scoliosis can be in the lower part of the spine (lumbar curve), in the upper part of the spine (thoracic curve), or go from the top to the bottom of the spine (thoracolumbar curve). In some cases, a double curve appears, forming an S-shape4.
There are several types of scoliosis, each with different causes.
Non-structural scoliosis (functional or postural scoliosis) involves curvature of the spine due to different leg lengths or muscle spasm in the back. The back straightens when a person changes position.
Structural scoliosis is a fixed curvature that does not go away with changes in position. This type of scoliosis has several types:
Idiopathic scoliosis involves an unknown cause. This is the most common type, occurring in 8 out of 10 people.
Neuromuscular scoliosis is caused by a special condition of the muscles or nerves in the back, such as in people with muscular dystrophy, polio, cerebral palsy, or neurofibromatosis. Each of these conditions has other symptoms and problems besides scoliosis. In about 1 in 10 people, scoliosis is associated with a neuromuscular problem.
- Osteopathic scoliosis is caused by a bone abnormality.
- Congenital scoliosis develops in a baby in the womb.
How to treat idiopathic scoliosis?
Most people have moderate scoliosis that does not require treatment. However, regular checkups are necessary for children to ensure that scoliosis does not worsen as they get older. When bone growth stops after puberty, scoliosis usually does not get worse. Special gymnastics, some sports and yoga help support the body. But it is better to consult a doctor who will determine which sports or exercises are best avoided for a particular type of scoliosis.
Kyphosis
This is the name given to the physiological curvature of the thoracic spine with a backward convexity. The normal range of curvature varies from 20 to 50 degrees. This curvature corresponds to reverse curvatures called lordosis, which are found in the cervical and lumbar spine. This combination of curves allows people to sit, stand and move without damaging the spine.
The term kyphosis is commonly used to describe an excessive curvature of the upper back greater than 50 degrees, resulting in a forward lean. Kyphosis can develop at any age. As a rule, this is a disease of the thoracic spine, but kyphosis may develop in the cervical or lumbar spine5.
The most common causes of kyphosis:
- Kyphosis associated with osteoporosis. Because osteoporosis weakens bones, the vertebrae become deformed: the front part of the vertebra “sags”, while the back part maintains height. This results in an excessive kyphotic curve.
- Congenital kyphosis usually occurs in infants and young children due to abnormal development of the spine in the womb. This form most often requires surgery in childhood to realign the spine and prevent progressive deformity.
- Degenerative kyphosis develops due to wear and tear on the spine over time. The main cause is arthritis of the spine, accompanied by disc degeneration.
- Neuromuscular kyphosis may occur in children with certain neuromuscular disorders, such as cerebral palsy, spina bifida, or muscular dystrophy.
- Nutritional kyphosis. This condition is caused by vitamin deficiencies in childhood, such as vitamin D deficiency.
- Postural kyphosis is associated with poor posture. It occurs in people of all ages and is more pronounced in women than in men. To correct postural kyphosis, exercises to strengthen the abdominal and back muscles can help.
- Scheuermann-Mao disease occurs in adolescents due to the rapid growth of the spine and discs. Clinically, it can manifest itself in adolescents and adults along with a mild form of scoliosis. This condition is corrected with bracing, exercises and physical therapy. Surgery is used in cases of painful curvatures that exceed 70 degrees or progress.
- Traumatic kyphosis can develop due to improper healing of a spinal fracture or injury to the ligaments that support the spine6.
ORMED devices
Ormed devices allow for axial dosed traction of the spine with vibration and mechanical effects on the entire muscular-ligamentous apparatus. The effect on the spine and joints is invaluable during rehabilitation, and is important in the prevention of diseases of the neurological spectrum. Possible impact:
- on the cervical
- chest,
- lumbar spine.
The ORMED device is effective in the treatment of osteochondrosis, incl. joints. The complex is primarily used by specialists who place high demands on medical equipment. A special feature of the ORMED device is the possibility of traction of the spine in alternating mode.
The process is controlled by reflecting the treatment procedure on the screen during the process; it is possible to change the method of influence. The traction levers are responsible for influencing at different angles - vertically and horizontally.
The device supports complex procedures - for example, paravertebral vibration massage, in which you can perform traction on the lumbar and cervical spine, as well as traction on the joints of the arms and legs.
Exercises for kyphosis of the thoracic spine
If thoracic kyphosis is not corrected, other problems may arise, such as hyperlordosis, an excessive curvature of the lower back. To compensate for a hunched back, you need to constantly stretch your neck forward to keep your head upright. Thus, the weight of the head falls on the cervical region. This, in turn, leads to neck pain and headaches. As you age, thoracic kyphosis can cause neurological problems due to restricted blood flow to the brain.
What exercises are indicated for thoracic kyphosis?
Cobra pose
First of all, in this position there is a weakening of the chronically tense press. As a result, the spine returns to a more or less neutral position due to the working muscles of the abs and chest.
- Lie on your stomach, legs slightly apart.
- Place your palms under your shoulders and move your elbows back.
- Lift your upper body off the floor as high as possible without lifting your hips off the floor.
- Push your chest forward and lower your shoulders down.
- Try to arch in your upper back, not your lower back.
Pectoralis major muscle strain
The exercise helps lengthen shortened chest muscles and works the upper back.
- Stand facing the wall, raise your left arm to shoulder level parallel to the floor, press your palm against the wall.
- Begin to slowly turn to the right. The left palm remains on the wall.
- To facilitate traction, the left arm can be lowered below shoulder level. To strengthen it, raise it above shoulder level.
- Repeat the exercise on the other hand.
In yoga there is an asana for stretching the pectoral muscle - Bhuja Swastikasana, which is performed in a lying position.
Shalabhasana
Good for stretching the abdominal muscles and strengthening the back.
- Lie on your stomach and extend your arms forward.
- The spine is in a neutral position.
- In one movement, lift your arms, legs and chest off the floor as high as possible.
- Hold for 2-3 seconds and then slowly lower down to the mat.
- Perform several repetitions.
Exercises for scoliosis of the thoracic spine
In most cases, scoliosis manifests itself in a mild form and does not cause serious problems. However, you need to maintain your back health so as not to worsen the condition of your spine. There are several exercises that strengthen your core, improve posture, reduce pain, and relieve fatigue. Regular performance of the complex helps to slightly correct the position of the spine.
Half Bridge (Setu Bandhasana)
It will help strengthen the muscles of the buttocks, opens the thoracic region.
- Lie with your back on the floor or on a mat, place your arms along your body, palms down.
- Bend your knees, bring your feet to your buttocks and place them parallel to each other.
- Begin to lift your pelvis off the floor, raising it as high as possible. Stay in this position for 5 seconds.
- Lower your pelvis to the floor.
- Do 5-6 reps.
Cat/cow (Marjariasana)
Improves the flexibility of the spine, increases blood supply to tissues.
- Get on all fours. The wrists are under the shoulders and the hips are perpendicular to the floor. The back is in a neutral position.
- Inhale and gently arch your back. Raise your head up.
- As you exhale, round your back. Lower your head down.
Alternate stretching of arms and legs
Increases core strength, improves posture, and tones the muscles of the arms and legs.
- Get into the cat/cow position.
- Extend your left arm in front of you at shoulder level.
- Extend your right leg back parallel to the floor.
- Hold this position for 7-10 seconds. Do not arch or round your back.
- Lower your arm and leg to the previous position, then repeat the same on the other side.
- If this is done easily, you can raise and lower your arm and leg at the same time.
Plank
This is a simple yet effective core strengthening exercise. There are several plank variations that can be performed depending on your fitness level. The fixation time for each bar depends on the capabilities or recommendations of a doctor or trainer.
Plank on knees and elbows
- Lie on your stomach.
- Raise your body using your elbows. Forearms are parallel to each other, elbows bent at approximately 90 degrees, palms facing down.
- Knees on the floor.
- Keep your back in a neutral position.
Plank on knees and hands
- Get on all fours.
- The wrists are under the shoulders.
- Move your knees further away from your pelvis.
- The body is straight from the shoulders to the knees.
Elbow plank
- Get on all fours and move your legs back, keeping your feet on your toes.
- Lower your forearms to the floor parallel to each other.
- Align your body in a straight line from shoulders to heels.
Plank on extended arms
- Get on all fours and move your legs back.
- Wrists under shoulders.
- The body is in one line from shoulders to heels.
- Try not to arch your lower back or raise your pelvis.
Before performing exercises, you should consult your doctor. Each case of scoliosis is individual, so there may be exercises that will help someone, but may harm others.
Exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic spine
How to get rid of pain with cervical osteochondrosis? Exercises for the cervical spine are not very intense, but require increased attention to execution and the sensations that arise. Movements should not cause acute pain, discomfort, or tremors of the limbs. If you feel warmth in the shoulders and back area, it means that the muscle tissue is receiving the necessary physical activity.
By the way, these exercises help get rid of headaches due to osteochondrosis.
- Stand up straight, straighten your shoulders, lower your arms along your body. First tilt your head to the right, then to the left shoulder. Do the bends 10–15 times or until you feel warmth in your neck muscles.
- Turn your head to the right and stay in this position for 10-15 seconds. Return your head to the starting position, then turn your head to the left. Perform 3-5 turns in both directions.
- Lower your head and try to touch your chin to your chest. Stay in this position for 5-10 seconds. Then slowly move your head back. Stay in this position for 5-10 seconds. Try not to throw your head back too much.
- Slowly rotate your head, first clockwise, then counterclockwise. Perform 3-5 rotations in each direction.
- Raise your arms up, inhale and turn your body to the right. As you exhale, turn your body to the left. Perform 6-8 reps on each side.
- Stand up straight, raise your arms. Lean first to the right, then to the left. Try not to round your back.
- Raise your arms above your head. Rise up on your toes and stretch along the entire length of your spine. Hold for 5-10 seconds.
- Lie on your stomach, place your forearms parallel to each other so that the angle at your elbows is approximately 90 degrees. Lightly pull the mat toward you, bending your chest. Move your shoulders down, point the top of your head up. Hold this position for 5–7 seconds.
- Get on all fours and begin to stretch your arms forward, moving your palms along the mat. The hips remain in place, perpendicular to the mat. Place your chin on the mat and try to bend your chest as much as possible. When performing an easier version, you can place your hands on a block or chair.
If you perform these exercises correctly and regularly, you can achieve significant results:
- improve the elasticity of soft tissues, ligaments and joints;
- normalize general blood flow and lymph flow in the body;
- make your posture straight and beautiful;
- avoid displacement of spinal discs and vertebral injuries;
- relieve the load on the cartilage tissue and eliminate the possibility of pinching nerve endings.
For most people, these exercises are safe. However, pay attention to some contraindications:
- Do not exercise if the pain is severe.
- Stop the exercise if pain occurs during exercise.
- Approach the practice with caution if you have recently had injuries to your wrists, knees, hip joints, or spine.
- It is better not to do abdominal exercises during periods of exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases.
Twisting with thoracic osteochondrosis
Twisting is a set of exercises in which parts of the body, and with them the parts of the spine, are rotated in different directions. These exercises stretch your back muscles and free up space for your intervertebral discs.
It is important to remember that you need to perform twisting exercises on already warmed muscles. Therefore, first perform the exercises from the general complex, and then proceed to twisting the thoracic region.
- Stand up straight and step your left foot forward. Turn both feet forward, lower your right leg to your knee, and bend your left. As you inhale, raise your arms straight above your head. As you exhale, bring your right elbow behind your left knee, while rotating your body. If you don't feel pain in this position, try making the exercise more difficult. Clasp your hands behind your back so that your right hand passes under your left leg and your left hand passes through the back of your body.
- Get on your knees and lean on your elbows. Place the palm of one hand on your shoulder, move the bent arm back, rotating the thoracic region behind it. The second elbow does not come off the floor. Fix in this position, repeat the exercise in the opposite direction.
- Repeat the twisting exercise on your elbows, but place your working hand on your lower back.
- Sit with your legs extended forward and your back straight, your right leg slightly bent at the knee, but do not pull it towards your chest. With your left hand, grab the shin of your right leg. Slowly move your right arm behind your back, followed by your body and head.
In the position from the previous exercise, place your left hand on the floor, stretching back, move your arm and lift your left leg, preferably so that it is straight.
Exercises from the “Twisting” group are most effective for the thoracic region. While performing them, you may feel the strongest tension in your lower back, but this is a false feeling associated with muscle tension. It is the vertebrae of the thoracic spine that are most prone to twisting. At the same time, the shoulders are very mobile and give great freedom to perform a variety of exercises.
How to strengthen the thoracic spine
Of course, it is best to prevent spinal diseases from occurring. But, if you feel back pain, notice a curvature of the spine, or have been diagnosed with a musculoskeletal disease, start working on the problem! Even in the case when doctors say that the curvature is insignificant and nothing can be done at present. The sooner you start strengthening your back, the more likely you are to stop the progression of the disease.
Relaxation is an important step on the path to health. Practice breathing exercises (pranayama): full yogic breathing, breath stretching, anuloma viloma pranayama. These techniques will help relax the body and mind, allow you to calm down and remove tension in the muscles.
Not only exercises to strengthen the thoracic spine help, but also lifestyle changes. If you have a sedentary job, you need to create a schedule that allows you to take breaks and exercise.
Watch your posture
Today people spend more and more time on their phones. The position with the head tilted forward compresses the spinal cord and blood vessels, leading to displacement of the vertebrae.
Don't sleep on your stomach
This is the worst position for scoliosis because it causes the thoracic region to flatten. Scoliosis is three-dimensional: if the condition worsens in one plane, then it also worsens in others. Sleeping on your stomach also requires turning your head to the side, which increases the curvature of the spine.
Don't run long distances
Every time you take a step, the vertebrae are compressed. And this leads to the progression of changes in the spine. Therefore, it is better to limit not only running, but also jumping and horse riding or even exclude it from practice.
Don't carry heavy things
When you carry a heavy bag with one hand, the deformation of the spine increases. A backpack worn on both shoulders is best suited for such purposes.
Change your position more often
Sitting or standing in one place for too long increases the stress on the spine. Exercise or go for walks more often. If you have a sedentary job, choose a chair with good support.
Unfortunately, diseases of the musculoskeletal system are firmly rooted in people's lives. As the studies above show, more than half of the cases of scoliosis, osteochondrosis and kyphosis are idiopathic.
In other words, the cause of their occurrence is unknown. Therefore, any person is at risk. We are required to take daily care of the spine and be attentive to our health. A healthy lifestyle, regular physical activity and a clear daily routine will help minimize the risk of developing diseases,
which are very difficult to treat.
The effects of spinal traction
After 2-3 sessions, improvements are noted:
- back pain stops,
- muscle tone is normalized,
- blood circulation in the spine increases,
- blood circulation to the brain increases,
- There is an improvement in blood circulation in the spinal cord.
Treatment is carried out at a special orthopedic complex “ORMED-professional” . The effectiveness of the technique is combined with a complete absence of pain.
The Ormed device for mechanical therapy of a professional level allows you to perform traction - dosed traction of the spine. Exposure to heat and vibration can achieve significant results.
This type of roller massage has been clinically tested. Medical reports of working with devices of the ORMED series show how effective traction equipment can be:
- in the prevention of spinal diseases,
- during treatment,
- during the rehabilitation period.